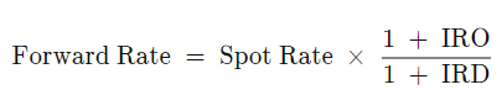Definition of Interest Rate Parity
Interest rate parity is a theory that states that the difference in interest rates of two different countries is the difference of spot and a forward exchange rate of currencies of both the countries. The theory assumes that the gap between the currency exchange rates will eventually be closed with a factor of interest rates in each of the countries. This is why often interest rate parity is used to estimate forward rates.
The mathematical expression for interest rate parity is as follows:
Where IRO =Interest rate in an overseas country
IRD = Interest rate in the domestic country
Assume the current spot rate for 1 USD = Euro 0.75, the interest rate in the US is 3% and in Germany is 4%. The forward rate will be calculated as follows:
Forward rate=0.7500 eu/$ *(1+4%)/(1+3%) =0.7573 eu/$
View More Financial Management Definitions
Related Questions of Interest Rate Parity
Define interest rate parity. What is the relationship between interest rate
Assume that interest rate parity holds. In both the spot market
James Clark is a currency trader with Wachovia. He notices the
Use Figure 21.1 to answer the following questions: Suppose interest
Assume that interest rate parity holds and that 90-day risk
Use Figure 31.1 to answer the following questions. Suppose
Discuss the implications of interest rate parity for exchange rate determination.
Six-month T-bills have a nominal rate of 7
Does interest rate parity imply that interest rates are the same in
The Brazilian real has appreciated 33 percent against the U.S
Show All