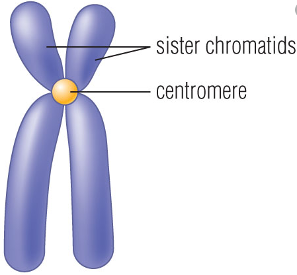
Definition of Chromatid
A chromosome is composed of two identical halves which are known as chromatids. The chromatids are formed after the uncoiling of the chromosome; hence they are less compact and less condensed structures. Those chromatids which are derived from the same chromosome and are linked with each other at the centromere are termed as sister chromatids.
The chromatids exist in the form of non-sister chromatids too when they belong to two different chromosomes but are connected through chiasmata in order to exchange the genetic material and form genetic recombination. They are the structures that exist for a temporary moment and help in the processes like chromosome duplication and separation. Chromatids lack the ability to transcribe proteins.
View More Genetics Definitions
Related Questions of Chromatid
How does the attachment of kinetochore microtubules to the kinetochore differ in
Describe the similarities and differences between homologous recombination involving sister chromatid exchange
The molecular mechanism of SCE is similar to homologous recombination between homologs
Show All