Definition of Conjugate Acid Base Pair
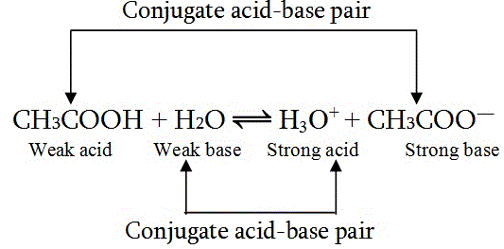
The Bronsted Lowry explained the acid-base theory according to which the acid is such a species that has a tendency to donate a proton and the base is that species that can accept a proton. The conjugate acid is formed when the base accepts the proton.
On the contrary, the conjugate base is formed when the acid donates the proton. The conjugate acid-base pair are such compounds that are different from each other by just one proton.
Example of Conjugate Acid Base Pair:
The reaction of the acetic acid with water leads to the formation of hydronium ion and acetate ion.
View More General Chemistry Definitions
Related Questions of General Chemistry
Which of the following statement(s) is(are)
Students approaching the study of chemistry must learn certain basic facts (
Suppose 325 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is needed for
When ethanol (grain alcohol, C2H5OH) is burned in oxygen
Read the “Chemistry in Focus” segment A Mystifying Problem,
Is the process represented below a physical or chemical change?
Why is the ability to solve problems important in the study of
Discuss several political, social, or personal considerations that might affect
Although reviewing your lecture notes and reading your textbook are important,
Evaluate each of the following and write the answer to the appropriate
Show All