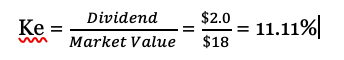Definition of Cost Of Equity
Cost of equity or Ke is the rate of return required by the equity shareholders of a company. In case of debt the rate at which the interest is paid to the debtholders is called as cost of debt. The cost of equity is calculated using various methods depending on the way the return is awarded to shareholders. If the company has a history of paying dividends then the return can be calculated using the dividend valuation method.
Another method of calculating the cost of equity is through the capital asset pricing model or CAPM. As per CAPM, the cost of equity is as follows:
Ke = Risk-free rate + Beta x (Market return – Risk-free rate)
Ke = 3% + 1.2 x (9%-3%) = 10.2%
View More Financial Management Definitions
Related Questions of Cost Of Equity
Shadow Corp. has no debt but can borrow at 8 percent
Weston Industries has a debt–equity ratio of 1.5
Rogot Instruments makes fine violins, violas, and cellos. It
Phoenix Corp. faltered in the recent recession but is recovering.
Bruce & Co. expects its EBIT to be $185,
Sheldon Corporation projects the following free cash flows (FCFs) and
Maryland Light, a U.S. manufacturer of light fixtures
Suppose Microsoft has no debt and a WACC of 9.2
ABC Co. and XYZ Co. are identical firms in all
Williamson, Inc., has a debt–equity ratio of 2
Show All