Definition of Hydrogen Bonding
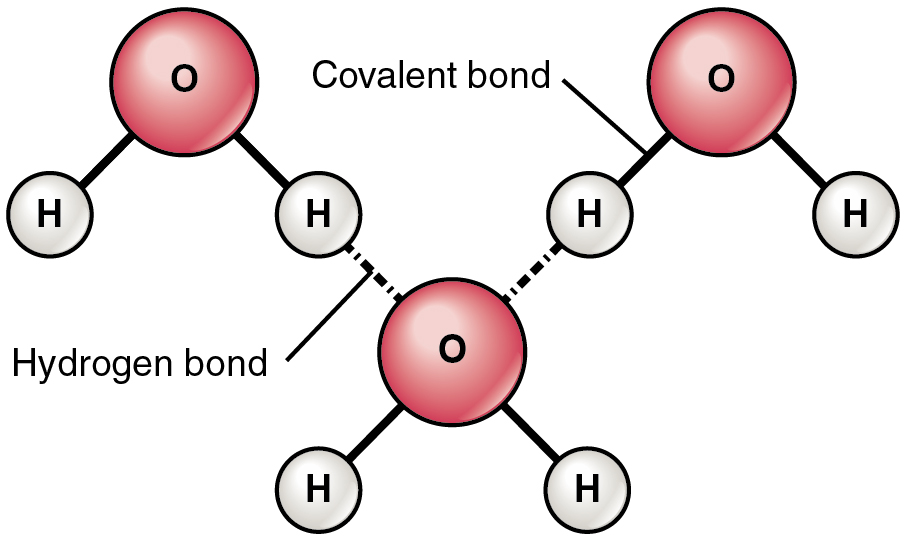
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular bond in which there is a dipole-dipole attraction between the molecules. The hydrogen in hydrogen bonding forms an attractive force with a high electronegative atom. Nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine are highly electronegative atoms. The strength of hydrogen bonds ranges between 4 to 50 kJ per mole.
The molecules that are the result of hydrogen bonding are greatly polar. This is because the difference of electronegativity between N, O, F, and hydrogen is quite large which renders a partial positive charge over the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge over the electronegative atom. Bonding present in the molecules of water and ammonia is hydrogen bonding.
View More Organic Chemistry Definitions
Related Questions of Hydrogen Bonding
The bases on opposite strands of DNA are said to be to
The text implies that hydrogen bonding is a special case of very
Which of the following substances exhibit hydrogen bonding interactions? a
The normal boiling point of water is unusually high, compared to
What is a dipole–dipole attraction? How do the strengths
Formaldehyde has the formula CH2O, where C is the central atom
In Chapter 3, we will explore the factors that render compounds
An article in the Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (Vol. 80
As described in Chapter 15, the methylation of cytosine bases can
Refer to Figure 15.2 and draw hydrogen bonding between two
Show All

