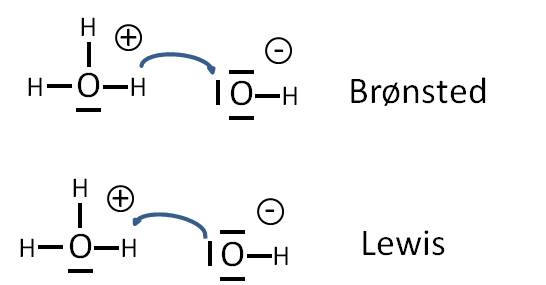
Definition of Lewis Acid
A Lewis acid is defined as a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. Hence, they are known to be the electron pair acceptors. In the Lewis acid-base reaction, the pair of electrons are transferred from the base to an acid.
According to Lewis and Bronsted Lowry, the hydrogen ion (H+) is said to be acid as it is deficient in electrons and therefore accepts a pair of electrons. Whereas, ammonia (NH3) is known to be a Lewis base as the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons that can be donated to acid to form a covalent bond.
View More Organic Chemistry Definitions