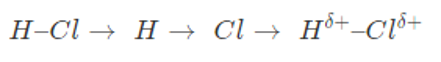Definition of Polar Covalent Bond
The covalent bond is formed by the mutual sharing of electrons between the two atoms. If these bonding atoms belong to two different non-metals that exhibit different electronegativities, then the covalent bond formed is termed a polar covalent bond.
The compounds which are formed by polar covalent bonds generally have greater interactive forces between the bonding atoms, hence they usually exist in the solid form. They have very high melting as well as boiling point. Moreover, they have the ability to conduct electricity and to get solubilized in the polar solvents.
Example of Polar Covalent Bond:
Consider a molecule of HCl, the electronegativity value of carbon is 2.5 whereas that of hydrogen is 2.1. The atom of carbon has a greater tendency to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself as compared to a hydrogen atom. In this way, two poles are created i.e., partial positive and partial negative.
View More General Chemistry Definitions
Related Questions of General Chemistry
Which of the following statement(s) is(are)
Students approaching the study of chemistry must learn certain basic facts (
Suppose 325 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is needed for
When ethanol (grain alcohol, C2H5OH) is burned in oxygen
Read the “Chemistry in Focus” segment A Mystifying Problem,
Is the process represented below a physical or chemical change?
Why is the ability to solve problems important in the study of
Discuss several political, social, or personal considerations that might affect
Although reviewing your lecture notes and reading your textbook are important,
Evaluate each of the following and write the answer to the appropriate
Show All