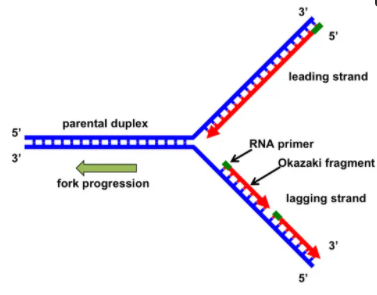
Definition of Replication Fork
During the phenomenon of DNA replication, the proteins that are responsible for the process of replication organize themselves into a structure which is known as a replication fork. It happens during the synthesis (S) phase of the cell cycle. At the replication fork, the group of proteins coordinate to replicate the DNA. The structure is named as a fork as the simplified form of it resembles the fork that is two-tined.
The unwinding of DNA and its synthesis are the two main activities that occur at the replication fork. The fork with the help of the helicase enzyme unwinds the DNA and separates the strands. The synthesis of DNA is brought about by the help of DNA polymerase which adds up the bases in the new strand that are complementary to the template strand.
View More Genetics Definitions