Question: A 200-lb trap door (AB) is
A 200-lb trap door (AB) is supported by a strut (BC) which is pin connected to the door at B (see figure).
(a) Find reactions at supports A and C.
(b) Find internal stress resultants N, V, and M on the trap door at 20 in. from A.
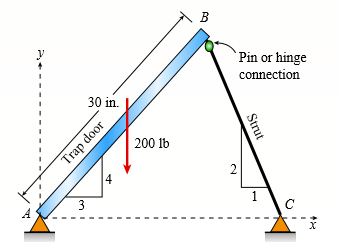
Transcribed Image Text:
B Pin or hinge connection 30 in. 200 1b 2 1 3 C Strut Joop de
> A special-purpose eye bolt with a shank diameter d = 0.50 in. passes through a hole in a steel plate of thickness tp = 0.75 in. (see figure) and is secured by a nut with thickness t = 0.25 in. The hexagonal nut bears directly against the steel plate. The
> A plane truss has joint loads P, P2, and P3 at joints D, C, and B, respectively (see figure) where load variable P = 5200 lb. All members have two end plates that are pin- connected to gusset plates. Each end plate has a thickness tp = 0.625 in, and all
> A steel plate of dimensions 2.5 × 1.5 × 0.08 m and weighing 23.1 kN is hoisted by steel cables with lengths L1 = 3.2m and L2 = 3.9m that are each attached to the plate by a clevis and pin (see figure). The pins through the clevi
> The inclined ladder AB supports a house painter (85 kg) at C and the weight (q = 4 0N/m) of the ladder itself. Each ladder rail (tr = 4 mm) is supported by a shoe (ts = 5 mm) that is attached to the ladder rail by a bolt of diameter dp = 8mm. Typica
> The upper deck of a football stadium is supported by braces, each of which transfers a load P = 160 kips to the base of a column (see figure part a). A cap plate at the bottom of the brace distributes the load P to four flange plates (tf = 1 in.) through
> Truss members supporting a roof are connected to a 26-mm-thick gusset plate by a 22-mm diameter pin, as shown in the figure and photo. The two end plates on the truss members are each 14 mm thick. (a) If the load P = 80 kN, what is the largest bearing st
> The piston in an engine is attached to a connecting rod AB, which in turn is connected to a crank arm BC (see figure). The piston slides without friction in a cylinder and is subjected to a force P (assumed to be constant) while moving to the right in th
> A sign of weight W is supported at its base by four bolts anchored in a concrete footing. Wind pressure p acts normal to the surface of the sign; the resultant of the uniform wind pressure is force F at the center of pressure (C.P.). The wind force is as
> A solid steel bar of a diameter d1 = 60 mm has a hole of a diameter d2 = 32 mm drilled through it (see figure). A steel pin of a diameter d2 passes through the hole and is attached to supports. Determine the maximum permissible tensile load Pallow in the
> A solid bar of circular cross section (diameter d) has a hole of diameter d/5 drilled laterally through the center of the bar (see figure). The allowable average tensile stress on the net cross section of the bar is sallow. (a) Obtain a formula for the a
> A plane truss is subjected to loads P2 and P at joints B and C, respectively, as shown in the figure part a. The truss bars are made of two L 102 × 76 × 6.4 steel angles having an ultimate stress in tensi
> A metal bar AB of a weight W is suspended by a system of steel wires arranged as shown in the figure. The diameter of the wires is 5/64 in., and the yield stress of the steel is 65 ksi. Determine the maximum permissible weight Wmax for a factor of safety
> Lateral bracing for an elevated pedestrian walkway is shown in the figure part a. The thickness of the clevis plate tc = 16 mm and the thickness of the gusset plate tg = 20 mm (see figure part b). The maximum force in the diagonal bracing is expected to
> What is the maximum possible value of the clamping force C in the jaws of the pliers shown in the figure if the ultimate shear stress in the 5-mm diameter pin is 340 MPa? What is the maximum permissible value of the applied load P to maintain a factor of
> A ship’s spar is attached at the base of a mast by a pin connection (see figure). The spar is a steel tube of outer diameter d2 = 3.5 in. and inner diameter d1 = 2.8 in. The steel pin has a diameter d = 1 in., and the two plates connect
> A cable and pulley system in the figure part a supports a cage of a mass 300 kg at B. Assume that this includes the mass of the cables as well. The thickness of each of the three steel pulleys is t = 40 mm. The pin diameters are dpA = 25 mm, dpB = 30 mm,
> A lifeboat hangs from two ship’s davits, as shown in the figure. A pin of diameter d = 0.80 in. passes through each davit and supports two pulleys, one on each side of the davit. Cables attached to the lifeboat pass over the pulleys and
> The rear hatch of a van (BDCG in figure part a) is supported by two hinges at B1 and B2 and by two struts A1B1 and A2B2 (diameter ds = 10 mm), as shown in figure part b. The struts are supported at A1 and A2 by pins, each with a diameter dp =
> A steel riser pipe hangs from a drill rig. Individual segments of equal length L = 50 ft are joined together using bolted flange plates (see figure part b). There are six bolts at each pipe segment connection. The outer and inner pipe diameters are d2 =
> A steel pad supporting heavy machinery rests on four short, hollow, cast iron piers (see figure). The ultimate strength of the cast iron in compression is 400 MPa. The total load P that may be supported by the pad is 900 kN. Using a factor of safety 3.0
> A steel pad supporting heavy machinery rests on four short, hollow, cast iron piers (see figure). The ultimate strength of the cast iron in compression is 50 ksi. The outer diameter of the piers is d = 4.5 in., and the wall thickness is t = 0.40 in. Usin
> Two steel tubes are joined at B by four pins (dp = 1 1mm), as shown in the cross section a–a in the figure. The outer diameters of the tubes are dAB = 41 mmd and dBC = 28 mm. The wall thickness are tAB = 6.5mm and tBC = 7.5mm. The yield
> A tie-down on the deck of a sailboat consists of a bent bar bolted at both ends, as shown in the figure. The diameter dB of the bar is 1/4 in., the diameter dW of the washers is 7/8 in., and the thickness t of the fiberglass deck is 3/8 in. If the allowa
> A horizontal beam AB with cross-sectional dimensions (b = 0 .75 in.) × (h = 8.0in.) is supported by an inclined strut CD and carries a load P = 2700 lb at joint B (see figure part a). The strut, which consists of two bars each of thickness 5
> A torque To is transmitted between two flanged shafts by means of ten 20-mm bolts (see figure and photo). The diameter of the bolt circle is d = 250 mm. If the allowable shear stress in the bolts is 85 MPa, what is the maximum permissible torque? (Disreg
> Two bars AC and BC of the same material support a vertical load P (see figure). The length L of the horizontal bar is fixed, but the angle u can be varied by moving support A vertically and changing the length of bar AC to correspond with the new positio
> Continuous cable ADB runs over a small frictionless pulley at D to support beam OABC, which is part of an entrance canopy for a building (see figure). A downward distributed load with peak intensity qo = 5 kN/m at O acts on the beam (see figure). Assume
> Continuous cable ADB runs over a small frictionless pulley at D to support beam OABC, which is part of an entrance canopy for a building (see figure). The canopy segment has a weight W = 1700 lb that acts as a concentrated load in the middle of segment A
> A flat bar of a width 60 mm b 5 and thickness 10 mm t 5 is loaded in tension by a force P (see figure). The bar is attached to a support by a pin of a diameter d that passes through a hole of the same size in the bar. The allowable tensile stress on the
> An elevated jogging track is supported at intervals by a wood beam AB (L = 7 .5 ft) that is pinned at A and supported by steel rod BC and a steel washer at B. Both the rod (dBC = 3 /16 in.) and the washer (dB = 1 .0 in.) were designed using a rod tension
> An aluminum tube is required to transmit an axial tensile force P = 33 k (see figure part a). The thickness of the wall of the tube is 0.25 in. (a) What is the minimum required outer diameter dmin if the allowable tensile stress is 12,000 psi? (b) Repeat
> A bar of solid circular cross section is loaded in tension by forces P (see figure). The bar has a length L = 16.0in. and diameter d = 0.50 in. The material is a magnesium alloy having a modulus of elasticity E = 6.4 × 106psi. The allowable
> An angle bracket having a thickness t = 0.75Â in. is attached to the flange of a column by two 5/8-inch diameter bolts (see figure). A uniformly distributed load from a floor joist acts on the top face of the bracket with a pressure p = 275 ps
> A bar made of structural steel having the stress strain diagram shown in the figure has a length of 60 in. The yield stress of the steel is 50 ksi, and the slope of the initial linear part of the stress-strain curve is 29,000 ksi. (a) The bar is loaded a
> Imagine that a long steel wire hangs vertically from a high-altitude balloon. (a) What is the greatest length (feet) it can have without yielding if the steel yields at 40 ksi? (b) If the same wire hangs from a ship at sea, what is the greatest length?
> A hollow circular post ABC (see figure) supports a load P1 = 1700 lb acting at the top. A second load 2 P is uniformly distributed around the cap plate at B. The diameters and thicknesses of the upper and lower parts of the post are dab = 1.25 in, tab =
> A steel column of hollow circular cross section is supported on a circular, steel base plate and a concrete pedestal (see figure). The column has an outside diameter d = 250 mm and supports a load P = 750 kN. (a) If the allowable stress in the column is
> A mountain bike is moving along a flat path at constant velocity. At some instant, the rider (weight = 670 N) applies pedal and hand forces, as shown in the figure part a. (a) Find reaction forces at the front and rear hubs. (Assume that the bike is pin
> An elliptical exerciser machine (see figure part a) is composed of front and back rails. A simplified plane-frame model of the back rail is shown in figure part b. Analyze the plane-frame model to find reaction forces at supports A, B, and C for the posi
> A soccer goal is subjected to gravity loads (in the 2z direction, w = 73 N/m for DG, BG, and BC; w = 29 N/m for all other members; see figure) and a force F = 200 N applied eccentrically at the mid-height of member DG. Find reactions at supports C, D, an
> Space frame ABC is clamped at A, except it is free to rotate at A about the x and y axes. Cables DC and EC support the frame at C. Force Py = 250lb is applied at the mid-span of AB, and a concentrated moment Mx = 220 in.-lb acts at joint B. (a) Find reac
> Space frame ABCD is clamped at A, except it is free to translate in the x direction. There is also a roller support at D, which is normal to line CDE. A triangularly distributed force with peak intensity qo = 75 N/m acts along AB in the positive z direct
> A special vehicle brake is clamped at O when the brake force 1 P is applied (see figure). Force P1 = 50lb and lies in a plane that is parallel to the x-z plane and is applied at C normal to line BC. Force P2 = 40 lb and is applied at B in the 2y directio
> A plane frame has a pin support at A and roller supports at C and E (see figure). Frame segments ABD and CDEF are joined just left of joint D by a pin connection. (a) Find reactions at supports A, C, and E. (b) Find the resultant force in the pin just le
> A 150-lb rigid bar AB, with frictionless rollers at each end, is held in the position shown in the figure by a continuous cable CAD. The cable is pinned at C and D and runs over a pulley at A. (a) Find reactions at supports A and B. (b) Find the force in
> A plane frame with a pin support at A and roller supports at C and E has a cable attached at E, which runs over frictionless pulleys at D and B (see figure). The cable force is known to be 400 N. There is a pin connection just to the left of joint C. (a)
> A plane frame with pin supports at A and E has a cable attached at C, which runs over a frictionless pulley at F (see figure). The cable force is known to be 500 lb. (a) Find reactions at supports A and E. (b) Find internal stress resultants N, V, and M
> A large precast concrete panel for a warehouse is raised using two sets of cables at two lift lines, as shown in the figure part a. Cable 1 has a length L1 = 22 ft, cable 2 has a length L2 = 10 ft, and the distance along the panel between lift points B a
> A plane frame is constructed by using a pin connection between segments ABC and CDE. The frame has pin supports at A and E and joint loads at B and D (see figure). (a) Find reactions at supports A and E. (b) Find the resultant force in the pin at C.
> Find support reactions at A and D and then calculate the axial force N, shear force V, and bending moment M at mid-span of column BD. Let L = 4 m, qo = 160 N/m, P 5 200 N, and Mo = 380 Nm? Mo 4 4 L/2 3 B 3 L L/2 y D
> Find support reactions at A and D and then calculate the axial force N, shear force V, and bending moment M at mid-span of AB. Let L = 14 ft, qo = 12 lb/ft, P = 50 lb, and Mo = 300 lb-ft. Mo 4 B A L 40 L/2 L
> A plane frame is restrained at joints A and D, as shown in the figure. Members AB and BCD are pin connected at B. A triangularly distributed lateral load with peak intensity of 80 N/m acts on CD. An inclined concentrated force of 200 N acts at the mid-sp
> A plane frame is restrained at joints A and C, as shown in the figure. Members AB and BC are pin connected at B. A triangularly distributed lateral load with a peak intensity of 90 lb/ft acts on AB. A concentrated moment is applied at joint C. (a) Find r
> A stepped shaft ABC consisting of two solid, circular segments is subjected to uniformly distributed torque t1 acting over segment 1 and concentrated torque T2 applied at C, as shown in the figure. Segment 1 of the shaft has a diameter of d1 = 57 mm and
> A stepped shaft ABC consisting of two solid, circular segments is subjected to torques T1 and T2 acting in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. The larger segment of the shaft has a diameter of d1 = 2.25 in. and a length L1 = 30 in.; the smaller
> A space truss is restrained at joints A, B, and C, as shown in the figure. Load P acts in the 1z direction at joint B and in the 2z directions at joint C. Coordinates of all joints are given in terms of dimension variable L (see figure). Let P = 5 kN and
> A space truss is restrained at joints A, B, and C, as shown in the figure. Load 2P is applied at in the 2x direction at joint A, load 3P acts in the 1z direction at joint B, and load P is applied in the 1z direction at joint C. Coordinates of all joints
> A tubular post of outer diameter d2 is guyed by two cables fitted with turnbuckles (see figure). The cables are tightened by rotating the turnbuckles, producing tension in the cables and compression in the post. Both cables are tightened to a tensile for
> A space truss is restrained at joints O, A, B, and C, as shown in the figure. Load P is applied at joint A and load 2P acts downward at joint C. (a) Find reaction force components Ax, By, and Bz in terms of load variable P. (b) Find the axial force in tr
> A space truss has three-dimensional pin supports at joints O, B, and C. Load P is applied at joint A and acts toward point Q. Coordinates of all joints are given in feet (see figure). (a) Find reaction force components Bx, Bz, and Oz. (b) Find the axial
> Repeat 1.3-10 but use the method of sections to find member forces in AB and DC. Data from Problem 10: Find support reactions at A and B and then use the method of joints to find all member forces. Let b = 3 m and P = 80 kN. y 2P b/2 2
> Repeat 1.3-9 but use the method of sections to find member forces in AC and BD. Data from Problem 9: Find support reactions at A and B and then use the method of joints to find all member forces. Let c = 8 ft and P = 20 kips. -2P -Oc = 80° a O3 =
> Find support reactions at A and B and then use the method of joints to find all member forces. Let b = 3 m and P = 80 kN. y 2P b/2 2P D ec = 80° b/2 Og = 40° = 60° B
> Find support reactions at A and B and then use the method of joints to find all member forces. Let c = 8 ft and P = 20 kips. -2P -Oc = 80° a O3 = 40° = 60° D A B 2P c/2- c/2-
> A plane truss has a pin support at F and a roller support at D (see figure). (a) Find reactions at both supports. (b) Find the axial force in truss member FE. 16 kN 19 kN 3 m 13 kN A 3 m B 3 m D 3 m E 4.5 m f1 m
> A plane truss has a pin support at A and a roller support at E (see figure). (a) Find reactions at all supports. (b) Find the axial force in truss member FE. |3 kips 2 kips 10 ft D 1 kips A 10 ft B 10 ft C 10 ft 15 ft 3 ft G
> Consider the plane truss with a pin support at joint 3 and a vertical roller support at joint 5 (see figure). (a) Find reactions at support joints 3 and 5. (b) Find axial forces in truss members 11 and 13. 20 N 45 N 4 5 6 6. 7 12 11 7 10) 2 m 13 9 6
> Segments AB and BCD of beam ABCD are pin connected at x 5 10 ft. The beam is supported by a pin support at A and roller supports at C and D; the roller at D is rotated by 308 from the x axis (see figure). A trapezoidal distributed load on BC varies in in
> A pressurized circular cylinder has a sealed cover plate fastened with steel bolts (see figure). The pressure p of the gas in the cylinder is 290 psi, the inside diameter D of the cylinder is 10.0 in., and the diameter dB of the b
> A copper alloy pipe with a yield stress sY = 290 MPa is to carry an axial tensile load P = 1500 kN (see figure part a). Use a factor of safety of 1.8 against yielding. (a) If the thickness t of the pipe is one-eighth of its outer diameter, what is the mi
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. x = y2 - z2
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. y = z2 - x2
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. 3x2 - y2 + 3z2 = 0
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. 3x2 + y + 3z2 = 0
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. 9y2 + 4z2 = x2 1 36
> Differentiate the function. f (x) = ln(sin2x)
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. z2 - 4x2 - y2 = 4
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. x2 = 4y2 + z2
> Draw a diagram to show that there are two tangent lines to the parabola that y = x2 pass through the point (0, -4). Find the coordinates of the points where these tangent lines intersect the parabola.
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. 4x2 + 9y2 + 9z2 = 36
> Use traces to sketch and identify the surface. x = y2 + 4z2
> (a). Find and identify the traces of the quadric surface 2x2 - y2 + z2 = 1 and explain why the graph looks like the graph of the hyperboloid of two sheets in Table 1. (b). If the equation in part (a) is changed to x2 - y2 - z2 = 1, what happens to the gr
> (a). Find and identify the traces of the quadric surface x2 + y2 - z2 = 1 and explain why the graph looks like the graph of the hyperboloid of one sheet in Table 1. (b). If we change the equation in part (a) to x2 - y2 + z2 = 1, how is the graph affected
> Find a vector equation and parametric equations for the line. The line through the point (1, 0, 6) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y + z = 5
> Find a vector equation and parametric equations for the line. The line through the point (0, 1 4, -10) and parallel to the line x = -1 + 2t, y = 6 - 3t, z = 3 + 9t
> Determine whether each statement is true or false in R3. (a). Two lines parallel to a third line are parallel. (b). Two lines perpendicular to a third line are parallel. (c). Two planes parallel to a third plane are parallel. (d). Two planes perpendicula
> Find the distance between the skew lines with parametric equations x = 1 + t, y = 1 + 6t, z = 2t, and x = 1 + 2s, y = 5 + 15s, z = -2 + 6s.
> Differentiate the function. f (x) = sin(ln x)
> Show that the lines with symmetric equations x = y = z and x + 1 = y/2 = z/3 are skew, and find the distance between these lines.
> Where does the normal line to the parabola y = x2 - 1 at the point (-1,0) intersect the parabola a second time? Illustrate with a sketch.
> Find equations of the planes that are parallel to the plane x + 2y - 2z = 1 and two units away from it.
> Show that the distance between the parallel planes ax + by + cz + d1 = 0 and ax + by + cz + d2 = 0 is //
> Find the distance between the given parallel planes. 6z = 4y - 2x, 9z = 1 - 3x + 6y
> Which of the following four lines are parallel? Are any of them identical? Li: x= 1 + 6t, y=1 – 3t, z= 12t + 5 L2: x= 1 + 2t, y= t, z =1 + 4t L3: 2x – 2 = 4 – 4y = z + 1 L4: r = (3, 1, 5) + t(4, 2, 8)
> Which of the following four planes are parallel? Are any of them identical? Pi: 3x + 6у — 32 — 6 Р:: 4х — 12у + 82 3D 5 Р:: 9у — 1 + 3х + 62 Р:: z — х + 2у — 2
> Find parametric equations for the line through the point (0, 1, 2) that is perpendicular to the line x = 1 + t, y = 1 - t, z = 2t and intersects this line.
> Find parametric equations for the line through the point (0, 1, 2) that is perpendicular to the line x = 1 + t, y = 1 - t, z = 2t and intersects this line.
> (a) Find the point at which the given lines intersect: (b). Find an equation of the plane that contains these lines. r = (1, 1, 0) + 1(1, –1, 2) r= (2,0, 2) + s(-1, 1,0)
> Find an equation of the plane with x-intercept a, y-intercept b, and z-intercept c.
> Differentiate the function. f (x) = x ln x - x

