Question: A newly formed firm must decide on
A newly formed firm must decide on a plant location. There are two alternatives under consideration: locate near the major raw materials or locate near the major customers. Locating near the raw materials will result in lower fixed and variable costs than locating near the market, but the owners believe there would be a loss in sales volume because customers tend to favor local suppliers. Revenue per unit will be $185 in either case. Using the following information, determine which location would produce the greater profit.
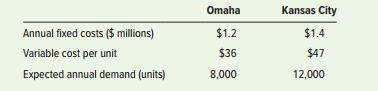
Transcribed Image Text:
Omaha Kansas City Annual fixed costs ($ millions) $1.2 $1.4 Variable cost per unit $36 $47 Expected annual demand (units) 8,000 12,000
> An automatic filling machine is used to fill 1-liter bottles of cola. The machine’s output is approximately normal with a mean of 1.0 liter and a standard deviation of .01 liter. Output is monitored using means of samples of 25 observations. a. Determine
> A production process consists of a three-step operation. The scrap rate is 10 percent for the first step and 6 percent for the other two steps. a. If the desired daily output is 450 units, how many units must be started to allow for loss due to scrap? b.
> Specifications for a part for a DVD player state that the part should weigh between 24 and 25 ounces. The process that produces the parts has a mean of 24.5 ounces and a standard deviation of .2 ounce. The distribution of output is normal. a. What percen
> Use the three-step process described in the previous section on Using Control Charts and Runs Tests Together to decide if the following observations represent a process that is in control. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 0 3 2 0 1 3 2 1 0 2 Observation
> The following is a control chart for the average number of minor errors in 22 service reports. What can you conclude from these data? Explain how you reached your conclusion UCL LCL
> Many organizations use the same process capability standard for all their products or services (e.g., 1.33), but some companies use multiple standards: different standards for different products or services (e.g., 1.00, 1.20, 1.33, and 1.40). What reason
> The Good Chocolate Company makes a variety of chocolate candies, including a 12-ounce chocolate bar (340 grams) and a box of six 1-ounce chocolate bars (170 grams). a. Specifications for the 12-ounce bar are 330 grams to 350 grams. What is the largest s
> As part of an insurance company’s training program, participants learn how to conduct an analysis of clients’ insurability. The goal is to have participants achieve a time in the range of 30 to 45 minutes. Test results for three participants were: Armand
> An appliance manufacturer wants to contract with a repair shop to handle authorized repairs in Indianapolis. The company has set an acceptable range of repair time of 50 minutes to 90 minutes. Two firms have submitted bids for the work. In test trials, o
> Briefly define or explain each of these tools: a. Brainstorming b. Benchmarking c. Run charts
> Garden Variety Flower Shop uses 750 clay pots a month. The pots are purchased at $2 each. Annual carrying costs per pot are estimated to be 30 percent of cost, and ordering costs are $20 per order. The manager has been using an order size of 1,500 flower
> Each of the processes listed is non centered with respect to the specifications for that process. Compute the appropriate capability index for each, and decide if the process is capable Process Мean Standard Deviation Lower Spec Upper Spec 15.0 0.32
> (Refer to Solved Problem 2.) Suppose the process specs are 9.65 and 10.35 minutes. Based on the data given, does it appear that the specs are being met? If not, what should one look for?
> A company has just negotiated a contract to produce a part for another firm. In the process of manufacturing the part, the inside diameter of successive parts becomes smaller and smaller as the cutting tool wears. However, the specs are so wide relative
> Arrange six departments into a 2 × 3 grid so that these conditions are satisfied: 1 close to 2, 5 close to 2 and 6, 2 close to 5, and 3 not close to 1 or 2.
> Briefly describe each of the seven quality tools.
> Use both types of run tests to analyze the daily expense voucher listed. Assume a median of $31. Day Amount Day Amount Day Amount Day Amount 1 $27.69 16 $29.65 31 $40.54 46 $25.16 2 28.13 17 31.08 32 36.31 47 26.11 3 33.02 18 33.03 33 27.14 48 29.84
> Analyze the data in the following problems using median and up/down run tests with z = ± 2. a. Given the following run test results of process output, what do the results of the run tests suggest about the process? Test z–……………..score Median ……………….+ 1
> For each of the accompanying control charts, analyze the data using both median and up/down run tests with z = ± 1.96 limits. Are nonrandom variations present? Assume the center line is the long term median. UCL A. LCL UCL B. LCL
> What is the goal of line balancing? What happens if a line is unbalanced?
> Compare equipment maintenance strategies in product and process layouts.
> The time needed for checking in at a hotel is to be investigated. Historically, the process has had a standard deviation equal to .146. The means of 39 samples of n = 14 are a. Construct an x¯ -chart for this process with three-sigma limits
> The lower and upper specifications for the computer upgrades in Problem 4 are 78 minutes and 81 minutes. Based on the data in the problem, would you say that the specifications are being met? Estimate the percentage of process output that can be expected
> What characteristics of potato chips concern Jays in terms of quality?
> Do you feel that Jays is overdoing it with its concern for quality?Explain.
> What is a run? How are run charts useful in process control?
> Make a check sheet and then a Pareto diagram for the following car repair shop data. Ticket No. Work Ticket No. Work Ticket No. Work 1 Tires 11 Brakes 21 Lube & oil 2 Lube & oil 12 Lube & oil 22 Brakes 3 Tires 13 Battery 23 Transmission Battery 14 L
> Briefly explain the purpose of each of these control charts: a. x-bar b. Range c. p-chart d. c-chart
> What are the key elements of the TQM approach? What is the driving force behind TQM?
> What are the key concepts that underlie the construction and interpretation of control charts?
> How did Jim conclude that the process was not capable based on his first set of samples?
> List the steps in the control process.
> Classify each of the following as either a Type I error or a Type II error: a. Putting an innocent person in jail b. Releasing a guilty person from jail c. Eating (or not eating) a cookie that fell on the floor d. Not seeing a doctor as soon as possible
> A computer repair shop had received a number of complaints on the length of time it took to make repairs. The manager responded by increasing the repair staff by 10 percent. Complaints on repair time quickly decreased, but then complaints on the cost of
> How important is it for managers to maintain and promote ethical behavior in dealing with quality issues? Does your answer depend on the product or service involved?
> Give three examples of what would be considered unethical behavior involving management of quality, and state which ethical principle (see Chapter 1) is violated.
> What quality-related trade-offs might there be between having a single large, centralized produce processing facility and having many small, decentralized produce-processing facilities?
> More and more people are using the Internet. And when these people want information about a company’s products or services, they often go to the company’s website. In a study of the home pages of Fortune 500 companies, 13 factors were deemed critical to
> What trade-offs are involved in deciding to have a single large, centrally located facility instead of several smaller, dispersed facilities?
> Who needs to be involved in facility location decisions?
> List some common reasons for redesigning layouts.
> In what ways have tech tools improved the process of site selection?
> Rework Problem 4b using this additional information: Expansion would result in an increase of $70,000 per year in transportation costs, subcontracting would result in an increase of $25,000 per year, and adding a new location would result in an increase
> Who needs to be involved in setting priorities for quality improvement?
> a. The following table contains figures on the monthly volume and unit costs for a random sample of 16 items from a list of 2,000 inventory items at a health care facility. Develop an A-B-C classification for these items. b. Given the monthly usages in
> Why are routing and scheduling continual problems in process layouts?
> A company that produces pleasure boats has decided to expand one of its lines. Current facilities are insufficient to handle the increased workload, so the company is considering three alternatives, A (new location), B (subcontract), and C (expand existi
> A small producer of machine tools wants to move to a larger building, and has identified two alternatives. Location A has annual fixed costs of $800,000 and variable costs of $14,000 per unit; location B has annual fixed costs of $920,000 and variable co
> The owner of Genuine Subs, Inc., hopes to expand the present operation by adding one new outlet. She has studied three locations. Each would have the same labor and materials costs (food, serving containers, napkins, etc.) of $1.76 per sandwich. Sandwich
> An analysis of sites for a distribution center has led to two possible sites (L1 and L2 on the map). The sites are comparable on every key factor. The one remaining factor is the center of gravity. Use the center of gravity method to select the better si
> A company that handles hazardous waste wants to minimize the shipping cost for shipments to a disposal center from five receiving stations it operates. Given the locations of the receiving stations and the volumes to be shipped daily, determine the locat
> A clothing manufacturer produces women’s clothes at four locations in Mexico. Relative locations have been determined, as shown in the table below. The location of a central shipping point for bolts of cloth must now be determined. Week
> A toy manufacturer produces toys in five locations throughout the country. Raw materials (primarily barrels of powdered plastic) will be shipped from a new, centralized warehouse whose location is to be determined. The monthly quantities to be shipped to
> What are the trade-offs that occur when a process layout is used? What are the trade-offs that occurwhen a product layout is used?
> A manager has received an analysis of several cities being considered for a new office complex. The data (10 points maximum) are as follows: a. If the manager weights the factors equally, how would the locations stack up in terms of their composite facto
> Answer these questions about inspection: a. What level of inspection is optimal? b. What factors guide the decision of how much to inspect? c. What are the main considerations in choosing between centralized inspection and on-site inspection? d. What poi
> a. Determine an A-B-C classification for these items: b. Find the EOQ given this information: D = 4,500 units/year, S = $36, and H = $10 per unit per year. c. Find the economic production quantity given this information. D = 18,000 units/year, S = $100
> Prepare a cause-and-effect diagram to analyze the possible causes of late delivery of parts ordered from a supplier.
> Determine which location has the highest composite score: Factor Weight East #1 East #2 West Initial cost 8 100 150 140 Traffic 10 40 40 30 Maintenance 20 25 18 Dock space 6 25 10 12 Neighborhood 4 12 8 15
> Using the following factor ratings, determine which location alternative (A, B, or C) should be chosen on the basis of maximum composite score. Location Score Factor (100 points each) Weight A B Convenience .15 80 70 60 Parking facilities .20 72 76
> For each of the four types of organizations shown, rate the importance of each factor in terms of making location decisions using L = low importance, M = moderate importance, and H = high importance. Factor Local Bank Steel Mill Food Warehouse Publi
> A retired auto mechanic hopes to open a rustproofing shop. Customers would be local new-car dealers. Two locations are being considered, one in the center of the city and one on the outskirts. The central city location would involve fixed monthly costs o
> A firm that has recently experienced enormous growth is seeking to lease a small plant in Memphis, TN; Biloxi, MS; or Birmingham, AL. Prepare an economic analysis of the three locations given the following information: Annual costs for building, equipmen
> Town residents, and residents of nearby towns how might a Walmart representative respond to the negative criticisms that might be brought up, and what other benefits could the representative offer the planning board to bolster Walmart’s case of gaining t
> Walmart is one of the largest corporations in the world, and it has obviously enjoyed tremendous success. But while many welcome its location in their communities, others do not. Some complain that its presence has too many negative effects on a communit
> What are the potential benefits of locating in foreign countries? Potential drawbacks?
> A new order has come into your department. The capability of the process used for this type of work will enable virtually all of the output to be well within the specs. a. What benefits might be derived from this situation? b. What alternatives might be
> How are manufacturing and nonmanufacturing location decisions similar? Different?
> Offwego Airlines has a daily flight from Chicago to Las Vegas. On average, 18 ticket holders cancel their reservations, so the company intentionally overbooks the flight. Cancellations can be described by a normal distribution with a mean of 18 passenger
> Why might the choice of equipment that provides flexibility sometimes be viewed as a management cop-out?
> Suppose that a table lamp fails to light when turned on. Prepare a simple cause-and-effect diagram to analyze possible causes.
> Respond to this statement: “The importance of the location decision is often vastly overrated; the fact that virtually every type of business is located in every section of the country means there should be no problem in finding a suitable location.”
> Discuss recent trends in location and possible future strategies.
> What are the basic assumptions in locational cost-profit-volume analysis?
> Outline the general approach for developing location alternatives.
> What is factor rating, and how does it work?
> A company is considering the relocation of its manufacturing plant and administrative offices from a small city in the Midwest to a similar-sized city in the South. Approximately 20 percent of the residents of the city are employed by the company, and ma
> A customer has recently tightened the specs for a part your company supplies. The specs are now much tighter than the machine being used for the job is capable of. Briefly identify alternatives you might consider to resolve this problem.
> Give three examples of unethical behavior involving location selection, and indicate which ethical principle is violated.
> Corruption and bribery are common in some countries. Would you avoid locating in such a country,or locate there and deal with it? If the latter, how would you deal with it?
> A Las Vegas supermarket bakery must decide how many wedding cakes to prepare for the upcoming weekend. Cakes cost $33 each to make, and they sell for $60 each. Unsold cakes are reduced to half-price on Monday, and typically one-third of those are sold. A
> The owner of a fast-food franchise has exclusive rights to operate in a medium-sized metropolitanarea. The owner currently has a single outlet open, which has proved to be very popular, and thereare often waiting lines of customers. The owner is therefor
> What are the trade-offs in the following? a. Using self-directed teams instead of a more conventional approach with occasional use of teams. b. Deciding how often to update standard times due to minor changes in work methods. c. Choosing between time stu
> Prepare a run diagram for this emergency call data. Use five-minute intervals (i.e., count the calls received in each five-minute interval. Use intervals of 0 to 4, 5 to 9, etc.). Note: Two or more calls may occur in the same minute; there were three ope
> Why is management of technology important?
> In what ways does technology have an impact on job design?
> Who uses the results of work measurement in an organization, and how do they use them?
> Explain the term knowledge-based pay system.
> Select one of the quality gurus and briefly describe his major contributions to quality management.
> a. What is ergonomics and why is it important in job design? b. Explain how it can relate to quality of work life.
> a. Contrast the meanings of the terms job enlargement and job enrichment. b. What is the purpose of approaches such as job enlargement and job enrichment?
> What are some of the main advantages and disadvantages of specialization from a management perspective? From a worker’s perspective?
> A manager is going to purchase new processing equipment and must decide on the number of spare parts to order with the new equipment. The spares cost $200 each, and any unused spares will have an expected salvage value of $50 each. The probability of usa
> What is work sampling? How does it differ from time study?
> Comment on the following: “At any given instant, the standard times for many jobs will not be strictly correct.” a. Why is this so? b. Does this mean that those standards are useless? Explain.
> Name some reasons why methods analyses are needed. How is methods analysis linked to productivity improvements?
> What are the main advantages of a process layout? The main disadvantages?
> Some Japanese firms have a policy of rotating their managers among different managerial jobs. In contrast, American managers are more likely to specialize in a certain area (e.g., finance or operations). Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each o
> Briefly describe the five process types, and indicate the kinds of situations in which each would be used.
> Define and contrast control limits, specifications, and process variability.

