Question: A schedule of intercompany investment interests and
A schedule of intercompany investment interests and separate earnings for Par Corporation, Sit Corporation, and Tot Corporation is presented as follows:
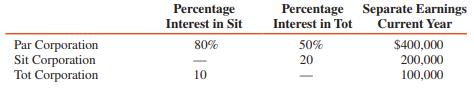
REQUIRED:
1. Compute controlling interest share and noncontrolling interest share of consolidated net income assuming no investment differences between fair value and book value or unrealized profits.
2. Compute controlling interest share and noncontrolling interest share assuming $20,000 unrealized inventory profits on Tot’s sales to Sit and a $40,000 gain on Par’s sale of land to Sit.
Transcribed Image Text:
Percentage Interest in Sit Percentage Separate Earnings Interest in Tot Current Year Par Corporation Sit Corporation Tot Corporation 80% 50% $400,000 200,000 100,000 20 10
> San is a 90 percent–owned foreign subsidiary of Par, acquired by Par on January 1, 2016, at book value equal to fair value, when the exchange rate for LCUs of San’s home country was $0.24. San’s funct
> PWA Corporation paid $1,710,000 for 100 percent of the stock of SAA Corporation on January 1, 2016, when the stockholders’ equity of SAA consisted of 5,000,000 LCU capital stock and 3,000,000 LCU-retained earnings. SAA’
> Pel, a U.S. firm, paid $308,000 for all the common stock of Sar of Israel on January 1, 2016, when the exchange rate for sheqels was $0.35. Sar’s equity on this date consisted of 500,000 sheqels common stock and 300,000 sheqels retained
> Phi, a U.S. firm, acquired 100 percent of Stu’s outstanding stock at book value on January 1, 2016, for $112,000. Stu is a New Zealand–based company, and its functional currency is the U.S. dollar. The exchange rate for New Zealand dollars (NZ$) was $0.7
> Par of Chicago acquired all the outstanding capital stock of Sar of London on January 1, 2016, for $1,120,000. The exchange rate for British pounds was $1.40 and Sar’s stockholders’ equity was £800,000, consisting of £500,000 capital stock and £300,000 r
> The affiliation structure for Pad Corporation and its subsidiaries is diagrammed as follows: The incomes and dividends for the affiliates for 2016 are (in thousands): ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: 1. Axe sold land to Sal during 2016 at a $20,000 gain. The
> On January 1, 2016, Pan acquired all the stock of Sim of Belgium for $1,200,000, when Sim had 20,000,000 euros (Eu) capital stock and 15,000,000 euros (Eu) retained earnings. Sim’s net assets were fairly valued on this date and any cost/ book value diffe
> Stadt Corporation of the Netherlands is a 100 percent–owned subsidiary of Port Corporation, a U.S. firm, and its functional currency is the U.S. dollar. Stadt’s books of record are maintained in euros and its inventory is carried at cost. The current exc
> On January 1, 2016, Pai, a U.S. firm, purchases all the outstanding capital stock of Sta, a British firm, for $880,000, when the exchange rate for British pounds is $1.55. The book values of Sta’s assets and liabilities are equal to fai
> 1. When consolidated financial statements for a U.S. parent and its foreign subsidiary are prepared, the account balances expressed in foreign currency must be converted into the currency of the reporting entity. One objective of the translation process
> 1. A German subsidiary of a U.S. firm has the British pound as its functional currency. Under the provisions of ASC Topic 830, the U.S. dollar from the subsidiary’s viewpoint would be: a Its local currency b Its recording currency c A foreign currency d
> 1. Fay had a realized foreign exchange loss of $15,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, and must determine whether the following items will require year-end adjustment: Fay had an $8,000 equity adjustment resulting from the translation of the accou
> Pac of the United States purchased all the outstanding stock of Swi of Switzerland for $1,350,000 cash on January 1, 2016. The book values of Swi’s assets and liabilities were equal to fair values on this date except for land, which was
> Pal acquired all the stock of Sta of Britain on January 1, 2016, for $163,800, when Sta had capital stock of £60,000 and retained earnings of £30,000. Sta’s assets and liabilities were fairly valued, except for equipment with a three-year life that was u
> Interest rate swaps were used in the chapter to highlight the differences between fair-value and cash-flow hedge accounting. Explain what type of risk is being hedged when a pay-fixed, receive variable swap is used to hedge an existing variable-rate loan
> A hedged firm purchase or sale commitment typically qualifies for fair-value hedge accounting if the hedge is documented to be effective. Compare the accounting for both the derivative and the firm purchase or sale commitment under each of these circumst
> Pop Corporation purchased an 80 percent interest in Son Corporation for $170,000 on January 1, 2016, when Son’s stockholders’ equity was $200,000. The excess of fair value over book value is due to goodwill. At Decembe
> Hedge effectiveness must be documented before a particular hedge qualifies for hedge accounting. Describe the most common approaches used to determine hedge effectiveness and when they are appropriate. In each of the approaches, when would a particular h
> Explain the differences between options, forward contracts, and futures contracts and the potential benefits and potential costs of each type of contract.
> Explain the objective of hedge accounting and how this objective should improve the transparency of financial statements.
> Briefly describe how derivatives are accounted for according to the International Accounting Standards Board. Is the accounting similar to U.S. GAAP? How is it different?
> Briefly describe how derivatives are accounted for according to the International Accounting Standards Board. Is the accounting similar to U.S. GAAP? How is it different?
> ASC 815 allows companies to account for certain hedges of existing foreign currency–denominated receivables and payables as cash-flow hedges. Also in ASC 815, hedges of existing assets and liabilities must be accounted for as fair-value hedges. Explain t
> Explain the circumstances under which fair-value hedge accounting should be used and when cash-flow hedge accounting should be used.
> Interest rate swaps were used in the chapter to highlight the differences between fair-value and cash-flow hedge accounting. Explain what type of risk is being hedged when a receive-fixed, pay-variable swap is used to hedge an existing fixed-rate loan.
> What criteria are required for a hedged item to qualify for special accounting as a fair-value hedge?
> What criteria are required for a hedged item to qualify for special accounting as a cash-flow hedge?
> Par Corporation acquired an 80 percent interest in Sip Corporation for $180,000 cash on January 1, 2016, when Sip had capital stock of $50,000 and retained earnings of $150,000. The excess of fair value over book value acquired is due to a patent, which
> On January 1, 2016, Cam borrows $400,000 from Ven. The five-year term note is a variable-rate one in which the 2016 interest rate is determined to be 8 percent, the LIBOR rate at January 1, 2016, +2%. Subsequent years’ interest rates are determined in a
> Ins makes sophisticated medical equipment. A key component of the equipment is Grade A silver. On May 1, 2016, Ins enters into a firm purchase agreement to buy 1,200,000 troy ounces (equal to 100,000 pounds) of Grade A silver from Sil, for delivery on Fe
> NGW, a consumer gas provider, estimates a rather cold winter. As a result it decides to enter into a futures contract on the NYMEX for natural gas on November 2, 2016. The trading unit is 10,000 million British thermal units (MMBtu). The three-month futu
> Mar, a U.S. firm, purchased equipment for 400,000 British pounds from Thc on December 16, 2016. The terms were n/30, payable in British pounds. On December 16, 2016, Mar also entered into a 30-day forward contract to hedge the account payable to Thc. The
> Bat, a U.S. corporation, anticipates a contract based on December 2, 2016, discussions to sell heavy equipment to Ram of Scotland for 500,000 British pounds. The equipment is likely to be delivered and the amount collected on March 1, 2017. In order to h
> On October 2, 2016, Flx, a U.S. company, entered into a forward contract to purchase 50,000 euros for delivery in 180 days at a forward rate of $0.6350. The forward contract is a derivative instrument hedging an identifiable foreign currency purchase com
> On April 1, 2016, Bay delivers merchandise to Ram for 200,000 pesos when the spot rate for pesos is 6.0496 pesos. The receivable from Ram is due May 31. Also on April 1, Bay hedges its foreign currency asset and enters into a 60-day forward contract to s
> Refer to Problem P 13-3 and assume that instead of initially signing a variable-rate loan, Cam receives a fixed rate of 8 percent on the loan on January 1, 2016. Instead of entering into a pay-fixed, receive-variable interest rate swap with Gra, Cam ente
> Brk signs a firm sales commitment with Riv. The contract is to sell 100,000 widgets deliverable in three months, on January 31, 2017, at the prevailing market price of widgets at that date. On November 1, 2016, the current sales price of widgets is $5 ea
> Refer to Exercise E 13-1 and assume that Jol enters into the forward contract to hedge a firm purchase commitment. Repeat parts 1 and 2 under this assumption. Data from Exercise E 13-1 On December 1, 2016, Jol Company enters into a 90-day forward contr
> Pin Corporation acquired a 90 percent interest in Sun Corporation for $360,000 cash on January 2, 2014, when Sun had capital stock of $200,000 and retained earnings of $150,000. Sun purchased its 10 percent interest in Pin in 2015 for $80,000. The excess
> On December 1, 2016, Jol Company enters into a 90-day forward contract with a rice speculator to purchase 500 tons of rice at $1,000 per ton. Jol enters into this contract in order to hedge an anticipated rice purchase. The contract is to be settled net.
> On November 2, 2016, Baz, a U.S. retailer, ordered merchandise from Mat of Japan. The merchandise is to be delivered to Baz on January 31, 2017, at a price of 1,000,000 yen. Also on November 2, Baz hedged the foreign currency commitment with Mat by contr
> On April 1, 2016, Win of Canada ordered customized fittings from Ace, a U.S. firm, to be delivered on May 31, 2016, at a price of 50,000 Canadian dollars. The spot rate for Canadian dollars on April 1, 2016, was $0.71. Also on April 1, in order to fix th
> On December 12, 2016, Car entered into three forward exchange contracts, each to purchase 100,000 Canadian dollars in 90 days. Assume a 12 percent interest rate. The relevant exchange rates are as follows: 1. Car entered into the first forward contract
> Wil has 100,000 units of widgets in its inventory on October 1, 2016. Wil purchased them for $1 per unit one month ago. It hedges the value of the widgets by entering into a forward contract to sell 100,000 widgets on January 31, 2017, for $2 each. The c
> Assume that one euro can be exchanged for 1.20 U.S. dollars. What is the exchange rate if the exchange rate is quoted directly? Indirectly?
> Criticize the following statement: “Exchange losses arise from foreign import activities, and exchange gains arise from foreign export activities.”
> Assume that a U.S. corporation imports electronic equipment from Japan in a transaction denominated in U.S. dollars. Is this transaction a foreign currency transaction? A foreign transaction? Explain the difference between these two concepts and their ap
> Explain the differences between forward contracts and futures contracts and the potential benefits and potential costs of each type of contract.
> Define the term derivative and provide examples of risks that derivative contracts are designed to reduce.
> A U.S. corporation imported merchandise from a British company for £1,000 when the spot rate was $1.45. It issued financial statements when the current rate was $1.47, and it paid for the merchandise when the spot rate was $1.46. What amount of exchange
> When are exchange gains and losses reflected in a business’s financial statements?
> How are assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency measured and recorded at the transaction date? At the balance sheet date?
> What is a spot rate with respect to foreign currency transactions? Could a spot rate ever be a historical rate? Could a spot rate ever be a fixed exchange rate? Discuss.
> What is the difference between official and floating foreign exchange rates? Does the United States have floating exchange rates?
> Distinguish between measurement and denomination in a particular currency.
> What does “Net Settlement” mean?
> Explain the differences between options and swaps and the potential benefits and potential costs of each type of contract.
> What are the primary characteristics that define a derivative? How many paragraphs does it take the ASC to define a derivative completely?
> In July of 2016, Sue enters into a forward agreement with Ann to lock in a sales price for wheat. Sue anticipates selling 300,000 bushels of wheat at the market in March of 2017. Ann agrees to a forward with Sue to buy 300,000 bushels at $5.20. Sue’s cos
> Comparative financial statements for Pen Corporation and its subsidiaries, Sir and Tip Corporations, for the year ended December 31, 2016, are as follows (in thousands): ADDITIONAL INFORMATION: 1. Pen acquired its 80 percent interest in Sir Corporation
> On June 1, 2016, TCO enters into a forward agreement with XYZ to buy 100,000 gallons of fuel oil at $2.40 on December 31, 2016. At the time of inception of the forward, the price of fuel oil is $2.45. On December 31, 2016, the price of fuel oil is $2.48.
> Sho of New York is an international dealer in jewelry and engages in numerous import and export activities. Sho’s receivables and payables in foreign currency units before year-end adjustments on December 31, 2016, are summarized as fol
> The accounts of Lin, a U.S. corporation, show $81,300 accounts receivable and $38,900 accounts payable at December 31, 2016, before adjusting entries are made. An analysis of the balances reveals the following: Accounts Receivable Receivable denominated
> Consider the same basic facts as in P12-2, but instead of a forward contract Sue purchases put options to sell 300,000 bushels at $5.20 per bushel. The options cost $0.05 a bushel. REQUIRED: 1. Determine the economic income of the sales transaction at v
> Zip purchased merchandise from Tas of Japan on November 1, 2016, for 10,000,000 yen, payable on December 1, 2016. The spot rate for yen on November 1 was $0.0075, and on December 1 the spot rate was $0.0076. REQUIRED: 1. Did the dollar weaken or strengt
> 1. If $1.5625 can be exchanged for 1 British pound, the direct and indirect exchange rate quotations are: a $1.5625 and 1 British pound, respectively b $1.5625 and 0.64 British pounds, respectively c $1.00 and 1.5625 British pounds, respectively d $1.00
> 1. Which of the following is true about the seller of a put option? a They have the right to buy the underlying b They have the right to sell the underlying c They have the obligation to buy the underlying d They have the obligation to sell the underlyin
> 1. What is a characteristic of a forward contract? a Traded on an exchange b Negotiated with a counterparty c Covers a stream of future payments d Must be settled daily 2. What is a characteristic of a swap? a Traded on an exchange b Only interest rates
> ATV had two foreign currency transactions during December 2016, as follows: December 12 Purchased electronic parts on account from Tok of Japan at an invoice price of 50,000,000 yen when the spot rate for yen was $0.00750.
> Meo imports merchandise from some Canadian companies and exports its own products to other Canadian companies. The unadjusted accounts denominated in Canadian dollars at December 31, 2016, are as follows: Account receivable from the sale of merchandise
> Pug Corporation acquired a 70 percent interest in Sat Corporation for $238,000 on January 2, 2015, when Sat’s equity consisted of $200,000 capital stock and $50,000 retained earnings. The excess is due to a patent amortized over a 10-ye
> 1. On September 1, 2016, Ban received an order for equipment from a foreign customer for 300,000 euros, when the U.S. dollar equivalent was $400,000. Ban shipped the equipment on October 15, 2016, and billed the customer for 300,000 euros when the U.S. d
> Dot, a U.S. company, sold inventory items on account to Roa of Great Britain for £200,000 on May 1, 2016, when the spot rate was 0.7000 pounds. The invoice was paid by Roa on May 30, 2016, when the spot rate was 0.7050 pounds. REQUIRED: Prepare Dot’s jo
> On November 16, 2016, Wik of the United States sold inventory items to Can of Canada for 90,000 Canadian dollars, to be paid on February 14, 2017. Exchange rates for Canadian dollars on selected dates are as follows: November 16, 2016...................
> On December 16, 2016, Ava Corporation, a U.S. firm, purchased merchandise from Wig Company for 40,000 euros to be paid on January 15, 2017. Relevant exchange rates for euros are as follows: December 16, 2016..................... $1.20 December 31, 2016.
> Assume that Pop Corporation acquires 60 percent of the voting common stock of Son Corporation for $6,000,000 and that a consolidated balance sheet is prepared immediately after the acquisition. Would total consolidated assets be equal to their fair value
> To what extent does push-down accounting facilitate the consolidation process?
> If income from a subsidiary is measured under the equity method and the statements are consolidated under entity theory, will consolidated net income equal parent net income?
> Under the entity theory, a total valuation of the subsidiary is imputed on the basis of the price paid by the parent company for its controlling interest. Do you see any practical or conceptual problems with this approach?
> Compare the parent-company and entity theories of consolidated financial statements.
> What is a joint venture and how are joint ventures organized?
> Pet Corporation owns 90 percent of Sod Corporation’s common stock and Sod owns 15 percent of Pet, both acquired at fair value equal to book value. Separate incomes and dividends of the affiliates for 2016 are as follows: 1. If the tre
> What is a joint venture and how are joint ventures organized?
> Cite the conditions under which consolidated net income under parent-company theory would equal income to controlling stockholders under entity theory.
> What disclosures are required for a variable interest entity? Are the disclosures only required for VIEs that will be consolidated?
> This chapter noted that an acquired firm may elect push-down accounting. If the transaction results in recognition of goodwill, should that goodwill also be reflected on the acquiree’s financial statements?
> At December 31, 2016, when the fair values of Sun Corporation’s net assets were equal to their book values of $2,400,000, Pam Corporation acquired an 80 percent interest in Sun for $2,240,000. One year later, at December 31, 2017, the c
> Pop Corporation paid $1,190,000 cash for 70 percent of the outstanding voting stock of Son Corporation on January 2, 2017, when Son Corporation’s stockholders’ equity consisted of $1,000,000 of $10 par common stock and
> Pam Corporation acquires an 80 percent interest in Sun Company on January 3, 2016, for $640,000. On this date Sun’s stockholders’ equity consists of $400,000 capital stock and $280,000 retained earnings. The fair value
> The adjusted trial balances of Pop Corporation and its 80 percent–owned subsidiary, Son Corporation, at December 31, 2017, are as follows (in thousands): Pop acquired its interest in Son for $1,280,000 on January 1, 2016, when Son&aci
> Pop Corporation owns a 40 percent interest in Son Company, a joint venture that is organized as an undivided interest. In its separate financial statements, Pop accounts for Son under the equity method, but for reporting purposes, the proportionate conso
> Use the information and assumptions from Problem P 11-9 for this problem. The accompanying financial statements are for Pam and Sun Corporations, one year after the acquisition. Note that Sun’s statements are presented first under 90 pe
> Pin, Inc., owns 80 percent of the capital stock of Son Company and 70 percent of the capital stock of Tin, Inc. Son owns 15 percent of the capital stock of Tin. Tin owns 25 percent of the capital stock of Pin. These ownership interrelationships are illus
> Pam Corporation paid $180,000 cash for a 90 percent interest in Sun Corporation on January 1, 2017, when Sun’s stockholders’ equity consisted of $100,000 capital stock and $20,000 retained earnings. Sun Corporation&aci
> Pop Corporation paid $3,000,000 for an 80 percent interest in Son Corporation on January 1, 2016, when the book values and fair values of Son’s assets and liabilities were as follows (in thousands): REQUIRED: 1. Prepare a journal entr
> Pam Corporation paid $960,000 cash for a 100 percent interest in Sun Corporation on January 1, 2017, when Sun’s stockholders’ equity consisted of $400,000 capital stock and $160,000 retained earnings. Sunâ€&
> The individual and consolidated balance sheets and income statements of P and S Companies for the current year are presented in the accompanying table. The entity theory is used. ADDITIONAL INFO R MATION: 1. P Company purchased its interest in S Company
> Balance sheets for Pop Corporation and its 80 percent–owned subsidiary, Son Company, at December 31, 2017, are summarized as follows (in thousands): ADDITIONAL INFO R MATION: 1. Pop Corporation paid $256,000 for its 80 percent interes
> 1. Pet Company pays $1,440,000 for an 80 percent interest in Sit Corporation on December 31, 2016, when Sit’s net assets at book value and fair value are $1,600,000. Under entity theory, the noncontrolling interest at acquisition is: a $288,000 b $320,00
> 1. A joint venture would not be organized as a(an): a Corporation b Can participate in the overall management of the venture c Partnership d Undivided interest 2. Corporate joint ventures should be accounted for by the equity method, provided that the j

