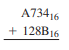Question: Add in the indicated base. /
> The numerals in a base 5 numeration system are as illustrated with their equivalent Hindu–Arabic numerals. Add the following base 5 numerals.
> The numerals in a base 5 numeration system are as illustrated with their equivalent Hindu–Arabic numerals. Add the following base 5 numerals.
> Numbers in Circles Place the numbers 1 through 6 in the circles below so that the sum along each of the three straight lines is the same. Each number must be used exactly once. (Note: There is more than one correct answer.)
> The numerals in a base 5 numeration system are as illustrated with their equivalent Hindu–Arabic numerals. Add the following base 5 numerals.
> The numerals in a base 5 numeration system are as illustrated with their equivalent Hindu–Arabic numerals. Add the following base 5 numerals.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Write the statement in symbolic form and construct a truth table. I have worked all week, but I have not been paid.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Write the Hindu–Arabic numerals in the numeration system discussed in Exercises 45–48 19
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Write the statement in symbolic form and construct a truth table. Mr. Hart got his car started, but he was late for class.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Divide in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> F = {15, 16, 17, … , 100}
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Write the statement in symbolic form and construct a truth table. Apples are a good source of fiber and oranges are a good source of vitamin C.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Multiply in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Assume the numerals given are in a base 5 numeration system. Assume the numerals in this system and their equivalent Hindu–Arabic numerals are Write the Hindu–Arabic numerals equivalent to each of the following.
> Airport Parking The chart below shows parking rates at John F. Kennedy (JFK) Airport in New York, New York, as of July 8, 2014. (a) Jeff is going out of town for 5 full days. How much will he save by parking in the long-term lot rather than the short-ter
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Subtract in the indicated base.
> Add in the indicated base.
> Construct a truth table for the statement. ( r ( q ) ( ( p
> Below is a photo of the keyboard of a phone. Certain businesses like to use a word to help people remember their phone number. For example, a doctor’s office may use the word medical to represent its phone number, which would be 633-422
> Add in the indicated base.
> Add in the indicated base.
> Add in the indicated base.
> Add in the indicated base.
> Add in the indicated base.
> Add in the indicated base.
> Add in the indicated base.
> Write the Hindu–Arabic numeral in expanded form. 562
> Write the Hindu–Arabic numeral in expanded form. 712
> Construct a truth table for the statement. ( r ( ( p ) ( ( q
> Write the Hindu–Arabic numeral in expanded form. 89
> Assume the numerals given are in a base 5 numeration system. Assume the numerals in this system and their equivalent Hindu–Arabic numerals are Write the Hindu–Arabic numerals equivalent to each of the following.
> Write the Hindu–Arabic numeral in expanded form. 63
> First convert each numeral to Hindu–Arabic numeral and then perform the indicated operation. Finally, convert the answer back to a numeral in the original numeration system.
> First convert each numeral to Hindu–Arabic numeral and then perform the indicated operation. Finally, convert the answer back to a numeral in the original numeration system.
> First convert each numeral to Hindu–Arabic numeral and then perform the indicated operation. Finally, convert the answer back to a numeral in the original numeration system.
> First convert each numeral to Hindu–Arabic numeral and then perform the indicated operation. Finally, convert the answer back to a numeral in the original numeration system.
> ( a) Write the Mayan numeral for 999,999 (b) Write the Babylonian numeral for 999,999.
> (a)The Babylonian system did not have a symbol for zero. Why did this lead to some confusion? (b) Write 133 and 7980 as Babylonian numerals.
> Describe two ways that the Mayan place-value system dif-fers from the Hindu–Arabic place-value system.
> Construct a truth table for the statement. ( p ( ( q ( r )
> In Exercises 13–22, show that the set has cardinal number / by establishing a one-to-one correspondence between the set of counting numbers and the given set. Be sure to show the pairing of the general terms in the sets. {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, ….}
> Suppose a place-value numeration system has base , with digits represented by the symbols / . Write each expression in expanded form.
> Suppose a place-value numeration system has base , with digits represented by the symbols /Write each expression in expanded form.
> Palindromes A palindrome is a number (or word) that reads the same forward and backward. The numbers 1991 and 43234 are examples of palindromes. How many palindromes are there between the numbers 2000 and 3000? List them.
> Write the numeral in the indicated systems of numeration. / in Hindu–Arabic and Mayan
> Write the numeral in the indicated systems of numeration. / in Hindu–Arabic and Babylonian
> Write the numeral as a Mayan numeral. 21,846
> Write the numeral as a Mayan numeral. 2163
> Write the numeral as a Mayan numeral. 406
> Write the numeral as a Mayan numeral. 297
> Write the numeral as a Mayan numeral. 33
> Construct a truth table for the statement. ( p ( ( q ) ( r
> Write the numeral as a Mayan numeral. 13
> Write the Mayan numeral as a Hindu–Arabic numeral.
> Write the Mayan numeral as a Hindu–Arabic numeral.
> Assume the numerals given are in a base 5 numeration system. Assume the numerals in this system and their equivalent Hindu–Arabic numerals are Write the Hindu–Arabic numerals equivalent to each of the following.
> Write the Mayan numeral as a Hindu–Arabic numeral.
> Write the Mayan numeral as a Hindu–Arabic numeral.
> Write the Mayan numeral as a Hindu–Arabic numeral.
> Write the Mayan numeral as a Hindu–Arabic numeral.
> Write the numeral as a Babylonian numeral. 12,435
> Write the numeral as a Babylonian numeral. 3605
> Construct a truth table for the statement. ( p ( ( q ) ( r
> Write the numeral as a Babylonian numeral. 512
> Write the numeral as a Babylonian numeral. 471
> Write the numeral as a Babylonian numeral. 243
> Write the numeral as a Babylonian numeral. 32
> Ties, Ties, Ties I have at least three ties. All my ties are red except two. All my ties are blue except two. All my ties are brown except two. How many ties do I have?