Question: Alligators perform a spinning maneuver, referred to
Alligators perform a spinning maneuver, referred to as a “death roll,” to subdue their prey. Videos were taken of juvenile alligators performing this maneuver in a study for the article “Death Roll of the Alligator, Mechanics of Twist and Feeding in Water” (Journal of Experimental Biology, Vol. 210, pp. 2811–2818) by F. Fish et al. One of the variables measured was the degree of the angle between the body and head of the alligator while performing the roll. A sample of 20 rolls yielded the following data, in degrees.
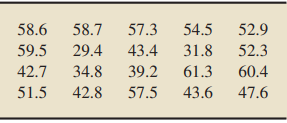
At the 5% significance level, do the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that, on average, the angle between the body and head of an alligator during a death roll is greater than 45◦?
> Contain graphs portraying the decision criterion for a one-mean z-test. The curve in each graph is the normal curve for the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. For each exercise, determine the: a. rejection region. b. n
> Contain graphs portraying the decision criterion for a one-mean z-test. The curve in each graph is the normal curve for the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. For each exercise, determine the: a. rejection region. b. n
> Contain graphs portraying the decision criterion for a one-mean z-test. The curve in each graph is the normal curve for the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. For each exercise, determine the: a. rejection region. b. n
> Suppose that a variable of a population has a reverse-J-shaped distribution and that two simple random samples are taken from the population. a. Would you expect the distributions of the two samples to have roughly the same shape? If so, what shape? b. W
> Contain graphs portraying the decision criterion for a one-mean z-test. The curve in each graph is the normal curve for the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. For each exercise, determine the: a. rejection region. b. n
> Define critical values?
> Define nonrejection region?
> Define rejection region?
> Define test statistic?
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test led to nonrejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or
> What role does the decision criterion play in a hypothesis test?
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test led to rejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or as a
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test lead to rejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or as
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test lead to nonrejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or
> Suppose that a variable of a population has a bell-shaped distribution. If you take a large simple random sample from the population, roughly what shape would you expect the distribution of the sample to be? Explain your answer.
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test lead to nonrejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test lead to rejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or as
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test lead to rejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or as
> Explain what each of the following would mean. a. Type I error b. Type II error c. Correct decision Now suppose that the results of carrying out the hypothesis test led to nonrejection of the null hypothesis. Classify that conclusion by error type or as
> Data on salaries in the public school system are published annually in Ranking of the States and Estimates of School Statistics by the National Education Association. The mean annual salary of (public) classroom teachers is $55.4 thousand. A hypothesis t
> A study by researchers at the University of Maryland addressed the question of whether the mean body temperature of humans is 98.6◦F. The results of the study by P. Mackowiak et al. appeared in the article “A Critical Appraisal of 98.6◦F, the Upper Limit
> A study by M. Chen et al. titled “Heat Stress Evaluation and Worker Fatigue in a Steel Plant” (American Industrial Hygiene Association, Vol. 64, pp. 352–359) assessed fatigue in steel plant workers due to heat stress. Among other things, the researchers
> Regarding the term null hypothesis: a. Originally, what did the word null in null hypothesis stand for? b. What has the term null hypothesis come to mean now?
> According to the Bureau of Crime Statistics and Research of Australia, as reported on Lawlink, the mean length of imprisonment for motor-vehicle-theft offenders in Australia is 16.7 months. You want to perform a hypothesis test to decide whether the mean
> Dementia is the loss of the intellectual and social abilities severe enough to interfere with judgment, behavior, and daily functioning. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia. In the article “Living with Early Onset Dementia: Exploring
> Give two reasons why the use of smooth curves to describe shapes of distributions is helpful.
> Iron is essential to most life forms and to normal human physiology. It is an integral part of many proteins and enzymes that maintain good health. Recommendations for iron are provided in Dietary Reference Intakes, developed by the Institute of Medicine
> Grey seals are one of several types of earless seals. The length of time that a female grey seal nurses her pup is studied by S. Twiss et al. in the article “Variation in Female Grey Seal (Halichoerus grypus) Reproductive Performance Correlates to Proact
> Cadmium, a heavy metal, is toxic to animals. Mushrooms, however, can absorb and accumulate cadmium at high concentrations. The Czech and Slovak governments have set a safety limit for cadmium in dry vegetables at 0.5 part per million (ppm). M. Melgar et
> In the U.S. court system, a defendant is assumed innocent until proven guilty. Suppose that you regard a court trial as a hypothesis test with null and alternative hypotheses H0: Defendant is innocent Ha: Defendant is guilty. a. Explain the meaning of a
> We introduced one-sided one-mean t-intervals. The following relationship holds between hypothesis tests and confidence intervals for one-mean t-procedures: For a right-tailed hypothesis test at the significance level α, the null hypothesis H0: μ = μ0 wil
> Suppose that you are performing a statistical test to decide whether a nuclear reactor should be approved for use. Further suppose that failing to reject the null hypothesis corresponds to approval. What property would you want the Type II error probabil
> We introduced one-sided one-mean t-intervals. The following relationship holds between hypothesis tests and confidence intervals for one-mean t-procedures: For a left-tailed hypothesis test at the significance level α, the null hypothesis H0: μ = μ0 will
> The following relationship holds between hypothesis tests and confidence intervals for one-mean t-procedures: For a two-tailed hypothesis test at the significance level α, the null hypothesis H0: μ = μ0 will be rejected in favor of the alternative hypoth
> Suppose that you want to perform a hypothesis test for a population mean. Assume that the variable under consideration has a symmetric nonnormal distribution and that the population standard deviation is unknown. Further assume that the sample size is la
> Suppose that you want to perform a hypothesis test for a population mean. Assume that the variable under consideration is normally distributed and that the population standard deviation is unknown. a. Is it permissible to use the t-test to perform the hy
> Explain the meaning of Distribution of a variable.
> According to the document Out of Reach, published by the National Low Income Housing Coalition, the fair market rent (FMR) for a two-bedroom unit in the United States is $949. A sample of 100 randomly selected two-bedroom units yielded the data on monthl
> In 2011, the average car in the United States was driven 13.5 thousand miles, as reported by the Federal Highway Administration in Highway Statistics. On the WeissStats site, we provide last year’s distance driven, in thousands of miles, by each of 500 r
> Previous studies have shown that urban bus drivers have an extremely stressful job, and a large proportion of drivers retire prematurely with disabilities due to occupational stress. In the paper, “Hassles on the Job: A Study of a Job Intervention with U
> Use the technology of your choice to decide whether applying the t -test to perform a hypothesis test for the population mean in question appears reasonable. Explain your answers. In the paper “Reassessment of TL Age Estimates of Burnt Flint from the Pal
> Use the technology of your choice to decide whether applying the t -test to perform a hypothesis test for the population mean in question appears reasonable. Explain your answers. An issue of Brokerage Report discussed the capital spending of telecommuni
> Use the technology of your choice to decide whether applying the t -test to perform a hypothesis test for the population mean in question appears reasonable. Explain your answers. In the article “Material Culture as Memory: Combs and Cremations in Early
> Suppose that a hypothesis test is performed at a small significance level. State the appropriate conclusion in each case by referring to Key Fact. a. The null hypothesis is rejected. b. The null hypothesis is not rejected.
> Use the technology of your choice to decide whether applying the t -test to perform a hypothesis test for the population mean in question appears reasonable. Explain your answers. From the Florida State Center for Health Statistics report, Women and Card
> Dirt bikes are simpler and lighter motorcycles that are designed for off-road events. Specifications for dirt bikes can be found through Motorcycle USA on their website www.motorcycle-usa.com. A random sample of 30 dirt bikes have a mean fuel capacity of
> The ankle brachial index (ABI) compares the blood pressure of a patient’s arm to the blood pressure of the patient’s leg. The ABI can be an indicator of different diseases, including arterial diseases. A healthy (or normal) ABI is 0.9 or greater. In a st
> Explain the meaning of Population distribution.
> According to the document Consumer Expenditures, a publication of the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average consumer unit spent $1736 on apparel and services in 2012. That same year, 25 consumer units in the Northeast had the following annual expenditu
> Serious golfers and golf equipment companies sometimes use golf equipment testing labs to obtain precise information about particular club heads, club shafts, and golf balls. One golfer requested information about the Jazz Fat Cat 5-iron from Golf Labora
> According to Communications Industry Forecast & Report, published by Veronis Suhler Stevenson, the average person watched 4.55 hours of television per day in 2005. Random sample of 20 people gave the following number of hours of television watched per da
> We have provided a sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample size. In each case, use the one-mean t -test to perform the required hypothesis test at the 5% significance level. x¯ = 20, s = 4, n = 24, H0: μ = 22, Ha: μ ≠ 22
> We have provided a sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample size. In each case, use the one-mean t -test to perform the required hypothesis test at the 5% significance level. x¯ = 23, s = 4, n = 24, H0: μ = 22, Ha: μ ≠ 22
> We have provided a sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample size. In each case, use the one-mean t -test to perform the required hypothesis test at the 5% significance level. x¯ = 23, s = 4, n = 15, H0: μ = 22, Ha: μ > 22
> Identify the two types of incorrect decisions in a hypothesis test. For each incorrect decision, what symbol is used to represent the probability of making that type of error?
> We have provided a sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample size. In each case, use the one-mean t -test to perform the required hypothesis test at the 5% significance level. x¯ = 24, s = 4, n = 15, H0: μ = 22, Ha: μ > 22
> We have provided a sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample size. In each case, use the one-mean t -test to perform the required hypothesis test at the 5% significance level. x¯ = 21, s = 4, n = 32, H0: μ = 22, Ha: μ < 22
> Explain the meaning of Sample distribution.
> We have provided a sample mean, sample standard deviation, and sample size. In each case, use the one-mean t -test to perform the required hypothesis test at the 5% significance level. x¯ = 20, s = 4, n = 32, H0: μ = 22, Ha: μ < 22
> Two-tailed test, n = 8, and t = 3.725 a. Use Table IV in Appendix A to estimate the P-value. b. Based on your estimate in part (a), state at which significance levels the null hypothesis can be rejected, at which significance levels it cannot be rejected
> Two-tailed test, n = 17, and t = −2.733 a. Use Table IV in Appendix A to estimate the P-value. b. Based on your estimate in part (a), state at which significance levels the null hypothesis can be rejected, at which significance levels it cannot be reject
> Left-tailed test, n = 30, and t = −1.572 a. Use Table IV in Appendix A to estimate the P-value. b. Based on your estimate in part (a), state at which significance levels the null hypothesis can be rejected, at which significance levels it cannot be rejec
> Left-tailed test, n = 10, and t = −3.381 a. Use Table IV in Appendix A to estimate the P-value. b. Based on your estimate in part (a), state at which significance levels the null hypothesis can be rejected, at which significance levels it cannot be rejec
> Right-tailed test, n = 11, and t = 1.246 a. Use Table IV in Appendix A to estimate the P-value. b. Based on your estimate in part (a), state at which significance levels the null hypothesis can be rejected, at which significance levels it cannot be rejec
> Right-tailed test, n = 20, and t = 2.235 a. Use Table IV in Appendix A to estimate the P-value. b. Based on your estimate in part (a), state at which significance levels the null hypothesis can be rejected, at which significance levels it cannot be rejec
> Fill in the following blanks. a. The t-test is to moderate violations of the normality assumption. b. The t-test can sometimes be unduly affected by outliers because the sample mean, and sample standard deviation are not to outliers.
> Answer true or false and explain your answer: For a fixed sample size, decreasing the significance level of a hypothesis test results in an increase in the probability of making a Type II error.
> Explain the meaning of the term hypothesis as used in inferential statistics.
> Explain the meaning of Population data.
> A study by researchers at the University of Maryland addressed the question of whether the mean body temperature of humans is 98.6◦F. The results of the study by P. Mackowiak et al. appeared in the article “A Critical Appraisal of 98.6◦F, the Upper Limit
> The U.S. Census Bureau estimates the mean value of the land and buildings per corporate farm. Those estimates are published in the Census of Agriculture. Suppose that an estimate, x¯, is obtained and that the margin of error is $1000. Does this result im
> Professor Thomas Stanley of Georgia State University has surveyed millionaires since 1973. Among other information, Professor Stanley obtains estimates for the mean age, μ, of all U.S. millionaires. Suppose that one year’s study involved a simple random
> Consider again the problem of estimating the mean age, μ, of all people in the civilian labor force. We found that a sample size of 2250 is required to have a margin of error of 0.5 year and a 95% confidence level. Suppose that, due to financial constrai
> Consider again the problem of estimating the mean age, μ, of all people in the civilian labor force. We found that a sample size of 2250 is required to have a margin of error of 0.5 year and a 95% confidence level. Suppose that, due to financial constrai
> According to the document All About Diabetes, found on the website of the American Diabetes Association, “... diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin, a hormone that is needed to convert sugar, starches, and other
> The U.S. Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Bureau of Justice Statistics provides information on prison sentences in the document National Corrections Reporting Program. A random sample of 20 maximum sentences for murder yielded the data,
> The Professional Golfer’s Association of America (PGA) organizes golf tournaments for professional golfers. The following table lists the longest drives, in yards, recorded during a PGA tournament for a random sample of 26 golfers. Use the technology of
> Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and compact fluorescent lights (CFLs) are lightbulbs that are supposed to last up to fifty times longer than old fashioned incandescent lightbulbs and also use less energy. Consumer Reports sampled eighteen different 60-watt
> You found a 99% confidence interval of $2.03 million to $2.51 million for the mean gross earnings of all Rolling Stones concerts. a. Determine the margin of error, E. b. Explain the meaning of E in this context in terms of the accuracy of the estimate. c
> Explain the meaning of Sample data.
> Refer to Exercise 8.7 and find a point estimate for the population standard deviation (i.e., the standard deviation of the variable). Data from Exercise 8.7: A simple random sample is taken from a population and yields the following data for a variable
> You found a 95% confidence interval of 18.8 months to 48.0 months for the mean duration of imprisonment, μ, of all East German political prisoners with chronic PTSD. a. Determine the margin of error, E. b. Explain the meaning of E in this context in term
> You found a 90% confidence interval for the mean number of tongue flicks per 20 minutes for all juvenile common lizards to be from 456.4 to 608.0. Obtain the margin of error by a. taking half the length of the confidence interval. b. using Formula 8.1 on
> You found a 95% confidence interval for the mean amount of all venture-capital investments in the fiber optics business sector to be from $5.389 million to $7.274 million. Obtain the margin of error by: a. taking half the length of the confidence interva
> In estimating the mean monthly fuel expenditure, μ, per household vehicle, the Energy Information Administration takes a sample of size 6841. Assuming that σ = $20.65, determine the margin of error in estimating μ at the 95% level of confidence.
> In the paper “Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate and Asymmetric Growth Restriction” (Obstetrics & Gynecology, Vol. 91, No. 3, pp. 336–341), M. Williams et al. reported on a study of characteristics of neonates. Infants treated for pulmonary
> J. McWhorter et al. of the College of Health Sciences at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas, studied physical therapy students during their graduate-school years. The researchers were interested in the fact that, although graduate physical-therapy stude
> Recall that a simple random sample of 36 new mobile homes yielded the prices, in thousands of dollar. We found the mean of those prices to be $63.28 thousand. a. Use this information and Procedure 8.1 on page 322 to find a 95% confidence interval for the
> Refer to Exercise 8.78. a. The mean duration for a sample of 612 dives was 322 seconds. Find a 99% confidence interval for μ based on that data. b. Compare the 99% confidence intervals obtained here and in Exercise 8.78(b) by drawing a graph. c. Compare
> Refer to Exercise 8.77. a. The mean number of days that 30 adolescents in substance abuse treatment used medical marijuana in the last 6 months was 105.43. Find a 95% confidence interval for μ based on that data. b. Compare the 95% confidence intervals o
> Explain the meaning of Distribution of a data set.
> We presented data on shoe size and height for a sample of students at Arizona State University. Using the regression and correlation techniques that you learned in Chapter 4 and this chapter, solve the following problems. Note: We recommend that you use
> Refer to Exercise 8.78. a. Determine the margin of error for the 95% confidence interval. b. Determine the margin of error for the 99% confidence interval. c. Compare the margins of error found in parts (a) and (b). d. What principle is being illustrated
> A simple random sample is taken from a population and yields the following data for a variable of the population: Find a point estimate for the population mean (i.e., the mean of the variable).
> Refer to Exercise 8.77. a. Determine the margin of error for the 95% confidence interval. b. Determine the margin of error for the 90% confidence interval. c. Compare the margins of error found in parts (a) and (b). d. What principle is being illustrated
> Multi-sensor data loggers were attached to free-ranging American alligators in a study conducted by Y. Watanabe for the article “Behavior of American Alligators Monitored by Multi-Sensor Data Loggers” (Aquatic Biology, Vol. 18, pp. 1–8). The mean duratio
> An issue with legalization of medical marijuana is “diversion,” the process in which medical marijuana prescribed for one person is given, traded, or sold to someone who is not registered for medical marijuana use. Researchers S. Sautel et al. study the
> Refer to Exercise 8.70. a. Find a 90% confidence interval for μ. b. Why is the confidence interval you found in part (a) shorter than the one in Exercise 8.70? c. Draw a graph similar to that shown in Fig. 8.6 on page 326 to display both confidence inter
> Refer to Exercise 8.69. a. Find a 99% confidence interval for μ. b. Why is the confidence interval you found in part (a) longer than the one in Exercise 8.69? c. Draw a graph like that shown in Fig. 8.6 on page 326 to display both confidence intervals. d
> The Rolling Stones, a rock group formed in the 1960s, have toured extensively in support of new albums. Pollstar has collected data on the earnings from the Stones’s North American tours. For 30 randomly selected Rolling Stones concerts, the mean gross e

