Question: Aloha Company uses a perpetual inventory system.
Aloha Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions. (For specific identification, units sold consist of 80 units from beginning inventory, 300 units from the May 6 purchase, and 100 units from the May 25 purchase.)
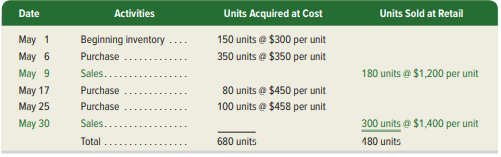
Required
1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale.
2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory.
3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and
(d) specific identification. (Round all amounts to cents.)
4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3.
> MAX produces and sells power adapters. Its contribution margin income statement follows. A potential customer offers to buy 10,000 units for $5.80 each. These sales would not affect the company’s sales through its normal channels. Detai
> Ace produces and sells energy drinks. Its contribution margin income statement follows. A potential customer offers to buy 50,000 units for $3.00 each. These sales would not affect the company’s sales through its normal channels. Detail
> Matsu Company’s annual accounting period ends on October 31. The following information concerns the adjusting entries that need to be recorded as of that date. Entries can draw from the following partial chart of accounts: Cash; Accounts Receivable; Offi
> The accounting records of Tama Co. show the following assets and liabilities as of December 31 for Year 1 and for Year 2. Required 1. Prepare balance sheets for the business as of December 31 for Year 1 and Year 2. Hint: Report only total equity on the
> Refer to Apple’s financial statements in Appendix A to answer the following. 1. What percent of the original cost of Apple’s Property, Plant and Equipment account remains to be depreciated as of (a) September 28, 2019, and (b) September 29, 2018? Assume
> Use the information in Problem 1-3B to prepare the current year-end balance sheet for Audi Company.
> Use the information in Problem 1-3B to prepare the statement of owner’s equity for Audi Company for the current year ended December 31. Hint: The owner invested $100 cash during the year.
> As of December 31 of the current year, Audi Company’s records show the following. Required Prepare the income statement for Audi Company for the current year ended December 31.
> Archer Foods is considering whether to overhaul an old freezer or replace it with a new freezer. Information about the two alternatives follows. Management requires a 10% rate of return on its investments. Alternative 1: Keep the old freezer and have it
> Aster Company is considering an investment in technology to improve its operations. The investment costs $800,000 and yields the following net cash flows. Management requires a 10% return on its investments. Required 1. Determine the payback period for t
> Milan Co. is considering two alternative investment projects. Each requires a $300,000 initial investment. Project A is expected to generate net cash flows of $90,000 per year over the next five years. Project B is expected to generate net cash flows of
> Lopez Co. can invest in one of two alternative projects. Project Y requires a $240,000 initial investment for new machinery with a four-year life and no salvage value. Project Z requires a $240,000 initial investment for new machinery with a three-year l
> Project A requires a $240,000 investment for new machinery with a four-year life and no salvage value. The project yields the following annual results. Cash flows occur evenly within each year. Required 1. Compute Project A’s annual net
> Cortino Company is planning to add a new product to its line. To manufacture this product, the company needs to buy a new machine at a $300,000 cost with an expected four-year life and a $20,000 salvage value. Additional annual information for this new p
> King Company builds custom order fulfillment centers for large e-commerce companies. On June 1, the company had no inventories of work in process or finished goods but held the following raw materials. On June 3, the company began work on Job 450 for Enc
> Use Apple’s financial statements in Appendix A to answer the following. 1. What is the amount of Apple’s accounts receivable as of September 28, 2019? 2. Compute Apple’s accounts receivable turnover as of September 28, 2019. 3. Apple’s most liquid assets
> At the beginning of the year, Paella Company’s manager estimated total direct labor cost to be $1,500,000. The manager also estimated the following overhead costs for the year. For the year, the company incurred $725,000 of actual over
> Perez Company shows the following costs for three jobs worked on in September. Additional Information a. Raw Materials Inventory has an August 31 balance of $150,000. b. Raw materials purchases in September are $400,000, and total factory payroll cost i
> At the end of May, the job cost sheets at Cool Pool show the following costs accumulated on three jobs. Additional information a. Job 8 was started in April, and the following costs were assigned to it in April: direct materials, $8,000; direct labor, $
> A manufacturing company reports the following information. Required 1. Compute raw materials inventory turnover for the most recent two years. 2. Is the current year change in raw materials inventory turnover ratio favorable or unfavorable? 3. Compute d
> The following year-end information is taken from the December 31 adjusted trial balance and other records of Best Bikes. Required Identify each cost as either a product cost or a period cost. If a product cost, classify it as direct materials, direct la
> Selected comparative financial statement information of Bluegrass Corporation follows. Required 1. Compute each year’s current ratio. Round ratios to one decimal. 2. Express the income statement data in common-size percentâ€
> Selected comparative financial statements of Tripoli Company follow. Required 1. Compute trend percent’s for all components of both statements using 2015 as the base year. Round percent’s to one decimal. Analysis Com
> Refer to the information in Problem 16-1B. Required Prepare the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows using the direct method for the current year.
> Salt Lake Company’s current-year income statement and selected balance sheet data at December 31 of the current and prior years follow. Required Prepare the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows using the indirect
> Valdez issues $450,000 of 13%, four-year bonds dated January 1, 2021, that pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. They are issued at $493,608 when the market rate is 10%. Required 1. Prepare the January 1 journal entry to record the bonds
> Use Apple’s financial statements in Appendix A to answer the following. 1. Identify the total amount of cash and cash equivalents for fiscal years ended (a) September 28, 2019, and (b) September 29, 2018. 2. Compute cash and cash equivalents as a percent
> Refer to the bond details in Problem 14-3B. Required 1. Compute the total bond interest expense over the bonds’ life. 2. Prepare an effective interest amortization table like the one in Exhibit 14B.2 for the bonds’ life. 3. Prepare the journal entries t
> Refer to the bond details in Problem 14-4B. Required 1. Prepare the January 1 journal entry to record the bonds’ issuance. 2. Determine the total bond interest expense to be recognized over the bonds’ life. 3. Prepare an effective interest amortization
> The following information is available for both Atlas Company and Bryan Company at the current year-end. Required 1. Compute the debt-to-equity ratio for both companies. 2. Which company has the riskier financing structure?
> On January 1, JCCC borrows $130,000 cash by signing a 4-year, 5% installment note. The note requires four equal payments consisting of accrued interest and principal on December 31 for each of the next four years. Required 1. Compute the amount of each
> On January 1, 2021, Gordon borrows $150,000 cash from a bank by signing a three-year installment note bearing 10% interest. The note requires equal payments of $60,316 each year on December 31. Required 1. Complete an amortization table for this install
> Gomez issues $240,000 of 6%, 15-year bonds dated January 1, 2021, that pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. They are issued at $198,494 when the market rate is 8%. Required 1. Prepare the January 1 journal entry to record the bonds’ iss
> Ripken Company issues 9%, five-year bonds dated January 1, 2021, with a $320,000 par value. The bonds pay interest on June 30 and December 31 and are issued at a price of $332,988. Their annual market rate is 8% on the issue date. Required 1. Calculate
> Romero issues $3,400,000 of 10%, 10-year bonds dated January 1, 2021, that pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. The bonds are issued at a price of $3,010,000. Required 1. Prepare the January 1 journal entry to record the bonds’ issuance
> Lasu, Ramirez, and Toney, who share income and loss in a 2:1:2 ratio (in percents: Lasu, 40%; Ramirez, 20%; and Toney, 40%), plan to liquidate their partnership. At liquidation, their balance sheet appears as follows. Required Prepare journal entries fo
> Gibbs, Hook, and Chan are partners and share income and loss in a 5:1:4 ratio (in percent’s: Gibbs, 50%; Hook, 10%; and Chan, 40%). The partnership’s capital balances are as follows: Gibbs, $606,000; Hook, $148,000; and Chan, $446,000. Gibbs decides to
> Refer to Apple’s financial statements in Appendix A. 1. What amount of accounts payable did Apple report on (a) September 28, 2019? (b) On September 29, 2018? 2. Compute days’ payable outstanding for fiscal year ended (a) September 28, 2019, and (b) Sep
> Cook, Jing, and Schwartz formed the CJS Partnership by making investments of $144,000, $216,000, and $120,000, respectively. They predict annual partnership net income of $240,000 and are considering the following alternative plans of sharing income and
> Albin, Peters, and Ramsey invested $164,000, $98,400, and $65,600, respectively, in a partnership. During its first calendar year, the firm earned $270,000. Required Prepare the entry to close the firm’s Income Summary account as of its December 31 year
> Bell and Green are forming a partnership. Bell invests $104,000 and Green invests $156,000. The partners agree that Bell will work one-fourth of the total time devoted to the partnership and Green will work threefourths. They have discussed the following
> Jen Novinska and Jeff Quinlan form a partnership. Novinska contributes the following items (at market value). Prepare the partnership’s journal entry to record Novinska’s investment.
> The July transactions of Acorn Industries are described in Problem 7-2B. Required 1. Prepare a general journal, purchases journal, and cash payments journal. Number all journal pages as page 3. Enter the transactions of Acorn Industries that should be j
> Acorn Industries completes these transactions during July of the current year (the terms of all its credit sales are 2/10, n/30). July 1 purchased $6,500 of merchandise on credit from Teton Company, terms 2/10, n/30. 3 Issued Check No. 300 to The Weekly
> Grassley Company completes these transactions during November of the current year (terms for all its credit sales are 2/10, n/30). Nov. 1 purchased $5,058 of office equipment on credit from Burn Supply, terms n/30. 2 Borrowed $88,500 cash from Wisconsin
> Shepard Company sold 4,000 units of its product at $100 per unit during the year and incurred operating expenses of $15 per unit in selling the units. It began the year with 840 units in inventory and made successive purchases of its product as follows.
> Seneca Co. began the year with 6,500 units of product in its January 1 inventory costing $35 each. It made four purchases of its product during the year as follows. The company uses a periodic inventory system. On December 31, a physical count reveals th
> Refer to the information in Problem 6-3B and assume the periodic inventory system is used. Required 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory. 3. Compute th
> Use Apple’s financial statements in Appendix A to answer the following. Required 1. What amount of inventories did Apple report as a current asset (a) on September 28, 2019? (b) On September 29, 2018? 2. Inventories make up what percent of total assets
> The adjusted trial balance for Amara Co. on December 31 of the current year follows. Petra Amara invested $40,000 cash in the business during the year. The P. Amara, Capital account balance was $52,800 on December 31 of the prior year. Required 1. Prepar
> Following is the unadjusted trial balance for Alonzo Institute as of December 31. The Institute provides one-on-one training to individuals who pay tuition directly to the business and offers extension training to groups in off-site locations. Shown afte
> Edge Company produces two models of its product with the same machine. The machine has a capacity of 176 hours per month. The following information is available. Required 1. Determine the contribution margin per machine hour for each model. 2. How many u
> Hip Manufacturing produces denim clothing. This year it produced 3,000 denim jackets at a cost of $90,000. These jackets were damaged in the warehouse during storage. Management identified three alternatives for these jackets. 1. Jackets can be sold as s
> Haver Company currently pays an outside supplier $15 per unit for a part for one of its products. Haver is considering two alternative methods of making the part. Method 1 for making the part would require direct materials of $5 per unit, direct labor of
> FURY produces and sells skateboards. Its contribution margin income statement follows. A potential customer offers to buy 10,000 units for $42.00 each. These sales would not affect the company’s sales through its normal channels. Detail
> JART manufactures and sells underwater markers. Its contribution margin income statement follows. A potential customer offers to buy 50,000 units for $3.20 each. These sales would not affect the company’s sales through its normal channe
> Techcom is designing a new smart phone. Each unit of this new phone will require $230 of direct materials; $10 of direct labor; $22 of variable overhead; $18 of variable selling, general, and administrative costs; $30 of fixed overhead costs; and $10 of
> Seminole Co. began the year with 23,000 units of product in its January 1 inventory costing $15 each. It made four purchases of its product during the year as follows. The company uses a periodic inventory system. On December 31, a physical count reveals
> Refer to Apple’s financial statements in Appendix A to answer the following. Required 1. Assume that the amounts reported for inventories and cost of sales reflect items purchased in a form ready for resale. Compute the net cost of goods purchased for t
> Arnos Company’s annual accounting period ends on December 31. The following information concerns the adjusting entries to be recorded as of that date. Entries can draw from the following partial chart of accounts: Cash; Accounts Receivable; Office Suppli
> The adjusted trial balance for Chiara Company as of December 31 follows. Required Use the information in the adjusted trial balance to prepare (a) the income statement for the year ended December 31; (b) the statement of owner’s equity
> Wells Technical Institute (WTI), a school owned by Tristan Wells, provides training to individuals who pay tuition directly to the school. WTI also offers training to groups in off-site locations. Its unadjusted trial balance as of December 31 follows, a
> Use the information in Problem 1-3A to prepare the statement of owner’s equity for Armani Company for the current year ended December 31. Hint: The owner invested $1,000 cash during the year.
> Interstate Manufacturing is considering either overhauling an old machine or replacing it with a new machine. Information about the two alternatives follows. Management requires a 10% rate of return on its investments. Alternative 1: Keep the old machine
> Salsa Company is considering an investment in technology to improve its operations. The investment costs $250,000 and will yield the following net cash flows. Management requires a 10% return on investments. Required 1. Determine the payback period for t
> Rowan Co. is considering two alternative investment projects. Each requires a $250,000 initial investment. Project A is expected to generate net cash flows of $60,000 per year over the next six years. Project B is expected to generate net cash flows of $
> Garcìa Co. can invest in one of two alternative projects. Project Y requires a $360,000 initial investment for new machinery with a four-year life and no salvage value. Project Z requires a $360,000 initial investment for new machinery with a
> Project Y requires a $350,000 investment for new machinery with a four-year life and no salvage value. The project yields the following annual results. Cash flows occur evenly within each year. Required 1. Compute Project Y’s annual net
> Factor Company is planning to add a new product to its line. To manufacture this product, the company needs to buy a new machine at a $480,000 cost with an expected four-year life and a $20,000 salvage value. Additional annual information for this new pr
> Refer to Apple’s financial statements in Appendix A to answer the following. 1. For the fiscal year ended September 28, 2019, what amount is credited to Income Summary to summarize its revenues earned? Hint: make sure to consider any “Other income” repor
> Sager Company builds custom retaining walls for large commercial customers. On May 1, the company had no inventories of work in process or finished goods but held the following raw materials. On May 4, the company began work on Job 102 for Woos Company a
> At the beginning of the year, Learner Company’s manager estimated total direct labor cost to be $2,500,000. The manager also estimated the following overhead costs for the year. For the year, the company incurred $1,520,000 of actual ov
> Marco Company shows the following costs for three jobs worked on in April. Additional Information a. Raw Materials Inventory has a March 31 balance of $80,000. b. Raw materials purchases in April are $500,000, and total factory payroll cost in April is
> At the end of June, the job cost sheets at Ace Roofers show the following costs accumulated on three jobs. Additional information a. Job 5 was started in May, and the following costs were assigned to it in May: direct materials, $6,000; direct labor, $1
> A manufacturing company reports the following information. Required 1. Compute raw materials inventory turnover for the most recent two years. 2. Is the current year change in raw materials inventory turnover ratio favorable or unfavorable? 3. Compute d
> The following year-end information is taken from the December 31 adjusted trial balance and other records of Leone Company. Required Identify each cost as either a product cost or a period cost. If a product cost, classify it as direct materials, direct
> Plum Corporation began the month of May with $700,000 of current assets, a current ratio of 2.50:1, and an acid-test ratio of 1.10:1. During the month, it completed the following transactions. The company uses a perpetual inventory system. May 2 Purchase
> Selected comparative financial statements of Korbin Company follow. Required 1. Compute each year’s current ratio. Round ratios to one decimal. 2. Express the income statement data in common-size percent’s. Round perc
> Selected comparative financial statements of Heroin Company follow. Required 1. Compute trend percent’s for all components of both statements using 2015 as the base year. Round percent’s to one decimal. Analysis Comp
> Refer to Golden Corporation’s financial statements and related information in Problem 16-6A. Required Prepare a complete statement of cash flows using the direct method for the current year.
> This Comprehensive Problem requires account balances from the April month-end, which are available in Connect or in the Working Papers. Assume it is Monday, May 1, the first business day of the month, and you have just been hired as the accountant for Co
> Refer to For ten Company’s financial statements and related information in Problem 16-3A. Required Prepare a complete statement of cash flows using the direct method. Disclose any noncash investing and financing activities in a note.
> Refer to the information in Problem 16-1A. Required Prepare the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows using the direct method for the current year.
> Lansing Company’s current-year income statement and selected balance sheet data at December 31 of the current and prior years follow. Required Prepare the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows using the indirect m
> Stoll Co.’s long-term available-for-sale portfolio at the start of this year consists of the following. Stoll enters into the following transactions involving its available-for-sale debt securities this year. Jan. 29 sold one-half of th
> Ike issues $180,000 of 11%, three-year bonds dated January 1, 2021, that pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. They are issued at $184,566 when the market rate is 10%. Required 1. Prepare the January 1 journal entry to record the bonds’
> Refer to the bond details in Problem 14-3A. Required 1. Compute the total bond interest expense over the bonds’ life. 2. Prepare an effective interest amortization table like the one in Exhibit 14B.2 for the bonds’ life. 3. Prepare the journal entries t
> Refer to the bond details in Problem 14-4A. Required 1. Prepare the January 1 journal entry to record the bonds’ issuance. 2. Determine the total bond interest expense to be recognized over the bonds’ life. 3. Prepare an effective interest amortization
> The following information is available for both Pulaski Company and Scott Company at the current year-end. Required 1. Compute the debt-to-equity ratio for both companies. 2. Which company has the riskier financing structure?
> On January 1, McNeil Company borrows $100,000 cash by signing a four-year, 9% installment note. The note requires four equal payments consisting of accrued interest and principal on December 31 for each of the next four years. Required 1. Compute the am
> On January 1, 2021, Norwood borrows $200,000 cash from a bank by signing a five-year installment note bearing 8% interest. The note requires equal payments of $50,091 each year on December 31. Required 1. Complete an amortization table for this installm
> Bug-Off Exterminators provides pest control services and sells extermination products manufactured by other companies. The following six-column table contains the company’s unadjusted trial balance as of December 31, 2021. The following
> Legacy issues $325,000 of 5%, four-year bonds dated January 1, 2021, that pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. They are issued at $292,181 when the market rate is 8%. Required 1. Prepare the January 1 journal entry to record the bonds’
> Ellis Company issues 6.5%, five-year bonds dated January 1, 2021, with a $250,000 par value. The bonds pay interest on June 30 and December 31 and are issued at a price of $255,333. The annual market rate is 6% on the issue date. Required 1. Calculate t
> Raphael Corporation’s balance sheet shows the following stockholders’ equity section. Required 1. Determine the par values of the corporation’s preferred stock and its common stock. 2. If two years&ac
> Required Prepare journal entries for (a) the sale of inventory, (b) the allocation of its gain or loss, (c) the payment of liabilities at book value, and (d) the distribution of cash in each of the following separate cases: Inventory is sold for (1) $600
> Meir, Benson, and Lau are partners and share income and loss in a 3:2:5 ratio (in percent’s: Meir, 30%; Benson, 20%; and Lau, 50%). The partnership’s capital balances are as follows: Meir, $168,000; Benson, $138,000; and Lau, $294,000. Benson decides t
> Mo, Lu, and Barb formed the MLB Partnership by making investments of $67,500, $262,500, and $420,000, respectively. They predict annual partnership net income of $450,000 and are considering the following alternative plans of sharing income and loss: (a)
> Ries, Bax, and Thomas invested $80,000, $112,000, and $128,000, respectively, in a partnership. During its first calendar year, the firm earned $249,000. Required Prepare the entry to close the firm’s Income Summary account as of its December 31 year-en
> Watts and Lyon are forming a partnership. Watts invests $42,000 and Lyon invests $63,000. The partners agree that Watts will work one-third of the total time devoted to the partnership and Lyon will work two thirds. They have discussed the following alte

