Question: An approach to decision making under uncertainty
An approach to decision making under uncertainty that is based on a weighted combination of the maximum and the minimum payoffs from each alternative is called the _____________.
a) Maximin criterion
b) Maximax criterion
c) Hurwicz criterion
d) Minimax regret strategy
e) Weighted regret criterion
16. Consider the decision table given below:

What decisions would an optimist and pessimist make?
a) d1 and d3
b) d1 and d2
c) d2 and d3
d) d3 and d2
17. Consider the decision table given below:

Suppose we are more optimistic than pessimistic and select ( = 0.8 for the weight of optimism. According to Hurwicz criterion, the payoff of the decision maker is_____________.
a) 190
b) 138
c) 360
d) 480
18. In decision making under uncertainty, a strategy that is based on lost opportunity is called the _____________.
a) Maximin regret strategy
b) Maximax criterion
c) Hurwicz criterion
d) Minimax regret strategy
e) Maximax regret strategy
19. Consider the problem faced by a decision maker who must choose one of two investment opportunities (I1 and I2) in a foreign country. The rewards to these alternatives are uncertain and depend on the outcome of the country’s national election. I1 will make a profit of $100 million if the political party A comes to power and will make a loss of $20 million if the political party B comes to power. I2 will make a profit of $200 million if the political party A comes to power and will make a loss of $80 million if the political party B comes to power. Suppose the decision maker is able to assign probabilities to the outcomes of the election and determines that party A will win the election with a probability 0.6. If the decision maker chooses the investment I1, his expected reward (in million $) will be _____________.
a) 200
b) 52
c) 20
d) 100
e) −20
20. Consider the problem faced by a decision maker who must choose one of two investment opportunities (I1 and I2) in a foreign country. The rewards to these alternatives are uncertain and depend on the outcome of the country’s national election. I1 will make a profit of $100 million if the political party A comes to power and will make a loss of $20 million if the political party B comes to power. I2 will make a profit of $200 million if the political party A comes to power and will make a loss of $80 million if the political party B comes to power. Suppose the decision maker is able to assign probabilities to the outcomes of the election and determines that party A will win the election with a probability 0.6. If the decision maker chooses the investment I2, his expected reward (in million $) will be _____________.
a) 200
b) 52
c) 20
d) 100
e) 88
21. Imagine a game in which there is a ten percent chance of winning. Winning brings a reward of $100 and losing brings nothing. If a decision maker is willing to pay $20 to play this game, the decision maker is _______________.
a) A risk-avoider
b) Is indifferent to the risk
c) A risk-taker
d) Willing to pay the expected value
e) Willing to pay less than the expected value
22. Consider the following decision table in which x, y, and z are decision alternatives and A and B are the two possible states of nature, with probabilities 0.30 and 0.70.
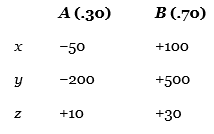
The expected value for decision y is ___________.
a) 24
b) 55
c) 209
d) 369
e) 290
23. Consider the following decision table.
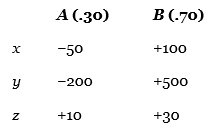
The expected value of perfect information is __________.
a) 55
b) 63
c) 185
d) 353
e) 500
24. A person has a 50-50 chance at winning $100,000 or $0. The person is offered $25,000 to quit the game, and he refuses to quit the game. He is offered $50,000 to quit the game, and he refuses. Finally, when he is offered $70,000 to quit the game, he takes the money. This person is _____________.
a) A risk taker
b) A risk avoider
c) An EMVer
d) A gambler
e) A profit mongerer
> Using the information from S12-8, a market price of $34 per share, and 50,000 and 60,000 shares of common stock outstanding in 2017 and 2018, respectively, compute the following for 2018. Round answers to two decimal places. 1. Earnings per share 2. Pric
> The 2018 financial statements for Inland Supply, Inc., show total assets of $572,000, total liabilities of $322,500, net sales of $1,276,000, net income of $191,400, income from operations of $227,600, cost of goods sold of $743,600, dividends of $24,600
> In addition to the information from S12-6, assume that cash on the 2018 balance sheet was $14,000 and current liabilities totaled $25,000. Compute the following ratios for 2018: 1. Current ratio 2. Quick ratio 3. Cash conversion cycle (round to whole day
> The 2017 and 2018 balance sheets for Flores, Inc., showed net accounts receivable of $13,000 and $17,000, respectively; inventory of $12,000 and $9,000, respectively; and accounts payable of $6,000 and $8,000, respectively. The company’s 2018 income stat
> Identify which question each of the ratios below helps answer. 1. Is the business a going concern? 2. How is the business earning a net income or loss? 3. Where is the business getting its money? Can it pay its debt obligations? 4. How is the business in
> You just got off the telephone with one of your clients, who wants to start a new business as a corporation. His question to you concerned the different types of stock that can be issued to the potential stockholders of this new corporation. You explaine
> Match the terms on the right with their definitions on the left: 1. Tells whether a company can pay all its current liabilities if they become due immediately 2. Measures a company’s success in using assets to earn income 3. The practice of comparing a c
> Wolfe, Inc., had net sales of $212,000 and cost of goods sold of $128,000 in 2016; net sales of $263,000 and cost of goods sold of $161,000 in 2017; and net sales of $325,000 and cost of goods sold of $200,000 in 2018. 1. Find the percentage of increase
> In 2018, common stockholders received $6 per share in annual dividends. The market price per share for common stock was $24. Compute the dividend yield for common stock.
> Nemo’s Spas began 2018 with cash of $32,000. During the year, Nemo’s Spas earned service revenue of $610,000 and collected $572,000 from customers. Expenses for the year totaled $449,000, of which Nemo’s Spas paid $417,000 in cash to suppliers and employ
> Use the statement of stockholders’ equity in Exhibit 10-8 to answer the following questions: 1. Make journal entries to record the declaration and payment of cash dividends during 2018. 2. How much cash did the issuance of common stock
> Trident Equipment’s accountants assembled the following data for the year ended April 30, 2018. Prepare Trident Equipment’s statement of cash flows for the year ended April 30, 2018, using the indirect method. The ca
> Use the Inland Medical Supply, Inc., data in S11-10 to compute the following amounts for 2018: 1. Borrowing or payment of long-term notes payable, assuming Inland had only one long-term note payable transaction during the year 2. Issuance of common stock
> Use the Inland Medical Supply, Inc., data in S11-10 to compute the amount of fixed assets acquired by Inland Medical Supply, Inc., assuming Inland sold no fixed assets in 2018. S11-10: Inland Medical Supply, Inc., reported the following financial statem
> Inland Medical Supply, Inc., reported the following financial statements for 2018: Requirement 1. Use the information in Inland Medical Supply, Inc.’s financial statements to compute the following: a. Collections from customers b. Pa
> Juarez Equipment, Inc., assembled the following data related to its cash transactions for the year ended June 30, 2018: Payment of dividends.......................................................................................... $ 16,000 Proceeds from
> You manage a small but growing business, like the Bold City Brewery. However, unlike the Bold City Brewery, your business has numerous stockholders. The company just completed its fiscal year, and the annual meeting is just a few weeks away. Your company
> The accounting records for Haskins Steel, Inc., for the year ended June 30, 2018, contain the following information: a. Purchase of fixed assets for cash, $97,400 b. Proceeds from issuance of common stock, $45,000 c. Payment of dividends, $47,400 d. Coll
> The 2018 comparative balance sheet and income statement of Bone Appetit Pet Supply, Inc., are: Bone Appetit Pet Supply, Inc., had no noncash investing and financing transactions during 2018. During the year, Bone Appetit Pet Supply, Inc., sold no land
> Data from the comparative balance sheet of Stevenson Building Materials, Inc., at July 31, 2018, follow: Stevenson Building Materials, Inc.’s transactions during the year ended July 31, 2018, included: Requirements 1. Prepare Steven
> Bannen Office Machines, Inc.’s accountants assembled the following selected data for the year ended December 31, 2018: Requirement 1. Prepare Bannen Office Machines, Inc.’s statement of cash flows using the indirect
> The balance sheet of Avery Hardware, Inc., at December 31, 2017, reported 700,000 shares of $3 par common stock authorized, with 95,000 shares issued and outstanding. Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par—Common had a balance of $320,000. Re
> Ralston Sports Corporation completed the following selected transactions during 2018: Requirement 1. Record the transactions in the journal.
> Zeranski Consulting, Inc., has 12,000 shares of $5.00, no-par preferred stock and 60,000 shares of no-par common stock outstanding for 2016–2018. Zeranski declared and paid the following dividends during a three-year period: 2016, $23,000; 2017, $115,000
> Cascade Inn, Inc., included the following stockholders’ equity on its year-end balance sheet at December 31, 2018: Requirements 1. Identify the different issues of stock Cascade Inn, Inc., has outstanding. 2. Give the two entries to r
> Cutter Furniture, Inc., was organized in 2017. At December 31, 2017, Cutter Furniture, Inc.’s balance sheet reported the following stockholders’ equity Requirement Answer the following questions and make journal entr
> You have been hired as an investment analyst at McNeice Securities, Inc. It is your job to recommend investments for your client. You have the following information for two different companies. Write a memo to your client recommending the company you b
> You own a business like the Bold City Brewery. You just returned from a meeting with your bank loan officer, and you were a little taken aback by his comments. You’ve been doing business with this bank for a number of years, and the off
> Identify whether each of the following items would be classified as: • Income from continuing operations (C) • Income from discontinued operations (D) _______ a. $12,000 insurance proceeds on a fully depreciated piece of equipment that was lost in a hurr
> For a skewed distribution, what is the minimum percentage of the observations that will lie within 2 standard deviations of the mean based on Chebyshev’s rule? a) 68% b) 75% c) 95% d) 99.7% 16. For a skewed distribution, what is the minimum percentage of
> The heights of four fifth grade students are 58, 56, 60 and 62 inches. What are the mean, median and standard deviation of this dataset, and the standard deviation of the new dataset by adding 2 to each number, i.e., 60, 58, 62, 64? a) 59, 58, 2.58 and 4
> Which of the following descriptive measure is not a statistic? a) Sample mean b) Population mean µ c) Sample standard deviation s d) Sample variance s2 e) Sample median 5. To study the impact of advertising on various market segments, marke
> The payoffs of a decision analysis problem are the payments to decision makers. 2. When it is uncertain which of the states of nature will occur and also the probability of each state of nature occurring is unknown, the scenario is referred to as decisio
> Reengineering is the approach to revise or redo the engineering design of a product in response to customer complaints.
> Chi-square goodness-of-fit tests are always one-tailed tests. 2. A chi-square goodness-of-fit test can be used as an alternative to z-test for population proportions if there are only two classifications. 3. A chi-square test of independence can be used
> In a one-way ANOVA the total variance is portioned into the variance due to treatments and the variance due to error. 2. A repeated measures design is a special case of the randomized block design.
> To test if the means of two populations are different, we test the significance of the difference between two sample means. 2. The distribution of the difference between two sample means may be considered to be normally distributed only if the two popula
> What is the relative frequency of type B in the previous question? a) 0.25 b) 0.35 c) 0.5 d) 0.64 29. In sciences and technology, use of pie charts is limited compared to other types of graphs such as a histogram, because __________. a) It is difficult
> A null hypothesis must always include the equality sign. 2. If the result of a hypothesis test is statistically significant, it must be considered a substantive result. 3. The null hypothesis is rejected if the p-value (i.e., the probability of getting a
> A statistic taken from a sample that is used to estimate a population parameter is called a point estimate. 2. An interval estimate is a range of values around the point estimate. 3. The width of the confidence interval does not depend on the desired le
> Systematic sampling is an example of random sampling which is often used because of its convenience and ease of administration. 2. Missing data and recording errors are examples of sampling error. 3. If a population is normal distributed, the means of th
> An exponential distribution, which is continuous, is closely related to the Poisson distribution, which is discrete.
> Binomial distribution applies only to experiments in which the trials are done with replacement or successive trials are independent. 2. A hypergeometric distribution is used in situations where the sampling is done from an infinite population and the s
> If two events with non-zero probabilities are mutually exclusive, they cannot be statistically independent. 2. The probability of the union of two events is always equal to the sum of the marginal probabilities of two independent events. 3. The joint pro
> An advantage of the median instead of using mean as the measure of central tendency is that it is not affected by extremely large or extremely small values in the data set. 2. The median and the second quartile of a data set are always equal. 3. Dependin
> Frequency distribution is a summary of data presented in the form of class intervals and frequencies. 2. Data that have been organized into a frequency distribution are called ungrouped data. 3. The sum of the frequencies of a grouped data set is always
> Virtually every area of business uses statistics in decision making. 2. The highest level of data measurement is the ratio-level measurement. 3. Since statistics deals with primarily with facts and figures, ethical considerations do not play any role in
> One strategy that can be used in making decisions under risk is the ___________. a) Expected monetary value approach b) Maximax risk criterion c) Minmax risk strategy d) Minimax regret strategy e) Maximax regret strategy 26. In a capacity expansion decis
> A histogram is vertical bar chart on an X-Y plane, in which the labels along horizontal (or X) axis represent the class end points and the bars along the vertical (or Y) axis show the ____. a) Class width b) Class range c) Class frequency d) Class mid-
> The payoffs of a decision analysis problem are_______________________. a) The various choices or options available to the decision maker in any given problem situation. b) The occurrences of nature that can happen after a decision is made that can affect
> Consider two products, A and B. The quality of A is determined by the characteristic, its weight. The quality of B is determined by the characteristic, whether it is acceptable or not. Which of the following statements is true? a) Quality characteristics
> Many times in the implementation of quality improvement techniques, it is useful to explore the relationship between two numerical variables (e.g., the strength of steel bars and the carbon content of steel). A graphical mechanism to explore such relatio
> A major stumbling block to studying and implementing quality improvement methodologies is that __________. a) Quality is a hindrance to production b) Quality means different things to different people c) Customers care about price and not quality d) Prod
> Consider the data set in the table below, use the Wilcoxon Matched-Pairs Signed-Ranks Test to calculate the test statistic, and the test statistic is __________. a) 28 b) 24 c) 4 d) −24 22. The nonparametric alternative to the one-way
> In the Mann-Whitney U test using two large samples (i.e., size greater than 10), the decision to reject the null hypothesis that the two populations are identical versus the alternative hypothesis that they are not identical is taken by __________. a) Ca
> The administrator of a large university wants to test if students elected to a large student council were randomly selected from its two campuses, east (E) and west (W). A sequence of 26 consecutive students sampled showed the following pattern: E E E E
> The test used to analyze the frequencies of two variables with multiple categories to determine whether the two variables are independent is __________. a) The F-test b) The chi-square goodness-of-fit test c) The chi-square test of independence d) Binomi
> A business analyst wants to use the chi-square goodness-of-fit test if a uniform distribution is a good fit for the following observed frequencies in eight categories along a single dimension. The desired level of significance is 0.05. The correct decis
> Given a small dataset: 2.3, 7.1, 6.3, 5.8, 4.2, what is the range for this data? a) 1.9 b) 2.5 c) 4.8 d) 2.3 10. A useful tool for grouping data is __________. a) A frequency distribution b) Group dynamics c) Segmentation d) Constructive statistics 11
> A firm believes that the distribution of the economic class of its customers is 25%, 50%, and 25% in the three possible categories (i.e., lower income class, middle-income class, or upper income class). To test if this belief is true, data from a random
> A regression model, Monthly Sales = 750 + 0.20 (Month), was developed to predict the monthly sales (in $1,000s) using the data from the months, 1, 2, …, 12 of the past year. The forecast using this model for the first month of the next year will be _____
> A forecasting technique that is not appropriate for forecasting time-series data that are stationary is __________. a) A naïve forecasting model b) An averaging model c) A simple linear regression model d) An exponential model 12. The techniques used for
> Data gathered on any characteristic of interest (e.g., a company’s sales) over a period of time (e.g., past five or ten years) at regular intervals (e.g., a month or a quarter) is called time-series data. Which of the following elements
> If a data set contains 6 independent variables, the number of all possible regression models will be __________. a) 31 b) 62 c) 63 d) 64 22. The main difference between forward selection and stepwise regression is this: __________. a) Forward selection i
> Which of the following statements is true with regard to higher order (third. fourth, etc.) multiple regression models? a) They do not usually fit the data better than lower-order models. b) The R2 of higher-order models will generally be less than that
> If the scatter plot of y variable versus x variable shows a parabolic shape, which of the following steps would be appropriate to explore the relationship between the two variables? a) Add two more x variables to the regression model b) Add a log x varia
> In a regression study, a multiple regression model with two explanatory variables is developed using a data set with 23 observations. In the ANOVA table for this model, the sum of squares total (SSyy) is = 12500 and the sum of squares error (SSE) = 3000.
> In testing the overall significance of a multiple regression model, the null hypothesis that each one of the β-coefficients of the x-variables in the model is equal to zero, is tested against the alternative hypothesis that __________. a) Each one of the
> The graph of a regression equation with one independent variable, y = b0 + b1 x, yields a straight line in a two-dimensional (x, y) space. To graph a regression equation with two independent variables, y = b0 + b1 x1 + b2 x2, we require a 3-dimensional s
> Which of the following categories of business analytics builds and assesses algorithmic models aimed at making empirical rather than theoretical predictions and is designed to predict future observations: a) Descriptive analytics b) Predictive analytics
> The data in the table below represent number of months spent training (x) and finish times in minutes (y) for a 5K footrace.. Interpret the relationship between the variables x and y. a) There is a strong positive correlation. b) There is a weak positi
> A runner tracks her average weekly mileage while marathon training along with her marathon finish times, given by the table below. Classify the correlation between two variables. Weekly Mileage ______ Marathon Time (mins) 55 …â&
> The proportion of the variability in the dependent variable (y) accounted for or explained by the independent variable (x) is called the __________. a) Correlation coefficient b) Regression slope coefficient c) Regression sum of squares d) Coefficient o
> For a least-squares regression line, the sum of the residuals is __________. a) Always zero b) Always positive c) Always negative d) Sometimes positive and sometimes negative 12. Residuals with large magnitudes can be used to located data points that l
> A graphical tool to illustrate the relationship between matched observations of two variables (e.g., y = the annual cost of operating a commercial airliner and x = the annual number of passengers served by the airline), is __________. a) A histogram b) A
> After establishing an overall significant difference between the means of several groups using ANOVA if we want to determine which pairs of means are significant when the sample sizes are unequal, it is appropriate to use __________. a) A series of t-tes
> A process analyst wants to conduct a study to compare five different welding techniques that have been newly developed. Fifty welders, who work in three different shifts, are randomly selected and randomly assigned to try out a welding technique (each op
> To understand how the weights of the cereal boxes vary among four different adjustable stabilizer settings of the rotary valve on the filling machine in three different production shifts, a manufacturing firm collects sample data using a structure or pla
> A manager wants to test if there is a significant difference in the variance of the output from two similar machines. It has been determined that the output of the two machines is normally distributed. To carry out the hypothesis test about the populatio
> A human resources manager wants to conduct a “before/after” study on 16 employees to determine if a motivation seminar results in an increase in their ratings of the company. The after-ratings are subtracted from the b
> Some common applications of statistics in business include which of the following: a) Predicting the outcome of an election b) Determining consumer sentiment c) Estimating salary data for various demographics d) Comparing the spending of two different gr
> To determine whether two brands of car tires differ in their performance measured in terms of the average wear over the first 10,000 miles, we should conduct __________. a) One hypothesis test for the difference in the two population means b) Two hypothe
> A nutritionist for a university wants to determine an average BMI of its students by taking a random sample of 50 students. The standard deviation of the BMIs of population of students is unknown. She is willing to accept a Type I error rate of 0.05. The
> The dean of a business school claims that the average starting salary of its graduates is more than 85 (in $000’s). It is known that the population standard deviation is 10 (in $000’s). Sample data on the starting salaries of 64 randomly selected recent
> A test of the hypotheses, H0: p = 0.18 and H1: p > 0.18 is a __________. a) One-tailed test b) Two-tailed test c) Test of two sample means d) Test of two sample proportions 14. A test of the hypotheses, H0: p = 0.18 and H1: p ≠ 0.18 is a __________. a) O
> All statistical hypotheses consist of two parts, __________ and __________. a) A null hypothesis; a full hypothesis b) A null hypothesis; a substitute hypothesis c) A null hypothesis; an alternate hypothesis d) A null hypothesis; a substantive hypothesis
> A t-distribution is similar to the z-distribution except that __________. a) It is not unimodal b) It is not symmetrical c) It has more area in the tails d) It is not bell-shaped 21. The following random sample was selected from a normal distribution: 4
> 9. In a normal distribution, what values of z should we choose if we want 90% of the area under the curve symmetrically distributed around the mean? a) ( 1.00 b) ( 1.50 c) ( 1.645 d) ( 1.96 10. In a normal distribution, if we consider the range of values
> The luggage weights for passengers for an airline are normally distributed with a mean of 25 lbs., and a standard deviation of 3 lbs. Suppose the limit on the total luggage weight is 2600 lbs. If 100 passengers are taking the airline, what is the probabi
> Suppose samples of size 100 are drawn randomly from a population that has a mean of 20 and a standard deviation of 5. What is the probability of observing a sample mean between 19 and 20.5? a) 0.3413 b) 0.6826 c) 8165 d) 0.1587 e) 0.6587 15. Suppose sa
> Selection of the winning numbers is a lottery is an example of __________. a) Convenience sampling b) Random sampling c) Nonrandom sampling d) Regulatory sampling 7. A random number generator is usually a computer program which allows computer-calculated
> A score on a 15-point multiple choices quiz measuring knowledge of statistics is an example of a(n) a) Nominal b) Ordinal c) Interval d) Ratio e) Exponential 24. Which level of data measurement allows the most or broadest application of statistical techn
> The shape of a symmetrical binomial distribution with large sample size, i.e., a large number of possible outcomes, would most likely look like a __________. a) Rectangle b) Whale c) Bell d) Hockey stick 23. In which of the following cases would the
> All normal distributions can be converted into a single distribution called the __________. a) Universal or U-distribution b) General or G-distribution c) Standard normal or the z- distribution d) Common or C-distribution 14. To convert any x value of a
> If a continuous random variable has a uniform distribution between 20 and 70, the graph of its distribution will be a rectangle with height equal to __________. a) 50 b) 1/50 c) 20 d) 70 3. The values of a random variable are uniformly distributed
> Which of the following is a characteristic of a hypergeometric distribution? a) It is a continuous distribution. b) It has undefined trials c) The outcome of each trial is a success or a failure or undefined. d) Sampling is done without replacement. e)
> In the distribution of a random variable x which is binomial with number of trials n = 30 and the probability of success p = 0.99, the largest value of x that can occur is __________. a) 24 b) 30 c) 15 d) Infinity 14. One fair coin is tossed 10 times, w
> The random variable defined as the “number of people who arrive at a store during a 15-minute interval,” is an example of __________. a) An experimental random variable b) A continuous random variable c) A discrete random variable d) Not a random variabl
> Fifty percent of all technical assistants would like to have a PC. Eighty percent of all technical assistants would like to have MAC. Fourty-five percent of all technical assistants would like to have both. If a technical assistant is randomly selected,
> A fair coin is tossed 4 times and the events A and B are defined as follows: A: {At least More than 2 heads is observed} B: {The number of heads is odd} Use the knowledge of marginal, union, intersection and conditional probabilities to describe the prob

