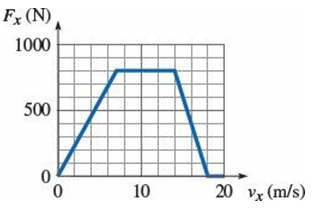
Question: An object moves in the positive x-
An object moves in the positive x-direction under the influence of a force Fx. A graph of Fx versus vx is shown.
(a) What is the instantaneous power (i.e., the rate at which the force does work on the object) when its speed is 10 m/s?
(b) What is the instantaneous power when its speed is 16 m/s?
> A bicycle wheel, of radius 0.30 m and mass 2 kg (concentrated on the rim), is rotating at 4.00 rev/s. After 50 s the wheel comes to a stop because of friction. What is the magnitude of the average torque due to frictional forces?
> A spherical balloon with a radius of 12.0 cm is filled with helium. The bottom of the balloon is attached to a 2.30 m length of ribbon that is anchored to the ground. The balloon alone has a mass of 2.80 × 10−3 kg. Ignore the mass of the ribbon. (a) Wha
> The figure shows a magnetic dipole antenna transmitting an electromagnetic wave. At a point P far from the antenna, what are the directions of the electric and magnetic fields of the wave?
> A bird perched on a power line is not harmed, but if you are pruning a tree and your metal pole saw comes in contact with the same wire, you risk being electrocuted. Explain.
> A negatively charged particle of mass 5.00 × 10−19 kg is moving with a speed of 35.0 m/s when it enters the region between two parallel capacitor plates. The initial velocity of the charge is parallel to the plate surfaces
> When a coin is tossed directly upward, what can you say about its velocity and acceleration at the high point of the toss?
> A container is filled with gas at a pressure of 4.0 × 105 Pa. The container is a cube, 0.10 m on a side, with one side facing south. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the south side of the container due to the gas inside?
> A fisherman notices a buoy bobbing up and down in the water in ripples produced by waves from a passing speedboat. These waves travel at 2.5 m/s and have a wavelength of 7.5 m. At what frequency does the buoy bob up and down?
> An RLC circuit has a resistance of 10.0 Ω, an inductance of 15.0 mH, and a capacitance of 350 µF. By what factor does the impedance of this circuit change when the frequency at which it is driven changes from 60 Hz to 120 Hz? Does the impedance increase
> An electrician working on “live” circuits wears insulated shoes and keeps one hand behind his or her back. Why?
> What average force is necessary to bring a 50.0 kg sled from rest to a speed of 3.0 m/s in a period of 20.0 s? Assume frictionless ice.
> While I1 is increasing, does current flow in loop 2? If so, does it flow clockwise or counterclockwise as viewed from the right? Explain.
> A packing carton slides down an inclined plane of angle 30.0° and of incline length 2.0 m. (a) If the initial speed of the carton is 4.0 m/s directed down the incline, what is the speed at the bottom? Ignore friction. (b) How long does it take the cart
> Verify that the collision between the proton and the nitrogen nucleus in Example 26.4 is elastic.
> A dentist holds a small mirror 1.9 cm from a surface of a patient's tooth. The image formed is upright and 5.0 times as large as the object. (a) Is the image real or virtual? (b) What is the focal length of the mirror? Is it concave or convex? (c) If
> A beam of neutrons is used to study molecular structure through a series of diffraction experiments. A beam of neutrons with a wide range of de Broglie wavelengths comes from the core of a nuclear reactor. In a time-offlight technique, used to select neu
> Refer to the pulse in Problem 9. (a) What is the speed of propagation of the pulse? (b) At what average speed does the point at x = 2.0 m move during this time interval?
> You decide to test your physics knowledge while going over a waterfall in a barrel. You take a baseball into the barrel with you, and as you are falling vertically downward, you let go of the ball. What do you expect to see for the motion of the ball rel
> The activity of a sample containing radioactive 108Ag is 6.4 × 104 Bq. Precisely 12 min later, the activity is 2.0 × 103 Bq. Calculate the half-life of 108Ag.
> A lens (n = 1.52) is coated with a magnesium fluoride film (n = 1.38). (a) If the coating is to cause destructive interference in reflected light for λ = 560 nm (the peak of the solar spectrum), what should its minimum thickness be? (b) At what two wav
> In an accelerator, two protons with equal kinetic energies collide head-on. The following reaction takes place: . What is the minimum possible kinetic energy of each of the incident proton beams?
> The magnetic flux through a flat surface is known. The area of the surface is also known. Is that information enough to calculate the average magnetic field on the surface? Explain.
> During a walk on the Moon, an astronaut accidentally drops his camera over a 20.0 m cliff. It leaves his hands with zero speed, and after 2.0 s it has attained a velocity of 3.3 m/s downward. How far has the camera fallen after 4.0 s?
> A 10.0 kg block is released from rest on a frictionless track inclined at an angle of 55°. (a) What is the net force on the block after it is released? (b) What is the acceleration of the block? (c) If the block is released from rest, how long will it
> Is it more dangerous to touch a “live” electric wire when your hands are dry or wet, everything else being equal? Explain.
> Questions 1–4: A satellite in orbit travels around Earth in uniform circular motion. In the figure, the satellite moves counterclockwise (ABCDA). Answer choices: (a) +x (b) +y (c) −x (d) −y (e) 45&Aci
> The photoelectric effect is studied using a tungsten target. The work function of tungsten is 4.5 eV. The incident photons have energy 4.8 eV. (a) What is the threshold frequency? (b) What is the stopping potential? (c) Explain why, in classical physi
> Why are astronomical observatories often located on mountaintops?
> Why are ammeters connected in series with a circuit element in which the current is to be measured and voltmeters connected in parallel across the element for which the potential difference is to be measured?
> When helium weather balloons are released, they are purposely underinflated. Why? [Hint: The balloons go to very high altitudes.]
> An object hanging vertically from a spring and a simple pendulum both have a period of oscillation of 1 s on Earth. An astronaut takes the two devices to another planet where the gravitational field is stronger than that of Earth. For each of the two sys
> The rogue starship Galaxa is being chased by the battle cruiser Millenia. The Millenia is catching up to the Galaxa at a rate of 0.55c when the captain of the Millenia decides it is time to fire a missile. First the captain shines a laser range finder to
> One cold and windy winter day, Zach notices a humming sound coming from his chimney, which is open at the top and closed at the bottom. He opens the chimney at the bottom and notices that the sound changes. He goes over to the piano to try to match the n
> Is the electric field inside a conductor always zero? If not, when is it not zero? Explain.
> If E = 0 everywhere throughout a region of space, what do we know is true about the potential at points in that region?
> A road with a radius of 75.0 m is banked so that a car can navigate the curve at a speed of 15.0 m/s without any friction. When a car is going 20.0 m/s on this curve, what minimum coefficient of static friction is needed if the car is to navigate the cur
> A sound wave of frequency 1231 Hz travels through air directly toward a wall, then through the wall out into air again. If the initial speed of the sound wave is 341 m/s and its speed in the wall is 620 m/s, what are (a) the initial wavelength of the so
> An object is placed on a scale. Under what conditions does the scale read something other than the object's weight, even though the scale is functioning properly and is calibrated correctly? Explain.
> Can the average speed and the magnitude of the average velocity ever be equal? If so, under what circumstances?
> For divers going to great depths, the composition of the air in the tank must be modified. The ideal composition is to have approximately the same number of O2 molecules per unit volume as in surface air (to avoid oxygen poisoning), and to use helium ins
> On a graph of vx versus time, what quantity does the area under the graph represent?
> The columns built by the ancient Greeks and Romans to support temples and other structures are tapered; they are thicker at the bottom than at the top. This certainly has an aesthetic purpose, but is there an engineering purpose as well? What might it be
> You are driving your car along a country road at a speed of 27.0 m/s. As you come over the crest of a hill, you notice a farm tractor 25.0 m ahead of you on the road, moving in the same direction as you at a speed of 10.0 m/s. You immediately slam on you
> Verify that the units of the rotational form of Newton's second law [Eq. (8-19)] are consistent. In other words, show that the product of a rotational inertia expressed in kg·m2 and an angular acceleration expressed in rad/s2 is a torque expressed in N·m
> An electron moving in the positive x-direction passes through a slit of width Δy = 85 nm. What is the minimum uncertainty in the electron's velocity in the y-direction?
> While testing speakers for a concert, Tomás sets up two speakers to produce sound waves at the same frequency, which is between 100 Hz and 150 Hz. The two speakers vibrate in phase with each other. He notices that when he listens at certain locations, th
> Two identical circular coils of wire are separated by a fixed center-to- center distance. Describe the orientation of the coils that would (a) maximize or (b) minimize their mutual inductance.
> Two loops of wire are next to each other in the same plane. (a) If the switch S is closed, does current flow in loop 2? If so, in what direction? (b) Does the current in loop 2 flow for only a brief moment, or does it continue? (c) Is there a magnetic
> What is the de Broglie wavelength of a proton with kinetic energy 1.0 TeV?
> Objects that are at rest relative to Earth’s surface are in circular motion due to Earth’s rotation. What is the radial acceleration of an African baobab tree located at the equator?
> If E = 0 at a single point, then a point charge placed at that point will feel no electric force. What does it mean if the potential is zero at a point? Are there any assumptions behind your answer?
> 21. A stone is thrown at an angle of 20° below the horizontal from the top of a cliff. Assume no air resistance. One second after being thrown, the stone's velocity is at angle θ below the horizontal. Which is true? (a) θ = 0 (b) θ = 20° (c) 0 < θ < 20°
> Why are all parts of a conductor at the same potential in electrostatic equilibrium?
> Coherent green light with a wavelength of 520 nm and coherent violet light with a wavelength of 412 nm are incident on a double slit with slit separation of 0.020 mm. The interference pattern is displayed on a screen 72.0 cm away. (a) Find the separatio
> An electron in an atom has an angular momentum quantum number of 2. (a) What is the magnitude of the angular momentum of this electron in terms of ħ? (b) What are the possible values for the z- components of this electron's angular momentum? (c) Draw a
> Magnetic induction is the principle behind the operation of mechanical speedometers used in automobiles and bicycles. In the drawing, a simplified version of the speedometer, a metal disk is free to spin about the vertical axis passing through its center
> An electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference ΔV. If the electron reaches a speed of 7.26 × 106 m/s, what is the potential difference? Be sure to include the correct sign. (Does the electron move through an increase or a decrease in
> Objects that are at rest relative to Earth’s surface are in circular motion due to Earth’s rotation. What is the radial acceleration of a painting hanging in the Prado Museum in Madrid, Spain, at a latitude of 40.2&Aci
> A point charge moves to a region of higher potential and yet the electric potential energy decreases. How is this possible?
> At the Stanford Linear Accelerator, electrons and positrons collide together at very high energies to create other elementary particles. Suppose an electron and a positron, each with rest energies of 0.511 MeV, collide to create a proton (rest energy 938
> In the United States, the ac household current oscillates at a frequency of 60 Hz. In the time it takes for the current to make one oscillation, how far has the electromagnetic wave traveled from the current- carrying wire? This distance is the wavelengt
> A circular conducting loop with radius 1.8 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.88 T with the plane of the coil perpendicular to the magnetic field as shown. The magnetic field decreases to 0.36 T in a time interval of 29 ms. What is the average
> A parallel plate capacitor has a capacitance of 2.0 µF and plate separation of 1.0 mm. (a) How much potential difference can be placed across the capacitor before dielectric breakdown of air occurs (Emax = 3 × 106 V/m)? (b) What is the magnitude of the
> Points A and B are at the same potential. What is the total work that must be done by an external agent to move a charge from A to B? Does your answer mean that no external force need be applied? Explain.
> A charged particle is accelerated from rest through a potential difference ΔV. The particle then passes straight through a velocity selector (field magnitudes E and B). Derive an expression for the charge-to-mass ratio (q/m) of the particle in terms of Δ
> What are some of the advantages of using mirrors rather than lenses for astronomical telescopes?
> 11. A woman stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator that is not moving. The scale reads 500 N. The elevator then moves downward at a constant velocity of 4.5 m/s. What does the scale read while the elevator descends with constant velocity? (a) 100 N (b
> In a reciprocating saw, a Scotch yoke converts the rotation of the motor into the back-and-forth motion of the blade. The Scotch yoke is a mechanical device used to convert oscillatory motion to circular motion or vice versa. A wheel with a fixed knob ro
> The motion of a simple pendulum is approximately SHM only if the amplitude is small. Consider a simple pendulum that is released from a horizontal position (θi = 90° in Fig. 10.23). (a) Using conservation of energy, find the speed of the pendulum bob at
> The f-stop of a camera lens is defined as the ratio of the focal length of lens to the diameter of the aperture. A large f-stop therefore means a small aperture. If diffraction is the only consideration, would you use the largest or the smallest f-stop t
> An object is subjected to two constant forces that are perpendicular to each other. Can a set of x- and y-axes be chosen so that the acceleration of the object has only one nonzero component? If so, how? Explain.
> Suppose some astronauts have landed on Mars. When the astronauts ask a question of mission control personnel on Earth, what is the shortest possible time they have to wait for a response? The average distance from Mars to the Sun is 2.28 × 1011 m.
> Two sheets of ideal polarizing material are placed with their transmission axes at right angles to each other. A third polarizing sheet is placed between them with its transmission axis at 45° to the axes of the other two. (a) If unpolarized light of in
> Four long straight wires, each with current I, overlap to form a square with side 2r. (a) Find the magnetic field at the center of the square. (b) Compare your answer with the magnetic field at the center of a circular loop of radius r carrying current
> A 1500 kg car moving east at 17 m/s collides with a 1800 kg car moving south at 15 m/s, and the two cars stick together. (a) What is the velocity of the cars right after the collision? (b) How much kinetic energy was converted to another form during th
> If a capacitor has a capacitance of 10.2 µF and we wish to lower the potential difference across the plates by 60.0 V, what magnitude of charge will we have to remove from each plate?
> In aviation, a standard rate turn proceeds at an angular speed of 180° per minute. What is the radius of a standard rate turn for a plane moving at 240 m/s?
> Roger is in a ship offshore and listening to a baseball game on his radio. He notices that there is destructive interference when seaplanes from the nearby Coast Guard station are flying directly overhead at elevations of 780 m, 975 m, and 1170 m. The br
> (a) If you measure the ship that passes you in Problem 76 to be 24 m long, how long will the observers on Earth measure that ship to be? (b) If there is a rod on your spaceship that you measure to be 24 m long, how long will the observers on Earth measu
> A portable radio requires an emf of 4.5 V. Olivia has only two nonrechargeable 1.5 V batteries, but she finds a larger 6.0 V battery. (a) How can she arrange the batteries to produce an emf of 4.5 V? Draw a circuit diagram. (b) Is it advisable to use th
> Zach insists that the seasons are caused by the elliptical shape of Earth’s orbit. He says that it is summer when Earth is closest to the Sun and winter when it is farthest away from the Sun. What evidence can you think of to show that the seasons are no
> In musical acoustics, a frequency ratio of 2:1 is called an octave. Humans with extremely good hearing can hear sounds ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which is approximately 10 octaves (since 210 = 1024 ≈ 1000). (a) Approximately how many octaves of visib
> (a) In double-slit interference, how does the slit separation affect the distance between adjacent interference maxima? (b) How does the distance between the slits and screen affect that separation? (c) If you are trying to resolve two closely spaced m
> The International Space Station (ISS) has a mass of 4.5 × 105 kg and orbits Earth at a speed of 7.7 km/s. By what percentage does the approximate momentum of the ISS calculated nonrelativistically differ from the relativistic momentum? [Hint: Use one of
> A positive charge is initially at rest in an electric field and is free to move. Does the charge start to move toward a position of higher or lower potential? What happens to a negative charge in the same situation?
> Light visible to humans consists of electromagnetic waves with wavelengths (in air) in the range 400–700 nm (4.0 × 10−7 m to 7.0 × 10−7 m). The speed of light in air is 3.0 × 108 m/s. What are the frequencies of electromagnetic waves that are visible?
> Using the results of Problem 75, we can find the electric field at any radius for any spherically symmetrical charge distribution. A solid sphere of charge of radius R has a total charge of q uniformly spread throughout the sphere. (a) Find the magnitud
> What is the potential energy if a third point charge q = −4.2 nC is placed at point b?
> 1. Which one of these statements is true? (a) The principal quantum number of the electron in a hydrogen atom does not affect its energy. (b) The principal quantum number of an electron in its ground state is zero. (c) The orbital angular momentum quantu
> A curve in a stretch of highway has radius 512 m. The road is unbanked. The coefficient of static friction between the tires and road is 0.70. (a) What is the maximum speed that a car can travel around the curve without skidding? (b) Explain what happe
> A beam of neutrons has the same de Broglie wavelength as a beam of photons. Is it possible that the energy of each photon is equal to the kinetic energy of each neutron? If so, at what de Broglie wavelength(s) does this occur? [Hint: For the neutron, use
> Glenda drops a coin from ear level down a wishing well. The coin falls a distance of 7.00 m before it strikes the water. If the speed of sound is 343 m/s, how long after Glenda releases the coin will she hear a splash?
> Find the molar mass of ammonia (NH3).
> A thin film of oil with index of refraction of 1.50 sits on top of a pool of water with index of refraction of 1.33. When light is incident on this film, a maximum is observed in reflected light at 480 nm and a minimum is observed in reflected light at 6
> If rays from points on an object are converging as they enter a lens, is the object real or virtual?
> Why must projectors and cameras form real images? Does the lens in the eye form real or virtual images on the retina?
> The windings of an electromagnet have inductance L = 8.0 H and resistance R = 2.0 Ω. A 100.0 V dc power supply is connected to the windings by closing switch S2. (a) A few minutes later, what is the current in the windings? (b) The electrom
> A car drives around a curve with radius 410 m at a speed of 32 m/s. The road is banked at 5.0°. The mass of the car is 1400 kg. (a) What is the frictional force on the car? (b) At what speed could you drive around this curve so that the force of fricti
> What causes chromatic aberration? What can be done to compensate for chromatic aberration?
> A star is moving away from Earth at a speed of 2.4 × 108 m/s. Light of wavelength 480 nm is emitted by the star. What is the wavelength as measured by an Earth observer?

