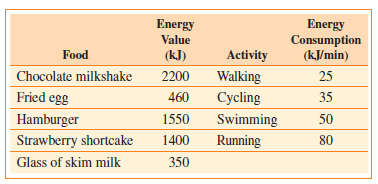
Question: Energy Value and Energy Consumption The table
Energy Value and Energy Consumption The table below gives the approximate energy values of some foods, in kilojoules (kJ), and the energy requirements of some activities.
(a) How soon would you use up the energy from a fried egg by walking?
(b) How soon would you use up the energy from a hamburger by swimming?
(c) How soon would you use up the energy from a piece of strawberry shortcake by cycling?
(d) How soon would you use up the energy from a hamburger and a chocolate milkshake by running?
> Let A = {1, 2, 3} B = {a, b} Does n(A ( B) = n(B ( A)?
> Let A = {1, 2, 3} B = {a, b} Determine n(B ( A).
> Let A = {1, 2, 3} B = {a, b} Determine n(A ( B)
> Let A = {1, 2, 3} B = {a, b} Does A ( B = B ( A?
> Let A = {1, 2, 3} B = {a, b} Determine B ( A.
> Saving for a Stereo Fernando works 40 hours per week and makes $8.50 per hour. (a) How much money can he expect to earn in 1 year (52 weeks)? (b) If he saves all the money he earns, how long will he have to work to save for a stereo receiver that costs
> Let A = {1, 2, 3} B = {a, b} Determine A ( B
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. (C - A)( - B
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. (A - B)( - C
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. (C ( B) ( (A( ( B)
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. (A( ( C) ( (A ( B)
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. A ( (C ( B)(
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. (A ( B) ( C
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. (A ( C)(
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. A( ( B(
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. A ( C
> Convert the given numeral to a numeral inbase 10. 50328
> Let U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, c, d, f, g, i} B = {b, c, d, f, g} C = {a, b, f, i, j} Determine the following. B ( C
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. A( - B(
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. (A - B)(
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. A( ( (A ( B)
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. (B ( A)( ( (B( ( A()
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. (A ( B)((A ( B)(
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. (A ( B)( ( B
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. A( ( B(
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. (A ( B)(
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. A ( B
> Gas Mileage Wendy fills her gas tank completely and makes a note that the odometer reads 38,451.4 miles. The next time she put gas in her car, filling the tank took 12.6 gal and the odometer read 38,687.0 miles. Determine the number of miles per gallon t
> Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 2, 4, 5, 7} B = [2, 3, 5, 6} Determine the following. A ( B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. (A - B)(
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. A( - B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. (A ( B)(
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. A( ( B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. A ( B(
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. A( ( B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. A ( B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. U
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. B
> Convert the given numeral to a numeral inbase 10. 76548
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.13 to list the set of elements in roster form. A
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. A - B(
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. A - B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. (A ( B)(
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. A( ( B(
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. (A ( B)(
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. A ( B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. U
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. A ( B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. B
> Use the Venn diagram in Fig. 2.12 to list the set of elements in roster form. A
> In Exercises 29–34, U is the set of furniture stores. A is the set of furniture stores that sell mattresses. B is the set of furniture stores that sell outdoor furniture. C is the set of furniture stores that sell leather furniture. Describe the followin
> In Exercises 29–34, U is the set of furniture stores. A is the set of furniture stores that sell mattresses. B is the set of furniture stores that sell outdoor furniture. C is the set of furniture stores that sell leather furniture. Describe the followin
> In Exercises 29–34, U is the set of furniture stores. A is the set of furniture stores that sell mattresses. B is the set of furniture stores that sell outdoor furniture. C is the set of furniture stores that sell leather furniture. Describe the followin
> In Exercises 29–34, U is the set of furniture stores. A is the set of furniture stores that sell mattresses. B is the set of furniture stores that sell outdoor furniture. C is the set of furniture stores that sell leather furniture. Describe the followin
> In Exercises 29–34, U is the set of furniture stores. A is the set of furniture stores that sell mattresses. B is the set of furniture stores that sell outdoor furniture. C is the set of furniture stores that sell leather furniture. Describe the followin
> In Exercises 29–34, U is the set of furniture stores. A is the set of furniture stores that sell mattresses. B is the set of furniture stores that sell outdoor furniture. C is the set of furniture stores that sell leather furniture. Describe the followin
> In Exercises 23–28, U is the set of cities in the United States. A is the set of cities that have a professional sports team. B is the set of cities that have a symphony. Describe each of the following sets in words. A ( B(
> In Exercises 23–28, U is the set of cities in the United States. A is the set of cities that have a professional sports team. B is the set of cities that have a symphony. Describe each of the following sets in words. A ( B(
> In Exercises 23–28, U is the set of cities in the United States. A is the set of cities that have a professional sports team. B is the set of cities that have a symphony. Describe each of the following sets in words. A ( B
> Convert the given numeral to a numeral inbase 10. 11101112
> In Exercises 23–28, U is the set of cities in the United States. A is the set of cities that have a professional sports team. B is the set of cities that have a symphony. Describe each of the following sets in words A ( B
> In Exercises 23–28, U is the set of cities in the United States. A is the set of cities that have a professional sports team. B is the set of cities that have a symphony. Describe each of the following sets in words B(
> In Exercises 23–28, U is the set of cities in the United States. A is the set of cities that have a professional sports team. B is the set of cities that have a symphony. Describe each of the following sets in words. A(
> Let U represent the set of animals in U.S. zoos. Let Arepresent the set of animals in the San Diego zoo. Describe A(.
> Let U represent the set of retail stores in the United States. Let A represent the set of retail stores that sell children’s clothing. Describe A(.
> Racing Standings The table on the top of the next page shows the 2013 NASCAR Sprint Cup Final Standings. The table shows the 12 drivers having the highest point total and the number of Sprint Cup races they won. Let the drivers in the table represent the
> Facebook The table below shows the annual sales revenue and net income, in millions of dollars, for Facebook for the years 2009–2013. Let the years in the table represent the universal set. Let A = the set of years in which the sales re
> National Parks For the sets U, A, and B, construct a Venn diagram and place the elements in the proper regions. U = {Acadia, Badlands, Death Valley, Glacier, Mammoth Cave, Mount Rainier, North Cascades, Shenandoah, Yellowstone, Zion} A = {Acadia, Badla
> Cellular Telephones For the sets U, A, and B, construct a Venn diagram and place the elements in the proper regions. U = {Desire, Fire, Galaxy S5, iPhone, Lumia, Nexus, One, Xperia} A = {Desire, Galaxy S5, iPhone, One, Xperia} B = {Fire, Nexus, One, Xp
> For the sets U, A, and B, construct a Venn diagram and place the elements in the proper regions. U = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, k} A = {a, b, e, f, h, j} B = {b, c, d, f, j}
> A survey of 500 farmers in a midwestern state showed the following. 125 grew only wheat. 110 grew only corn. 90 grew only oats. 200 grew wheat. 60 grew wheat and corn. 50 grew wheat and oats. 180 grew corn. Determine the number of farmers who (a) grew a
> For the sets U, A, and B, construct a Venn diagram and place the elements in the proper regions. U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8} A = {1, 6, 8} B = {2, 4, 6, 7, 8}
> For the sets U, A, and B, construct a Venn diagram and place the elements in the proper regions. U = {a, b, c, d, e, f} A = {a, c} B = {b, e, f}
> In Exercises 9–13, use Fig. 2.2 on page 55 as a guide to draw a Venn diagram that illustrates the situation described. Set A and set B are overlapping sets.
> In Exercises 9–13, use Fig. 2.2 on page 55 as a guide to draw a Venn diagram that illustrates the situation described. A = B
> If A ( B and B ( C, must A ( C?
> If A (B and B ( C, must A ( C?
> If A ( B and B ( C, must A ( C?
> How many elements must a set have if the number of proper subsets of the set is ½ of the total number of subsets of the set?
> Hospital Expansion A hospital has four members on the board of directors: Arnold, Benitez, Cathy, and Dominique. a) When the members vote on whether to add a wing to the hospital, how many different ways can they vote (abstentions are not allowed)? For e
> For the set D = {a, b, c} (a) is a an element of set D? (b) is c a subset of set D? (c) is {a, b} a subset of set D?
> Playing a Lottery In one state lottery game, you must select four digits (digits may be repeated). If your number matches exactly the four digits selected by the lottery commission, you win. (a) How many different numbers may be chosen? (b) If you purc
> Blueprints Tony, an architect, is designing a new enclosure for the giraffes at a zoo. The scale of his plan is 1 in. = 2.5 yd. He draws a 22.4-in. line on the blueprint to represent the northern boundary of the enclosure. What actual distance does this
> How can you determine whether the set of boys is equivalent to the set of girls at a roller-skating rink?
> If E ( F and F ( E, what other relationship exists between E and F?
> Telephone Features A customer with Verizon can order telephone service with some, all, or none of the following features: call waiting, call forwarding, caller identification, three-way calling, voice mail, fax line. How many different variations of the
> Salad Toppings Donald is ordering a salad at a Ruby Tuesday restaurant. He can purchase a salad consisting of just lettuce, or he can add any of the following items: cucumbers, onions, tomatos, carrots, green peppers, olives, mushrooms. How many differe
> Installing an Inground Pool The Fitzgeralds are installing an inground pool in their back yard. They can either install the base model offered by the pool company or add any of the following options: automatic pool cleaner, solar cover, waterfall, hot tu
> Buying a Boat Soonyee is purchasing a pontoon boat. She can add any of the following options: cell phone holder, bluetooth radio, anchor lights, cupholders, depth gauge, navigation lights, dinette table, battery charging system, ski mirror. How many diff
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. U ( Ø
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. Ø ( Ø
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. U ( Ø
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. Ø ( U
> Convert the given numeral to a numeral inbase 10. 1101012
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. Ø ( Ø
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. A ( U
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. Ø ( A
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. Ø ( A
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. A ( A
> In Exercises 41–52, if the statement is true for all sets A and B, write “true.” If it is not true for all sets A and B, write “false.” Assume that A ≠ Ø, U ≠ Ø, and A ( U. A ( A

