Question: For each of the following independent cases,
For each of the following independent cases, compute cash flows from operating activities using the direct method. Assume the list below includes all items relevant to operating activities.
> In recent years, the managerial concepts of activity-based management (ABM), activity-based costing (ABC), and total quality management (TQM) have received considerable attention from manufacturing and other companies. The development of a global economy
> Keller Company makes two models of battery-operated boats, the Sandy Beach and the Rocky River. Basic production information follows: Keller has monthly overhead of $22,360, which is divided into the following cost pools: The company has also compiled th
> Harbour Company makes two models of electronic tablets, the Home and the Work. Basic production information follows: Harbour has monthly overhead of $175,200, which is divided into the following cost pools: The company has also compiled the following inf
> Carlise has identified the following information about its overhead activity cost pools and the two product lines: Required: 1. Suppose Carlise used a traditional costing system with machine hours as the cost driver. Determine the amount of overhead assi
> Hazelnut Corp. manufactures lawn ornaments. It currently has two product lines, the basic and the luxury. Hazelnut has a total of $171,500 in overhead. The company has identified the following information about its overhead activity cost pools and the tw
> Refer to the information in PA3-5 for Glencove Company. Required: Complete all requirements for PA3-5 using the FIFO method. Data from PA3-5: Glencove Co. makes one model of radar gun used by law enforcement officers. All direct materials are added at t
> Glencove Co. makes one model of radar gun used by law enforcement officers. All direct materials are added at the beginning of the manufacturing process. Information for the month of September follows: Required: 1. Using the weighted-average method of pr
> Refer to the information in PA3-3 for Saddleback Company. Required: Complete all requirements for PA3-3 using the FIFO method. Data from PA3-3: Saddleback Company makes camping lanterns using a single production process. All direct materials are added a
> Saddleback Company makes camping lanterns using a single production process. All direct materials are added at the beginning of the manufacturing process. Information for the month of March follows: Required: 1. Using the weighted-average method of proce
> Refer to E3-13 for information regarding Arboles Company. Required: Complete all requirements for E3-13 using the FIFO method of process costing. Data from E3-13: Arboles Company manufactures pencils and has the following information available for the m
> Wilson’s Furniture Company incurs the costs listed in the following table. Required: Use an X to categorize each of the following costs. You may have more than one X for each item.
> Refer to the information for Sandia Corporation in PA3-1. Required: Complete all requirements for PA3-1 using the FIFO method. Data from PA3-1: Sandia Corporation manufactures metal toolboxes. It adds all materials at the beginning of the manufacturing
> Sandia Corporation manufactures metal toolboxes. It adds all materials at the beginning of the manufacturing process. The company has provided the following information: Required: 1. Using the weighted-average method of process costing, complete each of
> Refer to the information in PA2–3 for Tyler Tooling Company. Required: 1. Prepare a journal entry showing the transfer of Job 102 into Finished Goods Inventory upon its completion. 2. Prepare the journal entries to recognize the sales r
> Tyler Tooling Company uses a job order cost system with overhead applied to products on the basis of machine hours. For the upcoming year, the company estimated its total manufacturing overhead cost at $420,000 and total machine hours at 60,000. During t
> Refer to the information presented in PA2–1 for Lamonda Corp. Required: Prepare all of Lamonda’s necessary journal entries for the month of April. Data from PA2-1: Lamonda Corp. uses a job order cost system. On April
> Lamonda Corp. uses a job order cost system. On April 1, the accounts had the following balances: The following transactions occurred during April: a. Purchased materials on account at a cost of $136,000. b. Requisitioned materials at a cost of $122,000,
> Dobson Manufacturing Company uses a job order cost system with manufacturing overhead applied to products on the basis of direct labor dollars. At the beginning of the most recent period, the company estimated its total direct labor cost to be $65,000 an
> Amberjack Company is trying to decide on an allocation base to use to assign manufacturing overhead to jobs. The company has always used direct labor hours to assign manufacturing overhead to products, but it is trying to decide whether it should use a d
> The following information was obtained from the records of Appleton Corporation during 2018. - Manufacturing Overhead was applied at a rate of 125 percent of direct labor dollars. . Beginning value of inventory follows: . Beginning Work in Process Invent
> Christopher’s Custom Cabinet Company uses a job order cost system with overhead applied as a percentage of direct labor costs. Inventory balances at the beginning of 2018 follow: The following transactions occurred during January: a. Pu
> Arboles Company manufactures pencils and has the following information available for the month of July: Required: Using the weighted-average method of process costing, complete each of the following steps: 1. Reconcile the number of physical units worked
> Assume that Suzie Whitson (PA1-2) has decided to begin production of her outdoor children’s toy. Her company is Jiffy Jet and costs for last month follow. Required: 1. Identify each of the preceding costs as either a product or a period
> Match each of the terms with the appropriate definition. Not all definitions will be used. Terms: 1. Conversion Costs 2. Differential Costs 3. Indirect Costs 4. Manufacturing Costs 5. Manufacturing Firms 6. Nonmanufacturing Costs 7. Opportunity Costs 8.
> Match each of the terms with the appropriate definition. Not all definition will be used. Terms: 1. Budget 2. Controlling 3. Direct Costs 4. Financial Accounting 5. Fixed Costs 6. General and Administrative Expenses 7. Merchandising Companies 8. Product
> Comparing Financial and Managerial Accounting Match each of the following characteristics that describe financial accounting, managerial accounting, both financial and managerial accounting, or neither financial nor managerial accounting. 1. Is future or
> Mystic Laboratories reported total assets of $11,200,000 and noncurrent assets of $1,480,000. The company also reported a current ratio of 1.5. What amount of current liabilities did the company report?
> A manufacturer reported an inventory turnover ratio of 8.6 last year. During the current year, management introduced a new inventory control system that was expected to reduce average inventory levels by 25 percent without affecting sales volume. Given t
> Given the following data, compute the return on equity ratio for the current year (expressed as a percentage with one decimal place).
> A consumer products company reported a 25 percent increase in sales from last year to this year. Sales last year were $200,000. This year, the company reported Cost of Goods Sold in the amount of $150,000. What was the gross profit percentage this year?
> Your campus computer store reported Sales Revenue of $168,000. The company’s gross profit percentage was 60.0 percent. What amount of Cost of Goods Sold did the company report?
> Refer to the calculations from M13–2. Which of the ratios from Exhibit 13–5 have been included in these calculations? Have these two ratios improved or deteriorated in the current year compared to the previous year? D
> Refer to E3-11 for information regarding Legacy Company. Required: Complete all requirements for E3-11 using the FIFO method. Data from E3-11: Legacy Company manufactures umbrellas and has the following information available for the month of May:
> Refer to the calculations from M13–1. What are the two most significant year-over-year changes in terms of dollars and in terms of percentages? Give one potential cause of each of these changes. Data from M13-1: Using the following inc
> Refer to M13–1. Perform the calculations needed for vertical analyses. Round percentages to one decimal place. Data from M13-1: Using the following income statements, perform the calculations needed for horizontal analyses. Round perce
> Generally speaking, do the following indicate good news or bad news? a. Increase in times interest earned ratio. b. Decrease in days to sell. c. Increase in gross profit percentage. d. Decrease in EPS. e. Increase in fixed asset turnover ratio.
> Identify the ratio that is relevant to answering each of the following questions. a. How much net income does the company earn from each dollar of sales? b. Is the company financed primarily by debt or equity? c. How many dollars of sales were generated
> Last year, Big W Company reported earnings per share of $2.50 when its stock was selling for $50.00. If its earnings this year increase by 10 percent and the P/E ratio remains constant, what will be the price of its stock? Explain.
> Using the following income statements, perform the calculations needed for horizontal analyses. Round percentages to one decimal place
> Which of the following transactions would be considered noncash investing and financing activities? 1. Additional borrowing from bank. 2. Purchase of equipment with investments. 3. Dividends paid in cash. 4. Purchase of a building with a promissory note.
> Using the data from M12–6, calculate the maximum investing cash inflows that could be reported under IFRS. Using data from M12–7, calculate the maximum financing cash flows that could be reported under IFRS. Data From
> Based on the following information, compute cash flows from financing activities under GAAP.
> Based on the following information, compute cash flows from investing activities under GAAP.
> Legacy Company manufactures umbrellas and has the following information available for the month of May: Required: Using the weighted-average method of process costing, complete each of the following steps: 1. Reconcile the number of physical units worked
> For the following two independent cases, show the cash flows from operating activities section of the statement of cash flows for year 2 using the indirect method.
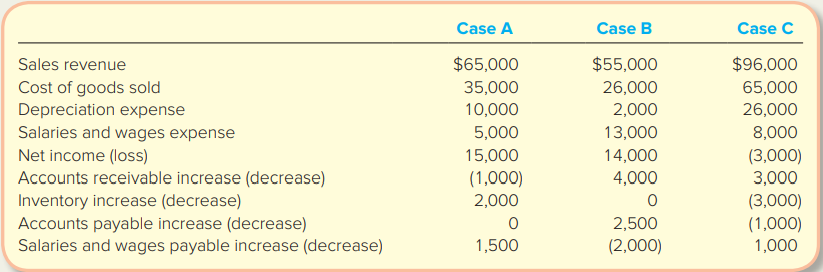
> For each of the following independent cases, compute cash flows from operating activities. Assume the list below includes all balance sheet accounts related to operating activities.
> Indicate whether each item would be added (+) or subtracted (−) in the computation of cash flows from operating activities using the indirect method. 1. Depreciation. 2. Inventory decrease. 3. Accounts payable decrease. 4. Accounts receivable increase. 5
> The Buckle, Inc., included the following in its statement of cash flows presented using the indirect method. Indicate whether each item is disclosed in the operating activities (O), investing activities (I), or financing activities (F) section of the sta
> Refer to the two cases presented in M12–5, and for each case show the cash flow from operating activities section of the Year 2 statement of cash flows using the direct method. Data from M12-5: For the following two independent cases,
> Prestige Manufacturing Corporation reports the following items in its statement of cash flows presented using the direct method. Indicate whether each item is disclosed in the operating activities (O), investing activities (I), or financing activities (F
> Quantum Dots, Inc., is a nanotechnology company that manufactures “quantum dots,” which are tiny pieces of silicon consisting of 100 or more molecules. Quantum dots can be used to illuminate very small objects, enablin
> Based on the cash flows shown, classify each of the following cases as a growing start-up company (S), a healthy established company (E), or an established company facing financial difficulties (F).
> Cullumber Corp. is considering three projects. Project A has a present value of $265,000 and an initial investment of $110,000. Project B has a present value of $400,000 and an initial investment of $220,000. Project C has a present value of $115,000 and
> Refer to E3-9 for information regarding Ridgecrest Company. Required: Complete all requirements for E3-9 using the FIFO method. Data from E3-9: Ridgecrest Company manufactures plastic storage crates and has the following information available for the mo
> Vaughn Company has the following information about a potential capital investment: 1. Calculate and evaluate the net present value of this project. 2. Without any calculations, explain whether the internal rate of return on this project is more or less t
> Olive Company is considering a project that is estimated to cost $286,500 and provide annual net cash flows of $57,523 for the next five years. What is the internal rate of return for this project?
> Citrus Company is considering a project that has estimated annual net cash flows of $32,000 for six years and is estimated to cost $150,000. Citrus’s cost of capital is 8 percent. Calculate the net present value of the project and whether it is acceptabl
> Blue Marlin Company is considering the purchase of new equipment for its factory. It will cost $250,000 and have a $50,000 salvage value in five years. The annual net income from the equipment is expected to be $25,000, and depreciation is $40,000 per ye
> A project has estimated annual net cash flows of $80,000 and is estimated to cost $340,000. What is the payback period?
> What is the accounting rate of return for a project that is estimated to yield total income of $390,000 over three years and costs $920,000?
> Matching Terminology 1. Compounding 2. Discounted cash flow methods 3. Discounting 4. Discount rate 5. Sensitivity analysis 6. Simple rate of return A. How changing underlying assumptions affect decisions. B. The rate at which the current value of future
> An investment manager is currently evaluating three projects: 1. Project 1 requires an initial investment of $10,000, will provide future cash flows of $26,000, and the PV of the future cash flows is $17,000. 2. Project 2 requires an initial investment o
> Tremaine Company is considering two mutually exclusive long-term investment projects. Project ABC would require an investment of $240,000, have a useful life of 4 years, and annual cash flows of $78,000. Project XYZ would require an investment of $230,00
> You plan to retire in 20 years. Calculate whether it is better for you to save $30,000 a year for the last 10 years before retirement or $15,000 for each of the next 20 years. Assume you are able to earn 8 percent interest on your investments.
> Suppose your sister Becky and her three best friends start a small business making beaded bracelets. They plan to purchase the materials, assemble the jewelry themselves, and sell the finished pieces to friends at school. Other than minor color and desig
> As a result of a slowdown in operations, Tradewind Stores is offering employees who have been terminated a severance package of $100,000 cash paid today; $50,000 to be paid in one year; and an annuity of $20,000 to be paid each year for 20 years. What is
> A number of terms and concepts from this chapter and a list of descriptions, definitions, and explanations appear as follows. For each term listed (1 through 9), choose at least one corresponding item (a through k). Note that a single term may have more
> Augusta Corp’s Golf Division has sales of $200,000, cost of goods sold of $105,000, operating expenses of $35,000, average invested assets of $900,000, and a hurdle rate of 12 percent. Calculate the Golf Division’s return on investment and its residual i
> Myrtle Company has sales of $140,000, cost of goods sold of $70,000, operating expenses of $20,000, average invested assets of $400,000, and a hurdle rate of 6 percent. Calculate Myrtle’s return on investment and its residual income.
> Violet Company has sales of $520,000, net operating income of $310,000, average invested assets of $940,000, and a hurdle rate of 10 percent. Calculate Violet’s return on investment and its residual income.
> Choose a company that has an online sales segment; it can be a company that operates entirely online or a brick-and-mortar store with an online site. Assuming a balanced scorecard approach, identify five specific measures that the company could use to me
> Consider the manager of your local Applebee’s restaurant. Using a balanced scorecard approach, identify three measures for each of the four dimensions of the balanced scorecard.
> In each of the following situations, identify which type of responsibility center is appropriate based on the decision-making authority the manager would possess: 1. The manager of the accounting department in Ford’s corporate office. 2. The sales manage
> Responsibility centers can be created in a variety of ways. Give a real-world example of a company whose responsibility centers would likely be created on the basis of each of the following: functional area, product line, and geographic area.
> Lupe Bornes recently graduated from college and received job offers in management from two different companies. The positions are similar in terms of title, salary, and benefits, but the companies vary in organizational structure. Alpha Company is centra
> Manufacturing costs for Davenport Company during 2018 were as follows: Required: 1. Compute direct material used. 2. Compute applied overhead if the company applies overhead at a rate of 0.75 (75 percent) of direct labor cost. 3. Compute total manufactur
> Tuckey Company is considering allowing the managers of its two divisions to negotiate a transfer price for the component that Division A manufactures and sells to Division B. Identify the range of possible transfer prices that could result from the negot
> Medlock Company has two divisions, Wheel and Chassis. The Wheel Division manufactures a wheel assembly that the Chassis Division uses. The variable cost to produce this assembly is $4.00 per unit; full cost is $5.00. The component sells on the open marke
> Peppertree Company has two divisions, East and West. Division East manufactures a component that Division West uses. The variable cost to produce this component is $2.00 per unit; full cost is $2.75. The component sells on the open market for $3.10. Assu
> Assume that your cousin Matilda Flores manages a local glass shop that was recently bought by a company that produces custom picture frames. As a result, Matilda will soon be providing glass to the Frame Division. She has heard upper management mention a
> The Western Division of Claremont Company had net operating income of $135,000 and average invested assets of $560,000. Claremont has a required rate of return of 15 percent. Western has an opportunity to increase operating income by $12,000 with a $108,
> Use the following terms to complete the sentences that follow; terms may be used once, more than once, or not at all: 1. Managers of a(n) center are evaluated based on measures such as ROI and residual income? 2. Suboptimal decisions and duplication of
> Acoma, Inc., has determined a standard direct materials cost per unit of $8 (2 feet × $4 per foot). Last month, Acoma purchased and used 4,200 feet of direct materials for which it paid $15,750. The company produced and sold 2,000 units during the month.
> Kelton Corp. has calculated its direct materials price and quantity variances to be $500 favorable and $800 unfavorable, respectively. Kelton’s production manager believes that these variances indicate that the purchasing department is doing a good job b
> For each of the following independent cases, fill in the missing amounts in the table:
> Dabney Company manufactures widgets and would like to use a standard cost system. Explain how Dabney will determine the standards for direct materials and direct labor to use in its costing system.
> Refer to the information presented in E2–7 for Cambridge Manufacturing Company. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries to record actual and applied manufacturing overhead. 2. Prepare the journal entry to transfer the overhead balance to Cost of Goods S
> Evanson Company expects to produce 500,000 units of their product during the year. Monthly production is expected to range from 40,000 to 80,000 units. The company has budgeted manufacturing costs per unit to be as follows: Prepare a flexible manufacturi
> When preparing a company’s flexible budget, which manufacturing cost(s) will change as the volume increases or decreases? Which manufacturing cost(s) will not change as the volume changes?
> Consider the grading scale for a university class that has 500 possible points. The possible course grades are A, B, C, D, and F. Create a grading scale for the class that would fall into each of the following categories: an ideal standard, an easily att
> Match each of the terms by inserting the appropriate definition letter in the space provided. Not all definitions will be used. 1. Actual Accounting System 2. Direct Labor Efficiency Variance 3. Direct Labor Rate Variance 4. Direct Materials Price Varian
> Andora Company reported the following information for the month of November. The standard cost of labor for the month was $38,000, but actual wages paid were $37,300. Andora has calculated its direct labor rate and efficiency variances to be $1,500 favor
> During May, Camino Corp. purchased direct materials for 4,400 units at a total cost of $63,800. Camino’s standard direct materials cost is $14 per unit. Prepare the journal entry to record this transaction.
> Refer to M9–12 for Cholla Company. Calculate Cholla’s fixed overhead rate and the fixed overhead volume variance. Data from M9-12: Cholla Company’s standard fixed overhead rate is based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $10,200 and budgeted pr
> Cholla Company’s standard fixed overhead rate is based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $10,200 and budgeted production of 30,000 units. Actual results for the month of October reveal that Cholla produced 28,000 units and spent $9,900 on fixed
> Beverly Company has determined a standard variable overhead rate of $2.50 per direct labor hour and expects to incur 0.5 labor hour per unit produced. Last month, Beverly incurred 950 actual direct labor hours in the production of 2,000 units. The compan
> Paradise Corp. has determined a standard labor cost per unit of $12 (0.5 hour × $24 per hour). Last month, Paradise incurred 950 direct labor hours for which it paid $22,325. The company produced and sold 1,950 units during the month. Calculate the direc
> Cambridge Manufacturing Company applies manufacturing overhead on the basis of machine hours. At the beginning of the year, the company estimated its total overhead cost to be $325,000 and machine hours to be 25,000. Actual manufacturing overhead and mac
> Use the following terms to complete the sentences that follow; terms may be used once, more than once, or not at all: Static Flexible Volume Spending Production manager Variable overhead rate Variable overhead efficiency Fixed overhead spending Purchasin
> Refer to the information in M8–8 for Becker Bikes. Each unit requires 3 wheels at a cost of $5 per wheel. Becker requires 20 percent of next month’s material production needs on hand each month. July’s production units is expected to be 450 units. Prepar

