Question: For exercises marked with an asterisk, it
For exercises marked with an asterisk, it is advised that you use a statistical software package that accommodates the Spearman rank correlation test.
Consider the following sample data:
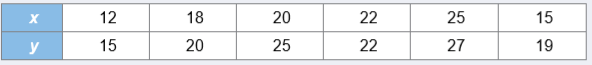
a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the Spearman rank correlation coefficient differs from zero.
b. Calculate and interpret rs.
c. The p-value associated with the test statistic in part b is 0.017. At the 5% significance level, what is the conclusion to the hypothesis test?
Transcribed Image Text:
12 18 20 22 25 15 y 15 20 25 22 27 19
> The dot-com period, roughly between 1995 and 2000, was characterized by extreme investor optimism for Internet-based businesses. This period was also marked by young, bold managers who made a good deal of money by reaching consumers over the Internet. Ar
> The consumption function, developed by John Maynard Keynes, captures one of the key relationships in economics. It expresses consumption as a function of disposable income, where disposable income is defined as income after taxes. For the years 2000&acir
> There has been a lot of discussion lately surrounding the levels and structure of executive compensation. It is well documented that in general, compensation received by senior executives has risen steeply in recent years. The accompanying table lists a
> In order to analyze differences in home prices between coastal and inland areas in California, an economist gathers 20 recent home sales (in $1,000s) in Southern California and 20 recent home sales (in $1,000s) in the Inland Empire. A portion of the resu
> The following table shows a portion of the percent change in the consumer price index (CPI) for the United States from 1980 through 2008. Use the method of runs above and below the median with a significance level of 5% to test the null hypothesis of ran
> A research analyst follows the monthly price data for the Dow Jones Industrial Average for the years 2008–2010. The accompanying table shows a portion of the price data. The analyst wants to test the random-walk hypothesis that suggests that prices move
> The following table shows a portion of the growth rate in the gross domestic product (GDP) for China from 1980 through 2008. Use the method of runs above and below the median with a significance level of 5% to test the null hypothesis of randomness again
> In order to ensure the public’s health and safety, state health inspectors are required to rate the cleanliness and quality of all restaurants in the state. Restaurants that consistently score below a certain level often lose their lice
> A research analyst believes that a positive relationship exists between a firm’s advertising expenditures and its sales. For 65 firms, she collects data on each firm’s yearly advertising expenditures and subsequent sales. She calculates a Spearman rank c
> An entrepreneur examines monthly sales (in $1,000s) for 40 convenience stores in Rhode Island. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether median sales differ from $130,000. b. At the 5% significance level, do median sales differ from $130
> The following table shows a portion of the annual returns (in percent) for two of Fidelity’s mutual funds: the Fidelity Advisor’s Electronic Fund and the Fidelity Advisor’s Utilities Fund. a. Specif
> An economist wants to determine whether the Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio is the same for firms in three industries. Five firms were randomly selected from each industry. Their P/E ratios are shown in the accompanying table. a. Specify the competing hypot
> A psychiatrist believes that the location of a test center may influence a test taker’s performance. To test his claim, he collects SAT scores from four different locations. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to test whether some med
> A consumer advocate researches the length of life between two brands of refrigerators, Brand A and Brand B. He collects data on the longevity of 40 refrigerators for Brand A and repeats the sampling for Brand B. A portion of the data is shown in the acco
> The table below shows a portion of the returns for Fidelity’s Equity Income mutual fund and Vanguard’s Equity Income mutual fund from 2000 through 2010. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the me
> A farmer is concerned that a change in fertilizer to an organic variant might change his crop yield. He subdivides six lots and uses the old fertilizer on one half of each lot and the new fertilizer on the other half. The following table shows the result
> The following are the closing stock prices for a pharmaceutical firm over the past five days. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the median stock price is greater than $61.25. b. Calculate the value of the Wilcoxon signed-rank te
> A research analyst follows the biotechnology industry and examines the daily stock price of Amgen, Inc. over the past year. The table below shows a portion of the daily stock price of Amgen (in $) for the 252 trading days in 2010. The research analyst wa
> The superintendent of a large suburban high school must decide whether to close the school for at least two days due to the spread of flu. If she can confirm a trend in absenteeism, then she will close the high school. The following are the number of stu
> The following table shows a portion of the growth rate in the gross domestic product (GDP) for India from 1980 through 2008. Use the method of runs above and below the median with a significance level of 5% to test the null hypothesis of randomness again
> A realtor in Mission Viejo, California, believes that the median price of a house is more than $500,000. The accompanying data is in $1,000s. a. Specify the competing hypotheses for the test. b. At the 5% significance level, is the realtor’s claim supp
> A gambler suspects that a coin may be weighted more heavily toward the outcome of tails (T) over heads (H). He flips the coin 25 times and notes the following sequence: T T H T T T H H T H T T H T T T H H T H T H TT H a. Specify the competing hypothese
> Given the digits zero through nine, a computer program is supposed to generate even and odd numbers randomly. The computer produced the following sequence of numbers: 5 3 4 6 8 0 2 9 7 7 1 6 8 3 1 5 2 4 3 3 9 2 a. Specify the competing hypotheses to te
> Let D denote a desirable outcome and U denote an undesirable outcome. The sequence of the outcomes is as follows: DDDUUDUUUUUDDDUUDUUUDDDUUUUDDD At the 1% significance level, conduct a hypothesis test to determine if the outcomes are nonrandom.
> Let A and B be two possible outcomes of a single experiment. The sequence of the outcomes is as follows: BBAABAABBABABBBABBAAABABBABBABA At the 5% significance level, conduct a hypothesis test to determine if the outcomes are nonrandom.
> Consider the following information: n1 = 10, n2 = 13, and R = 8, where R is the number of runs, n1 and n2 are the number of elements in a sequence possessing and not possessing a certain attribute, and n1 + n2 = n. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to
> Consider the following information: n1 = 24, n2 = 28, and R = 18, where R is the number of runs, n1 and n2 are the number of elements in a sequence possessing and not possessing a certain attribute, and n1 + n2 = n. a. Specify the competing hypotheses t
> For scholarship purposes, two graduate faculty members rate 12 applicants to the PhD program on a scale of 1 to 10 (with 10 indicating an excellent candidate). These ratings are shown in the following table. a. Using the sign test, specify the competin
> In March 2009, 100 registered voters were asked to rate the effectiveness of President Obama. In March 2010, these same people were again asked to make the same assessment. Seventy percent of the second ratings were lower than the first ratings and 30% w
> In March 2009, 100 registered voters were asked to rate the effectiveness of President Obama. In March 2010, these same people were again asked to make the same assessment. Seventy percent of the second ratings were lower than the first ratings and 30% w
> Concerned with the increase of plastic water bottles in landfills, a leading environmentalist wants to determine whether there is any difference in taste between the local tap water and the leading bottled water. She randomly selects 14 consumers and con
> An economist wants to test whether the median hourly wage is less than $22. a. Specify the competing hypotheses for the test. b. At the 5% significance level, can you conclude that the median hourly wage is less than $22? Explain.
> Consider the following sign data, produced from a matched-pairs sample of ordinal data. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the proportion of negative signs is significantly greater than the proportion of positive signs. b. Calcul
> Consider the following sign data, produced from a matched-pairs sample of ordinal data. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the proportion of negative signs differs from the proportion of positive signs. b. Calculate the value of
> Consider the following competing hypotheses and sample data. a. Calculate the value of the test statistic for the sign test. b. Calculate the p-value. c. At the 1% significance level, what is the conclusion? Explain. Hoip <0.50 n= 25 p= 0.64 HẠ:
> Consider the following competing hypotheses and sample data. a. Calculate the value of the test statistic for the sign test. b. Calculate the p-value. c. At the 5% significance level, what is the conclusion? Explain. Hoip= 0.50 Hai P # 0.50 n= 40
> The accompanying table shows a portion of the number of cases of crime related to gambling and offenses against the family and children for the 50 states in the United States during 2010. Using the Spearman rank correlation coefficient, determine wheth
> . Many attempts have been made to relate happiness with various factors. One such study relates happiness with age and finds that, holding everything else constant, people are least happy when they are in their mid-40s (The Economist, December 16, 2010).
> An engineer examines the relationship between the weight of a car and its average miles per gallon (MPG). For a sample of 100 cars, he calculates a Spearman rank correlation coefficient of −0.60. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether
> A social scientist analyzes the relationship between educational attainment and salary. For 65 individuals, he collects data on each individual’s educational attainment (in years) and his/her salary (in $1,000s). He then calculates a Spearman rank correl
> The director of graduate admissions at a local university is analyzing the relationship between scores on the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) and subsequent performance in graduate school, as measured by a student’s grade point average (GPA). She uses
> In an attempt to determine whether a relationship exists between the price of a home (in $1,000s) and the number of days it takes to sell the home, a real estate agent collected the relevant data from recent sales in his city. A portion of the data is sh
> During the fourth quarter of 2009, rents declined in almost all major cities in the United States. The largest fall was in New York, where average rents fell nearly 20% to $44.69 per square foot annually (The Wall Street Journal, January 8, 2010). The fo
> You are interested in whether the returns on Asset A (in %) are negatively correlated with the returns on Asset B (in %). Consider the following annual return data on the two assets: a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the Spearman
> The following table shows a portion of the World Bank’s 2008 ranking of the richest countries, as measured by per capita GNP. In addition, it gives each country’s respective rank with respect to infant mortality accord
> Applications The following table shows the ranks given by two judges to the performance of six finalists in a men’s figure skating competition: a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the Spearman rank correlation coe
> Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. a. What is the value of the test statistic and its associated p-value? Assume the normal approximation for rs. b. At the 1% significance level, what is the conclusion? Hoi P
> Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. a. What is the value of the test statistic and its associated p-value? Assume the normal approximation for rs. b. At the 10% significance level, what is the conclusion? Ho:P
> Consider the following sample data: a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the Spearman rank correlation coefficient is less than zero. b. Calculate and interpret rs. c. The p-value associated with the test statistic in part b is 0.
> A human resource specialist wants to determine whether the median job satisfaction score (on a scale of 0 to 100) differs depending on a person’s field of employment. She collects scores from 30 employees in three different fields. A po
> A statistics instructor wonders whether significant differences exist in her students’ median exam scores in her three different sections. She randomly selects scores from 10 different students in each section. A portion of the data is
> A well-known conglomerate claims that its detergent “whitens and brightens better than all the rest.” In order to compare the cleansing action of the top three detergents, 15 swatches of white cloth were soiled with re
> The following table lists a portion of the data representing the annual returns (in percent) over a 10-year period for the Balanced mutual fund, a top-performing mutual fund from the Janus Capital Group. Year …………………………………………………………………………………………… Return 2
> A research analyst examines annual returns (in percent) for Industry A, Industry B, and Industry C, as shown in the accompanying table. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to test whether some differences exist in the median returns by industry. b. Ca
> A quality-control manager wants to test whether there is any difference in the median length of life of light bulbs between three different brands. Random samples were drawn from each brand, where the duration of each light bulb (in hours) was measured.
> Consider the following competing hypotheses and sample data. a. Assuming that the sampling distribution of T is normally distributed, calculate the value of the test statistic. b. Calculate the p-value. c. At the 5% significance level, what is the co
> Consider the following sample data. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the median is less than 10. b. Calculate the value of the test statistic T. c. The p-value corresponding to the test statistic in part b is approximately equ
> Consider the following sample data: a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the median is greater than 140. b. Calculate the value of the test statistic T. c. The p-value corresponding to the test statistic in part b is equal to 0.04
> Consider the following sample data: a. Specify the competing hypotheses to determine whether the median differs from 20. b. Calculate the value of the test statistic T. c. The p-value corresponding to the test statistic in part b is equal to 0.188. A
> Consider the sample regressions for the linear, the logarithmic, the exponential, and the log-log models. For each of the estimated models, predict y when x equals 50. Response Variable: y Response Variable: In(y) Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Int
> Consider the sample regressions for the linear, the logarithmic, the exponential, and the log-log models. For each of the estimated models, predict y when x equals 100. Response Variable: y Response Variable: In(y) Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 In
> According to a report by the government, new home construction fell to an 18-month low in October 2010 (CNNMoney.com, November 17, 2010). Housing starts, or the number of new homes being built, experienced an 11.7% drop in the seasonally adjusted annual
> A research analyst wants to test whether the median unemployment rate differs from one region of the country to another. She collects the unemployment rate (in percent) of similar-sized cities in three regions of the United States. The results are shown
> Learning curves are used in production operations to estimate the time required to complete a repetitive task as an operator gains experience. Suppose a production manager has compiled 30 time values (in minutes) for a particular operator as she progress
> The inventory manager at a warehouse distributor wants to predict inventory cost (Cost in $) based on order quantity (Quantity in units). She thinks it may be a nonlinear relationship since its two primary components move in opposite directions: (1) ord
> The accompanying table shows a portion of the monthly data on the personal savings rate (Savings in %) and personal disposable income (Income in $ billions) in the U.S. from January 2007 to November 2010. a. Estimate the linear model, Savings = Î
> A nutritionist wants to understand the influence of income and healthy food on the incidence of smoking. He collects 2009 data on the percentage of smokers in each state in the U.S., the percentage of the state’s population that regular
> The operator’s manager at an electronics company believes that the time required for workers to build a circuit board is not necessarily proportional to the number of parts on the board. He wants to develop a regression model to predict time (in minutes)
> A realtor examines the factors that influence the price of a house. He collects data on the prices (in $) for 36 single-family homes in Arlington, Massachusetts, sold in the first quarter of 2009. For explanatory variables, he uses the houseâ€
> A horticulturist is studying the relationship between tomato plant height and fertilizer amount. Thirty tomato plants grown in similar conditions were subjected to various amounts of fertilizer (in ounces) over a four-month period, and then their heights
> A sports enthusiast wants to examine the factors that influence a quarterback’s salary (Salary in $ millions). In particular, he wants to assess the influence of the pass completion rate (PC), the total touchdowns scored (TD), and a qua
> Economists often examine the relationship between the inputs of a production function and the resulting output. A common way of modeling this relationship is referred to as the Cobb–Douglas production function. This function can be expr
> Use the data in Exercise 24 to answer the same four questions regarding life expectancy of males. Who is more likely to benefit from adding more physicians to the population? Explain. Exercise 24: Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years
> Random samples were drawn from four independent populations. The results are shown in the accompanying table. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to test whether some differences exist between the medians. b. At the 5% significance level, do some medi
> Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years that a person is expected to live. There is a huge variation in life expectancies between countries, with the highest being in Japan, and the lowest in some African countries. An important factor fo
> Chad Dobson has heard about the positive outlook for real estate investment in college towns. He is interested in investing in Davis, California, which houses one of the University of California campuses. He uses zillow.com to access data on 2011 monthly
> The facility manager at a pharmaceutical company wants to build a regression model to forecast monthly electricity cost (Cost in $). Three main variables are thought to influence electricity cost: (1) average outdoor temperature (Temp in °F),
> Professor Orley Ashenfelter of Princeton University is a pioneer in the field of wine economics. He claims that, contrary to old orthodoxy, the quality of wine can be explained mostly in terms of weather conditions. Wine romantics accuse him of undermini
> A manufacturing manager uses a dexterity test on 20 current employees in order to predict watch production based on time to completion (in seconds). A portion of the data is shown below. Watches ………………………………………………………………………………………… Time 23 ………………………………………
> According to the World Health Organization, obesity has reached epidemic proportions globally. While obesity has generally been linked with chronic disease and disability, researchers argue that it may also affect wages. Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely
> An economist is interested in examining how an individual’s cigarette consumption (C) may be influenced by the price for a pack of cigarettes (P) and the individual’s annual income (I). Using data from 50 individuals,
> Consider the following sample regressions for the log-log and the exponential models. a. Justify which model fits the data best. b. Use the selected model to predict y for x = 20. Log-Log Exponential Intercept 1.8826 2.0219 NA 0.0513 In(x) 0.3663
> Consider the following sample regressions for the linear and the logarithmic models. a. Justify which model fits the data best. b. Use the selected model to predict y for x = 10. Linear Logarithmic Intercept 6.7904 -5.6712 1.0607 NA In(x) NA 10.54
> Brendan Connolly, a statistician for a Major League Baseball (MLB) team, wants to elaborate on the salary of baseball players. Excluding pitchers from his analysis, he believes that a baseball player’s batting average (BA), runs batted
> Random samples were drawn from three independent populations. The results are shown in the accompanying table. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to test whether some differences exist between the medians. b. Calculate the value of the test statistic
> Executive compensation has risen dramatically beyond the rising levels of an average worker’s wage over the years. Consider the following portion of data that link total compensation (in $ millions) of the 455 highest-paid CEOs in 2006
> Consider the following estimated models: a. Interpret the slope coefficient in each of these estimated models. b. For each model, what is the predicted change in y when x increases by 5%, from 10 to 10.5? ŷ = 10 + 4.4x ŷ = 2 + 23In(x) In() = 3.0 +
> Consider the following four estimated models: a. Interpret the slope coefficient in each of these estimated models. b. For each model, what is the predicted change in y when x increases by 1%, from 100 to 101? ŷ = 500 – 4.2x ŷ = 1370 – In() = 8.4
> You collect data on 26 metropolitan areas to analyze average monthly debt payments (Debt in $) in terms of income (Inc in $1,000s) and the unemployment rate (Unemp in %). A portion of the data is shown in the accompanying table. a. Estimate the model D
> A lead inspector at ElectroTech, an electronics assembly shop, wants to convince management that it takes longer, on a per-component basis, to inspect large devices with many components than it does to inspect small devices because it is difficult to kee
> Consider a sample comprised of firms that were targets of tender offers during the period 1978–1985. Conduct an analysis where the response variable represents the number of bids (Bids) received prior to the takeover of the firm. The ex
> The project manager at a construction company is evaluating how crew size affects the productivity of framing jobs. He has experimented with varying crew size (the number of workers) on a weekly basis over the past 27 weeks and has recorded productivity
> Numerous studies have shown that watching too much television hurts school grades. Others have argued that television is not necessarily a bad thing for children (Mail Online, July 18, 2009). Like books and stories, television not only entertains, it als
> Consider the following sample regressions for the linear, the quadratic, and the cubic models along with their respective R2 and adjusted R2. a. Predict y for x = 2 and 3 with each of the estimated models. b. Select the most appropriate model. Explain
> Consider the following sample regressions for the linear, the quadratic, and the cubic models along with their respective R2 and adjusted R2. a. Predict y for x = 1 and 2 with each of the estimated models. b. Select the most appropriate model. Explain
> Consider the following sample information: k = 5 and H = 12.4. a. Specify the competing hypotheses to test whether some differences exist between the medians. b. At the 5% significance level, do some medians differ? Explain.
> Consider the following sample regressions for the linear and quadratic models along with their respective R2 and adjusted R2. a. Use the appropriate goodness-of-fit measure to justify which model fits the data best. b. Given the best-fitting model, pr
> Consider the following sample regressions for the linear and quadratic models along with their respective R2 and adjusted R2. a. Use the appropriate goodness-of-fit measure to justify which model fits the data best. b. Given the best-fitting model, pre
> Consider the following three models: For each of the estimated models, predict y when x equals 10 and 15. ŷ = 80 + 1.2x ŷ = 200 + 2.1x – 0.6x? ŷ = 100 + 16x – 2.2x² + 0.08x³
> Consider the following two estimated models: For each of the estimated models, predict y when x equals 5 and 10. ŷ = 25 + 1.2x ŷ = 30 + 1.4x – 0.12x²

