Question: Glassworks Inc. produces two types of glass
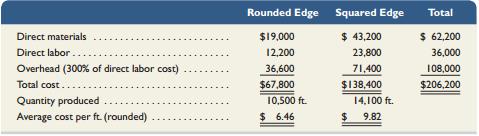
Glassworks Inc. produces two types of glass shelving, rounded edge and squared edge, on the same production line. For the current period, the company reports the following data.
Glassworks’s controller wishes to apply activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate the $108,000 of overhead costs incurred by the two product lines to see whether cost per foot would change markedly from that reported above. She has collected the following information.

She has also collected the following information about the cost drivers for each category (cost pool) and the amount of each driver used by the two product lines.

Required1. Assign these three overhead cost pools to each of the two products using ABC.2. Determine average cost per foot for each of the two products using ABC.3. Compare the average cost per foot under ABC with the average cost per foot under the current method for each product. Explain why a difference between the two cost allocation methods exists.
Transcribed Image Text:
Rounded Edge Squared Edge Total $19,000 $ 43,200 $ 62,200 Direct materials Direct labor. 12,200 23,800 36,000 Overhead (300% of direct labor cost) 36,600 71,400 108,000 Total cost.. $67,800 $138,400 $206,200 Quantity produced 10,500 ft. 14,100 ft. Average cost per ft (rounded) $ 6.46 $4 9.82
> What are the major limitations of variable costing?
> Why are overhead costs allocated to products and not traced to products as direct materials and direct labor are?
> Mathwerks produces two electronic, handheld educational games: Fun with Fractions and Count Calculus. Data on these products follow. Additional data from its two production departments follow. Required1. Using ABC, determine the cost of each product l
> Ryan Foods produces gourmet gift baskets that it distributes online as well as from its small retail store. The following details about overhead costs are taken from its records. Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follo
> Midwest Paper produces cardboard boxes. The boxes require designing, cutting, and printing. (The boxes are shipped flat and customers fold them as necessary.) Midwest has a reputation for providing highquality products and excellent service to customers,
> Wade Company makes two distinct products with the following information available for each. The company’s direct labor rate is $20 per direct labor hour (DLH). Additional information follows. Required 1. Compute the manufacturing co
> The following data are for the two products produced by Tadros Company. The company’s direct labor rate is $20 per direct labor hour (DLH). Additional information follows. Required1. Compute the manufacturing cost per unit using the
> Sara’s Salsa Company produces its condiments in two types: Extra Fine for restaurant customers and Family Style for home use. Salsa is prepared in department 1 and packaged in department 2. The activities, overhead costs, and drivers as
> Bright Day Company produces two beverages, Hi-Voltage and EasySlim. Data about these products follow. Additional data from its two production departments follow. Required1. Determine the cost of each product line using ABC.2. What is the cost per bottl
> Craft Pro Machining produces machine tools for the construction industry. The following details about overhead costs were taken from its company records. Additional information on the drivers for its production activities follows. Grinding . . . . . .
> Xylon Company manufactures custom-made furniture for its local market and produces a line of home furnishings sold in retail stores across the country. The company uses traditional volume-based methods of assigning direct materials and direct labor to it
> Smythe Crystal makes fine tableware in its Ireland factory. The following data are taken from its production plans for the year. Direct labor costs . . . . . . . . . €5,870,000 Setup costs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 630,000 Required
> Prescott Company’s predetermined overhead rate is 200% of direct labor. Information on the company’s production activities during September 2013 follows. a. Purchased raw materials on credit, $125,000. b. Paid $84,000 cash for factory wages. c. Paid $11,
> Polaris must assign overhead costs to its products. Activity-based costing is generally considered more accurate than other methods of assigning overhead. If this is so, why do all manufacturing companies not use it?
> Textra Plastics produces parts for a variety of small machine manufacturers. Most products go through two operations, molding and trimming, before they are ready for packaging. Expected costs and activities for the molding department and for the trimming
> Label each statement below as either true (“T”) or false (“F”). 1. The cost per equivalent unit is computed as the total costs of a process divided by the number of equivalent units passing through that process. 2. Service companies are not able to use p
> List the headings of the three major sections of a process cost summary.
> Put the four steps in accounting for production activities in the order in which they would occur. a. Determine physical flow of units b. Compute the cost per equivalent unit c. Compute equivalent units of production d. Assign and reconcile costs
> The cost of beginning inventory plus the costs added during the period should equal the cost of units _____________________ plus the cost of _____________________.
> The following refers to units processed in Sunfllower Printing’s binding department in March. Compute the total equivalent units of production with respect to labor for March using the weighted-average inventory method. Units of Per
> Blanche’s Boxes completed 20,000 boxes costing $275,000 and transferred them to finished goods. Prepare its journal entry to record the transfer of the boxes from production to finished goods inventory.
> Blanche’s Boxes incurred $135,000 in factory payroll costs, of which $125,000 was direct labor. Prepare journal entries to record its (1) total factory payroll incurred and (2) direct labor used in production.
> What conditions must exist to achieve accurate short-run pricing decisions using variable costing?
> Blanche’s Boxes makes cardboard shipping cartons in a single operation. This period, Blanche purchased $62,000 in raw materials. Its production department requisitioned $50,000 of those materials for use in producing cartons. Prepare journal entries to r
> For each of the following products and services, indicate whether it is most likely produced in a process operation or in a job order operation. 1. Tennis courts 2. Apple juice 3. Vanilla ice cream 4. Luxury cars
> Why is overhead allocation under ABC usually more accurate than either the plantwide overhead allocation method or the departmental overhead allocation method?
> Refer to QS 3-14 and compute the total equivalent units of production with respect to labor for July using the FIFO inventory method. Information from QS 3-14: The following refers to units processed by an ice cream maker in July. Compute the total equi
> The computer workstation furniture manufacturing that Adria Lopez started in January is progressing well. As of the end of June, Success Systems’ job cost sheets show the following total costs accumulated on three furniture jobs. Job
> Anheuser-Busch InBev is attempting to reduce its water usage. How could a company manager use a process cost summary to determine if the program to reduce water usage is successful?
> Refer to QS 3-6 and compute the total equivalent units of production with respect to labor for March using the FIFO inventory method. Information from QS 3-6: The following refers to units processed in Sunfllower Printing’s binding dep
> Explain how a car maintenance and repair garage might use a hybrid costing system.
> Blanche’s Boxes requisitioned $9,000 of indirect materials from its raw materials and used $10,000 of indirect labor in its production of boxes. Also, it incurred $156,000 of other factory overhead costs. It applies factory overhead at the rate of 140% o
> Belda Co. manufactures a single product in one department. Direct labor and overhead are added evenly throughout the process. Direct materials are added as needed. The company uses the FIFO method of process costing. During March, the company completed a
> What costs are normally included as part of product costs under the method of absorption costing?
> Refer to the information in Problem 3-2B and complete its parts (1) through (4) using the FIFO method of process costing. Round cost per equivalent unit calculations to two decimal places. Information from Problem 3-2B: Abraham Company uses process cost
> During May, the production department of a process manufacturing system completed a number of units of a product and transferred them to finished goods. Of these transferred units, 62,500 were in process in the production department at the beginning of M
> Refer to the information in Problem 3-5B. Assume that Switch uses the FIFO method to account for its process costing system. The following additional information is available. ● Beginning goods in process consists of 10,000 units that w
> 1. When using departmental overhead rates, which of the following cost objects is the first in the cost allocation process? a. Activities b. Units of product c. Product lines d. Departments 2. Which costing method assumes all products use overhead costs
> Switch Co. manufactures a single product in one department. Direct labor and overhead are added evenly throughout the process. Direct materials are added as needed. The company uses monthly reporting periods for its weighted-average process cost accounti
> Braun Company produces its product through a single processing department. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. Direct labor and overhead are added to the product evenly throughout the process. The company uses monthly reporting pe
> Refer to the chapter opener regarding David Schottenstein and his company, Astor and Black. All successful businesses track their costs, and it is especially important for start-up businesses to monitor and control costs. Required 1. Assume that Astor a
> Oslo Company produces large quantities of a standardized product. The following information is available for its production activities for May. Additional information about units and costs of production activities follows. During May, 10,000 units of
> Abraham Company uses process costing to account for its production costs. Direct labor is added evenly throughout the process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. During September, the production department transferred 80,000 unit
> Dream Toys Company manufactures video game consoles and accounts for product costs using process costing. The following information is available regarding its June inventories. The following additional information describes the companyâ€
> What costs are normally included as part of product costs under the method of variable costing?
> Dengo Co. manufactures a single product in one department. Direct labor and overhead are added evenly throughout the process, while direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. The company uses the FIFO method of process costing. During Oc
> Refer to the information in Problem 3-2A and complete its parts (1) through (4) using the FIFO method of process costing. Round cost per equivalent unit calculations to two decimal places. Information from problem 3-2A: Victory Company uses weighted-ave
> During May, the production department of a process manufacturing system completed a number of units of a product and transferred them to finished goods. Of these transferred units, 37,500 were in process in the production department at the beginning of M
> Refer to the data in Problem 3-5A. Assume that Tamar uses the FIFO method to account for its process costing system. The following additional information is available: ● Beginning goods in process consisted of 3,000 units that were 100%
> Tamar Co. manufactures a single product in one department. All direct materials are added at the beginning of the manufacturing process. Direct labor and overhead are added evenly throughout the process. The company uses monthly reporting periods for its
> Fast Co. produces its product through a single processing department. Direct materials are added at the start of production, and direct labor and overhead are added evenly throughout the process. The company uses monthly reporting periods for its weighte
> Elliott Company produces large quantities of a standardized product. The following information is available for its production activities for March. Additional information about units and costs of production activities follows. During March, 10,000 u
> Consider the activities undertaken by a medical clinic in your area. Required 1. Do you consider a job order cost accounting system appropriate for the clinic? 2. Identify as many factors as possible to lead you to conclude that it uses a job order syst
> Victory Company uses weighted-average process costing to account for its production costs. Direct labor is added evenly throughout the process. Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. During November, the company transferred 700,000 u
> Assume that Arctic Cat has received a special order from a retailer for 100 specially outfitted snowmobiles. This is a one-time order, which will not require any additional capacity or fixed costs. What should Arctic Cat consider when determining a selli
> Sierra Company manufactures woven blankets and accounts for product costs using process costing. The following information is available regarding its May inventories. The following additional information describes the company’s produc
> Label each item a through h below as a feature of either a job order or process operation. a. Heterogeneous products and services b. Custom orders c. Low production volume d. Routine, repetitive procedures e. Focus on individual batch f. Low product s
> For each of the following products and services, indicate whether it is most likely produced in a process operation or in a job order operation. 1. Beach towels 2. Bolts and nuts 3. Lawn chairs 4. Headphones 5. Designed patio 6. Door hardware 7. Cu
> Prepare journal entries to record the following production activities. 1. Transferred completed products with a cost of $135,600 to finished goods inventory. 2. Sold $315,000 of products on credit. Their cost is $175,000.
> Refer to information in Exercise 3-3. Prepare journal entries to record the following production activities. 1. Paid overhead costs (other than indirect materials and indirect labor) of $38,750. 2. Applied overhead at 110% of direct labor costs. Data fr
> Cardiff and Delp is an architectural firm that provides services for residential construction projects. The following data pertain to a recent reporting period. Required1. Using ABC, compute the firm’s activity overhead rates. Form ac
> Prepare journal entries to record the following production activities. 1. Incurred total labor cost of $95,000, which is paid in cash. 2. Used $75,000 of direct labor in production. 3. Used $20,000 of indirect labor.
> Prepare journal entries to record the following production activities. 1. Purchased $80,000 of raw materials on credit. 2. Used $42,000 of direct materials in production. 3. Used $22,500 of indirect materials.
> Match each of the following items A through G with the best numbered description of its purpose. A. Factory Overhead account B. Process cost summary C. Equivalent units of production D. Goods in Process Inventory account E. Raw Materials Inventory acc
> Hi-Test Company uses the weighted-average method of process costing to assign production costs to its products. Information for September follows. Assume that all materials are added at the beginning of its production process, and that direct labor and f
> Polaris uses variable costing for several business decisions. How can variable costing income statements be converted to absorption costing?
> Visit a local hotel and observe its daily operating activities. The costs associated with some of its activities are variable while others are fixed with respect to occupancy levels. Required 1. List cost items that are likely variable for the hotel. 2.
> Samanta Shoes, which was launched by entrepreneurs Samanta and Kelvin Joseph, produces high-quality shoes in unique styles and limited quantities. Selling prices for a pair of Samanta shoes can range from $100 per pair to $350 per pair. Required 1. Base
> This chapter identified many decision contexts in which variable costing information is more relevant than absorption costing. However, absorption costing is still used by many companies and remains the only acceptable basis for external (and tax) report
> This chapter discussed the variable costing method and how to use variable costing information to make various business decisions. We also can find several Websites on variable costing and its business applications. Required 1. Review the Website of Val
> Mertz Chemical has three divisions. Its consumer product division faces strong competition from companies overseas. During its recent teleconference, Ryan Peterson, the consumer product division manager, reported that his division’s sales for the current
> The purpose of this team activity is to ensure that each team member understands processoperations and the related accounting entries. Find the activities and flows identified in Exhibit 3.4 with numbers 1 – 10. Pick a member of the tea
> FDP Company produces a variety of home security products. Gary Price, the company’s president, is concerned with the fourth quarter market demand for the company’s products. Unless something is done in the last two months of the year, the company is like
> Polaris offers its dealers financing plans while Arctic Cat currently relies on outside companies to provide its dealers’ financing. Assume Arctic Cat is considering starting its own finance unit to provide financing directly to its dealers. Required 1.
> Explain the two basic stages of cost flows for activity-based costing.
> Assume that KTM (KTM.com) is considering offering financing services for its dealers. However, instead of developing the division internally, KTM is considering buying a company that already offers such services. Required Would absorption or variable co
> Success Systems sells upscale modular desk units and office chairs in the ratio of 3:2 (desk unit:chair). The selling prices are $1,250 per desk unit and $500 per chair. The variable costs are $750 per desk unit and $250 per chair. Fixed costs are $120,0
> A recent income statement for Volkswagen reports the following (in € millions). Assume 75 percent of the cost of sales and 75 percent of the selling and administrative costs are variable costs, and the remaining 25 percent of each is fixed. Compute the c
> Corme Company expects sales of $34 million (400,000 units). The company’s total fixed costs are $17.5 million and its variable costs are $35 per unit. Prepare a CVP chart from this information.
> Which one of the following is an assumption that underlies cost-volume-profit analysis? 1. The selling price per unit must change in proportion to the number of units sold. 2. All costs have approximately the same relevant range. 3. For costs classified
> Assume that SBD Phone Co. is subject to a 30% income tax rate. Compute the units of product that must be sold to earn after-tax income of $140,000. (Round to the nearest whole unit.)
> Refer to QS 5-6. Determine the (1) contribution margin ratio and (2) break-even point in dollars.
> How will the break-even point in units change in response to each of the following independent changes in selling price per unit, variable cost per unit, or total fixed costs? Use I for increase and D for decrease. (It is not necessary to compute new bre
> Many companies acquire software to help them monitor and control their costs and as an aid to their accounting systems. One company that supplies such software is proDacapo (prodacapo.com). There are many other such vendors. Access proDacapo’s Website, c
> SBD Phone Company sells its cordless phone for $90 per unit. Fixed costs total $162,000, and variable costs are $36 per unit. Determine the (1) contribution margin per unit and (2) break-even point in units.
> Surgery Center is an outpatient surgical clinic that was profitable for many years, but Medicare has cut its reimbursements by as much as 40%. As a result, the clinic wants to better understand its costs. It decides to prepare an activity-based cost anal
> Compute and interpret the contribution margin ratio using the following data: sales, $5,000; total variable cost, $3,000.
> This scatter diagram reflects past maintenance hours and their corresponding maintenance costs. 1. Draw an estimated line of cost behavior.2. Estimate the fixed and variable components of maintenance costs. $12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1,
> The following information is available for a company’s maintenance cost over the last seven months. Using the high-low method, estimate both the fixed and variable components of its maintenance cost. Month Maintenance Hours Mainten
> Determine whether each of the following is best described as a fixed, variable, or mixed cost with respect to product units. 1. Rubber used to manufacture athletic shoes. 2. Maintenance of factory machinery. 3. Packaging expense. 4. Wages of an assembly-
> Listed here are four series of separate costs measured at various volume levels. Examine each series and identify whether it is best described as a fixed, variable, step-wise, or curvilinear cost. (It can help to graph the cost series.) Volume (Unit
> A high proportion of Company A’s total costs are variable with respect to units sold; a high proportion of Company B’s total costs are fixed with respect to units sold. Which company is likely to have a higher degree of operating leverage (DOL)? Explain.
> US-Mobile Company manufactures and sells two products, conventional phones and smart phones, in the ratio of 5:3. Fixed costs are $105,000, and the contribution margin per composite unit is $125. What number of both conventional and smart phones is sold
> The following costs result from the production and sale of 12,000 CD sets manufactured by Gilmore Company for the year ended December 31, 2013. The CD sets sell for $18 each. The company has a 25% income tax rate. Variable manufacturing costs Plastic fo
> Milano Co. manufactures and sells three products: product 1, product 2, and product 3. Their unit sales prices are product 1, $40; product 2, $30; and product 3, $20. The per unit variable costs to manufacture and sell these products are product 1, $30;
> You hire a new assistant production manager whose prior experience is with a company that produced goods to order. Your company engages in continuous production of homogeneous products that go through various production processes. Your new assistant e-ma
> Arctic Cat’s production requires activities. What are value-added activities?
> This year Best Company earned a disappointing 5.6% after-tax return on sales (net income/sales) from marketing 100,000 units of its only product. The company buys its product in bulk and repackages it for resale at the price of $20 per unit. Best incurre
> Mingei Co. produces and sells two products, BB and TT. It manufactures these products in separate factories and markets them through different channels. They have no shared costs. This year, the company sold 50,000 units of each product. Sales and costs
> Rivera Co. sold 20,000 units of its only product and incurred a $50,000 loss (ignoring taxes) for the current year as shown here. During a planning session for year 2014’s activities, the production manager notes that variable costs can

