Question: Graduation rate—the percentage of entering freshmen
Graduation rate—the percentage of entering freshmen attending full time and graduating within 5 years— and what influences it is a concern in U.S. colleges and universities. U.S. News and World Report’s “College Guide” provides data on graduation rates for colleges and universities as a function of the percentage of freshmen in the top 10% of their high school class, total spending per student, and student-to-faculty ratio. A random sample of 10 universities gave the following data on student-to-faculty ratio (S/F ratio) and graduation rate (Grad rate).
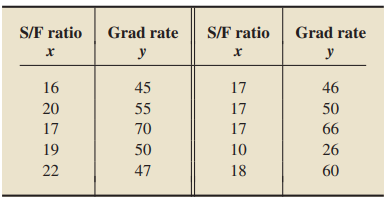
Discuss what satisfying the assumptions for regression inferences would mean with student-to-faculty ratio as the predictor variable and graduation rate as the response variable.
> The U.S. Federal Highway Administration conducts studies on motor vehicle travel by type of vehicle. Results are published annually in Highway Statistics. A sample of 15 cars yields the following data on number of miles driven, in thousands, for last yea
> Consider these sample data: x1 = 1, x2 = 7, x3 = 4, x4 = 5, x5 = 10. a. Find n. b. Compute Σxi. c. Determine x
> The U.S. National Center for Health Statistics compiles data on the length of stay by patients in short-term hospitals and publishes its findings in Vital and Health Statistics. A random sample of 21 patients yielded the following data on length of stay,
> In the article “Sweetening Statistics—What M&M’s Can Teach Us” (Minitab Inc., August 2008), M. Paret and E. Martz discussed several statistical analyses that they performed on bags of M&Ms. The authors took a random sample of 30 small bags of peanut M&Ms
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Explain why a census is often not the best way to obtain information about a population.
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> Use the specified grouping method to a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on your result from part (a). d. construct a relative-frequency histogram based on your resu
> An online article from the Washington Post, titled “Facebook Joins Ranks of Largest IPOs in U.S. History,” gave the following information on the top 10 IPOs (initial public offerings) in the United States as of May 2012. a. What type of data is presented
> Construct a stem-and-leaf diagram for the data, using the specified number of lines per stem. Ese two lines per stem.
> Construct a stem-and-leaf diagram for the data, using the specified number of lines per stem. Use five lines per stem.
> Construct a stem-and-leaf diagram for the data, using the specified number of lines per stem. Use one line per stem.
> Construct a stem-and-leaf diagram for the data, using the specified number of lines per stem. Use one line per stem.
> Construct a dotplot for the data.
> Construct a dotplot for the data.
> Construct a dotplot for the data.
> In the special report, “Bitter Pill: Why Medical Bills Are Killing Us” (TIME, Vol. 181, No. 8, 2013), S. Brill presented an in-depth investigation of hospital billing practices that reveals why U.S. health care spending is out of control. One of the many
> Construct a dotplot for the data.
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> Each year, Forbes magazine publishes a list of the world’s richest people. On page 37, we constructed a table, based on a 2013 Forbes article, that shows the 25 richest people in the world, as of March of that year. a. For each of the five columns of the
> At the beginning of this chapter, we discussed the results of a survey by the American Film Institute (AFI). Now that you have learned some of the basic terminology of statistics, we want you to examine that survey in greater detail. Answer each of the f
> Almost any inferential study involves aspects of descriptive statistics. Explain why.
> This problem is about variables. a. What is a variable? b. Identify two main types of variables. c. Identify the two types of quantitative variables.
> The U.S. Geological Survey monitors and reports on earthquakes, providing daily real-time, worldwide earthquake lists. Some of the information for four of the 105 earthquakes that occurred on May 10, 2013, is shown in the following table. Magnitude is gi
> Fill in the blank: x¯ is to μ as r is to .
> Generally speaking, what is the difference between a confidence interval and a prediction interval?
> For a particular value of a predictor variable, is there a difference between the predicted value of the response variable and the point estimate for the conditional mean of the response variable? Explain your answer.
> Identify three statistics that can be used as a basis for testing the utility of a regression.
> Suppose that you perform a hypothesis test for the slope of the population regression line with the null hypothesis H0: β1 = 0 and the alternative hypothesis Ha: β1 = 0. If you reject the null hypothesis, what can you say about the utility of the regress
> Regarding analysis of residuals, decide in each case which assumption for regression inferences may be violated. a. A residual plot—that is, a plot of the residuals against the observed values of the predictor variable—shows curvature. b. A residual plot
> What two plots did we use in this chapter to decide whether we can reasonably presume that the assumptions for regression inferences are met by two variables of a population? What properties should those plots have?
> From the website Golf.com, part of Sports Illustrated Sites, we obtained the scores for the first and second rounds of the 2013 U.S. Open golf tournament. You will find those scores on the WeissStats site. - For the estimations and predictions, use a fir
> Suppose that x and y are two variables of a population and that the assumptions for regression inferences are met with x as the predictor variable and y as the response variable. a. What statistic is used to estimate the slope of the population regressio
> The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration publishes temperature and precipitation information for cities around the world in Climates of the World. Data on average high temperature (in degrees Fahrenheit) in July and average precipitation (in i
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> From the International Data Base, published by the U.S. Census Bureau, we obtained data on infant mortality rate (IMR) and life expectancy (LE), in years, for a sample of 60 countries. The data are presented on the WeissStats site. - For the estimations
> Refer to Problem 11. At the 2.5% significance level, do the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the variables student-to-faculty ratio and graduation rate are positively linearly correlated? Data from Problem 11: Graduation rate—the percen
> Refer to Problems 11 and 12. a. Find the predicted graduation rate for a university that has a student-to-faculty ratio of 17. b. Find a 95% prediction interval for the graduation rate of a university that has a student-to faculty ratio of 17. c. Explain
> Refer to Problems 11 and 12. a. Find a point estimate for the mean graduation rate of all universities that have a student-to faculty ratio of 17. b. Determine a 95% confidence interval for the mean graduation rate of all universities that have a student
> Refer to Problems 11 and 12. a. At the 5% significance level, do the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that student to-faculty ratio is useful as a predictor of graduation rate? b. Determine a 95% confidence interval for the slope, β1, of the
> Refer to Problems 11 and 12. Perform a residual analysis to decide whether considering the assumptions for regression inferences to be met by the variables student-to-faculty ratio and graduation rate is reasonable. Data from Problem 12: Refer to Proble
> Refer to Problem 11. a. Determine the regression equation for the data. b. Compute and interpret the standard error of the estimate. c. Presuming that the assumptions for regression inferences are met, interpret your answer to part (b). Data from Proble
> Identify the relationship between two variables and the terminology used to describe that relationship if a. ρ > 0. b. ρ = 0. c. ρ < 0.
> Suppose that x and y are two variables of a population with x a predictor variable and y a response variable. a. The distribution of all possible values of the response variable y corresponding to a particular value of the predictor variable x is called
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> Consider an F-curve with d f = (2, 14). Identify the degrees of freedom for the denominator.
> Consider an F-curve with d f = (2, 14). Identify the degrees of freedom for the numerator.
> For a one-way ANOVA, a. identify one purpose of one-way ANOVA tables. b. construct a generic one-way ANOVA table.
> In one-way ANOVA, a. list and interpret the three sums of squares. b. state the one-way ANOVA identity and interpret its meaning with regard to partitioning the total variation among all the data.
> In one-way ANOVA, identify a statistic that measures a. the variation among the sample means. b. the variation within the samples.
> Suppose that you want to compare the means of three populations by using one-way ANOVA. If the sample sizes are 5, 6, and 6, determine the degrees of freedom for the appropriate F-curve.
> On what distribution does one-way ANOVA rely?
> The U.S. Census Bureau collects information on incomes of employed persons and publishes the results in Historical Income Tables. Independent simple random samples of 100 employed persons in each of four age groups gave the data on annual income, in thou
> Another characteristic compared in the hip bone density study discussed in Problem 19 was Maximum Nottingham leg power, in watts. On the WeissStats site, we provide the leg-power data for the three groups, based on the results obtained by the researchers
> State the four assumptions for one-way ANOVA, and explain howthose assumptions can be checked.
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> In the paper “Voluntary Weight Reduction in Older Men Increases Hip Bone Loss: The Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study” (Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, Vol. 90, Issue 4, pp. 1998–2004), K. Ensrud et al. reported on the effect of voluntar
> Smoking during pregnancy is hazardous to both the mother and baby. Passive smoking, or inhalation of second-hand smoke, is also a concern. In the article “Detection of Cotinine in Neonate Meconium as a Marker for Nicotine Exposure in Utero” (Eastern Medi
> Genu valgum, commonly known as “knee-knock,” is a condition in which the knees angle in and touch one another when standing. Genu varum, commonly known as “bow-legged,” is a condition in which the knees angle out and the legs bow when standing. In the ar
> Refer to Problem 14. At the 5% significance level, do the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that a difference in mean losses exists among the three types of robberies? Use one-way ANOVA to perform the required hypothesis test. Data from Probl
> Refer to Problem 14. a. Obtain individual normal probability plots and the standard deviations of the samples. b. Perform a residual analysis. c. Decide whether presuming that the assumptions of normal populations and equal standard deviations are met is
> The Federal Bureau of Investigation conducts surveys to obtain information on the value of losses from various types of robberies. Results of the surveys are published in Population-at-Risk Rates and Selected Crime Indicators. Independent simple random s
> Consider the following hypothetical samples. a. Obtain the sample mean and sample variance of each of the three samples. b. Obtain SST, SSTR, and SSE by using the defining formulas and verify that the one-way ANOVA identity holds. c. Obtain SST, SSTR, an
> Consider an F-curve with d f = (2, 14). Find the F-value with area 0.05 to its right.
> Consider an F-curve with d f = (2, 14). Find the F-value with area 0.01 to its right.
> Consider an F-curve with d f = (2, 14). Determine F0.05.
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> For what is one-way ANOVA used?
> Suppose that you have bivariate data for a sample of a population. a. How would you decide whether an association exists between the two variables under consideration? b. Assuming that you make no calculation mistakes, could your conclusion be in error?
> Suppose that you have bivariate data for an entire population. a. How would you decide whether an association exists between the two variables under consideration? b. Assuming that you make no calculation mistakes, could your conclusion be in error? Expl
> The U.S. Census Bureau collects information on the U.S. population by ancestry and region of residence and publishes the results in American Community Survey. According to that document, 18% of the population resides in the Northeast. a. If ancestry and
> Regarding the expected-frequency assumptions for a chi-square goodness-of-fit test, a chi-square independence test, or a chi-square homogeneity test, a. state them. b. how important are they?
> If the observed and expected frequencies for a chi-square goodness-of-fit test, a chi-square independence test, or a chi-square homogeneity test matched perfectly, what would be the value of the test statistic?
> Explain why a chi-square goodness-of-fit test, a chi-square independence test, or a chi-square homogeneity test is always right tailed.
> Recall that the number of degrees of freedom for the t-distribution used in a one-mean t-test depends on the sample size. Is that true for the chi-square distribution used in a chi-square a. goodness-of-fit test? b. independence test? c. homogeneity test
> Several years ago, a poll by Gallup asked 1528 adults the following question: “The New Jersey Supreme Court recently ruled that all life-sustaining medical treatment may be withheld or withdrawn from terminally ill patients, provided that is what the pat
> The document Arizona Residential Property Valuation System, published by the Arizona Department of Revenue, describes how county assessors use computerized systems to value single-family residential properties for property tax purposes. On the WeissStats
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> The Quinnipiac University Poll conducts nationwide surveys as a public service and for research. This problem is based on the results of one such poll. Independent simple random samples of registered Democrats, Republicans, and Independents were asked, “
> The U.S. Census Bureau compiles information on money income of people by type of residence and publishes its finding in Current Population Reports. Independent simple random samples of people residing inside principal cities (IPC), outside principal citi
> Regarding a χ2-curve: a. At what point on the horizontal axis does the curve begin? b. Classify its shape as symmetric, left skewed, or right skewed. c. As the number of degrees of freedom increases, a χ2-curve begins to look like another type of curve.
> In the article “Happier and Less Isolated: Internet Use in Old Age” (Journal of Poverty & Social Justice, Vol. 21, Issue 1, pp. 33–45), researcher O. Lelkes explores the impact of Internet use. The following problem is based on the article. A random samp
> Refer to Problems 15–17. a. What percentage of hospitals are under proprietary control? b. What percentage of psychiatric hospitals are under proprietary control? c. What percentage of hospitals are psychiatric hospitals? d. What percentage of hospitals
> Refer to Problems 15 and 16. a. In view of your answer to Problem 16(b), without doing any further calculations, respond true or false to the following statement and explain your answer: “The conditional distributions of facility type within control type
> Refer to Problem 15. a. Obtain the conditional distribution of control type within each facility type. b. Does an association exist between facility type and control type? Explain your answer. c. Find the marginal distribution of control type. d. Constru
> From data in Hospital Statistics, published by the American Hospital Association, we obtained the following contingency table for U.S. hospitals and nursing homes by type of facility and type of control. We used the abbreviations Gov for Government, Prop
> Refer to Problem 12. a. Find the conditional distributions of birth region by party and the marginal distribution of birth region. b. Does an association exist between the variables “birth region” and “party” for the U.S. presidents? Explain your answer.
> Refer to Problem 12. a. Find the conditional distributions of party by birth region and the marginal distribution of party. b. Does an association exist between the variables “birth region” and “party” for the U.S. presidents? Explain your answer. c. Wha
> We have presented some quantitative data sets and specified a grouping method for practicing the concepts. For each data set, a. determine a frequency distribution. b. obtain a relative-frequency distribution. c. construct a frequency histogram based on
> In its Summer 2013 Animal Action Report, the National Anti-Vivisection Society stated that “59% of Americans between the ages of 18 and 29 oppose medical testing on animals.” The percentage of 59% was computed from sample data. a. Identify the population
> From the Information Please Almanac, we compiled the following table on U.S. region of birth and political party of the first 44 U.S. presidents. The table uses these abbreviations: F = Federalist, DR = Democratic-Republican, D = Democratic, W = Whig, R
> The U.S. Census Bureau compiles census data on educational attainment of Americans. From the document Current Population Survey, we obtained the 2010 distribution of educational attainment for U.S. adults 25 years old and older. Here is that distribution
> Consider a χ2-curve with 17 degrees of freedom. Use Table V to determine a. χ20.10. b. χ20.01. c. the χ2-value that has area 0.05 to its right.

