Question: In the diagram, the positive terminal of
In the diagram, the positive terminal of the 12 V battery is grounded —it is at zero potential. At what potential is point X?
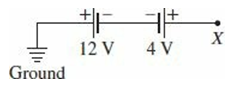
> In a defibrillator (see Example 17.12), a charged capacitor is connected to paddles that make electrical contact with the patient's skin. If gel is applied to the patient's chest to make a good connection between the paddles and the skin, the effective r
> (a) What is the position of the peak of the pulse shown in the figure at t = 3.00 s? (b) When does the peak of the pulse arrive at x = 4.00 m?
> In the circuit of Problem 88, at what time after switch S is closed is the voltage across the combination of three capacitors 50% of its final value?
> Consider the circuit shown with R1 = 25 Ω, R2 = 33 Ω, C1 = 12 µF, C2 = 23 µF, C3 = 46 µF, and V = 6.0 V. (a) Draw an equivalent circuit with one resistor and one capacitor an
> In the circuit, R = 30.0 kΩ and C = 0.10 µF. The capacitor is allowed to charge fully, and then the switch is changed from position a to position b. What will the voltage across the resistor be 8.4 ms later?
> In the Cornell Electron Storage Ring, electrons and positrons circulate in opposite directions with kinetic energies of 6.0 GeV each. When an electron collides with a positron and the two annihilate, one possible (though unlikely) outcome is the producti
> A wind turbine converts some of the kinetic energy of the wind into electric energy. Suppose that the blades of a small wind turbine have length L = 4.0 m. (a) When a 10 m/s (22 mi/h) wind blows head-on, what volume of air (in m3) passes through the cir
> In the circuit shown, assume the battery emf is 20.0 V, R = 1.00 MΩ, and C = 2.00 µF. The switch is closed at t = 0. At what time t will the voltage across the capacitor be 15.0 V?
> A tangent galvanometer is an instrument, developed in the nineteenth century, designed to measure current based on the deflection of a compass needle. A coil of wire in a vertical plane is aligned in the magnetic north-south direction. As illustrated, a
> An ammeter with a full-scale deflection for I = 10.0 A has an internal resistance of 24 Ω. We need to use this ammeter to measure currents up to 12.0 A. The lab instructor advises that we get a resistor and use it to protect the ammeter. (a) What size r
> Show that c2 = 931.494 MeV/u. [Hint: Start with the conversion factors to SI units for MeV and atomic mass units.]
> A 0.15 kg baseball traveling in a horizontal direction with a speed of 20 m/s hits a bat and is popped straight up with a speed of 15 m/s. (a) What is the change in momentum (magnitude and direction) of the baseball? (b) If the bat was in contact with
> Find the potential at the sodium ion, Na+, which is surrounded by two chloride ions, Cl−, and a calcium ion, Ca2+, in water as shown in the diagram. The effective charge of the positive sodium ion in water is 2.0 × 10â
> Consider the circuit in the diagram. Given: I1 = 2.50 A /, / , R1 = 8.00 Ω, and R2 = 5.00 Ω. Find the values of I2, I3, and R3.
> Two cars, a Porsche Boxster convertible and a Toyota Scion xB, are traveling at constant speeds in the same direction, although the Boxster is 186 m behind the Scion. The speed of the Boxster is 24.4 m/s and the speed of the Scion is 18.6 m/s. Sketch gra
> Iodine is eliminated from the body through biological processes with an effective half-life of about 140 days. The radioactive half-life of iodine-131 is 8 days. Suppose some radioactive 131I nuclei are present in the body. Assuming that no new 131I nucl
> A BMW of mass 2.0 × 103 kg is traveling at 42 m/s. It approaches a 1.0 × 103 kg Volkswagen going 25 m/s in the same direction and strikes it in the rear. Neither driver applies the brakes. Ignore the relatively small frictional forces on the cars due to
> Transverse waves travel on five stretched strings with the following properties. Rank the strings according to the time it takes a transverse wave pulse to travel from one end to the other, from largest to smallest. (a) length L, total mass m, tension F
> Derive Eq. (12-5): (a) Starting with Eq. (12-4), substitute T = TC + 273.15. (b) Apply the binomial approximation to the square root (see Appendix A.9) and simplify.
> The longest “string” (a thick metal wire) on a particular piano is 2.0 m long and has a tension of 300.0 N. It vibrates with a fundamental frequency of 27.5 Hz. What is the total mass of the wire?
> A guitar's E-string has length 65 cm and is stretched to a tension of 82 N. It vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 329.63 Hz. Determine the mass per unit length of the string.
> A shark is able to detect the presence of electric fields as small as 1.0 µV/m. To get an idea of the magnitude of this field, suppose you have a parallel plate capacitor connected to a 1.5 V battery. How far apart must the parallel plates be to have an
> Tension is maintained in a string by attaching one end to a wall and by hanging a 2.20 kg object from the other end of the string after it passes over a pulley that is 2.00 m from the wall. The string has a mass per unit length of 3.55 mg/m. What is the
> Randomly polarized light with intensity I0 passes through two ideal polarizers, one after the other. The transmission axes of the first and second polarizers are at angles θ1 and θ2, respectively, to the horizontal. Rank the intensities of the light tran
> A source of emf / has internal resistance r. (a) What is the terminal voltage when the source supplies a current I? (b) The net power supplied is the terminal voltage times the current. Starting with P = IΔV, derive Eq. (18-39) for the net power sup
> A guitar string has a fundamental frequency of 300.0 Hz. (a) What are the next three lowest standing wave frequencies? (b) If you press a finger lightly against the string at its midpoint so that both sides of the string can still vibrate, you create a
> During a “brownout,” which occurs when the power companies cannot keep up with high demand, the voltage of the household circuits drops below its normal 120 V. (a) If the voltage drops to 108 V, what would be the power consumed by a “100 W” incandescent
> A battery has a 6.00 V emf and an internal resistance of 0.600 Ω. (a) What is the voltage across its terminals when the current drawn from the battery is 1.20 A? (b) What is the power supplied by the battery?
> Strontium-90 / is a radioactive element that is produced in nuclear fission. It decays by β− decay to yttrium (Y) with a half-life of 28.8 yr. (a) Write down the decay scheme for /. (b) What is the initial activity of 2.0 kg of /? (c) What will
> In the circuit shown, R1 = 15.0 Ω, R2 = R4 = 40.0 Ω, R3 = 20.0 Ω, and R5 = 10.0 Ω. (a) What is the equivalent resistance of this circuit? (b) What current flows through resi
> A moving source emits a sound wave that is heard by a moving observer. Imagine a thin wall at rest between the source and observer. The wall completely absorbs the sound and instantaneously emits an identical sound wave. Use this scenario to explain why
> Jason drives due west with a speed of 35.0 mi/h for 30.0 min, continues in the same direction with a speed of 60.0 mi/h for 2.00 h, and then drives farther west at 25.0 mi/h for 10.0 min. What is Jason’s average velocity? Sketch a motion diagram at 10 mi
> In lab tests it was found that rats can detect electric fields of about 5.0 kN/C or more. If a point charge of 1.0 µC is sitting in a maze, how close must the rat come to the charge in order to detect it?
> (a) If you were stranded on an island with a pair of 3.5 D reading glasses, could you make a useful telescope? If so, what would be the length of the telescope and what would be the angular magnification? (b) Answer the same questions if you also had a
> For a safe reentry into Earth's atmosphere, the pilots of a space capsule must reduce their speed from 2.6 × 104 m/s to 1.1 × 104 m/s. The rocket engine produces a backward force on the capsule of 1.8 × 105 N. The mass of the capsule is 3800 kg. For how
> In Problem 86, the +2.0 µC charge is at x = 0 and the −4.0 µC charge is at x = d. Find the x-coordinates of the point(s) where the electric field is zero.
> At what rate is energy dissipated in the 4.00 Ω and 5.00 Ω resistors in the circuit shown?
> Two conducting wires perpendicular to the page are shown in cross section as gray dots in the figure. They each carry 10.0 A out of the page. What is the magnetic field at point P?
> A long straight wire carries a 4.70 A current in the positive x- direction. At a particular instant, an electron moving at 1.00 × 107 m/s in the positive y-direction is 0.120 m from the wire. Determine the magnetic force on the electron at this instant.
> In a lab experiment, a string has a mass per unit length of 0.120 g/m. It is attached to a vibrating device and weight similar to that shown in Figure 11.23. The vibrator oscillates at a constant frequency of 110 Hz. How heavy should the weight be in ord
> In a carbon-dating experiment, a particular type of mass spectrometer is used to separate 14C from 12C. Carbon ions from a sample are first accelerated through a potential difference ΔV1 between the charged accelerating plates. Then the ions
> A 1.6 m long string fixed at both ends vibrates at resonant frequencies of 780 Hz and 1040 Hz, with no other resonant frequency between these values. The tension in the string is 1200 N. (a) What is the fundamental frequency of this string? (b) What is
> Explain why the pitch of a bassoon is more sensitive to a change in air temperature than the pitch of a cello. (That's why wind players keep blowing air through the instrument to keep it in tune.)
> Why is the number of electron neutrinos reaching Earth from the Sun smaller than had originally been predicted?
> Six sources emit sound equally in all directions with average power P. A microphone is placed at a distance d from each source. Rank the situations in order of the intensity at the location of the microphone, smallest to largest. (a) P = 10 W, d = 2 m (
> Show that A2 × Ω = W (amperes squared times ohms = watts).
> How much work are the batteries in the circuit doing in every 10.0 s time interval?
> For the train in Fig. 3.2 and Example 3.3, find the average velocity between 3:14 P.M. when the train is at 3 km east of the origin and 3:28 P.M. when it is 10 km east of the origin.
> A cord of length 1.5 m is fixed at both ends. Its mass per unit length is 1.2 g/m and the tension is 12 N. (a) What is the frequency of the fundamental oscillation? (b) What tension is required to make the n = 3 mode have a frequency of 0.50 kHz?
> What is the resistance of a 40.0 W, 120 V incandescent lightbulb?
> Use Gauss’s law to derive an expression for the electric field outside the thin spherical shell of Conceptual Example 16.8.
> A negative point charge −Q is situated near a large metal plate that has a total charge of +Q. Sketch the electric field lines.
> Zorba and Boris are at a water park. There are two water slides with straight slopes that start at the same height and end at the same height. Slide A has a more gradual slope than slide B. Boris says he likes slide B better because you reach a faster sp
> A mechanic turns a wrench using a force of 25 N at a distance of 16 cm from the rotation axis. The force is perpendicular to the wrench handle. What magnitude torque does she apply to the wrench?
> A bungee jumper leaps from a bridge and comes to a stop a few centimeters above the surface of the water below. At that lowest point, is the tension in the bungee cord equal to the jumper’s weight? Explain why or why not.
> Two blocks, masses m1 and m2, are connected by a massless cord. If the two blocks are pulled with a constant tension on a frictionless surface by applying a force of magnitude T2 to a second cord connected to m2, what is the ratio of the tensions in the
> Radioactive iodine, 131I, is used in some forms of medical diagnostics, (a) If the initial activity of a sample is 64.5 mCi, what is the mass of 131I in the sample? (b) What will the activity be 4.5 d later?
> A bird (mass 31 g) is flying at 11.1 m/s when it flies into a glass window and bounces off at a speed of 4.1 m/s. The bird is in contact with the glass for 0.071 s. What is the average force on the bird during the collision?
> What is the current in a 60.0 W bulb when connected to a 120 V emf?
> The Sun emits electromagnetic waves (including light) equally in all directions. The intensity of the waves at Earth's upper atmosphere is 1.4 kW/m2. At what rate does the Sun emit electromagnetic waves? (In other words, what is the power output?)
> At what rate does the jet airplane in Problem 4 radiate energy in the form of sound waves?
> For a transverse wave on a string described by find the maximum speed and the maximum acceleration of a point on the string. Plot a graph showing one cycle of velocity vy versus t at the point x = 0.
> A 75 kg man is at rest on ice skates. A 0.20 kg ball is thrown to him. The ball is moving horizontally at 25 m/s just before the man catches it. How fast is the man moving just after he catches the ball?
> See Problem 7. During Michaela’s travel from Killarney to Cork via Mallow, her travel time is 48 min. (a) What is her average speed in m/s? (b) What is the magnitude of her average velocity in m/s?
> (a) What is the mass defect of the 1H atom due to the binding energy of the electron (in the ground state)? (b) Should we worry about this mass defect when we calculate the mass of the 1H nucleus by subtracting the mass of one electron from the mass of
> A coaxial cable consists of a wire of radius a surrounded by a thin metal cylindrical shell of radius b. The wire has a uniform linear charge density λ > 0 and the outer shell has a uniform linear charge density −Î
> A small plane is flying directly west with an airspeed of 30.0 m/s. The plane flies into a region where the wind is blowing at 10.0 m/s at an angle of 30° to the south of west. (a) If the pilot does not change the heading of the plane, what will be the
> In the construction of railroads, curvature of the track is measured in the following way. First a 100.0 ft long chord is measured. Then the curvature is reported as the angle subtended by two radii at the endpoints of the chord. (The angle is measured b
> (a) Plot a graph for versus x at t = 0 and at / . From the plots determine the amplitude, wavelength, and speed of the wave. (b) For the same function, plot a graph of y(x, t) versus t at x = 0 and find the period of the vibration. Show that X = vT.
> A sine wave is traveling to the right on a cord. The lighter line in the figure represents the shape of the cord at time t = 0; the darker line represents the shape of the cord at time t = 0.10 s. (Note that the horizontal and vertical scales are differe
> Find the electric field at point B, midway between the upper left and right corners.
> Five stretched strings have the following properties. Rank the strings according to their fundamental frequencies (for transverse standing waves), from greatest to least. (a) length L, total mass m, tension F (b) length 2L, total mass m, tension F (c) le
> Rank the waves in order of maximum transverse speed, largest to smallest.
> Rank the waves in order of amplitude, largest to smallest.
> Rank the waves in order of frequency, largest to smallest.
> What is the average binding energy per nucleon for /?
> Five cars are traveling on a highway. Their masses and initial speeds are: (a) 1500 kg, 30 m/s (b) 1500 kg, 20 m/s (c) 1000 kg, 30 m/s (d) 1000 kg, 20 m/s (e) 2000 kg, 40 m/s The cars use the same braking force to slow down and stop. Rank the cars in ord
> Once Rutherford and Geiger determined the charge-to-mass ratio of the alpha particle (see Problem 93), they performed another experiment to determine its charge. An alpha source was placed in an evacuated chamber with a fluorescent screen. Through a glas
> Write the equation for a harmonic wave with amplitude 2.50 cm and angular frequency 2.90 rad/s that is moving in the +x-direction with a wave speed that is 5.00 times as fast as the maximum transverse speed of a point on the string. At t = 0, the point x
> At time t = 0, block A of mass 0.225 kg and block B of mass 0.600 kg rest on a horizontal frictionless surface a distance 3.40 m apart, with block A located to the left of block B. A horizontal force of 2.00 N directed to the right is applied to block A
> A scout troop is practicing its orienteering skills with map and compass. First they walk due east for 1.2 km. Next, they walk 45° west of north for 2.7 km. In what direction must they walk to go directly back to their starting point? How far will they h
> The intensity of the sound wave from a jet airplane as it is taking off is 100 W/m2 at a distance of 5.0 m. What is the intensity of the sound wave that reaches the ears of a person standing at a distance of 120 m from the runway? Assume that the sound w
> In a game of shuffleboard, a disk with an initial speed of 3.2 m/s travels 6.0 m before coming to rest. (a) What was the acceleration of the disk? (b) What was the coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the disk?
> (a) Write an equation for a harmonic wave with amplitude 0.750 mm, frequency 36.0 Hz, and wave speed 144 m/s traveling in the +x- direction. At t = 0, the point x = 0 is at its maximum displacement in the +y-direction. (b) What is the maximum accelerati
> Prove that, in an EM wave traveling in vacuum, the electric and magnetic energy densities are equal; that is, prove that at any point and at any instant of time.
> You are swimming in the ocean as water waves with wavelength 9.6 m pass by. What is the closest distance that another swimmer could be so that his motion is exactly opposite yours (he goes up when you go down)?
> What is the mass defect of the 14N nucleus?
> A mass of 1.4 kg of water at 22°C is poured from a height of 2.5 m into a vessel containing 5.0 kg of water at 22°C. (a) How much does the internal energy of the 6.4 kg of water increase? (b) Is it likely that the water temperature increases? Explain.
> Rank the points in order of mechanical energy, from greatest to least, assuming no friction or air resistance.
> Steel railroad tracks of length 18.30 m are laid at 10.0°C. How much space should be left between the track sections if they are to just touch when the temperature is 50.0°C?
> Sketch a graph of y versus x for the function for the times t = 0 and 0.96 s. Make the graphs on the same axes, using a solid line for the first and a dashed line for the second. Use the values k = (Ï€/5.0) rad/cm and ω = (Ï
> The photosensitive cells (rods and cones) in the retina are most densely packed in the fovea—the part of the retina used to see straight ahead. In the fovea, the cells are all cones spaced about 1 µm apart. Would our vision have much better resolution if
> An object of mass m is hung from the base of an ideal spring that is suspended from the ceiling. The spring has a spring constant k. The object is pulled down a distance D from equilibrium and released. Later, the same system is set oscillating by pullin
> Two 35.0 cm metal rods, one made of copper and one made of aluminum, are placed end to end, touching each other. One end is fixed, so that it cannot move. The rods are heated from 0.0°C to 150°C. How far does the other end of the system of rods move?
> A 6.0 pF capacitor is needed to construct a circuit. The only capacitors available are rated as 9.0 pF. How can a combination of three 9.0 pF capacitors be assembled so that the equivalent capacitance of the combination is 6.0 pF?
> Is e the smallest fundamental unit of charge? The smallest observable unit of charge? [Hint: Try to come up with a meson or baryon with a charge that is not an integral multiple of e.] Explain.
> Isolated atoms (or atoms in a dilute gas) radiate photons at discrete energies characteristic of that atom. In dense matter, the spectrum radiated is quasi-continuous. Why doesn’t the same thing happen with nuclear spectra: why do the gamma rays have the
> What is the mass of an 16O atom in units of MeV/c2? (1 MeV/c2 is the mass of a particle with rest energy 1 MeV.)
> A 2.4 m length of copper pipe extends directly from a water heater in a basement to a faucet on the first floor of a house. If the faucet isn't fixed in place, how much will it rise when the pipe is heated from 20.0°C to 90.0°C? Ignore any increase in th
> The size of an atom is about 0.1 nm. Can a light microscope make an image of an atom? Explain.

