Question: Is it ever possible for an increase
Is it ever possible for an increase in pollution to make society better off? Briefly explain, using a graph like Figure 5.3 on page 154.
Figure 5.3:
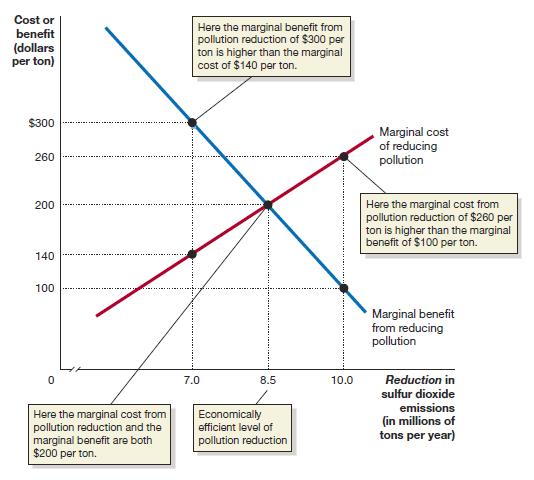
Transcribed Image Text:
Cost or Here the marginal benefit from pollution reduction of $300 per ton is higher than the marginal cost of $140 per ton. benefit (dollars per ton) $300 Marginal cost of reducing pollution 260 Here the marginal cost from pollution reduction of $260 per ton is higher than the marginal benefit of $100 per ton. 200 140 100 Marginal benefit from reducing pollution 7.0 8.5 10.0 Reduction in sulfur dioxide Here the marginal cost from pollution reduction and the marginal benefit are both $200 per ton. emissions (in millions of tons per year) Economically efficient level of pollution reduction
> Sally looks at her college transcript and asks you, “How is this possible? My grade point average for this semester’s courses is higher than my grade point average for last semester’s courses, but my cumulative grade point average still went down from la
> Briefly explain whether you agree with the following argument: Adam Smith’s idea of the gains to firms from the division of labor makes a lot of sense when the good being manufactured is something complex like automobiles or computers, but it doesn’t app
> A student looks at the numbers in Table 11.3 on page 371 and draws this conclusion: The marginal product of labor is increasing for the first two workers hired, and then it declines for the next four workers. I guess each of the first two workers must ha
> Use the numbers from problem 3.4 to draw one graph that shows how total output increases with the quantity of workers hired and a second graph that shows the marginal product of labor and the average product of labor. Problem 3.4: Marginal Product of
> Fill in the missing values in the following table. Marginal Product of Product of Labor Average Quantity of Workers Total Output Labor 1 400 900 3 1,500 4 1,900 2,200 2,400 7. 2,300 2. 6.
> What is the law of diminishing returns? Does it apply in the long run?
> Would a business be expected to survive in the long run if it earned a positive accounting profit but a negative economic profit? Briefly explain.
> When the DuPont chemical company first attempted to enter the paint business, it was not successful. According to a company report, in one year it “lost nearly $500,000 in actual cash in addition to an expected return on investment of nearly $500,000, wh
> How do specialization and division of labor typically affect the marginal product of labor?
> Draw a graph that shows the usual relationship between the marginal product of labor and the average product of labor. Why do the marginal product of labor and the average product of labor curves have the shapes you drew?
> Briefly discuss each of the following economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to economic incentives, and optimal decisions are made at the margin.
> What is the production function? What does the short run production function hold constant?
> Although New York State is second only to Washington State in production of apples, its production has been declining during the past 20 years. The decline has been particularly steep in counties close to New York City. In 1985, there were more than 11,0
> What are implicit costs? How are they different from explicit costs?
> Distinguish between a firm’s fixed costs and variable costs and give an example of each.
> What is the difference between the short run and the long run? Is the amount of time that separates the short run from the long run the same for every firm?
> Suppose the market for ice cream cones is made up of three consumers: Tiago, Terrell, and Tim. Use the information in the following table to construct the market demand curve for ice cream cones. Show the information in a table and in a graph. Tiago
> The following table shows the hourly output per worker for Greece and Italy measured as quarts of olive oil and pounds of pasta. Calculate the opportunity cost of producing olive oil and pasta in both Greece and Italy. Output per Hour of Work Olive
> If you deposit $20,000 in a savings account at a bank, you might earn 1 percent interest per year. Someone who borrows $20,000 from a bank to buy a new car might have to pay an interest rate of 6 percent per year on the loan. Knowing this, why don’t you
> What is an externality? Are there externalities in the market for health care? Briefly explain.
> In an opinion column about improving the performance of doctors in the United States, a health economist observed that “it’s very hard to measure the things we really care about, like quality of life and improvements in functioning.” Why is it difficult
> What are network externalities? For what types of products are network externalities likely to be important? What is path dependence?
> The price elasticity of demand for crude oil in the United States has been estimated to be 20.06 in the short run and 20.45 in the long run. Why would the demand for crude oil be more price elastic in the long run than in the short run? Source: John C.
> Discuss the factors that determine the marginal cost of reducing crime. Discuss the factors that determine the marginal benefit of reducing crime. Would it be economically efficient to reduce the amount of crime to zero? Briefly explain.
> According to a Wall Street Journal article, many restaurant chains, including McDonald’s and Chick-fil-A, have begun serving only chickens that were raised without being fed antibiotics. Using this method of raising chickens increases their cost. Suppose
> An article in the Wall Street Journal discusses the visual effects industry, which is made up of firms that provide visual effects for films and television programs. The article notes: “Blockbusters … often have thousands of visual effects shots. Even dr
> Suppose that the curves in the following graph represent two supply curves for traditional chicken wings (basket of six) at Buffalo Wild Wings. What would cause a movement from point A to point B on S1? Name two variables that if their values were to cha
> According to Forbes magazine, in 2015 Bill Gates was the world’s richest person, with wealth of $79.2 billion. Does Bill Gates face scarcity? Does everyone? Are there any exceptions? Source: “The World’s Billionaires,” forbes.com, March 2, 2015.
> According to an article in Forbes, the cost of materials in Apple’s iPhone 6 with 16 gigabytes of memory was estimated to be $227. Apple was selling the iPhone 6 for $650. Most phone carriers, like AT&T and Verizon, made payments to Apple that reduced th
> The chapter states that “when the price of an inferior good falls, the income effect and substitution effect work in opposite directions.” Explain what this statement means.
> Briefly explain whether you agree with the following argument: “Unfortunately, Bolivia does not have a comparative advantage with respect to the United States in the production of any good or service.” (Hint: You do not need any specific information abou
> An article in the Wall Street Journal about the financial problems of the New York Metropolitan Opera contained the observation that “a ticket-price increase in 2012 backfired.” a. What does the author mean that the increase in ticket prices to the opera
> What is the difference between technology and technological change?
> Suppose you originally invested in a firm when it was small and un-profitable. Now the firm has grown to be large and profitable. Would you be better off if you had bought the firm’s stock or the firm’s bonds? Briefly explain.
> According to an article in the Economist about the health care system in the United Kingdom: “A defining principle of the National Health Service is that it is ‘free at the point of delivery.’” What does “free at the point of delivery” mean? Is health ca
> One study found that the price elasticity of demand for soda is 20.78, while the price elasticity of demand for Coca-Cola is 21.22. Coca-Cola is a type of soda, so why isn’t its price elasticity the same as the price elasticity for soda as a product? So
> If the marginal cost of reducing a certain type of pollution is zero, should all that type of pollution be eliminated? Briefly explain.
> Briefly explain whether you agree with the following statement: “If at the current quantity, marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost, there will be a deadweight loss in the market. However, there is no deadweight loss when marginal cost is greater
> Sony suffered losses for a decade selling televisions before finally earning a profit in 2014. Given the strong consumer demand for plasma, LCD, and LED television sets, shouldn’t Sony have been able to raise prices to earn a profit during that decade of
> According to a news story about the International Energy Agency, the agency forecast that “the current slide in [oil] prices won’t [reduce] global supply.” Would a decline in oil prices ever cause a reduction in the supply of oil? Briefly explain. Sourc
> Briefly explain whether each of the following statements describes a change in supply or a change in quantity supplied. a. To take advantage of high prices for snow shovels during a snowy winter, Alexander Shovels, Inc., decides to increase output. b. Th
> Considering only the income effect, if the price of an inferior good decline, would a consumer want to buy a larger quantity or a smaller quantity of the good? Does your answer mean that the demand curves for inferior goods should slope upward? Briefly e
> An article in the New York Times quoted an economist as arguing that “global free trade and the European single market … encourage countries to specialize in sectors where they enjoy comparative advantage. Germany’s [comparative advantage] is in cars and
> What is the economic definition of utility? Is it possible to measure utility?
> Suppose that instead of being highly inelastic, the demand for oil is highly elastic. a. Given the situation illustrated by the first graph in the Making the Connection on page 203, would the resulting price change be larger, smaller, or the same as the
> Some coal is mined by private companies on land owned by the federal government. Two economists writing in an opinion column argue, “The federal government should also take into account the economic consequences of burning coal when pricing this fuel. Th
> Suppose that a firm in which you have invested is losing money. Would you rather own the firm’s stock or the firm’s bonds? Briefly explain.
> What is meant by the phrase “health outcome”? How do health outcomes in the United States compare with those of other high-income countries? What problems arise in attempting to compare health outcomes across countries?
> According to a news story about the bus system in the Lehigh Valley in Pennsylvania, “Ridership fell 14 percent in 2012 after a 33 percent increase” in bus fares. Based on this information, is the demand for bus trips price elastic or price inelastic? Ex
> Briefly explain whether you agree with the following statement: “A lower price in a market always increases economic efficiency in that market.”
> What is the law of supply? What are the main variables that cause a supply curve to shift? Give an example of each.
> Suppose you read the following item in a newspaper article, under the headline “Price Gouging Alleged in Pencil Market”: Consumer advocacy groups charged at a press conference yesterday that there is widespread price gouging in the sale of pencils. They
> What would need to be true for a demand curve to be upward sloping?
> In the 2012 Summer Olympic Games, Ashton Eaton (from the United States) won a gold medal in the decathlon, which requires athletes to compete in 10 different track and field events. In one of these events Eaton ran a 100-meter race in 10.35 seconds. In a
> In the preface to the 2004 reprint of In Search of Excellence, Thomas Peters and Robert Waterman wrote: “Our main detractors point to the decline of some of the companies we featured. They miss the point… . We weren’t writing Forever Excellent, just as i
> How do the stock and bond markets provide information to businesses? Why do stock and bond prices change over time?
> Can economic analysis provide a final answer to the question of whether the government should intervene in markets by imposing price ceilings and price floors? Briefly explain.
> Briefly compare the health care systems in Canada, Japan, and the United Kingdom with the health care system in the United States.
> Briefly explain whether the demand for each of the following products is likely to be elastic or inelastic: a. Milk b. Frozen cheese pizza c. Cola d. Prescription medicine
> What are transactions costs? When are we likely to see private solutions to the problem of externalities?
> A Wall Street Journal article about a drought in California indicated that one result would be a smaller tomato crop. Use a demand and supply graph of the tomato market to illustrate the effect of the drought. Is economic efficiency affected? Briefly exp
> What is the difference between a change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied?
> How the market demand curve is derived from consumers’ individual demand curves?
> A World Trade Organization (WTO) publication calls comparative advantage “arguably the single most powerful insight in economics.” What is comparative advantage? What makes it such a powerful insight? Source: World Trade Organization, “Understanding the
> Discuss the following statement: “In a perfectly competitive market, in the long run consumer’s benefit from reductions in costs, but firms don’t.” Don’t firms also benefit from cost reductions because they are able to earn larger profits?
> Briefly explain whether the value of U.S. exports is typically larger or smaller than the value of U.S. imports.
> Why is a bond considered to be a loan but a share of stock is not? Why do corporations issue both bonds and shares of stock?
> What are the main sources of health insurance in the United States?
> Briefly explain whether you agree with the following statement: “When there is a shortage of a good, consumers eventually give up trying to buy it, so the demand for the good declines, and the price falls until the market is finally in equilibrium.”
> Is the demand for most agricultural products elastic or inelastic? Briefly explain.
> What is the Coase theorem? Why do the parties involved in an externality have an incentive to reach an efficient solution?
> What is economic efficiency? Why do economists define efficiency in this way?
> Why does scarcity imply that every society and every individual face trade-offs?
> Explain how a downward-sloping demand curve results from consumers adjusting their consumption choices to changes in price.
> What is the difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage? Will a country always be an exporter of a good in the production of which it has an absolute advantage? Briefly explain.
> What is the difference between direct finance and indirect finance? If you borrow money from a bank to buy a new car, are you using direct finance or indirect finance?
> What are the three major types of firms in the United States? Briefly discuss the most important characteristics of each type.
> Define the following terms: a. Health insurance b. Fee-for-service c. Single-payer health care system d. Socialized medicine
> The following graph represents the situation of Karl’s Kumquats, a kumquat grower. a. How much profit is Karl earning? b. Does the current situation of Karl’s firm illustrate productive efficiency or allocative effic
> Many people have predicted, using a model like the one in panel (b) of Figure 17.12 on page 583, that the price of natural resources should rise consistently over time in comparison with the prices of other goods because the demand curve for natural reso
> What is an entrepreneur? Why do entrepreneurs play a key role in a market system?
> What are the key determinants of the price elasticity of demand for a product? Which determinant is the most important?
> What do economists mean by “an economically efficient level of pollution”?
> Define economic surplus and deadweight loss.
> What is a supply schedule? What is a supply curve?
> What are the three economic questions that every society must answer? Briefly discuss the differences in the way centrally planned, market, and mixed economies answer these questions.
> According to an article in the Wall Street Journal in 2015, “Apple Inc.’s surging smartphone sales in China may have busted a myth: that many Chinese consumers couldn’t, or wouldn’t, shell out for an iPhone.” The article noted that iPhone sales were grow
> Briefly discuss the most important differences between the market for health care and the markets for other goods and services.
> A journalist wrote the following about the effects of falling gasoline prices: “With lower prices, demand rises and people consume more.” Briefly explain whether you agree with the journalist’s analysis. Source: Jeff Sommer, “Cheaper Oil, Fatter Wallets
> An article in the Wall Street Journal noted that an “increase in the price of oil quickly reduces demand for oil.” Do you agree with this statement? Briefly explain. Source: Josh Zumbrun, “Oil’s Plunge Could Help Send Its Price Back Up,” Wall Street Jour
> Private equity firms, such as Blackstone and Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co., search for firms where the managers appear not to be maximizing profits. A private equity firm can buy stock in these firms and have its employees elected to the firms’ boards of
> Suppose the following table shows the price of a base model Toyota Prius hybrid and the quantity of Priuses sold for three years. Do these data indicate that the demand curve for Priuses is upward sloping? Briefly explain. Year Price Quantity $31,88
> What is the difference between normative analysis and positive analysis? Is economics concerned mainly with normative analysis or positive analysis? Briefly explain.
> The chapter states, “Firms will supply all those goods that provide consumers with a marginal benefit at least as great as the marginal cost of producing them.” A student objects to this statement, arguing, “I doubt that firms will really do this. After
> Salespeople, whether selling life insurance, automobiles, or pharmaceuticals, typically get paid on commission instead of a straight hourly wage. How does paying a commission help solve the principal–agent problem between the owners of a business and the
> The following graph shows the market for tickets to a concert that will be held in a local arena that seats 15,000 people. What is the producer surplus in this market? How does it differ from the producer surplus in the markets you have studied up to thi
> Lawrence Summers served as secretary of the Treasury in the Clinton administration and as director of the National Economic Council in the Obama administration. He has been quoted as giving the following defense of the economic approach: There is nothing
> In a public corporation, the principal–agent problem between ownership and top management results from asymmetric information. What information, if known, would prevent this principal–agent problem?
> Write the formula for the price elasticity of demand. Why isn’t elasticity just measured by the slope of the demand curve?
> In an article in the agriculture magazine Choices, Oregon State University economist JunJie Wu made the following observation about the conversion of farmland to urban development: Land use provides many economic and social benefits, but often comes at a

