Question: Kestral Manufacturing identified the following
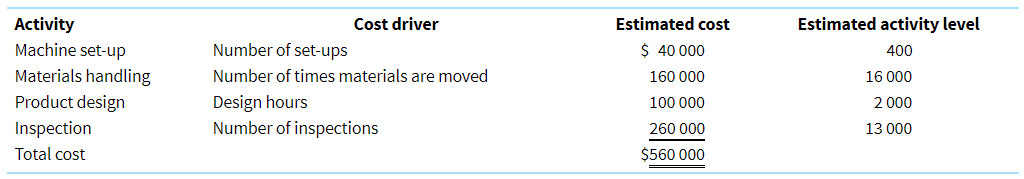
Kestral Manufacturing identified the following overhead costs and cost drivers for the current period. Kestral produces customised products that move through several different processes. Materials and intermediate products are moved among several different workstations. Custom features are designed by engineers.
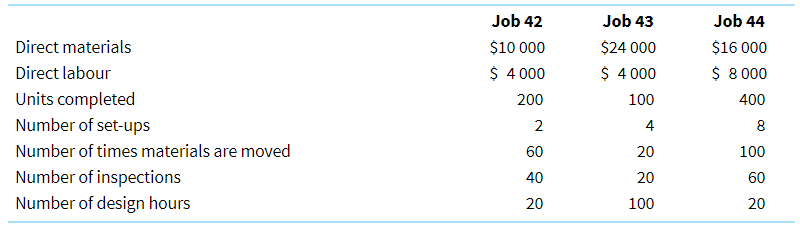
Information for three of the jobs completed during the period follows.
Required
(a) If the company uses ABC, how much overhead cost should be assigned to job 42?
(b) If the company uses ABC, calculate the cost per unit for job 43.
(c) Kestral would like to reduce the cost of its overhead activities. Describe non-value added activities and explain why reducing these specific activities might also reduce cost.
(d) How might Kestral benefit from the use of time-driven ABC?
Transcribed Image Text:
Activity Machine set-up Materials handling Product design Inspection Total cost Cost driver Number of set-ups Number of times materials are moved Design hours Number of inspections Estimated cost $ 40 000 160 000 100 000 260 000 $560 000 Estimated activity level 400 16 000 2 000 13 000 Direct materials Direct labour Units completed Number of set-ups Number of times materials are moved Number of inspections Number of design hours Job 42 $10 000 $ 4 000 200 2 60 40 20 Job 43 $24 000 $ 4 000 100 4 20 20 100 Job 44 $16 000 $ 8 000 400 8 100 60 20
> Giant Jets is a French company that produces jet airplanes for commercial cargo companies. The selling price per jet is €1 000 000. Currently the company uses actual volumes to allocate fixed manufacturing overhea
> King Island Lobster Company is a privately held company that buys lobsters from local fishermen and then delivers them to restaurants in several of Australia’s larger cities. The owners use variable costing income statements, but one owner’s daughter, wh
> Why do the accounting standards require absorption costing for financial reporting?
> Diggers is a coal mining company. Diggers has planned to invest in replacement equipment. Its existing equipment has come to the end of its useful life and will be scrapped with no resale value. The cost of the new replacement investment is $2 500 000. I
> MacArthur’s is a fast food company planning to invest in a restaurant expansion that entails the refurbishment and opening of four new stores across the country. The cost of this investment is $4 800 000. It is to be depreciated (straig
> Lymbo Company, must install safety devices throughout its plant or it will lose its insurance coverage. Two alternatives are acceptable to the insurer. The first costs $100 000 to install and $20 000 to maintain annually. The second costs $150 000 to ins
> Ferris Industries has $50Â 000 available to invest in new equipment. Management is considering four different equipment investments, each of which requires $50Â 000. The expected after-tax cash flow for each project has been estimat
> Equipment with a cost of $60 000 will, if acquired, generate annual savings of $30 000 for six years, at which time it will have no further use or value. The company has a marginal tax rate of 40 per cent and requires a 10 per cent rate of return. It use
> Clearwater Bottling Company sells bottled spring water for $12 per case, with variable costs of $7 per case. The company has been selling 200 000 cases per year and expects to continue at that rate unless it accepts a special order from Blue Danube Resta
> Refer question 15.23 above. Outline how Ceila might improve the investment decision-making model within the hospitality and conference facilities division to cater for strategic investments. Question 15.23: FreshTucker Limited allows divisional managers
> FreshTucker Limited allows divisional managers to make capital investment decisions up to $10 million. However, divisional managers are required to send to head office details of each decision taken, including their justifications. The manager of the hos
> Amaro Hospital, a not-for-profit entity not subject to income taxes, is considering the purchase of new equipment costing $20 000 to achieve cash savings of $5000 per year in operating costs. The estimated useful life is 10 years, with no salvage value.
> Garfield Construction is considering replacing an old machine that is currently being used. The old machine is fully depreciated, but it can be used for another five years, at which time it would have no terminal value. Garfield can sell the old machine
> If inventory physically increases during the period, income under absorption costing will be higher than income using variable costing. Explain.
> Axel Ltd is planning to buy a new machine with the expectation that this investment should earn a rate of return of at least 15 per cent. This machine, which costs $150 000, would yield an estimated net cash flow of $30 000 a year for 10 years. Required
> Overnight Laundry is considering the purchase of a new pressing machine that would cost $96 000 and produce incremental operating cash flows of $25 000 annually for 10 years. The machine has a terminal value of $6000 and is depreciated for income tax pur
> Government supervisors in a remote area of Queensland are considering the purchase of a small, used plane to save on travel costs. The plane will cost $400 000 and can be sold in five years for 20 per cent of the original cost. Required If 10 per cent i
> Diamond Ltd agreed to sell some used equipment to one of its employees. Alternative financing arrangements for the sale have been discussed, and the present and future values of each alternative have been determined. Required (a) Diamond offered to acce
> (a) What is the present value of $8000 received in seven years at 8 per cent interest? (b) Bonnie Lee buys a savings bond for $125. The bond pays 6 per cent and matures in 10 years. What amount will Bonnie receive when she redeems the bond? (c) Erik Pete
> Put the following six steps for capital budgeting in the most likely order, numbering the first activity as number 1, the second as 2, and so on. • Perform sensitivity analysis. • Identify decision alternatives. • Analyse qualitative factors. • Identify
> Marissa Nafsik commenced at Mana Consulting (MANA) in 2010. The company has grown from a one-person operation to a rather diverse consulting company specialising in management consulting, technology consulting, particularly with respect to internet techn
> Maddy is the divisional manager of the internet technologies division of IT World Ltd. The following information is currently available with respect to her role. • The internet technologies division is classified as a profit centre. • Maddy reports to th
> The income statement information for Kallapur and Trombley Cotton Growers follows: Required (a) Using the general decision rule, which product should the entity emphasise? Support your answer with calculations. (b) Using the general decision rule, shou
> Horton and Associates produces two products named the Big Winner and the Loser. Last month 1000 units of the Loser and 4000 units of the Big Winner were produced and sold. Average prices and costs for the two products for last month follow: The product
> Explain how breakeven point would be affected under both absorption and variable costing.
> Feed Barn packages and distributes three grades of animal feed. The material cost per tonne and estimated annual sales for each of the products are listed. The fixed cost of operating the machinery used to package all three products is $10Â
> Saguaro Systems produces and sells speakers and CD players. The following information has been collected about the costs related to the systems: Saguaro normally produces 25Â 000 of these systems per year. The managers have recently received
> Beautiful Biscuits (BB) sells biscuits, brownies, and beverages to small local shops. The selling price per brownie is $1.25, the variable cost is $0.75, and the average cost is $1.00. The principal of a primary school asked BB to provide 10 dozen browni
> The Cone Head House sells ice cream cones in a variety of flavours. Data for a recent week are as follows: The Cone Head’s manager received a call from a university student club requesting a bid on 100 cones to be picked up in three da
> Wildlife Foods prepares wild birdseed mixes and sells them to local pet stores, grocery stores, and wild bird stores. Two types of mixes have been most successful: Flight Fancy and Multigrain. Flight Fancy generates a contribution margin of $12 per 100 k
> Emily developed an innovative computer game, called Home By Myself (HBM). It was so successful that she quickly followed up with two sequels: Home By Myself II (HBM2) and Home By Myself III (HBM3). The costs of developing the games were $95Â 0
> The income statement for King Salmon Sales, which produces smoked salmon, follows: Assume that the administrative costs are fixed and that all of the other costs are variable. Required (a) Suppose the state government curtails fishing because of low f
> Mrs Meadows sells two popular brands of biscuits, Chip Dip and Soft Chunk Chocolate Chip. Both biscuits go through the mixing and baking departments, but Chip Dip is also dipped in chocolate in the coating department. Sales manager Frank Ronan believes t
> Snowbird Snowboards converts regular snowboards to enhance safety capabilities for children. The income statement for last year, in which 500 snowboards were produced and sold, appears here. Required (a) What volume of snowboards must be sold to earn pr
> Johnson and Sons Ltd produces organic orange juice from oranges it grows. Unfortunately, it has been a bad year for oranges because of severe frosts. Johnson only has 10 000 litres of juice. It usually sells 15 000 litres at $3 per litre. The variable co
> What is the difference between a cost that is variable and variable costing?
> Yoklic Ltd currently manufactures a subassembly for its main product. The costs per unit are as follows: Regina Ltd has contacted Yoklic with an offer to sell it 5000 subassemblies for $55.00 each. Required (a) Should Yoklic make or buy the subassembli
> The Palm Oil Company buys crude coconut and palm nut oil. Refining this oil results in four products at the split-off point: soap grade, cooking grade, light moisturiser and heavy moisturiser. Light moisturiser is fully processed at the split-off point.
> Deluxe Tours, a tour organiser, leased a cruise liner for a special round-the-world tour. The lease cost is $200 000. Two classes of passengers are booked on the tour: first class and economy class. The total revenue from the 100 first-class passengers i
> Outback Cattle Company raises cattle and sells beef products. Following is a list of costs for the operation. Required Identify whether each cost is most likely a (J) joint cost or a (S) separable cost. For each item, explain why. i. Veterinary costs fo
> Required (a) Which of the following related products would be considered joint products? Explain your choices. i. Sand produced with three levels of fineness ii. Motor vehicles and trucks iii. Milk, yoghurt, butter, and cheese iv. Motorcycles and mopeds
> For a given by-product, 100 units can be sold at the split-off point for $8 each, or processed further at a cost of $12 each and sold for $19. Required Should the by-product be processed further? Provide calculations and explain your answer.
> The management of SouthPak Company has asked for your assistance in deciding whether to continue manufacturing a part or to buy it from an outside supplier. The part, called AlphaB, is a component of SouthPak’s fi nished product. An analysis of the accou
> Diamond Light Company incurred the following costs to produce 25 000 light switches for floor lamps last year. The Ignition Company has offered to supply the switches for $8 per unit. An analysis of the overhead costs has identified that if the sw
> Crystal Lattice produces exercise mats for use in fitness centres. Production capacity is 20 000 mats per year. Due to a chain of fitness centres closing, Crystal Lattice now has spare capacity of 2000 mats per year. An international hotel chain, Resteas
> Chief accountant San Kean Indi at Lewinsky and Dikolli Architects has begun a pilot project exploring the use of time-driven-activity-based-costing (TDABC). Indi became aware of the attributes of TDABC at a recent professional development seminar. Indi h
> The basic issue in variable and absorption costing could be said to be one of timing rather than amount. Explain.
> You are asked for suggestions about increasing profitability for a customer that purchases low-margin products and requires costly services. Required (a) In your own words, define activity-based management (ABM). (b) In your own words, describe high-cos
> Elite Daycare provides two different services, full-time childcare for preschoolers, and after-school care for older children. The director would like to estimate an annual cost per child in each of the daycare programs, ignoring any facility-sustaining
> Palmer Company uses an activity-based costing system. It has the following manufacturing activity areas, related drivers used as allocation bases, and cost allocation rates: During the month, 100 units were produced, requiring two setups. Each unit con
> Applewood Electronics manufactures two large-screen television models, the Monarch, which has been produced since 20105 and sells for $900, and the Regal, a new model introduced in early 2016 that sells for $1,140. Applewood’s CEO, Harr
> Calder Products manufactures two component parts: AJ40 and AJ60. AJ40 components are being introduced currently, and AJ60 parts have been in production for several years. For the upcoming period, 1000 units of each product are planned for manufacturing.
> Prahan Daycare (PD) offers childcare services to the local community. For many years it simply offered services for preschoolers. In this environment, managing the costs and services seemed relatively straightforward. In recent years, government subsidie
> Taylors Cheesecakes supplies cheesecakes to three large supermarket chains. Management has become concerned about the rising costs associated with the processing and dispatch of orders. An activity analysis of the indirect costs identified the following
> Following are lists of potential cost pools and cost drivers. Required Match each cost driver to the most appropriate cost pool. Use each cost driver only once. Explain your choice. Cost pool (a) Machining (b) Purchasing activities (c) Inspection (
> In ABC systems, activities are often separated into a hierarchy of six categories. Required In your own words, define and give examples of the following types of activities and costs in an ABC system for a national car rental company such as Hertz or Eu
> The volume of manufacturing in a period has an effect on income calculated using absorption costing but has no effect on income calculated using variable costing. Explain.
> MicroBrew is a successful brewery engaged in the development and production of specialty micro brews. It uses an ABC system. During the past year, it has incurred $1 250 000 of product development costs, $850 000 of materials handling costs, $2 500 000 o
> Each of the costs below is incurred by Fairgood & Hernandez, a small CPA firm. Required Identify whether each of the following costs most likely relates to an (i) organisation- sustaining activity, (ii) customer-sustaining activity, (iii) product-sus
> The following data for Kitchen Tile Company relates to the production of 18Â 000 tiles during the past month. The entity allocates fixed overhead costs at a standard rate of $19 per direct labour hour. Required (a) How many actual labour hou
> Glen’s Landscaping Supplies uses a standard costing system to allocate overhead costs. The accountant estimated 8500 hours as the volume to develop standard overhead rates. Budgeted costs were $19 125 for fixed overhead and $15 300 for
> South Clinic charges its patients on the basis of actual direct costs incurred plus fixed costs at the rate of $40 per hour. The fixed cost rate of $40 per hour is based on the assumption of 6000 patient hours monthly, assuming that each patient requires
> The Neon Manufacturing Company is a joint venture between Australian and Chinese firms with an assembly plant located in Beijing. The company’s managers expected to produce 20 000 units of product in March. The standard cost for the materials used for 20
> Following is information about Pine Furniture’s direct labour hours and wages last period. Required (a) Calculate the direct labour efficiency variance. (b) Calculate the direct labour price variance. Actual labour hours at the st
> Sunset Solar installs solar panels throughout Australia. The accountants estimated the market size to be 2 million solar panels with Sunset Solar hoping to achieve 5% market share. The static budget shows that each panel is expected to provide a $2000 co
> The following data represents the flexible budget for Mountain Mist Brewery, a boutique brewery that manufactures and sells boutique ales. Overall, the increase in the final price of beer has contributed to the flattening of the Australian beer market.
> Following are the variances for Fine Products Manufacturing Company for the month of March. Assume that the price variance for direct materials is calculated at the time of purchase and that the amount of direct materials purchased is equal to the amount
> Explain how income could fall even though the unit sales level rises.
> Plush pet toys are produced in a largely automated factory in standard lots of 100 toys each. A standard cost system is used to control costs and to assign cost to inventory. Variable overhead, estimated at $5 per lot, consists of miscellaneous items s
> Derf Company allocates overhead on the basis of direct labour hours. Two direct labour hours are required for each unit of product. Planned production for the period was set at 9000 units. Manufacturing overhead is estimated at $135 000 for the period (2
> The following information pertains to Nell Company’s production of one unit of its manufactured product during the month of June. The company recognises the materials price variance when materials are purchased. Required (a) Calculate
> The managers of Bathroom Cabinets established the following standards for Model 535: Last month, 15Â 342 units of Model 535 were produced at a cost of $26Â 870 for direct materials and $47Â 000 for direct labour. A tota
> Plush pet toys are produced in a largely automated factory in standard lots of 100 toys each. A standard cost system is used to control costs and to assign cost to inventory. Variable overhead, estimated at $5 per lot, consists of miscellaneous items s
> Sherry North is the supply manager for West Industries, a manufacturer of garden furniture for the major department store in Australia. As part of her bonus plan, Sherry must meet the materials budget that was established at the beginning of the year. As
> The present value of a given cash flow gets smaller as the number of periods gets larger, regardless of whether cash flow is discounted with a real rate or nominal rate. Explain why this relationship happens and what it means from an economic perspective
> When projects have longer lives, it is more difficult to accurately estimate the cash flows and discount rates over the life of the project. Explain why this statement is true.
> Forecasting the terminal value of equipment 20 years from now is difficult to do accurately, but errors in estimation probably have a small effect on the NPV. Explain.
> At recent management meeting the following statement was made by the Chief Operating Officer – “ this project is strategic for the firm and therefore non-discretionary”. Briefly comment on this statement.
> Due to a newly released safety regulation, Red Rock Chocolates will have to replace the fire safety equipment throughout its production facilities. How should Red Rock management assess this asset replacement?
> Suppose an entity has five different capital budgeting projects from which to choose, but has constrained funds and cannot implement all of the projects. Explain why comparing the projects’ NPVs is better than comparing their IRRs.
> A community health clinic operates as a not-for-profit entity. Typical capital expenditure decisions involve acquiring equipment that will perform medical tests beyond those currently possible at the clinic (hence, adding revenues) and/or perform tests m
> Describe the pros and cons of each of the capital budgeting methods learned in this chapter: (a) net present value, (b) internal rate of return, (c) payback, and (d) accrual accounting rate of return.
> The accountant for Moon Industries has taken unexpected leave and has not completed the end-ofperiod budget analysis. The following incomplete budget analysis was found on her desk. Additional information: Required (a) Complete the variance analysis
> When we covered cost–volume–profit (CPV) analysis in chapter 4, we calculated the amount of pre-tax profit needed to achieve a given level of after-tax profit. We could calculate a pre-tax rate of return given an after-tax rate of return. Why would it be
> An international firm requires a rate of return of 15 per cent domestically and in developed countries, but 25 per cent in less-developed countries. Does this requirement mean that the firm is exploiting the less developed countries?
> If an entity has unlimited funds, what criterion should be used to determine which projects to invest in?
> How might inflation influence a decision to acquire an asset now rather than later?
> Two methods can be used to incorporate the effects of inflation or deflation into an NPV analysis. In your own words, explain how a nominal discount rate is different from a real discount rate. Why are analyses using the nominal approach potentially more
> State the three categories of capital investments and briefly explain the best capital investment evaluation tools suitable for each.
> Explain the meaning of span of control, span of accountability and span of attention.
> Outline the meaning of responsibility accounting.
> Differentiate between belief systems and boundary systems.
> Using examples, explain the meaning of informal controls.
> The photocopying department in the local polytechnic college has budgeted monthly costs at $40 000 per month plus $7 per student. Normally 800 students are enrolled. During March there were 730 students (which is within the relevant range). At the end of
> Distinguish between diagnostic and interactive use of specific control system tools.
> What role does management accounting and control information pay in monitoring the success of the new strategic direction taken by an entity?
> What role does management accounting and control information play in developing new strategic directions?
> Briefly explain the link(s) between strategy and managerial control systems.
> What factors would force an organisation such as an airline to review its strategic direction?
> Define strategy and differentiate between corporate-level strategy and business-unit level strategy.

