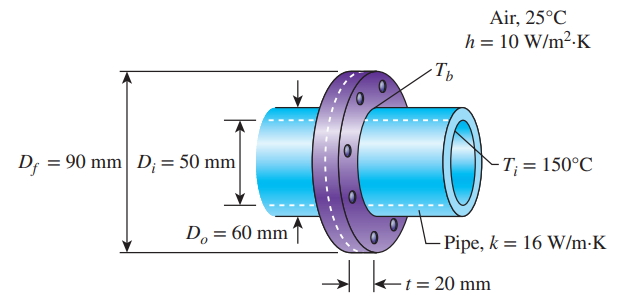
Question: Pipes with inner and outer diameters of
Pipes with inner and outer diameters of 50 mm and 60 mm, respectively, are used for transporting superheated vapor in a manufacturing plant. The pipes with thermal conductivity of 16 W/m⋅K are connected together by flanges with combined thickness of 20 mm and outer diameter of 90 mm. Air condition surrounding the pipes has a temperature of 25°C and a convection heat transfer coefficient of 10 W/m2⋅K. If the inner surface temperature of the pipe is maintained at a constant temperature of 150°C, determine the temperature at the base of the flange and the rate of heat loss through the flange.
> The wall of a refrigerator is constructed of fiberglass insulation (k = 0.035 W/m⋅K) sandwiched between two layers of 1-mm-thick sheet metal (k = 15.1 W/m⋅K). The refrigerated space is maintained at 2°C, and
> A 2-m × 1.5-m section of wall of an industrial furnace burning natural gas is not insulated, and the temperature at the outer surface of this section is measured to be 110°C. The temperature of the furnace room is 32°C, and the combined convection and ra
> A 7-hp (shaft) pump is used to raise water to an elevation of 15 m. If the mechanical efficiency of the pump is 82 percent, determine the maximum volume flow rate of water.
> What does the thermal resistance of a medium represent?
> The roof of a house consists of a 15-cm-thick concrete slab (k = 2 W/mâ‹…K) that is 15 m wide and 20 m long. The convection heat transfer coefficients on the inner and outer surfaces of the roof are 5 and 12 W/m2â‹…K, resp
> To defrost ice accumulated on the outer surface of an automobile windshield, warm air is blown over the inner surface of the windshield. Consider an automobile windshield with thickness of 5 mm and thermal conductivity of 1.4 W/mâ‹…K. The
> A transparent film is to be bonded onto the top surface of a solid plate inside a heated chamber. For the bond to cure properly, a temperature of 70°C is to be maintained at the bond, between the film and the solid plate. The transparent film
> To defog the rear window of an automobile, a very thin transparent heating element is attached to the inner surface of the window. A uniform heat flux of 1300 W/m2 is provided to the heating element for defogging a rear window with thickness of 5 mm. The
> A wall is constructed of two layers of 0.6-in-thick sheetrock (k = 0.10 Btu/h⋅ft⋅°F), which is a plasterboard made of two layers of heavy paper separated by a layer of gypsum, placed 7 in apart. The space be
> Reconsider Prob. 17–22. Using appropriate software, plot the rate of heat transfer through the window as a function of the width of airspace in the range of 2 mm to 20 mm, assuming pure conduction through the air. Discuss the results.
> Repeat Prob. 17–22, assuming the space between the two glass layers is evacuated. Data from Prob. 17-22: Consider a 1.5-m-high and 2.4-m-wide double pane window consisting of two 3-mm-thick layers of glass (k = 0.78 W/mâ‹
> Consider a 1.5-m-high and 2.4-m-wide double pane window consisting of two 3-mm-thick layers of glass (k = 0.78 W/mâ‹…K) separated by a 12-mm-wide stagnant airspace (k = 0.026 W/mâ‹…K). Determine the steady rate of heat tra
> Consider a 1.5-m-high and 2.4-m-wide glass window whose thickness is 6 mm and thermal conductivity is k = 0.78 W/m⋅K. Determine the steady rate of heat transfer through this glass window and the temperature of its inner surface for a day during which the
> The water in a large lake is to be used to generate electricity by the installation of a hydraulic turbine–generator at a location where the depth of the water is 50 m. Water is to be supplied at a rate of 5000 kg/s. If the electric power generated is me
> A 2-kg rock is thrown upward with a force of 200 N at a location where the local gravitational acceleration is 9.79 m/s2. Determine the acceleration of the rock, in m/s2.
> Consider a power transistor that dissipates 0.15 W of power in an environment at 30°C. The transistor is 0.4 cm long and has a diameter of 0.5 cm. Assuming heat to be transferred uniformly from all surfaces, determine (a) the amount of heat th
> Consider heat conduction through a plane wall. Does the energy content of the wall change during steady heat conduction? How about during transient conduction? Explain.
> A cylindrical resistor element on a circuit board dissipates 0.15 W of power in an environment at 35°C. The resistor is 1.2 cm long and has a diameter of 0.3 cm. Assuming heat to be transferred uniformly from all surfaces, determine (a) the amount of hea
> Water is boiling in a 25-cm-diameter aluminum pan (k = 237 W/m⋅K) at 95°C. Heat is transferred steadily to the boiling water in the pan through its 0.5-cm-thick flat bottom at a rate of 800 W. If the inner surface temperature of the bottom of the pan is
> A 12-cm × 18-cm circuit board houses on its surface 100 closely spaced logic chips, each dissipating 0.06 W in an environment at 40°C. The heat transfer from the back surface of the board is negligible. If the heat transfer coefficient on the surface of
> Consider an electrically heated brick house (k = 0.40 Btu/h⋅ft⋅°F) whose walls are 9 ft high and 1 ft thick. Two of the walls of the house are 50 ft long and the others are 35 ft long. The house is maintaine
> Consider a person standing in a room at 20°C with an exposed surface area of 1.7 m2. The deep body temperature of the human body is 37°C, and the thermal conductivity of the human tissue near the skin is about 0.3 W/m⋅K. The body is losing heat at a rate
> Consider a 3-m-high, 6-m-wide, and 0.25-m-thick brick wall whose thermal conductivity is k = 0.8 W/m⋅K. On a certain day, the temperatures of the inner and the outer surfaces of the wall are measured to be 14°C and 5°C, respectively. Determine the rate o
> A 0.2-cm-thick, 10-cm-high, and 15-cm-long circuit board houses electronic components on one side that dissipate a total of 15 W of heat uniformly. The board is impregnated with conducting metal fillings and has an effective thermal conductivity of 12 W/
> Steam in a heating system flows through tubes whose outer diameter is 3 cm and whose walls are maintained at a temperature of 120°C. Circular aluminum alloy fins (k = 180 W/m⋅K) of outer diameter 6 cm and constant thickness t
> A room is cooled by circulating chilled water through a heat exchanger located in the room. The air is circulated through the heat exchanger by a 0.25-hp (shaft output) fan. Typical efficiency of small electric motors driving 0.25-hp equipment is 60 perc
> A plane wall surface at 200°C is to be cooled with aluminum pin fins of parabolic profile with blunt tips. Each fin has a length of 25 mm and a base diameter of 4 mm. The fins are exposed to ambient air at 25°C, and the heat transfer coefficient is 45 W/
> A plane wall with surface temperature of 300°C is attached with straight aluminum triangular fins (k = 236 W/m⋅K). The fins are exposed to an ambient air condition of 25°C, and the convection heat transfer coeffici
> A total of 10 rectangular aluminum fins (k = 203 W/m⋅K) are placed on the outside flat surface of an electronic device. Each fin is 100 mm wide, 20 mm high, and 4 mm thick. The fins are located parallel to each other at a center-to-center distance of 8 m
> Circular fins of uniform cross section, with diameter of 10 mm and length of 50 mm, are attached to a wall with surface temperature of 350°C. The fins are made of material with thermal conductivity of 240 W/m⋅K, they are expo
> A 12-cm-long bar with a square cross section, as shown in Fig. P17–133, consists of a 1-cm-thick copper layer (k = 380W/m⋅K) and a 1-cm-thick epoxy composite layer (k = 0.4 W/m⋅K). Calculate the rate
> A typical section of a building wall is shown in Fig. P17–132. This section extends in and out of the page and is repeated in the vertical direction. The wall support members are made of steel (k = 50 W/m⋅K). The suppo
> A 4-m-high and 6-m-long wall is constructed of two large 0.8-cm-thick steel plates (k = 15 W/mâ‹…K) separated by 1-cm thick and 22-cm-wide steel bars placed 99 cm apart. The remaining space between the steel plates is filled with fibergla
> One wall of a refrigerated warehouse is 10.0 m high and 5.0 m wide. The wall is made of three layers: 1.0-cm-thick aluminum (k = 200W/m⋅K), 8.0-cm thick fiberglass (k = 0.038W/m⋅K), and 3.0-cm-thick gypsum board (k = 0.48 W/m⋅K). The warehouse inside and
> Consider a window glass consisting of two 4-mm thick glass sheets pressed tightly against each other. Compare the heat transfer rate through this window with that of one consisting of a single 8-mm-thick glass sheet under identical conditions.
> A spherical vessel, 3.0 m in diameter (and negligible wall thickness), is used for storing a fluid at a temperature of 0°C. The vessel is covered with a 5.0-cm-thick layer of an insulation (k = 0.20 W/m⋅K). The surrounding air is at 22°C. The inside and
> An exercise room has six weight-lifting machines that have no motors and seven treadmills each equipped with a 2.5-hp (shaft output) motor. The motors operate at an average load factor of 0.7, at which their efficiency is 0.77. During peak evening hours,
> Steam at 260°C is flowing inside a steel pipe (k = 61 W/m⋅K) whose inner and outer diameters are 10 cm and 12 cm, respectively, in an environment at 20°C. The heat transfer coefficients inside and outside the pipe are 120 W/m2⋅K and 14 W/m2⋅K, respective
> The plumbing system of a house involves a 0.5-m section of a plastic pipe (k = 0.16 W/mâ‹…K) of inner diameter 2 cm and outer diameter 2.4 cm exposed to the ambient air. During a cold and windy night, the ambient air temperature remains a
> Hot water is flowing at an average velocity of 1.5 m/s through a cast iron pipe (k = 52 W/m⋅K) whose inner and outer diameters are 3 cm and 3.5 cm, respectively. The pipe passes through a 15 m-long section of a basement whose temperature is 15°C. If the
> Cold conditioned air at 12°C is flowing inside a 1.5-cm-thick square aluminum (k = 237 W/m⋅K) duct of inner cross section 22 cm × 22 cm at a mass flow rate of 0.8 kg/s. The duct is exposed to air at 33°C with a combined convection radiation heat transfer
> Consider two identical people each generating 60 W of metabolic heat steadily while doing sedentary work and dissipating it by convection and perspiration. The first person is wearing clothes made of 1-mm-thick leather (k = 0.159 W/m⋅K) that covers half
> A 40-W power transistor is to be cooled by attaching it to one of the commercially available heat sinks shown in Table 17–6. Select a heat sink that will allow the case temperature of the transistor not to exceed 90°C in the
> Reconsider Prob. 17–121. Using appropriate software, investigate the effect of the center-to center distance of the fins on the rate of heat transfer from the surface and the overall effectiveness of the fins. Let the center-to center d
> A hot surface at 100°C is to be cooled by attaching 3-cm-long, 0.25-cm-diameter aluminum pin fins (k = 237 W/m⋅K) to it, with a center-to-center distance of 0.6 cm. The temperature of the surrounding medium is 30°C
> A 0.4-cm-thick, 12-cm-high, and 18-cm-long circuit board houses 80 closely spaced logic chips on one side, each dissipating 0.04 W. The board is impregnated with copper fillings and has an effective thermal conductivity of 30 W/m⋅K. All the heat generate
> Consider steady one-dimensional heat transfer through a multilayer medium. If the rate of heat transfer Q is known, explain how you would determine the temperature drop across each layer.
> A 75-hp (shaft output) motor that has an efficiency of 91.0 percent is worn out and is replaced by a high-efficiency 75-hp motor that has an efficiency of 95.4 percent. Determine the reduction in the heat gain of the room due to higher efficiency under f
> Steam in a heating system flows through tubes whose outer diameter is 5 cm and whose walls are maintained at a temperature of 130°C. Circular aluminum alloy 2024-T6 fins (k = 186 W/m⋅K) of outer diameter 6 cm and constant thi
> A plane wall with surface temperature of 350°C is attached with straight rectangular fins (k = 235 W/m⋅K). The fins are exposed to an ambient air condition of 25°C, and the convection heat transfer coefficient is 1
> A DC motor delivers mechanical power to a rotating stainless steel shaft (k = 15.1 W/m⋅K) with a length of 25 cm and a diameter of 25 mm. In a surrounding with ambient air temperature of 20°C and convection heat transfer coef
> Reconsider Prob. 17–114E. Using appropriate software, investigate the effects of the thermal conductivity of the spoon material and the length of its extension in the air on the temperature difference across the exposed surface of the s
> Consider a stainless steel spoon (k = 8.7 Btu/hâ‹…ft⋅°F)partially immersed in boiling water at 200°F in a kitchen at 75°F. The handle of the spoon has a cross section of 0.08 in Ã&
> A turbine blade made of a metal alloy (k = 17 W/m⋅K) has a length of 5.3 cm, a perimeter of 11 cm, and a cross sectional area of 5.13 cm2. The turbine blade is exposed to hot gas from the combustion chamber at 973°C with a co
> Two very long, slender rods of the same diameter and length are given. One rod (Rod 1) is made of aluminum and has a thermal conductivity k1 = 200 W/mâ‹…K, but the thermal conductivity of Rod 2, k2, is not known. To determine the thermal
> Consider a very long, slender rod. One end of the rod is attached to a base surface maintained at Tb, while the surface of the rod is exposed to an air temperature of 400°C. Thermocouples imbedded in the rod at locations 25 and 120 mm from the
> Consider a very long rectangular fin attached to a flat surface such that the temperature at the end of the fin is essentially that of the surrounding air, i.e., 20°C. Its width is 5.0 cm; thickness is 1.0 mm; thermal conductivity is 200 W/m⋅K; and base
> Reconsider Prob. 3–52E. Using appropriate software, study the effects of the unit cost of energy, the new combustion efficiency on the annual energy, and cost savings. Let the efficiency vary from 0.7 to 0.9, and let the unit cost vary from $12 to $14 pe
> Consider a surface of area A at which the convection and radiation heat transfer coefficients are hconv and hrad, respectively. Explain how you would determine (a) the single equivalent heat transfer coefficient, and (b) the equivalent thermal resistance
> A 4-mm-diameter and 10-cm-long aluminum fin (k = 237 W/mâ‹…K) is attached to a surface. If the heat transfer coefficient is 12 W/m2â‹…K, determine the percent error in the rate of heat transfer from the fin when the infini
> Obtain a relation for the fin efficiency for a fin of constant cross-sectional area Ac, perimeter p, length L, and thermal conductivity k exposed to convection to a medium at T∞ with a heat transfer coefficient h. Assume the fins are sufficiently long so
> Two finned surfaces are identical, except that the convection heat transfer coefficient of one of them is twice that of the other. For which finned surface is the (a) fin effectiveness and (b) fin efficiency higher? Explain.
> Two plate fins of constant rectangular cross section are identical, except that the thickness of one of them is twice the thickness of the other. For which fin is the (a) fin effectiveness and (b) fin efficiency higher? Explain.
> Two pin fins are identical, except that the diameter of one of them is twice the diameter of the other. For which fin is the (a) fin effectiveness and (b) fin efficiency higher? Explain.
> Does the (a) efficiency and (b) effectiveness of a fin increase or decrease as the fin length is increased?
> The heat transfer surface area of a fin is equal to the sum of all surfaces of the fin exposed to the surrounding medium, including the surface area of the fin tip. Under what conditions can we neglect heat transfer from the fin tip?
> Consider two finned surfaces that are identical except that the fins on the first surface are formed by casting or extrusion, whereas they are attached to the second surface afterwards by welding or tight fitting. For which case do you think the fins wil
> Hot water is to be cooled as it flows through the tubes exposed to atmospheric air. Fins are to be attached in order to enhance heat transfer. Would you recommend attaching the fins inside or outside the tubes? Why?
> The steam requirements of a manufacturing facility are being met by a boiler whose rated heat input is 5.5 × 106 Btu/h. The combustion efficiency of the boiler is measured to be 0.7 by a handheld flue gas analyzer. After tuning up the boiler, the combust
> How does the overall effectiveness of a finned surface differ from the effectiveness of a single fin?
> Consider two cold canned drinks, one wrapped in a blanket and the other placed on a table in the same room. Which drink will warm up faster?
> Consider heat conduction through a wall of thickness Land area A. Under what conditions will the temperature distributions in the wall be a straight line?
> Does any of the energy of the sun reach the earth by conduction or convection?
> How does heat conduction differ from convection?
> An electric heater with the total surface area of 0.25 m2 and emissivity 0.75 is in a room where the air has a temperature of 20°C and the walls are at 10°C. When the heater consumes 500 W of electric power, its surface has a steady
> Consider a flat-plate solar collector placed on the roof of a house. The temperatures at the inner and outer surfaces of the glass cover are measured to be 28°C and 25°C, respectively. The glass cover has a surface area of 2.5 m2, a thickness of 0.6 cm,
> A thin metal plate is insulated on the back and exposed to solar radiation on the front surface. The exposed surface of the plate has an absorptivity of 0.7 for solar radiation. If solar radiation is incident on the plate at a rate of 550 W/m2 and the su
> A soldering iron has a cylindrical tip of 2.5 mm in diameter and 20 mm in length. With age and usage, the tip has oxidized and has an emissivity of 0.80. Assuming that the average convection heat transfer coefficient over the soldering iron tip is 25 W/m
> Consider a 3-m × 3-m × 3-m cubical furnace whose top and side surfaces closely approximate black surfaces at a temperature of 1200 K. The base surface has an emissivity of ε = 0.7 and is maintained at 800 K. Determine the net rate of radiation heat trans
> Consider a 2.4-kW hooded electric open burner in an area where the unit costs of electricity and natural gas are $0.10/kWh and $1.20/therm (1 therm = 105,500 kJ), respectively. The efficiency of open burners can be taken to be 73 percent for electric bur
> Consider a person standing in a room maintained at 20°C at all times. The inner surfaces of the walls, floors, and ceiling of the house are observed to be at an average temperature of 12°C in winter and 23°C in summer. Determine the rates of radiation he
> A cylindrical fuel rod 2 cm in diameter is encased in a concentric tube and cooled by water. The fuel generates heat uniformly at a rate of 150 MW/m3. The convection heat transfer coefficient on the fuel rod is 5000 W/m2â‹…K, and the aver
> Consider an electrical wire submerged in liquid water at atmospheric conditions. The wire has a diameter of 1 mm and a length of 15 cm. The current through the wire is increased until the water reaches a temperature of 100°C. For this situatio
> An engine block with a surface area measured to be 0.95 m2 generates a power output of 50 kW with a net engine efficiency of 35 percent. The engine block operates inside a compartment at 157°C, and the average convection heat transfer coefficient is 50
> It is well known that wind makes the cold air feel much colder as a result of the wind-chill effect that is due to an increase in the convection heat transfer coefficient with increasing air velocity. The wind-chill effect is usually expressed in terms o
> Write down the expressions for the physical laws that govern each mode of heat transfer, and identify the variables involved in each relation.
> A 40-cm-long, 800-W electric resistance heating element with diameter 0.5 cm and surface temperature 120°C is immersed in 75 kg of water initially at 20°C. Determine how long it will take for this heater to raise the water temperature to 80°C. Also, dete
> A 0.3-cm-thick, 12-cm-high, and 18-cm-long circuit board houses 80 closely spaced logic chips on one side, each dissipating 0.06 W. The board is impregnated with copper fillings and has an effective thermal conductivity of 16 W/m·K. All the heat generate
> The heat generated in the circuitry on the surface of a silicon chip (k = 130 W/m⋅K) is conducted to the ceramic substrate to which it is attached. The chip is 6 mm × 6 mm in size and 0.5 mm thick and dissipates 3 W of powe
> A cylindrical resistor element on a circuit board dissipates 0.8 W of power. The resistor is 2 cm long and has a diameter of 0.4 cm. Assuming heat to be transferred uniformly from all surfaces, determine (a) the amount of heat this resistor dissipates du
> Can the combined turbine–generator efficiency be greater than either the turbine efficiency or the generator efficiency? Explain.
> The inner and outer surfaces of a 25-cm-thick wall in summer are at 27°C and 44°C, respectively. The outer surface of the wall exchanges heat by radiation with surrounding surfaces at 40°Cand by convection with ambient ai
> The roof of a house consists of a 15-cm-thick concrete slab (k = 2 W/m⋅K) that is 15 m wide and 20 m long. The emissivity of the outer surface of the roof is 0.9, and the convection heat transfer coefficient on that surface is estimated to be 15 W/m2⋅K.
> An AISI 304 stainless steel sheet is going through an annealing process inside an electrically heated oven. The ambient air inside the oven is 600°C, while the surrounding surfaces of the oven are at a uniform temperature of 750°C. If the emissivity of t
> Consider a flat-plate solar collector placed horizontally on the flat roof of a house. The collector is 5 ft wide and 15 ft long, and the average temperature of the exposed surface of the collector is 100°F. The emissivity of the exposed surfa
> A flat-plate solar collector is used to heat water by having water flow through tubes attached at the back of the thin solar absorber plate. The absorber plate has a surface area of 2 m2 with emissivity and absorptivity of 0.9. The surface temperature o
> Solar radiation is incident on a 5-m2 solar absorber plate surface at a rate of 800 W/m2. Ninety three percent of the solar radiation is absorbed by the absorber plate, while the remaining 7 percent is reflected away. The solar absorber plate has a surfa
> What are the mechanisms of heat transfer? How are they distinguished from each other?
> In the metal processing industry, heat treatment of metals is commonly done using electrically heated draw batch furnaces. Consider a furnace that is situated in a room with surrounding air temperature of 30°C and an average convection heat tr
> A 3-m-internal-diameter spherical tank made of 1-cm thick stainless steel is used to store iced water at 0°C. The tank is located outdoors at 25°C. Assuming the entire steel tank to be at 0°C and thus the thermal resistance of the tank to be negligible,

