Question: Prepare a scatter diagram for each of
Prepare a scatter diagram for each of these data sets and then express in words the apparent relationship between the two variables. Put the first variable on the horizontal axis and the second variable on the vertical axis.
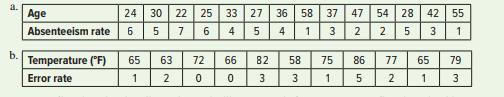
Transcribed Image Text:
a. Age 24 30 22 25 33 27 36 58 37 | 47 54 | 28 42 55 Absenteeism rate 6. 5 7 4 1 2 2 3 1 b. Temperature ("F) 65 63 72 66 82 58 75 86 77 65 79 Error rate 1 3 1. 3
> Use the dimensions of quality to describe typical characteristics of these products and services: a. A television set b. A restaurant meal (product) c. A restaurant meal (service) d. Painting a house e. Surgery and post surgery care
> What are some possible consequences of poor quality?
> Name several ways that technology has had an impact on quality.
> As a manager, how would you deal with the possibility that customer satisfaction does not always lead to customer retention?
> A bakery buys flour in 25-pound bags. The bakery uses 1,215 bags a year. Ordering cost is $10 per order. Annual carrying cost is $75 per bag. a. Determine the economic order quantity. b. What is the average number of bags on hand? c. How many orders per
> Suppose you are going to have a prescription filled at a local pharmacy. Referring to the dimensions of service quality for each dimension, give an example of how you would judge the quality of the service.
> A shop works a 400-minute day. The manager of the shop wants an output of 200 units per day for the assembly line that has the elemental tasks shown in the table. Do the following: a. Construct the precedence diagram. b. Assign tasks according to the mos
> A small grocery store sells fresh produce, which it obtains from a local farmer. During the strawberry season, demand for fresh strawberries can be reasonably approximated using a normal distribution with a mean of 40 quarts per day and a standard deviat
> Skinner’s Fish Market buys fresh Boston bluefish daily for $4.20 per pound and sells it for $5.70 per pound. At the end of each business day, any remaining bluefish is sold to a producer of cat food for $2.40 per pound. Daily demand can be approximated b
> A public utility intends to buy a turbine as part of an expansion plan and must now decide on the number of spare parts to order. One part, no. X135, can be purchased for $100 each. Carrying and disposal costs are estimated to be 145 percent of the purch
> Demand for jelly doughnuts on Saturdays at Don’s Doughnut Shoppe is shown in the following table. Determine the optimal number of doughnuts, in dozens, to stock if labor, materials, and overhead are estimated to be $3.20 per dozen, doug
> Given the following list of items, a. Classify the items as A, B, or C. b. Determine the economic order quantity for each item (round to the nearest whole unit). Holding Cost Estimated Annual Unit Ordering Cost Item Demand (%) Price H4-010 20,000 50
> A manager must set up inventory ordering systems for two new production items, P34 and P35. P34 can be ordered at any time, but P35 can be ordered only once every four weeks. The company operates 50 weeks a year, and the weekly usage rates for both items
> A drugstore uses fixed-order cycles for many of the items it stocks. The manager wants a service level of .98. The order interval is 14 days, and lead time is 2 days. Average demand for one item is 40 units per day, and the standard deviation of demand i
> Caring Hospital’s dispensary reorders doses of a drug when the supply on hand falls to 18 units. Lead time for resupply is three days. Given the typical usage over the last 10 days, what service level is achieved with the hospitalâ
> A service station uses 1,200 cases of oil a year. Ordering cost is $40, and annual carrying cost is $3 per case. The station owner has specified a service level of 99 percent. a. What is the optimal order quantity? b. What level of safety stock is approp
> The county sheriff’s department responded to an unusually large number of vehicular accidents along a quarter-mile stretch of highway in recent months. Prepare a cause-and-effect diagram for this problem.
> Regional Supermarket is open 360 days per year. Daily use of cash register tape averages 10 rolls. Usage appears normally distributed with a standard deviation of 2 rolls per day. The cost of ordering tape is $1, and carrying costs are 40 cents per roll
> For the given set of tasks, do the following: a. Develop the precedence diagram. b. Determine the minimum cycle time and then calculate the cycle time for a desired output of 500 units in a seven-hour day. Why might a manager use a cycle time of 50 secon
> Ned’s Natural Foods sells unshelled peanuts by the pound. Historically, Ned has observed that daily demand is normally distributed with a mean of 80 pounds and a standard deviation of 10 pounds. Lead time also appears normally distributed with a mean of
> A small copy center uses five 500-sheet boxes of copy paper a week. Experience suggests that usage can be well approximated by a normal distribution with a mean of five boxes per week and a standard deviation of one-half box per week. Two weeks are requi
> The manager of a car wash received a revised price list from the vendor who supplies soap, and a promise of a shorter lead time for deliveries. Formerly the lead time was four days, but now the vendor promises a reduction of 25 percent in that time. Annu
> One item a computer store sells is supplied by a vendor who handles only that item. Demand for that item recently changed, and the store manager must determine when to replenish it. The manager wants a probability of at least 96 percent of not having a s
> A company uses 85 circuit boards a day in a manufacturing process. The person who orders the boards follows this rule: Order when the amount on hand drops to 625 boards. Orders are delivered approximately six days after being placed. The delivery time is
> The injection molding department of a company uses an average of 30 gallons of special lubricant a day. The supply of the lubricant is replenished when the amount on hand is 170 gallons. It takes four days for an order to be delivered. Safety stock is 50
> Demand for walnut fudge ice cream at the Sweet Cream Dairy can be approximated by a normal distribution with a mean of 21 gallons per week and a standard deviation of 3.5 gallons per week. The new manager desires a service level of 90 percent. Lead time
> . Given this information: Lead-time demand = 600 pounds Standard deviation of lead time demand = 52 pounds (Assume normality.) Acceptable stockout risk during lead time = 4 percent a. What amount of safety stock is appropriate? b. When should this ite
> College students trying to register for a course sometimes find that the course has been closed, or the section they want has been closed. Prepare a cause-and-effect diagram for this problem.
> Given this information: Expected demand during lead time = 300 units Standard deviation of lead time demand = 30 units Determine each of the following, assuming that lead time demand is distributed normally: a. The ROP that will provide a risk of sto
> A newspaper publisher uses roughly 800 feet of baling wire each day to secure bundles of newspapers while they are being distributed to carriers. The paper is published Monday through Saturday. Lead time is six workdays. What is the appropriate reorder p
> Explain the consequences of task time variability on line balancing.
> A manager just received a new price list from a supplier. It will now cost $1.00 a box for order quantities of 801 or more boxes, $1.10 a box for 200 to 800 boxes, and $1.20 a box for smaller quantities. Ordering cost is $80 per order and carrying costs
> A company will begin stocking remote control devices. Expected monthly demand is 800 units. The controllers can be purchased from either supplier A or supplier B. Their price lists are as follows: Ordering cost is $40 and annual holding cost is 25 perc
> A manufacturer of exercise equipment purchases the pulley section of the equipment from a supplier who lists these prices: less than 1,000, $5 each; 1,000 to 3,999, $4.95 each; 4,000 to 5,999, $4.90 each; and 6,000 or more, $4.85 each. Ordering costs are
> A jewelry firm buys semiprecious stones to make bracelets and rings. The supplier quotes a price of $8 per stone for quantities of 600 stones or more, $9 per stone for orders of 400 to 599 stones, and $10 per stone for lesser quantities. The jewelry firm
> A mail-order house uses 18,000 boxes a year. Carrying costs are 60 cents per box a year, and ordering costs are $96. The following price schedule applies. Determine the following: a. The optimal order quantity b. The number of orders per year Number of
> A company manufactures hair dryers. It buys some of the components, but it makes the heating element, which it can produce at the rate of 800 per day. Hair dryers are assembled daily, 250 days a year, at a rate of 300 per day. Because of the disparity be
> A company is about to begin production of a new product. The manager of the department that will produce one of the components for the product wants to know how often the machine used to produce the item will be available for other work. The machine will
> Prepare a flowchart that describes going to the library to study for an exam. Your flowchart should include these items: finding a place at the library to study; checking to see if you have your book, paper, highlighter, and so forth; traveling to the li
> A chemical firm produces sodium bisulfate in 100-pound bags. Demand for this product is 20 tons per day. The capacity for producing the product is 50 tons per day. Setup costs $100, and storage and handling costs are $5 per ton a year. The firm operates
> The Friendly Sausage Factory (FSF) can produce hot dogs at a rate of 5,000 per day. FSF supplies hot dogs to local restaurants at a steady rate of 250 per day. The cost to prepare the equipment for producing hot dogs is $66. Annual holding costs are 45 c
> A food processor uses approximately 27,000 glass jars a month for its fruit juice product. Because of storage limitations, a lot size of 4,000 jars has been used. Monthly holding cost is 18 cents per jar, and reordering cost is $60 per order. The company
> Twelve tasks, with times and precedence requirements as shown in the following table, are to be assigned to workstations using a cycle time of 1.5 minutes. Two heuristic rules will be tried: (1)Â greatest positional weight, and (2) most follow
> A manager receives a forecast for next year. Demand is projected to be 600 units for the first half of the year and 900 units for the second half. The monthly holding cost is $2 per unit, and it costs an estimated $55 to process an order. a. Assuming tha
> A produce distributor uses 800 packing crates a month, which it purchases at a cost of $10 each. The manager has assigned an annual carrying cost of 35 percent of the purchase price per crate. Ordering costs are $28. Currently the manager orders once a m
> Bruegger’s maintains relatively little inventory at either its plants or its retail stores. List the benefits and risks of this policy.
> Bruegger’s has bagel-making machines at its plants. Another possibility would be to have a bagel-making machine at each store. What advantages does each alternative have?
> Quality is very important to Bruegger’s. a. What features of bagels do customers look at to judge their quality? b. At what points in the production process do workers check bagel quality? c. List the steps in the production process, beginning with purch
> How can managers use the results of A-B-C classification?
> Why might it be inappropriate to use inventory turnover ratios to compare inventory performance of companies that are in different industries?
> What potential benefits and risks do RFID tags have for inventory management?
> Briefly describe each of the costs associated with inventory.
> What are the requirements for effective inventory management?
> As part of a major plant renovation project, the industrial engineering department has been asked to balance a revised assembly operation to achieve an output of 240 units per eight-hour day. Task times and precedence relationships are as follows: Do e
> What are some ways in which a company can reduce the need for inventories?
> What is the single-period model, and under what circumstances is it appropriate?
> Explain how a decrease in setup time can lead to a decrease in the average amount of inventory a firm holds, and why that would be beneficial.
> The purchasing agent for a company that assembles and sells air-conditioning equipment in a Latin American country noted that the cost of compressors has increased significantly each time they have been reordered. The company uses an EOQ model to determi
> Describe briefly the A-B-C approach to inventory control.
> Prepare a cause-and-effect diagram to analyze why a machine has produced a large run of defective parts.
> What is meant by the term service level? Generally speaking, how is service level related to the amount of safety stock held?
> Under what circumstances would the amount of safety stock held be large? Small? Zero?
> a. List the major assumptions of the EOQ model. b. How would you respond to the criticism that EOQ models tend to provide misleading results because values of D, S, and H are, at best, educated guesses?
> As a supermarket manager, how would you go about evaluating the criticalness of an inventory shortage?
> To be competitive, many fast-food chains began to expand their menus to include a wider range of foods. Although contributing to competitiveness, this has added to the complexity of operations, including inventory management. Specifically, in what ways d
> Name some ways that a layout can help or hinder productivity.
> Sam is at the post office to mail a package. After he pays for mailing the package, the clerk asks if he would like to buy some stamps. Sam pauses to think before he answers. He doesn’t have a credit card with him. After paying for the package, he has ab
> UPD Manufacturing produces a range of health care appliances for hospital as well as for home use. The company has experienced a steady demand for its products, which are highly regarded in the health care field. Recently the company has undertaken a rev
> Would you recommend changing to the optimal order interval? Explain.
> Describe the importance of inventory management as it relates to the Farmers Restaurant.
> List and briefly explain: a. The dimensions of service quality b. The determinants of quality
> The supplier Kristin uses is located in Ohio. Why might Kristin consider dealing with a nearby supplier instead of the one in Ohio? What reasons might there be for not switching suppliers?
> Given the above information and an on-hand inventory of 12, determine the risk of stock out at the end of initial lead time and at the end of the second lead time. The lead time is 2 days and orders are placed once a week.
> Given the following information, provide an example of how much of Farmers Sausage Gravy Mix should be ordered. You are doing the order for Thursday. Also, Kristin would like a service level of 95 percent, and you have found that there is a standard devi
> What general trade-offs are involved in master scheduling in terms of the frozen portion of the schedule?
> How has technology had an impact on master scheduling?
> Who needs to interface with the master schedule and why?
> According to a study by the Alliance of American Insurers, it costs more than three times the original purchase price in parts and labor to reconstruct a wrecked Chevrolet. Explain the reasons for this large discrepancy in terms of the processes used to
> a. Given the following forecast and steady regular output of 550 every month, what total cost would result if overtime is limited to a maximum of 40 units a month, and subcontracting is limited to a maximum of 10 units a month? Unit costs are: Regular ou
> Determine the total cost for this plan given the following forecast: Use steady regular output of 400 units per month, use overtime as needed for up to 40 units per month, and use subcontracting to make up any needed output to match the forecast. Unit
> A manager would like to know the total cost of a chase strategy that matches the forecast below using a steady regular production rate of 200 units a month, a maximum of 20 units per month of overtime, and subcontracting as needed to make up any shortage
> What are the main advantages of a product layout? The main disadvantages?
> Compute the total cost for each aggregate plan using these unit costs: Regular output = $40 Overtime = $50 Subcontract = $60 Average Balance Inventory = $10 c. (Refer to part b.) After complaints from some workers about working overtime every month du
> Prepare a schedule like that shown in Figure 11.12 for the following situation: The forecast is 80 units for each of the first two periods and 60 units for each of the next three periods. The starting inventory is 20 units. The company uses a chase strat
> Determine the available-to-promise (ATP) quantities for each period for Problem 21.
> Prepare a master schedule like that shown in Figure 11.11 given this information: The forecast for each week of an eight-week schedule is 50 units. The MPS rule is to schedule production if the projected on-hand inventory would be negative without it. Cu
> Update the master schedule shown in Figure 11.11 given these updated inputs: It is now the end of week 1; customer orders are 25 for week 2, 16 for week 3, 11 for week 4, 8 for week 5, and 3 for week 6. Use the MPS rule of ordering production when projec
> Prepare a master production schedule for industrial pumps in the manner of Figure 11.11 in the chapter. Use the same inputs as the example, and lot sizes of 70, but change the MPS rule from “schedule production when the projected on-hand inventory would
> Dundas Bike Components Inc. of Wheelville, Illinois, manufactures bicycle wheels in two different sizes for the Big Bike Co. assembly plant located across town. David Dundas, the firm’s owner-manager, has just received Big Bikeâ&#
> What improvements can you suggest for the plant?
> Layout decisions affect a wide range of facilities, from factories, supermarkets, offices, department stores, and warehouses, to malls, parking lots and garages, and kitchens. Layout is also important in the design of some products such as the interiors
> Solve Problem 16 using an inventory carrying cost of $2 per unit per period.
> Select four tools and describe how they could be used for process improvement.
> Refer to Example 3. Suppose that regular-time capacity will be reduced to 440 units in period 3 to accommodate a companywide safety inspection of equipment. What will the additional cost of the optimal plan be as compared to the one shown in Example 3? A
> Suppose that an increase in warehousing costs and other costs brings inventory carrying costs to $2 per unit per month. All other costs and quantities remain the same. Determine a revised solution to this transportation problem. Solve by modifying Table
> Verify the transportation solution shown in Example 3.
> Refer to Example 2. Determine if a plan to use subcontracting at a maximum rate of 50 units per period as needed with no overtime would achieve a lower total cost than the plan shown in Example 2. Again, plan for a zero inventory balance at the end of pe
> Prepare an aggregate plan that uses overtime ($9 per unit, maximum output 25 units per period) and inventory variation. Try to minimize backlogs. The ending inventory in period 9 should be zero, and the limit on backlogs is 60 units per period. Compute t
> Suppose another option is to use part-time workers to assist during seasonal peaks. The cost per unit, including hiring and training, is $11. The output rate is 10 units per worker per period for all workers. A maximum of 10 part-time workers can be used
> Refer to Solved Problem 1. Prepare two additional aggregate plans. Call the one in the solved problem plan A. For plan B, hire one more worker at a cost of $200. Make up any shortfall using subcontracting at $8 per unit, with a maximum of 20 units per pe

