Question: Prepare an income statement for Rex Manufacturing
Prepare an income statement for Rex Manufacturing for the year ended December 31 using the following information. Hint: Not all information given is needed for the solution.
> Zulu sells its waterproof phone case for $90 per unit. Fixed costs total $200,000, and variable costs are $40 per unit. (a) Compute its break-even in units. (b) Will the break-even point in units increase or decrease in response to each of the following
> Refer to the CVP chart in QS 21-14 and solve for each of the items below. 1. Units produced at break-even point 2. Dollar sales at break-even point 3. Capacity in units is there a profit or a loss? 4. Are fixed costs greater than $10,000? 5. If 1
> Match the descriptions 1 through 5 with labels a through e on the CVP chart. 1. Break-even point 2. Total sales line 3. Loss area 4. Profit area 5. Total costs line
> Coors Company expects sales of $340,000 (4,000 units at $85 per unit). The company’s total fixed costs are $175,000 and its variable costs are $35 per unit. Compute (a) break-even in units and (b) the margin of safety in dollars.
> Solve for the missing amounts a through d for the following separate cases.
> Listed here are three separate series of costs measured at various volume levels. Examine each series and identify whether it is best described as a fixed, variable, or step-wise cost. Hint: It can help to graph each cost series.
> Zia Co. makes flowerpots from recycled plastic in two departments, Molding and Packaging. Zia uses the weighted average method, and units completed in the Molding department are transferred to the Packaging department. Production unit information for the
> Refer to the information in QS 20-8. (a) Compute the number of units started and completed this period. (b) Compute the total equivalent units of production for conversion. The company uses the FIFO method.
> An ice cream maker reports the following. Compute the total equivalent units of production for conversion. The company uses the weighted average method.
> Google uses variable costing for several business decisions. How can variable costing income be converted to absorption costing income?
> A production department reports the following conversion costs. Equivalent units of production for conversion total 450,000 units this period. Calculate the cost per equivalent unit of production for conversion. The company uses the weighted average meth
> A process manufacturer reports the following. Compute the total equivalent units of production for conversion. The company uses the weighted average method.
> Prepare a physical unit flow reconciliation with the following information.
> For each of the following products and services, indicate whether it is more likely produced in a process operation or a job order operation.
> Label each statement below as either true or false. 1. Cost per unit is computed by combining costs per unit across separate processes. 2. Service companies cannot use process costing. 3. Costs per job are computed in both job order and process costing s
> For the current period, an ice cream producer added raw materials to production that should have produced 50,000 gallons of ice cream. Actual production was 47,000 gallons of (non defective) ice cream. Compute the yield for this production process. Expre
> Trident Bikes uses a hybrid costing system and reports the following for its motorcycle assembly process. a. Compute the cost per unit for the Mega option. b. If the company has a target markup of 20% above cost, compute the selling price per unit for th
> Cool Scoops makes ice cream in two processes, Mixing and Packaging. During April, its first month of business, the packaging department transferred 50,000 units and $175,000 of production costs to finished goods. The company completed and sold 48,000 uni
> Prepare journal entries to record the following production activities for Hot wax. a. Requisitioned $9,000 of indirect materials for use in production of surfboard wax. b. Incurred $156,000 in actual other overhead costs (paid in cash). c. Applied overhe
> Prepare journal entries to record the following production activities for Hotwax. a. Incurred $75,000 of direct labor in its Mixing department and $50,000 of direct labor in its Shaping department. Hint: Credit Factory Wages Payable. b. Incurred indirect
> Apple produces tablet computers. Identify some of the variable and fixed product costs associated with that production. Hint: Limit costs to product costs.
> Refer to the information in QS 20-21. Using the FIFO method, assign direct materials costs to the Roasting department’s output—specifically, to the units completed and transferred out to the Mixing department and to the units that remain in work in proce
> BOGO Inc. has two sequential processing departments, Roasting and Mixing. BOGO uses the FIFO method. Production unit information for the Roasting department follows. Production cost information for the Roasting department for the same period follows. Com
> Azule Co. manufactures in two sequential processes, Cutting and Binding. The two processes report the information below for a recent month. Determine the ending balances in the Work in Process Inventory accounts for Cutting and for Binding. Hint: Set up
> For each of the following products and services, indicate whether it is more likely produced in a process operation or in a job order operation.
> At the beginning of the year, a company estimates total overhead costs of $560,000. The company applies overhead using machine hours and estimates it will use 1,400 machine hours during the year. What amount of overhead should be applied to Job 65A if t
> A company estimates the following manufacturing costs at the beginning of the period: direct labor, $468,000; direct materials, $390,000; and factory overhead, $117,000. Compute its predetermined overhead rate as a percent of (1) direct labor and (2) dir
> A company that uses job order costing incurred a monthly factory payroll of $180,000. Of this amount, $30,000 is indirect labor and $150,000 is direct labor. Prepare journal entries to record the (a) use of direct labor and (b) use of indirect labor.
> A company that uses job order costing purchases $50,000 in raw materials for cash. It then uses $12,000 of raw materials as indirect materials and uses $32,000 of raw materials as direct materials. Prepare journal entries to record the (a) purchase of ra
> The following partial job cost sheet is for a job lot of 2,500 units completed. 1. What is the total cost of this job lot? 2. What is the total cost per unit completed?
> Eco Skate makes skateboards from recycled plastic. For a recent job lot of 100 skateboards, the company incurred direct materials costs of $600 and direct labor costs of $200. Factory overhead applied to this job is $900. (1) What is the total manufactur
> What is the degree of operating leverage? How is it computed?
> Auto Safe’s job cost sheet for Job A40 shows that the total cost to add security features to a car was $10,500. The car was delivered to the customer, who paid $14,900 cash for this job. Prepare the journal entries for Job A40 to record (a) its completio
> A manufacturer reports sales of $80,000 and cost of goods sold of $60,000. 1. Compute its gross profit ratio. 2. If competitors average a 10% gross profit ratio, does this manufacturer compare favorably or unfavorably to its peers?
> Indicate whether each item a through e is a feature of a job order or process operation.
> A marketing agency used 60 hours of direct labor in creating advertising for a film festival. Direct labor costs $50 per hour. The agency applies overhead at a rate of $40 per direct labor hour. 1. What is the total estimated cost for this job? 2. If t
> Custom Co. reports the following (partial) T-account activity at the end of its first year of operations. 1. Compute the under- or over applied overhead for the year. 2. Prepare the journal entry to close Factory Overhead to Cost of Goods Sold.
> Raze Co. reports the following (partial) T-account activity at the end of its first year of operations. 1. Compute the under- or over applied overhead for the year. 2. Prepare the journal entry to close Factory Overhead to Cost of Goods Sold.
> A company applies overhead at a rate of 150% of direct labor cost. Actual overhead cost for the current period is $950,000, and direct labor cost is $600,000. 1. Compute the under- or over applied overhead. 2. Prepare the journal entry to close over- o
> Shin Co. reports the costs incurred below for the month ended May 31. The company has no beginning Work in Process Inventory. Overhead is applied using a predetermined overhead rate of 120% of direct materials costs. Job 4 was completed and Job 5 is stil
> A company that uses job order costing reports the costs incurred below. Overhead is applied at the rate of 60% of direct materials cost. The company has no beginning Work in Process or Finished Goods inventories. Jobs 1 and 3 are not finished by the end
> Built-Tate uses job order costing. The T-account below summarizes Factory Overhead activity for the current year. 1. Compute total applied overhead cost. 2. Compute total actual overhead cost. 3. Compute the under applied or over applied overhead.
> What important assumption underlies multiproduct CVP analysis?
> A custom manufacturer completed Jobs 103 and 104. Job 103 cost $12,000 and was sold (on credit) for $20,000. Job 104 cost $15,000. Prepare journal entries to record (a) the completion of both jobs, (b) the sale of Job 103, and (c) cost of goods sold for
> A manufacturer incurred the following actual factory overhead costs: indirect materials, $6,200; indirect labor (factory wages payable), $9,000; depreciation on factory equipment, $12,000; factory utilities (utilities payable), $800; and factory insuranc
> Ace Patios applies overhead using direct labor hours as its activity base. At the beginning of the year, the company estimates total direct labor hours of 20,000 and total overhead costs of $600,000 for the year. 1. Determine the company’s predetermined
> Indicate which of the following are most likely to be considered as a job and which as a job lot.
> Garcia Company reports beginning raw materials inventory of $855 and ending raw materials inventory of $717. If the company purchased $3,646 of raw materials during the month, what is the amount of materials used during the month? Note: Assume all raw ma
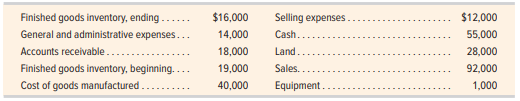
> Prepare the current assets section of the balance sheet at December 31 for Bin Manufacturing using the following information. Hint: Not all information given is needed for the solution.
> Determine the missing amount for each separate situation involving inventory cost flows.
> Compute cost of goods sold using the following information.
> Compute ending work in process inventory for a manufacturer using the following information.
> Why are fixed costs shown as a horizontal line on a CVP chart?
> A company manufactures guitars. Identify each of the following costs as either a prime cost, a conversion cost, or both. 1. Wood used to build the guitar body. 2. Glue used to bind the guitar wood. 3. Wages paid to assembly workers. 4. Depreciation on fa
> Classify each of the following costs as either a product cost or a period cost for a manufacturer. 1. Factory insurance. 2. Sales commissions. 3. Depreciation on factory equipment. 4. Depreciation on office equipment. 5. Rent on factory building. 6. Tax
> Sims Company reports beginning raw materials inventory of $900 and ending raw materials inventory of $1,100. Assume the company purchased $5,200 of raw materials and used $5,000 of raw materials during the year. Compute raw materials inventory turnover (
> A company reports cost of goods manufactured of $918,700 and cost of goods sold of $955,448. Compute the average manufacturing cost per unit assuming 18,374 units were produced.
> Determine the missing amount for each separate situation involving work in process cost flows.
> Refer to the data in Quick Study 18-16. Factory overhead of $39,000 consists of Indirect labor of $20,000, Depreciation expense—Factory of $15,000, and Factory utilities of $4,000. a. Compute total manufacturing costs. b. Prepare a schedule of cost of g
> Prepare the schedule of cost of goods manufactured for Barton Company using the following information for the year ended December 31.
> Determine the missing amount for each separate situation involving manufacturing costs.
> A company manufactures tennis balls. Classify each of the following costs as either direct materials, direct labor, or factory overhead. 1. Rubber used to form the cores. 2. Factory maintenance. 3. Wages paid to assembly workers. 4. Glue used in binding
> We are evaluating whether or not to invest in a company. Indicate whether each of the following separate trends would make us more or less likely to invest. a. Return on equity is increasing, from 19% to 24%. b. Days’ sales in inventory is increasing, fr
> CVP analysis relies on what four assumptions?
> We are evaluating whether or not to make a loan to a company. Indicate whether each of the following separate trends would make us more or less likely to make the loan. a. Current ratio is increasing, from 0.8 to 1.3. b. Acid-test ratio is increasing, fr
> Refer to the information in QS 17-7. Determine the prior year and current year common-size percent’s for cost of goods sold using net sales as the base.
> Use the following information to determine the prior year and current year trend percent’s for net sales using the prior year as the base year.
> Express the items from QS 17-5 in common-size percent’s.
> Financial data from three competitors in the same industry follow. 1. Rank the three companies from high to low on cash from operating activities. 2. Which company has the largest cash outflow for investing activities? 3. Which company has the largest ca
> Use the following information for VPI Co. to prepare a statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31 using the indirect method.
> Refer to the data in QS 16-7. 1. Assume that all common stock is issued for cash. What amount of cash dividends is paid during 2021? 2. Assume that no additional notes payable are issued in 2021. What cash amount is paid to reduce the notes payable balan
> Refer to the data in QS 16-7. Furniture costing $55,000 is sold at its book value in 2021. Acquisitions of furniture total $45,000 cash, on which no depreciation is necessary because it is acquired at year-end. What is the cash inflow from the sale of fu
> Refer to the balance sheet data in QS 16-10 from Anders Company. During 2021, a building with a book value of $70,000 and an original cost of $300,000 was sold at a gain of $60,000. 1. How much cash did Anders receive from the sale of the building? 2. Ho
> The plant assets section of the comparative balance sheets of Anders Company is reported below. Refer to the balance sheet data above from Anders Company. During 2021, equipment with a book value of $40,000 and an original cost of $210,000 was sold at a
> What is the relevant range of operations? How is it important in CVP analysis?
> Data below are from recent annual reports for Apple and Google. Required 1. Compute revenue per employee for both Apple and Google for the current year .Round answers to the nearest dollar. 2. Using revenue per employee from part 1, which companyâ
> The following information is from Ellerbe Company’s comparative balance sheets. The current-year income statement reports depreciation expense on furniture of $18,000. During the year, furniture costing $52,500 was sold for its book val
> Use the indirect method to prepare the operating activities section of Cruz’s statement of cash flows.
> Refer to the data in QS 16-7. Use the direct method to prepare the operating activities section of Cruz’s statement of cash flows.
> Refer to the data in QS 16-7. 1. How much cash is paid to acquire inventory during year 2021? 2. How much cash is paid for operating expenses (excluding depreciation) during year 2021? Hint: Examine prepaid expenses and wages payable.
> Refer to the data in QS 16-7. 1. How much cash is received from sales to customers for year 2021? 2. What is the net increase or decrease in the Cash account for year 2021?
> Use the following information to determine cash flows from operating activities using the indirect method.
> On January 1, $50,000 cash is borrowed from a bank in return for a 6% installment note with 24 monthly payments of $2,216 each. Prepare the journal entry to record (1) the issuance of the note and (2) the first monthly interest payment.
> Madrid Company plans to issue 8% bonds with a par value of $4,000,000. The company sells $3,600,000 of the bonds at par on January 1. The remaining $400,000 sells at par on July 1. The bonds pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. 1. Record
> Identify whether stockholders’ equity would increase, decrease, or have no effect as a result of each separate transaction listed below. 1. A stock dividend equal to 30% of the previously outstanding shares is declared. 2. New shares of common stock are
> Anthem Co. has 100,000 shares authorized, 90,000 shares issued, and 20,000 shares of treasury stock. Determine the number of shares outstanding.
> Identify two ways in which a contribution margin income statement differs in format from a traditional income statement.
> For each transaction, determine the impact—increase, decrease, or no effect—on total assets, total liabilities, and total equity.
> Use the information in QS 13-13 to compute the dividends paid each year to each of the two classes of stockholders assuming that the preferred stock is cumulative.
> Green Planet Corp. has 5,000 shares of noncumulative 10% preferred stock with a $2 par value and 17,000 shares of common stock with a $0.01 par value. During its first two years of operation, Green Planet declared and paid the following total cash divide
> For each of the following statements regarding dividends, indicate whether it is true or false. 1. Cash and stock dividends reduce retained earnings. 2. Dividends payable is recorded at the time a cash dividend is declared. 3. The date of record is the d
> Belkin Inc. has 100,000 shares of $3 par value common stock outstanding. Belkin declares a 40% stock dividend on March 2 when the stock’s market value is $72 per share. Prepare the journal entry for declaration of the stock dividend.
> Epic Inc. has 10,000 shares of $2 par value common stock outstanding. Epic declares a 5% stock dividend on July 1 when the stock’s market value is $8 per share. The stock dividend is distributed on July 20. Prepare journal entries for (a) declaration and
> On January 1, Payson Inc. had a retained earnings balance of $20,000. During the year, Payson reported net income of $30,000 and paid cash dividends of $17,000. Calculate the retained earnings balance at its December 31 year-end.
> On December 31, West world Inc. has the following equity accounts and balances. Prepare the stockholders’ equity section of West world’s balance sheet.
> Identify which of the following statements are true for the corporate form of organization. 1. Ownership rights cannot be easily transferred. 2. Owners have unlimited liability for corporate debts. 3. Capital is more easily accumulated than with most oth
> Field, Brown & Snow are partners and share income and losses equally. The partners decide to liquidate the partnership when their capital balances are as follows: Field, $131,250; Brown, $165,000; and Snow, $153,750. On May 31, the liquidation resulted i
> What four inputs are needed in cost-volume-profit analysis?
> Camila, Danni, and Olivia are members of an LLC and share net income and loss equally. Olivia withdraws from the business when equity for each member is Camila, $18,000; Danni, $5,000; and Olivia, $7,000. Olivia is paid $10,000 for her equity in the LLC.
> Lopez, Cruz, and Perez are partners and share net income and loss in a 6:4:1 ratio (in ratio form: Lopez, 6⁄11; Cruz, 4⁄11; and Perez, 1⁄11). On December 31, Perez withdraws from the partnership when the equities of the partners are Lopez, $3,000; Cruz,

