Question: Ramrod Manufacturing acquired all the assets and
Ramrod Manufacturing acquired all the assets and liabilities of Stafford Industries on January 1, 20X2, in exchange for 4,000 shares of Ramrod’s $20 par value common stock. Balance sheet data for both companies just before the merger are given as follows:
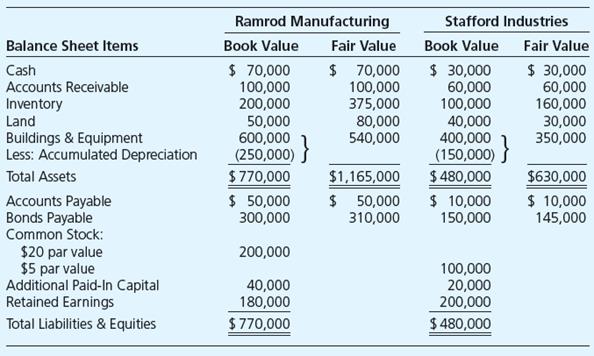
Ramrod shares were selling for $150 on the date of acquisition.
Required
Prepare the following:
a. Journal entries to record the acquisition on Ramrod’s books.
b. A balance sheet for the combined enterprise immediately following the business combination.
Transcribed Image Text:
Ramrod Manufacturing Stafford Industries Balance Sheet Items Book Value Fair Value Book Value Fair Value $ 70,000 100,000 200,000 50,000 600,000 (250,000) $770,000 $ 50,000 300,000 $ 70,000 100,000 375,000 80,000 540,000 $ 30,000 60,000 100,000 40,000 400,000 (150,000) } $ 480,000 $ 10,000 150,000 $ 30,000 60,000 160,000 30,000 350,000 Cash Accounts Receivable Inventory Land Buildings & Equipment Less: Accumulated Depreciation } Total Assets $1,165,000 $630,000 Accounts Payable Bonds Payable Common Stock: $ 50,000 310,000 $ 10,000 145,000 $20 par value $5 par value Additional Paid-In Capital Retained Earnings 200,000 40,000 180,000 $ 770,000 100,000 20,000 200,000 $ 480,000 Total Liabilities & Equities
> How is the receipt of a dividend recorded under the equity method? Under the cost method?
> How is the amount reported as consolidated retained earnings determined?
> Give a definition of consolidated retained earnings.
> What effect does a liquidating dividend have on the balance in the investment account under the cost method and the equity method?
> How is consolidated net income computed in a consolidation worksheet?
> How are a subsidiary’s dividend declarations reported in the consolidated retained earnings statement?
> From the point of view of an investor in common stock, what is a liquidating dividend?
> Describe an investor’s treatment of an investee’s prior-period dividends and earnings when the investor acquires significant influence through a purchase of additional stock.
> When will the balance in the intercorporate investment account be the same under the cost method and the equity method?
> When is equity-method reporting considered inappropriate even though sufficient common shares are owned to allow the exercise of significant influence?
> How is the ability to significantly influence the operating and financial policies of a company normally demonstrated?
> Which of the following is the appropriate basis for valuing fixed assets acquired in a business combination carried out by exchanging cash for common stock? a. Historical cost. b. Book value. c. Cost plus any excess of purchase price over book value of
> What types of investments in common stock normally are accounted for using (a) the equity method and (b) the cost method?
> Why is the beginning retained earnings balance for each company entered in the three-part consolidation worksheet rather than just the ending balance?
> A type of acquisition that was not discussed in the chapter is the leveraged buyout. Many experts argue that a leveraged buyout (LBO) is not a type of business combination but rather just a restructuring of ownership. Yet some would see an LBO as having
> Amazing Chemical Corporation’s president had always wanted his own yacht and crew and concluded that Amazing Chemical should diversify its investments by purchasing an existing boatyard and repair facility on the lakeshore near his summer home. He could
> Prime Company has been expanding rapidly and is now an extremely diversified company for its size. It currently owns three companies with manufacturing facilities, two companies primarily in retail sales, a consumer finance company, and two natural gas p
> At a recent staff meeting, the vice president of marketing appeared confused. The controller had assured him that the parent company and each of the subsidiary companies had properly accounted for all transactions during the year. After several other que
> Forth Company owned 85,000 of Brown Company’s 100,000 shares of common stock until January 1, 20X2, at which time it sold 70,000 of the shares to a group of seven investors, each of whom purchased 10,000 shares. On December 3, 20X2, Forth received a divi
> Most Company purchased 90 percent of the voting common stock of Port Company on January 1, 20X4, and 15 percent of the voting common stock of Adams Company on July 1, 20X4. In preparing the financial statements for Most Company at December 31, 20X4, you
> When does a noncontrolling interest arise in a business combination?
> Which of the costs incurred in completing a business combination are capitalized under the acquisition method?
> Arthur Levitt’s speech, “The Numbers Game,” is available on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov/ news/speech/speecharchive/1998/spch220.txt . Read the speech, and then answer the following questions. a. Briefly explain what motivations Levitt discusses for
> How is the amount of additional paid-in capital determined when recording a business combination?
> What is the maximum balance in retained earnings that can be reported by the combined entity immediately following a business combination?
> When a business combination occurs after the beginning of the year, the income earned by the acquired company between the beginning of the year and the date of combination is excluded from the net income reported by the combined entity for the year. Why?
> What impact does the level of ownership have on the amount of goodwill reported under the acquisition method?
> How is the amount reported as goodwill determined under the acquisition method?
> Describe each of the three legal forms that a business combination might take.
> Why did companies such as Enron find the use of special-purpose entities to be advantageous?
> How would the decision to dispose of a segment of operations using a split-off rather than a spin-off impact the financial statements of the company making the distribution?
> What types of circumstances would encourage management to establish a complex organizational structure?
> P Company reports its 10,000 shares of S Company at $40 per share. P Company then purchases an additional 60,000 shares of S Company for $65 each and gains control of S Company. What must be done with respect to the valuation of the shares previously own
> Not all business combinations are successful, and many entail substantial risk. Acquiring another company may involve a number of different types of risk. Obtain a copy of the 10-K report for Google Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2006, available at
> Within the measurement period following a business combination, the acquisition-date fair value of buildings acquired is determined to be less than initially recorded. How is the reduction in value recognized?
> When does a bargain purchase occur?
> When is goodwill considered impaired following a business combination?
> Which of the costs incurred in completing a business combination should be treated as a reduction of additional paid-in capital?
> What is a differential?
> Deal Corporation issued 4,000 shares of its $10 par value stock with a market value of $85,000 to acquire 85 percent ownership of Mead Company on August 31, 20X3. Mead’s fair value was determined to be $100,000 on that date. Deal had earlier purchased 15
> Thumb Company created New Company as a wholly owned subsidiary by transferring assets and accounts payable to New in exchange for its common stock. New recorded the following entry when it received the assets and accounts payable: Required a. What was
> Eagle Corporation established a subsidiary to enter into a new line of business considered to be substantially more risky than Eagle’s current business. Eagle transferred the following assets and accounts payable to Sand Corporation in
> Tab Corporation decided to establish Collon Company as a wholly owned subsidiary by transferring some of its existing assets and liabilities to the new entity. In exchange, Collon issued Tab 30,000 shares of $6 par value common stock. The following infor
> Bigtime Industries Inc. entered into a business combination agreement with Hydrolized Chemical Corporation (HCC) to ensure an uninterrupted supply of key raw materials and to realize certain economies from combining the operating processes and the market
> Plush Corporation purchased 100 percent of Common Corporation’s common stock on January 1, 20X3, and paid $450,000. The fair value of Common’s identifiable net assets at that date was $430,000. By the end of 20X5, the fair value of Common, which Plush co
> On January 1, 20X1, Alpha Corporation acquired all of Bravo Company’s assets and liabilities by issuing shares of its $3 par value stock to the owners of Bravo Company in a business combination. Alpha also made a cash payment to Banker
> On January 1, 20X2, End Corporation acquired all of Cork Corporation’s assets and liabilities by issuing shares of its common stock. Partial balance sheet data for the companies prior to the business combination and immediately followin
> Bilge Pumpworks and Seaworthy Rope Company agreed to merge on January 1, 20X3. On the date of the merger agreement, the companies reported the following data: Bilge Pumpworks has 10,000 shares of its $20 par value shares outstanding on January 1, 20X3,
> Following are the balance sheets of Boogie Musical Corporation and Toot-Toot Tuba Company as of December 31, 20X5. Following are the balance sheets of Boogie Musical Corporation and Toot-Toot Tuba Company as of December 31, 20X5. In preparation for a
> On January 1, 20X3, PURE Products Corporation issued 12,000 shares of its $10 par value stock to acquire the net assets of Light Steel Company. Underlying book value and fair value information for the balance sheet items of Light Steel at the time of acq
> The fair values of assets and liabilities held by three reporting units and other information related to the reporting units owned by Rover Company are as follows: Required a. Determine the amount of goodwill that Rover should report in its current fi
> Aspro Division is considered to be an individual reporting unit of Tabor Company. Tabor acquired the division by issuing 100,000 shares of its common stock with a market price of $7.60 each. Tabor management was able to identify assets with fair values
> Bower Company purchased Lark Corporation’s net assets on January 3, 20X2, for $625,000 cash. In addition, Bower incurred $5,000 of direct costs in consummating the combination. At the time of acquisition, Lark reported the following his
> Anchor Corporation paid cash of $178,000 to acquire Zink Company’s net assets on February 1, 20X3. The balance sheet data for the two companies and fair value information for Zink immediately before the business combination were: Requ
> A merger boom comparable to those of the 1960s and mid-1980s occurred in the 1990s and into the new century. The merger activity of the 1960s was associated with increasing stock prices and heavy use of pooling-of-interests accounting. The mid-1980s acti
> Flint Corporation exchanged shares of its $2 par common stock for all of Mark Company’s assets and liabilities in a planned merger. Immediately prior to the combination, Mark’s assets and liabilities were as follows: Assets Cas
> On January 1, 20X2, Frost Company acquired all of TKK Corporation’s assets and liabilities by issuing 24,000 shares of its $4 par value common stock. At that date, Frost shares were selling at $22 per share. Historical cost and fair val
> On January 1, 20X1, Rolan Corporation issued 10,000 shares of common stock in exchange for all of Sandin Corporation’s outstanding stock. Condensed balance sheets of Rolan and Sandin immediately before the combination follow: Rolan&ac
> On December 31, 20X3, Saxe Corporation was merged into Poe Corporation. In the business combination, Poe issued 200,000 shares of its $10 par common stock, with a market price of Chapter 1 Intercorporate Acquisitions and Investments in Other Entities 29
> Action Corporation issued nonvoting preferred stock with a fair market value of $4,000,000 in exchange for all the outstanding common stock of Master Corporation. On the date of the exchange, Master had tangible net assets with a book value of $2,000,000
> On April 1, 20X2, Jack Company paid $800,000 for all of Ann Corporation’s issued and outstanding common stock. Ann’s recorded assets and liabilities on April 1, 20X2, were as follows: Cash……………………………………………………………………………………………………..$ 80,000 Inventory…………………
> Which of the following actions is likely to result in recording goodwill on Randolph Company’s books? a. Randolph acquires Penn Corporation in a business combination recorded as a merger. b. Randolph acquires a majority of Penn’s common stock in a busin
> Which of the following is not an appropriate reason for establishing a subsidiary? a. The parent wishes to protect existing operations by shifting new activities with greater risk to a newly created subsidiary. b. The parent wishes to avoid subjecting a
> Peanut Company acquired 100 percent of Snoopy Company’s outstanding common stock for $300,000 on January 1, 20X8, when the book value of Snoopy’s net assets was equal to $300,000. Problem 2-27 summarizes the first year
> Peanut Company acquired 100 percent of Snoopy Company’s outstanding common stock for $300,000 on January 1, 20X8, when the book value of Snoopy’s net assets was equal to $300,000. Peanut uses the cost method to account
> Paper Company acquired 100 percent of Scissor Company’s outstanding common stock for $370,000 on January 1, 20X8, when the book value of Scissor’s net assets was equal to $370,000. Problem 2-25 summarizes the first yea
> Paper Company acquired 100 percent of Scissor Company’s outstanding common stock for $370,000 on January 1, 20X8, when the book value of Scissor’s net assets was equal to $370,000. Paper uses the equity method to accou
> Peanut Company acquired 100 percent of Snoopy Company’s outstanding common stock for $300,000 on January 1, 20X8, when the book value of Snoopy’s net assets was equal to $300,000. Problem 2-23 summarizes the first year
> Peanut Company acquired 100 percent of Snoopy Company’s outstanding common stock for $300,000 on January 1, 20X8, when the book value of Snoopy’s net assets was equal to $300,000. Peanut uses the equity method to accou
> Wealthy Manufacturing Company purchased 40 percent of the voting shares of Diversified Products Corporation on March 23, 20X4. On December 31, 20X8, Wealthy Manufacturing’s controller attempted to prepare income statements and retained
> Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. 1. Growth in the complexity of the U.S. business environment a. Has led to increased use of partnerships to avoid legal liability. b. Has led to increasingly complex organizational structures
> Dewey Corporation owns 30 percent of the common stock of Jimm Company, which it purchased at underlying book value on January 1, 20X5. Dewey reported a balance of $245,000 for its investment in Jimm Company on January 1, 20X5, and $276,800 at December 31
> Marlow Company acquired 40 percent of the voting shares of Brown Company on January 1, 20X8, for $85,000. The following results are reported for Brown Company: Required Give all journal entries recorded by Marlow for 20X8 and 20X9 assuming that it use
> Gant Company purchased 20 percent of the outstanding shares of Temp Company for $70,000 on January 1, 20X6. The following results are reported for Temp Company: Required Determine the amounts reported by Gant as income from its investment in Temp for
> Idle Corporation has been acquiring shares of Fast Track Enterprises at book value for the last several years. Fast Track provided data including the following: Fast Track declares and pays its annual dividend on November 15 each year. Its net book val
> Lang Company reports net assets with a book value and fair value of $200,000. Pace Corporation acquires 75 percent ownership for $150,000. Pace reports net assets with a book value of $520,000 and a fair value of $640,000 at that time, excluding its inve
> On December 31, 20X8, Banner Corporation acquired 80 percent of Dwyer Company’s common stock for $136,000. At the acquisition date, the book values and fair values of all of Dwyer’s assets and liabilities were equal. B
> Tall Corporation acquired 75 percent of Light Corporation’s voting common stock on January 1, 20X2, at underlying book value. At the acquisition date, the book values and fair values of Light’s assets and liabilities were equal, and the fair value of the
> Ambrose Corporation owns 75 percent of Kroop Company’s common stock, acquired at underlying book value on January 1, 20X4. At the acquisition date, the book values and fair values of Kroop’s assets and liabilities were
> Sanderson Corporation acquired 70 percent of Kline Corporation’s common stock on January 1, 20X7, for $294,000 in cash. At the acquisition date, the book values and fair values of Kline’s assets and liabilities were eq
> Belchfire Motors’ accountant was called away after completing only half of the consolidated statements at the end of 20X4. The data left behind included the following: Required a. Belchfire Motors acquired shares of Premium Body Shop
> When a company assigns goodwill to a reporting unit acquired in a business combination, it must record an impairment loss if’ a. The fair value of the net identifiable assets held by a reporting unit decreases. b. The fair value of the reporting unit dec
> One company may acquire another for a number of different reasons. The acquisition often has a significant impact on the financial statements. In 2005, 3M Corporation acquired CUNO Incorporated. Obtain a copy of the 3M 10-K filing for 2005. The 10-K repo
> Frazer Corporation owns 70 percent of Messer Company’s stock. In the 20X9 consolidated income statement, the noncontrolling interest was assigned $18,000 of income. There was no differential in the acquisition. Required What amount of net income did Me
> Teal Corporation is the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity with total assets of $500,000, liabilities of $470,000, and owners’ equity of $30,000. Because Teal owns 25 percent of the VIE’s voting stock, it reported a $7,500 investment in th
> Gamble Company convinced Conservative Corporation that the two companies should establish Simpletown Corporation to build a new gambling casino in Simpletown Corner. Although chances for the casino’s success were relatively low, a local bank loaned $140,
> Byte Computer Corporation acquired 90 percent of Nofail Software Company’s common stock on January 2, 20X3, by issuing preferred stock with a par value of $6 per share and a market value of $8.10 per share. A total of 10,000 shares of p
> Byte Computer Corporation acquired 75 percent of Nofail Software Company’s stock on January 2, 20X3, by issuing bonds with a par value of $50,000 and a fair value of $67,500 in exchange for the shares. Summarized balance sheet data pres
> Fineline Pencil Company acquired 80 percent of Smudge Eraser Corporation’s stock on January 2, 20X3, for $72,000 cash. Summarized balance sheet data for the companies on December 31, 20X2, are as follows: Required Prepare a consolida
> Potter Company acquired 90 percent of the voting common shares of Stately Corporation by issuing bonds with a par value and fair value of $121,500 to Stately’s existing shareholders. Immediately prior to the acquisition, Potter reported total assets of $
> On January 1, 20X3, Guild Corporation reported total assets of $470,000, liabilities of $270,000, and stockholders’ equity of $200,000. At that date, Bristol Corporation reported total assets of $190,000, liabilities of $135,000, and stockholders’ equity
> Amber Corporation reported the following summarized balance sheet data on December 31, 20X6: On January 1, 20X7, Purple Company acquired 100 percent of Amber’s stock for $500,000. At the acquisition date, the book values and fair valu
> Trim Corporation acquired 100 percent of Round Corporation’s voting common stock on January 1, 20X2, for $400,000. At that date, the book values and fair values of Round’s assets and liabilities were equal. Round repor
> When an existing company creates a new subsidiary and transfers a portion of its assets and liabilities to the new entity a. The new entity records both the assets and liabilities it received at fair values. b. The new entity records both the assets and
> Blank Corporation acquired 100 percent of Faith Corporation’s common stock on December 31, 20X2, for $150,000. Data from the balance sheets of the two companies included the following amounts as of the date of acquisition: At the date
> On December 31, 20X3, Broadway Corporation reported common stock outstanding of $200,000, additional paid-in capital of $300,000, and retained earnings of $100,000. On January 1, 20X4, Johe Company acquired control of Broadway in a business combination.
> Baldwin Corporation purchased 25 percent of Gwin Company’s common stock on January 1, 20X8, at underlying book value. In 20X8, Gwin reported a net loss of $20,000 and paid dividends of $10,000, and in 20X9, The company reported net income of $68,000 and
> Callas Corporation paid $380,000 to acquire 40 percent ownership of Thinbill Company on January 1, 20X9. The amount paid was equal to Thinbill’s underlying book value. During 20X9, Thinbill reported operating income of $45,000 and an increase of $20,000
> Reden Corporation purchased 45 percent of Montgomery Company’s common stock on January 1, 20X9, at underlying book value of $288,000. Montgomery’s balance sheet contained the following stockholders’ equity balances: Preferred Stock ($5 par value, 50,000
> Kent Company purchased 35 percent ownership of Lomm Company on January 1, 20X8, for $140,000. Lomm reported 20X8 net income of $80,000 and paid dividends of $20,000. At December 31, 20X8, Kent determined the fair value of its investment in Lomm to be $17

