Question: Sedona Company set the following standard costs
Sedona Company set the following standard costs for one unit of its product for this year.

The $5.60 ($4.00 + $1.60) total overhead rate per direct labor hour (DLH) is based on a predicted activity level of 37,500 units, which is 75% of the factory’s capacity of 50,000 units per month. The following monthly flexible budget information is available.
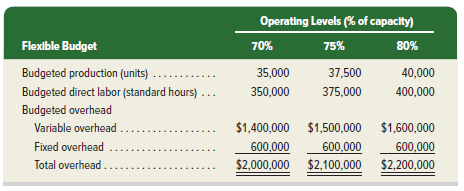
During the current month, the company operated at 70% of capacity, direct labor of 340,000 hours were used, and the following actual overhead costs were incurred.
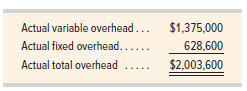
1. Compute the total variable overhead variance, and identify it as favorable or unfavorable.
2. Compute the total fixed overhead variance, and identify it as favorable or unfavorable.
> Key figures for Samsung follow (in $ millions). Required 1. Compute common-size percent’s for Samsung using the data given. Round percent’s to one decimal. 2. What is Samsung’s gross margin ratio on
> Key comparative information for Samsung, Apple, and Google follows. Required 1. Compute the recent two years’ cash flow on total assets ratio for Samsung. 2. Is the change in Samsung’s cash flow on total assets ratio
> Following are selected data from Samsung, Apple, and Google. Required 1. Compute Samsung’s return on total assets for the two most recent years. 2. for the current year, is Samsung’s return on total assets better or wo
> Selected results from Samsung, Apple, and Google follow Required 1. Compute Samsung’s debt-to-equity ratio for the current year and the prior year. 2. Is Samsung’s financing structure more risky or less risky in the cu
> Use the following financial information for Samsung. Required 1. Compute earnings per share (EPS) for Samsung. 2. If Samsung buys back outstanding shares from investors, would we expect EPS to increase or decrease from the buyback?
> Review Samsung’s 1938 to 1970 history at en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Samsung. 1. Byung-Chull Lee, the founder, organized/started the company in what year? What was the original name? 2. What was the original company’s operating focus? 3. Samsung lists its busi
> Comparative figures for Samsung, Apple, and Google follow. Required 1. Compute the times interest earned ratio for the most recent two years for Samsung using the data shown. 2. Is the change in Samsung’s time’s intere
> Information on assumed capital investments in the current year for Google and Apple follow. Required 1. Compute break-even time for both companies. 2. Based on break-even time, which company can expect its investment to more quickly yield positive net ca
> Comparative figures for Samsung, Apple, and Google follow. Required 1. Compute total asset turnover for the most recent two years for Samsung using the data shown. 2. Is the change in Samsung’s asset turnover favorable or unfavorable? 3
>  Key figures for Samsung follow. 1. Compute Samsung’s accounts receivable turnover for the current year. 2. In the current year, does Samsung’s accounts receivable turnover underperform or outperform
> Key figures for Samsung follow. Required 1. Compute cash and cash equivalents as a percent (rounded to one decimal) of total current assets, total assets, total current liabilities, and total shareholders’ equity for both years. 2. Comp
> Key figures for Samsung and Google follow. Required 1. Compute Samsung’s days’ payable outstanding for the most recent two years. 2. Assuming Samsung is not at risk of damaging its relationships with suppliers, does it
> Key figures for Samsung follow. Required 1. For the most recent two years, compute Samsung’s (a) inventory turnover and (b) days’ sales in inventory. 2. Is the change in Samsung’s inventory turnover f
> The production department described in Exercise 20-8 reports the cost information below. a. Compute cost per equivalent unit for both direct materials and conversion. b. Using the weighted average method, assign April’s costs to the dep
> The first production department of Stone Inc. reports the following for April. Compute the number of equivalent units of production for both direct materials and conversion for April using the weighted average method.
> Refer to the information in Exercise 20-6. Assume that Fields uses the FIFO method of process costing. a. Calculate the number of units started and completed this period for the Forming department. b. Calculate the equivalent units of production for both
> Fields Company has two manufacturing departments, Forming and Painting. The company uses the weighted average method and it reports the following unit data for the Forming department. Units completed in the Forming department are transferred to the Paint
> Refer to the information in Exercise 20-4 and compute the department’s equivalent units of production for direct materials for each of the three separate assumptions a, b, and c using the FIFO method.
> Apple and Google report the following income statement data (some are assumed). Use the companies’ service revenue and cost data to answer the requirements. Required 1. Compute the gross profit ratio for each of the two years shown for
> The first production department in a process manufacturing system reports the following unit data. Compute this production department’s equivalent units of production for direct materials under each of the following three separate assum
> Identify each of the following production features as applying more to job order operations, to process operations, or to both job order and process operations.
> For each of the following products and services, indicate whether it is more likely produced in a process operation or in a job order operation.
> A manufacturer reports the following for two of its divisions for a recent month. For each division, compute (1) return on investment, (2) profit margin, and (3) investment turnover.
> A growing chain is trying to decide which store location to open. The first location (A) requires a $1,000,000 investment in average assets and is expected to yield annual income of $160,000. The second location (B) requires a $600,000 investment in aver
> The Ski department reports sales of $605,000 and cost of goods sold of $425,000. Its expenses follow. For the Ski department only, prepare a (1) departmental income statement and (2) departmental contribution to overhead report. (3) Based on these two
> Gomez Company has two service departments (Personnel and Office) and two operating departments (Shoes and Clothing). Following are the direct expenses and square feet occupied by the four departments, and the total sales for the two operating departments
> Renata Co. has four departments: Materials, Personnel, Manufacturing, and Packaging. Information follows. The four departments share the following indirect expenses for supervision, utilities, and insurance. Allocate each of the three indirect expenses t
> Mia works in both the Jewelry department and the Cosmetics department of a retail store. She assists customers in both departments and organizes merchandise in both departments. The store allocates her wages between the two departments based on the time
> Lucia Company has two service departments: Office and Purchasing .Total expenses for the Office is $24,000 and for Purchasing is $34,000. Expenses for the Office are allocated to operating departments based on sales. Expenses for Purchasing are allocated
> For the current annual reports of Apple and Google, assume they report the following. Required 1. Compute the recent two years’ raw materials inventory turnover ratio for (a) Apple and (b) Google. 2. Is the current year change in Apple
> Refer to the information in Exercise 24-1 and prepare a responsibility accounting performance report for the ATV department.
> A dairy company processed raw milk for $60,000. This raw milk can be converted into the following types of milk with listed sales values. Use the value basis to (1) allocate the total cost of the raw milk to each type of milk and (2) determine the gross
> A manufacturer reports the data below. (1) Compute the number of days in the cash conversion cycle. (2) Is the company more efficient at managing cash than its competitor who has a cash conversion cycle of 14 days?
> A manufacturer reports the data below. (1) Compute the number of days in the cash conversion cycle for each year. (2) Did the company manage cash more effectively in the current year?
> Midwest Mfg. uses a balanced scorecard as part of its performance evaluation. The company wants to include information on its sustainability efforts in its balanced scorecard. For each performance measure below, indicate the most likely balanced scorecar
> The Food division of Garcia Company reports the following for the current year. Garcia wants to achieve at least a 10% profit margin next year. Two alternative strategies are proposed. Strategy 1: Increase advertising expenses by $225,000. The company ex
> A retailer reports the following for its geographic divisions for the year. Americas Europe China 1. Compute profit margin for each division. 2. Based on profit margin, which division performed best?
> A company reports the following for the past year. The company’s CFO believes that income for next year will be $1,200,000. Average assets will be the same as the past year. 1. Compute return on investment for the past year. 2. If the C
> Refer to the information in Exercise 24-12. Assume that each of the company’s divisions has a target income at 7% of average assets. Compute residual income for each division.
> Arctica manufactures snowmobiles and ATVs. These products are made in different departments, and each department has its own manager. Each responsibility performance report includes only those costs that the department manager can control: direct materia
> Key figures for Apple and Google follow. Required 1. Compute common-size percent’s for each company using the data given. Round percent’s to one decimal. 2. If Google paid a dividend, would retained earnings as a perc
> Refer to Exercise 23-13. Hart Company uses a standard costing system. Prepare the journal entry to charge direct materials costs to Work in Process Inventory and record the direct materials variances.
> Hart Company made 3,000 shelves using 22,000 pounds of wood costing $266,200. The company’s direct materials standards for one shelf are 8 pounds of wood at $12 per pound. 1. Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances along with the total
> Camila Company has set the following standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor. During June the company incurred the following actual costs to produce 9,000 units. Compute the (1) direct materials price and quantity variances and (2) d
> Lucia Company has set the following standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor. During May the company incurred the following actual costs to produce 9,000 units. Compute the (1) direct materials price and quantity variances and (2) dir
> A manufactured product has the following information for August. (1) Prepare the standard cost card showing standard cost per unit. (2) Compute total budgeted cost for production in August. (3) Compute total cost variance for August, and indicate whether
> Lewis Co. reports the following fixed budget and actual results for May. Prepare a flexible budget performance report showing variances between budgeted and actual results, and indicate whether each variance is favorable or unfavorable.
> Nina Co. prepared the following fixed budget for July using 7,500 units for budgeted sales. Actual sales were 7,200 units and actual costs are shown below. Prepare a flexible budget performance report for July that shows variances between budgeted and ac
> Refer to the information from Exercise 23-27. Compute the following. 1. Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. 2. Fixed overhead spending and volume variances. 3. Controllable variance.
> Mia Wiz sells computers. During May, it sold 350 computers at a $1,200 per unit price. The fixed budget for May predicted sales of 365 computers at an per unit price of $1,100. 1. Compute the sales price variance and identify it as favorable or unfavorab
> Key figures for Apple and Google follow. Required 1. Compute the recent two years’ cash flow on total assets ratios for Apple and Google. 2. For the current year, which company has the better cash flow on total assets ratio? 3. For the
> For May, Mariana Company planned production of 8,000 units (80% of its production capacity of 10,000 units) and prepared the following overhead budget. The company applies overhead with a standard of 3 DLH per unit and a standard overhead rate of $3.85 p
> Complete the following partial flexible budget performance report, and indicate whether each variance is favorable or unfavorable. The company budgets a selling price of $80 per unit and variable costs of $35 per unit.
> Shaw Inc. began this period with a budget for 1,000 units of predicted production. The budgeted overhead at this predicted activity follows. At period-end, total actual overhead was $92,000, and actual units produced were 900. The company applies overhea
> Shawke Company’s partially completed flexible overhead budget for the current period follows. This budget is based on its predicted activity of 50% of productive capacity. Complete its flexible overhead budgets for the current period us
> Compute total overhead variance using the following information.
> Shaw Co. produced 680 units. Its overhead allocation base is DLH and its standard amount per allocation base is 8 DLH per unit. Its standard overhead rate is $10 per DLH. The flexible overhead budget at an activity level of 680 units shows $26,000 in var
> Kenshaw Company’s flexible overhead budget at an activity level of 1,000 units shows $10,000 in variable overhead costs and $5,000 in fixed overhead costs. Actual total overhead is $13,000. Compute the controllable variance.
> Blaze Corp. allocates overhead on the basis of DLH and the standard amount per allocation base is 4 DLH per unit. For March, the company planned production of 8,000 units (80% of its production capacity of 10,000 units) and prepared the following budget.
> Refer to the information from Exercise 23-17. Compute the overhead (1) volume variance and (2) controllable variance, and identify each as favorable or unfavorable.
> Manuel Company predicts it will operate at 80% of its productive capacity. Its overhead allocation base is DLH and its standard amount per allocation base is 0.5 DLH per unit. The company reports the following for this period. 1. Compute the standard ove
> Key figures for Apple and Google follow Required 1. Compute return on total assets for Apple and Google for the two most recent years. 2. Which of these two companies has the better return on total assets for the current year? 3. Compute both profit mar
> Javon Co. set standards of 3 hours of direct labor per unit at a rate of $15 per hour. During October, the company actually uses 16,250 hours of direct labor at a $247,000 total cost to produce 5,600 units. In November, the company uses 22,000 hours of d
> The following information relates to production activities of Mercer Manufacturing for the year. 1. Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances and identify each as favorable or unfavorable. 2. Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency v
> JPAK manufactures and sells mountain bikes. Classify each of the following costs as fixed or variable with respect to the number of bikes made. a. Bike frames d. Property taxes g. Accountant salary b. Screws for assembly e. Bike tires h. Depreci
> Jasper Company has 70% of its sales on credit and 30% for cash. All credit sales are collected in full in the first month following the sale. The company budgets sales of $525,000 for April, $535,000 for May, and $560,000 for June. Total sales for March
> Garden Yeti manufactures garden sculptures. Each sculpture requires 8 pounds of direct materials at a cost of $3 per pound and 0.5 direct labor hour at a rate of $18 per hour. Variable overhead is budgeted at a rate of $3 per direct labor hour. Budgeted
> Ramos Co. provides the following (partial) production budget for the next three months. Each finished unit requires 0.50 hour of direct labor at the rate of $16 per hour. The company budgets variable overhead at the rate of $20 per direct labor hour and
> Ramos Co. provides the following budgeted production for the next four months. Each finished unit requires 5 pounds of direct materials. The company wants to end each month with direct materials inventory equal to 30% of next month’s pr
> Zira Co. reports the following production budget for the next four months. Each finished unit requires five pounds of direct materials, and the company wants to end each month with direct materials inventory equal to 30% of next month’s
> Rida Inc. is preparing its direct materials budget for the second quarter. It budgets production of 240,000 units in the second quarter and 52,500 units in the third quarter. Each unit requires 0.60 pound of direct material, priced at $175 per pound. The
> Ruiz Co. provides the following budgeted sales for the next four months. The company wants to end each month with ending finished goods inventory equal to 25% of next month’s budgeted unit sales. Finished goods inventory on April 1 is 1
> Key figures for Apple and Google follow. Required 1. Compute the debt-to-equity ratios for Apple and Google for both the current year and the prior year. 2. Use the ratios from part 1 to determine which company’s financing structure is
> MM Co. budgets sales of $30,000 for May. MM’s production manager discovered a way to use more sustainable packaging. As a result, MM’s product will receive better placement on store shelves and May sales are predicted to increase by 8%. Compute budgeted
> Prepare a budgeted balance sheet at March 31 using the following information from Zimmer Company. a. The cash budget for March shows an ending loan balance of $10,000 and an ending cash balance of $50,000. b. The sales budget for March shows sales of $14
> Hardy Co. reports budgeted merchandise purchases below. For those purchases, 40% of a month’s purchases is paid in the month of purchase, and 60% is paid in the first month after purchase. Prepare the schedule of cash payments for merch
> Use the budgeted information in Exercise 22-28, and the ending year balance of Retained Earnings of $78,000 on December 31, to prepare Lamonte Co.’s budgeted balance sheet as of December 31.
> Lamonte Co. reports the following budgeted December 31 adjusted trial balance. Prepare the budgeted income statement for the current year ended December 31. Ignore income taxes.
> Ahmed Company purchases all merchandise on credit. It recently budgeted the month-end accounts payable balances below. Cash payments on accounts payable during each month are expected to be June, $1,490,000; July, $1,425,000; and August, $1,495,000. Use
> Walker Company prepares monthly budgets. Company policy is to end each month with merchandise inventory equal to 15% of budgeted unit sales for the following month. Budgeted sales and merchandise purchases for the next three months follow. Beginning inve
> Fortune Inc. is preparing its master budget for the first quarter. The company sells a single product at a price of $25 per unit. Sales (in units) are budgeted at 150,000 for the first quarter. Cost of goods sold is $14 per unit. Other expense informatio
> Motors Corp. manufactures motors for dirt bikes. The company requires a minimum $30,000 cash balance at each month-end. If necessary, the company borrows to meet this requirement at a cost of 2% interest per month (paid at the end of each month). Any pre
> Zisk Co. purchases direct materials on credit. Budgeted purchases are April, $80,000; May, $110,000; and June, $120,000. Cash payments for purchases are: 70% in the month of purchase and 30% in the first month after purchase. Purchases for March are $70,
> Use the following comparative figures for Apple and Google. Required 1. Compute the basic EPS for each company using these data. 2. Compute the dividend yield for each company using these data. 3. Compute the price-earnings ratio for each company using t
> Match the definitions 1 through 6 with the phrase a through f. 1. Helps determine financing needs. 2. The usual starting point in the master budget process. 3. A report that shows predicted revenues and expenses for a budgeting period. 4. A budgetary cus
> Sunn Co. manufactures a single product that sells for $180 per unit and whose variable costs are $135 per unit. The company’s annual fixed costs are $562,500. Compute (a) contribution margin per unit, (b) contribution margin ratio, (c) break-even point i
> Compute the missing amounts a through j for the contribution margin income statements below.
> A jeans maker is designing a new line of jeans called Slams. Slams will sell for $205 per unit and cost $164 per unit in variable costs to make. Fixed costs total $60,000. 1. Compute the contribution margin per unit. 2. Compute the contribution margin ra
> Refer to the information from Exercise 21-5. Use spreadsheet software to use ordinary least squares regression to estimate the cost equation, including fixed and variable cost amounts.
> Felix & Co. reports the following information. (1) Use the high-low method to estimate the fixed and variable components of total costs. (2) Estimate total costs if 3,000 units are produced.
> Classify each of the following costs as either variable, fixed, or mixed. Costs are from a manufacturer of portable basketball hoops.
> Following are four series of costs measured at various volume levels. Identify each series as either fixed, variable, mixed, or step-wise. Hint: It can help to graph each cost series.
> A manufacturer reports the information below for three recent years. Compute income for each of the three years using absorption costing.
> Match each of the cost classifications a through e with its definition.
> Over the years, Apple and Google have evolved into large corporations. Today it is difficult to imagine them as fledgling start-ups. Research each company’s history online. Required 1. In what year was each company first organized/started as a business?
> Apple offers extended service contracts that provide repair coverage for its products. Assume its repair division reports the following annual results. Required 1. Compute the repair division’s degree of operating leverage. 2. Compute
> Information for two companies follows. (1) Compute the degree of operating leverage (DOL) for each company. (2) Which company is expected to produce a greater percent increase in income from a 20% increase in sales?
> A manufacturer’s contribution margin income statement for the year follows. Prepare contribution margin income statements for each of the three separate cases below. 1. The 10,000 units sold and produced increases to 10,400 units and fi
> Refer to the information in Exercise 21-11. The company is considering buying a new machine that will increase its fixed costs by $40,500 per year and decrease its variable costs by $9 per unit. Prepare a contribution margin income statement for the next
> Refer to the information in Exercise 21-11. If the company raises its selling price to $240 per unit, compute its (1) contribution margin per unit, (2) contribution margin ratio, (3) break-even point in units, and (4) break-even point in sales dollars.

