Question: See Table 2.5 showing financial statement
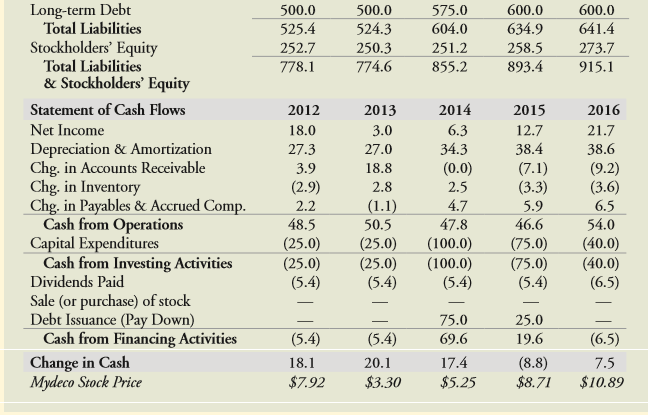
See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and stock price data for Mydeco Corp.
a. Compare Mydeco’s accounts payable days in 2012 and 2016.
b. Did this change in accounts payable days improve or worsen Mydeco’s cash position in 2016?
Table 2.5:
Transcribed Image Text:
Mydeco Corp. 2012–2016 (All data as of fiscal year end; in $ million) Income Statement 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Revenue 404.3 363.8 424.6 510.7 604.1 Cost of Goods Sold (206.2) 218.4 (188.3) (173.8) (246.8) 263.9 (293.4) 310.7 Gross Profit 216.0 190.0 Sales and Marketing Administration Depreciation & Amortization ЕBIT (66.7) (60.6) (27.3) (66.4) (59.1) (27.0) (82.8) (59.4) (34.3) 41.9 (102.1) (66.4) (38.4) (120.8) (78.5) (38.6) 61.4 37.5 57.0 72.8 Interest Income (Expense) (33.7) (32.9) (32.2) (37.4) 19.6 (39.4) 33.4 Pretax Income 27.7 4.6 9.7 Income Tax (9.7) (1.6) (3.4) (6.9) (11.7) Net Income 18.0 3.0 6.3 12.7 21.7 Shares outstanding (millions) Earnings per share 55.0 55.0 55.0 55.0 55.0 $0.33 $0.05 $0.11 $0.23 $0.39 Balance Sheet 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Assets Cash 48.8 68.9 86.3 77.5 85.0 Accounts Receivable 88.6 69.8 69.8 28.4 76.9 86.1 Inventory Total Current Assets 33.7 30.9 31.7 186.1 35.3 206.4 171.1 169.6 184.5 Net Property, Plant & Equip. Goodwill & Intangibles 245.3 243.3 309 345.6 347.0 361.7 361.7 361.7 361.7 361.7 Total Assets 778.1 774.6 855.2 893.4 915.1 Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity Accounts Payable Accrued Compensation Total Current Liabilities 18.7 17.9 22.0 26.8 31.7 6.7 6.4 7.0 8.1 9.7 25.4 24.3 29.0 34.9 41.4 Long-term Debt Total Liabilities Stockholders' Equity Total Liabilities & Stockholders' Equity 575.0 604.0 600.0 600.0 641.4 500.0 500.0 525.4 524.3 634.9 252.7 778.1 250.3 251.2 258.5 273.7 915.1 774.6 855.2 893.4 Statement of Cash Flows 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Net Income 18.0 3.0 6.3 12.7 21.7 Depreciation & Amortization Chg. in Accounts Receivable Chg. in Inventory Chg. in Payables & Accrued Comp. Cash from Operations Capital Expenditures Cash from Investing Activities Dividends Paid 27.3 27.0 34.3 38.4 38.6 (7.1) (3.3) 3.9 (0.0) 2.5 4.7 (9.2) (3.6) 18.8 (2.9) 2.8 (1.1) 5.9 46.6 2.2 6.5 48.5 50.5 47.8 54.0 (25.0) (25.0) (5.4) (25.0) (25.0) (5.4) (100.0) (100.0) (5.4) (75.0) (75.0) (5.4) (40.0) (40.0) (6.5) Sale (or purchase) of stock Debt Issuance (Pay Down) Cash from Financing Activities - - - - 75.0 25.0 (5.4) (5.4) 69.6 19.6 (6.5) Change in Cash Mydeco Stock Price 17.4 (8.8) $8.71 18.1 20.1 7.5 $7.92 $3.30 $5.25 $10.89
> Jim Campbell is founder and CEO of Open Start, an innovative software company. The company is all equity financed, with 100 million shares outstanding. The shares are trading at a price of $1. Campbell currently owns 20 million shares. There are two poss
> Indell stock has a current market value of $120 million and a beta of 1.50. Indell currently has risk-free debt as well. The firm decides to change its capital structure by issuing $30 million in additional risk-free debt, and then using this $30 million
> In mid-2015 Qualcomm Inc. had $11 billion in debt, total equity capitalization of $89 billion, and an equity beta of 1.43 (as reported on Yahoo! Finance). Included in Qualcomm’s assets was $21 billion in cash and risk-free securities. Assume that the ris
> Mercer Corp. has 10 million shares outstanding and $100 million worth of debt outstanding. Its current share price is $75. Mercer’s equity cost of capital is 8.5%. Mercer has just announced that it will issue $350 million worth of debt. It will use the p
> Hartford Mining has 50 million shares that are currently trading for $4 per share and $200 million worth of debt. The debt is risk free and has an interest rate of 5%, and the expected return of Hartford stock is 11%. Suppose a mining strike causes the p
> You are analyzing the leverage of two firms and you note the following (all values in millions of dollars): a. What is the market debt-to-equity ratio of each firm? b. What is the book debt-to-equity ratio of each firm? c. What is the EBIT/interest cov
> Hubbard Industries is an all-equity firm whose shares have an expected return of 10%. Hubbard does a leveraged recapitalization, issuing debt and repurchasing stock, until its debt-equity ratio is 0.60. Due to the increased risk, shareholders now expect
> Global Pistons (GP) has common stock with a market value of $200 million and debt with a value of $100 million. Investors expect a 15% return on the stock and a 6% return on the debt. Assume perfect capital markets. a. Suppose GP issues $100 million of n
> Suppose Visa Inc. (V) has no debt and an equity cost of capital of 9.2%. The average debt-to value ratio for the credit services industry is 13%. What would its cost of equity be if it took on the average amount of debt for its industry at a cost of debt
> Consider the entrepreneur described in Section 14.1 (and referenced in Tables 14.1–14.3). Suppose she funds the project by borrowing $750 rather than $500. a. According to MM Proposition I, what is the value of the equity? What are its
> Explain what is wrong with the following argument: “If a firm issues debt that is risk free, because there is no possibility of default, the risk of the firm’s equity does not change. Therefore, risk-free debt allows the firm to get the benefit of a low
> Your brother Joe is a surgeon who suffers badly from the overconfidence bias. He loves to trade stocks and believes his predictions with 100% confidence. In fact, he is uninformed like most investors. Rumors are that Vital Signs (a startup that makes war
> Why does the CAPM imply that investors should trade very rarely?
> You are trading in a market in which you know there are a few highly skilled traders who are better informed than you are. There are no transaction costs. Each day you randomly choose five stocks to buy and five stocks to sell (by, perhaps, throwing dart
> Explain what the following sentence means: The market portfolio is a fence that protects the sheep from the wolves, but nothing can protect the sheep from themselves.
> What are the only conditions under which the market portfolio might not be an efficient portfolio?
> Use the data in Problem 8 to determine the change, from 2012 to 2015, in GE’s a. book debt-equity ratio. b. market debt-equity ratio. Data from Problem 8: In early 2012, General Electric (GE) had a book value of equity of $116 billion, 10.6 billion sha
> You know that there are informed traders in the stock market, but you are uninformed. Describe an investment strategy that guarantees you will not lose money to the informed traders and explain why it works.
> Suppose the CAPM equilibrium holds perfectly. Then the risk-free interest rate increases, and nothing else changes. a. Is the market portfolio still efficient? b. If your answer to part a is yes, explain why. If not, describe which stocks would be buying
> You work for Microsoft Corporation (ticker: MSFT), and you are considering whether to develop a new software product. The risk of the investment is the same as the risk of the company. a. Using the data in Table 13.1 and in the table above, calculate the
> You are currently considering an investment in a project in the energy sector. The investment has the same riskiness as Exxon Mobil stock (ticker: XOM). Using the data in Table 13.1 and the table above, calculate the cost of capital using the FFC factor
> Using the factor beta estimates in the table shown here and the monthly expected return estimates in Table 13.1, calculate the risk premium of General Electric stock (ticker: GE) using the FFC factor specification. (Annualize your result by multiplying b
> Explain why an employee who cares only about expected return and volatility will likely underweight the amount of money he invests in his own company’s stock relative to an investor who does not work for his company.
> Explain why if some investors are subject to systematic behavioral biases, while others pick efficient portfolios, the market portfolio will not be efficient.
> Explain why you might expect stocks to have nonzero alphas if the market proxy portfolio is not highly correlated with the true market portfolio, even if the true market portfolio is efficient.
> If you can use past returns to construct a trading strategy that makes money (has a positive alpha), it is evidence that market portfolio is not efficient. Explain why.
> Explain how to construct a positive-alpha trading strategy if stocks that have had relatively high returns in the past tend to have positive alphas and stocks that have had relatively low returns in the past tend to have negative alphas.
> See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and stock price data for Mydeco Corp. a. How did Mydeco’s book debt-equity ratio change from 2012 to 2016? b. How did Mydeco’s market debt-equity ratio change from 2012 to
> In Problem 20, assume the risk-free rate is 3% and the market risk premium is 7%. a. What does the CAPM predict the expected return for each stock should be? b. Clearly, the CAPM predictions are not equal to the actual expected returns, so the CAPM does
> Consider the following stocks, all of which will pay a liquidating dividend in a year and nothing in the interim: a. Calculate the expected return of each stock. b. What is the sign of correlation between the expected return and market capitalization o
> Assume that the CAPM is a good description of stock price returns. The market expected return is 7% with 10% volatility and the risk-free rate is 3%. New news arrives that does not change any of these numbers but it does change the expected return of the
> Each of the six firms in the table below is expected to pay the listed dividend payment every year in perpetuity. a. Using the cost of capital in the table, calculate the market value of each firm. b. Rank the three S firms by their market values and l
> Assume all firms have the same expected dividends. If they have different expected returns, how will their market values and expected returns be related? What about the relation between their dividend yields and expected returns?
> Explain what the size effect is.
> Assume the economy consisted of three types of people. 50% are fad followers, 45% are passive investors (they have read this book and so hold the market portfolio), and 5% are informed traders. The portfolio consisting of all the informed traders has a b
> Allison and Bill are both mutual fund managers, although Allison is more skilled than Bill. Both have $100 million in assets under management and charge a fee of 1%/year. Allison is able to generate a 2% alpha before fees and Bill is able to generate a 1
> Davita Spencer is a manager at Half Dome Asset Management. She can generate an alpha of 2% a year up to $100 million. After that her skills are spread too thin, so cannot add value and her alpha is zero. Half Dome charges a fee of 1% per year on the tota
> Suppose that all investors have the disposition effect. A new stock has just been issued at a price of $50, so all investors in this stock purchased the stock today. A year from now the stock will be taken over, for a price of $60 or $40 depending on the
> See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and stock price data for Mydeco Corp. a. By how much did Mydeco increase its debt from 2012 to 2016? b. What was Mydeco’s EBITDA/Interest coverage ratio in 2012 and 2016? Did its coverage ratio ever fall bel
> Consider the price paths of the following two stocks over six time periods: Neither stock pays dividends. Assume you are an investor with the disposition effect and you bought at time 1 and right now it is time 3. Assume throughout this question that y
> How does the disposition effect impact investors’ tax obligations?
> To put the turnover of Figure 13.3 into perspective, let’s do a back of the envelope calculation of what an investor’s average turnover per stock would be were he to follow a policy of investing in the S&P 500 port
> Assume that all investors have the same information and care only about expected return and volatility. If new information arrives about one stock, can this information affect the price and return of other stocks? If so, explain why?
> From the start of 1999 to the start of 2009, the S&P 500 had a negative return. Does this mean the market risk premium we should have used in the CAPM was negative?
> Suppose that in place of the S&P 500, you wanted to use a broader market portfolio of all U.S. stocks and bonds as the market proxy. Could you use the same estimate for the market risk premium when applying the CAPM? If not, how would you estimate the co
> Standard and Poor’s also publishes the S&P Equal Weight Index, which is an equally weighted version of the S&P 500. a. To maintain a portfolio that tracks this index, what trades would need to be made in response to daily price changes? b. Is this index
> Suppose Best Buy stock is trading for $30 per share for a total market cap of $9 billion, and Walt Disney has 1.65 billion shares outstanding. If you hold the market portfolio, and as part of it hold 100 shares of Best Buy, how many shares of Walt Disney
> Aluminum maker Alcoa has a beta of about 2.0, whereas Hormel Foods has a beta of 0.45. If the expected excess return of the marker portfolio is 5%, which of these firms has a higher equity cost of capital, and how much higher is it?
> You would like to estimate the weighted average cost of capital for a new airline business. Based on its industry asset beta, you have already estimated an unlevered cost of capital for the firm of 9%. However, the new business will be 25% debt financed,
> Unida Systems has 40 million shares outstanding trading for $10 per share. In addition, Unida has $100 million in outstanding debt. Suppose Unida’s equity cost of capital is 15%, its debt cost of capital is 8%, and the corporate tax rate is 40%. a. What
> Your company operates a steel plant. On average, revenues from the plant are $30 million per year. All of the plants costs are variable costs and are consistently 80% of revenues, including energy costs associated with powering the plant, which represent
> Harrison Holdings, Inc. (HHI) is publicly traded, with a current share price of $32 per share. HHI has 20 million shares outstanding, as well as $64 million in debt. The founder of HHI, Harry Harrison, made his fortune in the fast food business. He sold
> Weston Enterprises is an all-equity firm with two divisions. The soft drink division has an asset beta of 0.60, expects to generate free cash flow of $50 million this year, and anticipates a 3% perpetual growth rate. The industrial chemicals division has
> Consider the following airline industry data from mid-2009: a. Use the estimates in Table 12.3 to estimate the debt beta for each firm (use an average if multiple ratings are listed). b. Estimate the asset beta for each firm. c. What is the average ass
> In mid-2015, Cisco Systems had a market capitalization of $130 billion. It had A-rated debt of $25 billion as well as cash and short-term investments of $60 billion, and its estimated equity beta at the time was 1.11. a. What is Cisco’s enterprise value?
> IDX Tech is looking to expand its investment in advanced security systems. The project will be financed with equity. You are trying to assess the value of the investment, and must estimate its cost of capital. You find the following data for a publicly t
> Suppose the market portfolio has an expected return of 10% and a volatility of 20%, while Microsoft’s stock has a volatility of 30%. a. Given its higher volatility, should we expect Microsoft to have an equity cost of capital that is higher than 10%? b.
> Consider the setting of Problem 18. You decided to look for other comparables to reduce estimation error in your cost of capital estimate. You find a second firm, Thurbinar Design, which is also engaged in a similar line of business. Thurbinar has a stoc
> Your firm is planning to invest in an automated packaging plant. Harburtin Industries is an all-equity firm that specializes in this business. Suppose Harburtin’s equity beta is 0.85, the risk free rate is 4%, and the market risk premium is 5%. If your f
> See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and stock price data for Mydeco Corp. a. How did Mydeco’s accounts receivable days change over this period? b. How did Mydeco’s inventory days change over this period? c.
> The Dunley Corp. plans to issue 5-year bonds. It believes the bonds will have a BBB rating. Suppose AAA bonds with the same maturity have a 4% yield. Assume the market risk premium is 5% and use the data in Table 12.2 and Table 12.3. a. Estimate the yiel
> During the recession in mid-2009, homebuilder KB Home had outstanding 6-year bonds with a yield to maturity of 8.5% and a BB rating. If corresponding risk-free rates were 3%, and the market risk premium was 5%, estimate the expected return of KB Home’s d
> In mid-2009, Rite Aid had CCC-rated, 6-year bonds outstanding with a yield to maturity of 17.3%. At the time, similar maturity Treasuries had a yield of 3%. Suppose the market risk premium is 5% and you believe Rite Aid’s bonds have a beta of 0.31. The e
> In mid-2012, Ralston Purina had AA-rated, 10-year bonds outstanding with a yield to maturity of 2.05%. a. What is the highest expected return these bonds could have? b. At the time, similar maturity Treasuries have a yield of 1.5%. Could these bonds actu
> Using the same data as in Problem 11, estimate the 95% confidence interval for the alpha and beta of Nike and Dell stock using Excel’s regression tool (from the data analysis menu) or the linest() function. Data from Problem 11: Go to Chapter Resources
> Using the same data as in Problem 11, estimate the alpha of Nike and Dell stock, expressed as % per month. Data from Problem 11: Go to Chapter Resources on and use the data in the spreadsheet provided to estimate the beta of Nike and Dell stock based o
> Go to Chapter Resources on and use the data in the spreadsheet provided to estimate the beta of Nike and Dell stock based on their monthly returns from 2011–2015.
> You need to estimate the equity cost of capital for XYZ Corp. You have the following data available regarding past returns: a. What was XYZ’s average historical return? b. Compute the market’s and XYZâ€
> Suppose Pepsico’s stock has a beta of 0.57. If the risk-free rate is 3% and the expected return of the market portfolio is 8%, what is Pepsico’s equity cost of capital?
> Suppose two stocks have a correlation of 1. If the first stock has an above average return this year, what is the probability that the second stock will have an above average return?
> At the end of 2015, Apple had cash and short-term investments of $41.60 billion, accounts receivable of $35.89 billion, current assets of $89.38 billion, and current liabilities of $80.61 billion. a. What was Apple’s current ratio? b. What was Apple’s qu
> Which organizational forms give their owners limited liability?
> Using the data from Table 11.3, what is the covariance between the stocks of Alaska Air and Southwest Airlines? Table 11.3: Alaska Air Šouthwest Airlines Ford Motor General Mills Microsoft HP Kellogg Volatility (Standard Deviation) 33% 37% 37% 31%
> Using your estimates from Problem 5, calculate the volatility (standard deviation) of a portfolio that is 70% invested in stock A and 30% invested in stock B. Data from Problem 5: Using the data in the following table, estimate (a) the average return a
> Use the data in Problem 5, consider a portfolio that maintains a 50% weight on stock A and a 50% weight on stock B. a. What is the return each year of this portfolio? b. Based on your results from part a, compute the average return and volatility of the
> What is the risk premium of a zero-beta stock? Does this mean you can lower the volatility of a portfolio without changing the expected return by substituting out any zero-beta stock in a portfolio and replacing it with the risk-free asset?
> Suppose Autodesk stock has a beta of 2.16, whereas Costco stock has a beta of 0.69. If the risk-free interest rate is 4% and the expected return of the market portfolio is 10%, what is the expected return of a portfolio that consists of 60% Autodesk stoc
> Using the data in the following table, estimate (a) the average return and volatility for each stock, (b) the covariance between the stocks, and (c) the correlation between these two stocks. Year 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Stock A -10% 20% 5% -5%
> Consider a portfolio consisting of the following three stocks: The volatility of the market portfolio is 10% and it has an expected return of 8%. The risk-free rate is 3%. a. Compute the beta and expected return of each stock. b. Using your answer from
> Suppose you group all the stocks in the world into two mutually exclusive portfolios (each stock is in only one portfolio): growth stocks and value stocks. Suppose the two portfolios have equal size (in terms of total value), a correlation of 0.5, and th
> Your investment portfolio consists of $15,000 invested in only one stock—Microsoft. Suppose the risk-free rate is 5%, Microsoft stock has an expected return of 12% and a volatility of 40%, and the market portfolio has an expected return of 10% and a vola
> A big pharmaceutical company, DRIg, has just announced a potential cure for cancer. The stock price increased from $5 to $100 in one day. A friend calls to tell you that he owns DRIg. You proudly reply that you do, too. Since you have been friends for so
> For fiscal year end 2015, Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. (WMT, brand name Walmart) had revenues of $485.65 billion, gross profit of $120.57 billion, and net income of $16.36 billion. Costco Wholesale Corporation (COST) had revenue of $116.20 billion, gross profit
> When the CAPM correctly prices risk, the market portfolio is an efficient portfolio. Explain why.
> Returning to Problem 38, assume you follow your broker’s advice and put 50% of your money in the venture fund. a. What is the Sharpe ratio of the Tanglewood Fund? b. What is the Sharpe ratio of your new portfolio? c. What is the optimal fraction of your
> Calculate the Sharpe ratio of each of the three portfolios in Problem 41. What portfolio weight in Hannah stock maximizes the Sharpe ratio? Data from Problem 41: You are currently only invested in the Natasha Fund (aside from risk-free securities). It
> You are currently only invested in the Natasha Fund (aside from risk-free securities). It has an expected return of 14% with a volatility of 20%. Currently, the risk-free rate of interest is 3.8%. Your broker suggests that you add Hannah Corporation to y
> The Optima Mutual Fund has an expected return of 20%, and a volatility of 20%. Optima claims that no other portfolio offers a higher Sharpe ratio. Suppose this claim is true, and the risk-free interest rate is 5%. a. What is Optima’s Sharpe Ratio? b. If
> There are two ways to calculate the expected return of a portfolio: either calculate the expected return using the value and dividend stream of the portfolio as a whole, or calculate the weighted average of the expected returns of the individual stocks t
> You have noticed a market investment opportunity that, given your current portfolio, has an expected return that exceeds your required return. What can you conclude about your current portfolio?
> In addition to risk-free securities, you are currently invested in the Tanglewood Fund, a broad based fund of stocks and other securities with an expected return of 12% and a volatility of 25%. Currently, the risk-free rate of interest is 4%. Your broker
> Assume all investors want to hold a portfolio that, for a given level of volatility, has the maximum possible expected return. Explain why, when a risk-free asset exists, all investors will choose to hold the same portfolio of risky stocks.
> Assume the risk-free rate is 4%. You are a financial advisor, and must choose one of the funds below to recommend to each of your clients. Whichever fund you recommend, your clients will then combine it with risk-free borrowing and lending depending on t
> See Table 2.5 showing financial statement data and stock price data for Mydeco Corp. a. What were Mydeco’s gross margins each year? b. Comparing Mydeco’s gross margin, EBIT margin, and net profit margin in 2012 to 2016
> You currently have $100,000 invested in a portfolio that has an expected return of 12% and a volatility of 8%. Suppose the risk-free rate is 5%, and there is another portfolio that has an expected return of 20% and a volatility of 12%. a. What portfolio
> You have $100,000 to invest. You choose to put $150,000 into the market by borrowing $50,000. a. If the risk-free interest rate is 5% and the market expected return is 10%, what is the expected return of your investment? b. If the market volatility is 15
> Suppose you have $100,000 in cash, and you decide to borrow another $15,000 at a 4% interest rate to invest in the stock market. You invest the entire $115,000 in a portfolio J with a 15% expected return and a 25% volatility. a. What is the expected retu
> You expect HGH stock to have a 20% return next year and a 30% volatility. You have $25,000 to invest, but plan to invest a total of $50,000 in HGH, raising the additional $25,000 by shorting either KBH or LWI stock. Both KBH and LWI have an expected retu
> You have $10,000 to invest. You decide to invest $20,000 in Google and short sell $10,000 worth of Yahoo! Google’s expected return is 15% with a volatility of 30% and Yahoo!’s expected return is 12% with a volatility of 25%. The stocks have a correlation
> Suppose Target’s stock has an expected return of 20% and a volatility of 40%, Hershey’s stock has an expected return of 12% and a volatility of 30%, and these two stocks are uncorrelated. a. What is the expected return and volatility of an equally weight

