Question: The following accounting events apply to Mary’
The following accounting events apply to Mary’s Designs for Year 1:
Asset Source Transactions
1. Began operations by acquiring $90,000 of cash from the issue of common stock.
2. Performed services and collected cash of $9,000.
3. Collected $36,000 of cash in advance for services to be provided over the next 12 months.
4. Provided $58,000 of services on account.
5. Purchased supplies of $5,200 on account.
Asset Exchange Transactions
6. Purchased $21,000 of land for cash.
7. Collected $49,000 of cash from accounts receivable
8. Purchased $3,150 of supplies with cash.
9. Paid $12,000 for one year’s rent in advance.
Asset Use Transactions
10. Paid $24,000 cash for salaries of employees.
11. Paid a cash dividend of $5,000 to the stockholders.
12. Paid off $3,600 of the accounts payable with cash.
Claims Exchange Transactions
13. Placed an advertisement in the local newspaper for $2,600 on account.
14. Incurred utility expense of $1,800 on account.
Adjusting Entries
16. Recognized $12,000 of revenue for performing services.
he collection of cash for these services occurred in a prior transaction. (See Event 3.
17. Recorded $8,000 of accrued salary expense at the end of Year 1.
18. Recorded supplies expense. Had $1,900 of supplies on hand at the end of the accounting period.
19. Recognized four months of expense for prepaid rent that had been used up during the accounting period.
Required:
a. Record each of the preceding events in T-accounts.
b. Prepare a before-closing trial balance.
c. Use a horizontal statements model to show how each event affects the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. Indicate whether the event increases (+), decreases (−), or does not affect (NA) each element of the financial statements. Also, in the Cash Flow column, use the letters OA to designate operating activity, IA for investing activity, and FA for financing activity. The first event is recorded as an example.
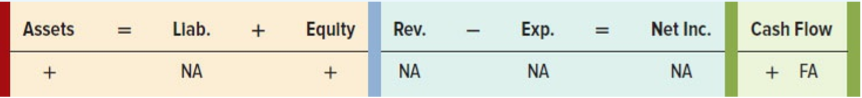
Transcribed Image Text:
Assets Llab. + Equity Rev. Exp. Net Inc. Cash Flow %3D NA + NA NA NA + FA
> What accounts normally have debit balances? What accounts normally have credit balances?
> How does a debit to an expense account ultimately affect retained earnings? Stockholders’ equity?
> Give an example of an asset exchange transaction.
> What are the three primary ways a business may use assets?
> What are the three primary sources of business assets?
> The trial balance of Pacilio Security Services, Inc. as of January 1, Year 2, was as follows: During Year 2, Pacilio Security Services experienced the following transactions: 1. Acquired an additional $2,000 from the issue of common stock. 2. Paid $3,0
> How is the balance of an account determined?
> Two introductory accounting students were arguing about how to record a transaction involving an exchange of cash for land. Laura stated that the transaction should have a debit to Land and a credit to Cash; Clark argued that the reverse (debit to Cash a
> What are the two fundamental equality requirements of the double-entry accounting system?
> Define debit and credit. How are assets, liabilities, common stock, retained earnings, revenues, expenses, and dividends affected (increased or decreased) by debits and by credits?
> What is U.S. GAAP? What is IFRS?
> Identify the three types of accounting transactions discussed in this chapter. Provide an example of each type of transaction, and explain how it affects the accounting equation.
> Why are temporary accounts closed at the end of the accounting period?
> List and describe the four stages of the accounting cycle discussed in Chapter 2.
> Explain how financial leverage impacts the return-on-equity ratio.
> Discuss the two views of the right side of the accounting equation.
> The following information is available for Pacilio Security Services, Inc. for Year 1, its first year of operations. Pacilio provides security services for local sporting events. The following summary transactions occurred during Year 1: 1. Acquired $6,0
> What does a double-entry bookkeeping system mean?
> Do all companies close their books on December 31? Why or why not?
> The following business scenarios are independent from one another: 1. Chris Hann purchased an automobile from Classic Auto Sales for $10,000. 2. Sal Pearl loaned $15,000 to the business in which he is a stockholder. 3. First State Bank paid interest to S
> Jan Perkins is a business consultant. She analyzed the business processes of one of her clients, Diamond Companies, in November Year 1. She prepared a report containing her recommendation for changes in some of the company’s business practices. She prese
> Daley Company was started on January 1, Year 1, and experienced the following events during its first year of operation: 1. Acquired $52,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Borrowed $20,000 cash from National Bank. 3. Earned cash revenues of $42,
> Blix Corp. started the Year 2 accounting period with total assets of $50,000 cash, $20,000 of liabilities, and $20,000 of retained earnings. During the Year 2 accounting period, the Retained Earnings account increased by $8,500. The bookkeeper reported t
> Marco’s Consulting experienced the following transactions for Year 1, its first year of operations, and Year 2. Assume that all transactions involve the receipt or payment of cash. Transactions for Year 1 1. Acquired $50,000 by issuing
> The following unrelated events are typical of those experienced by business entities: 1. Pay cash for operating expenses. 2. Pay an office manager’s salary with cash. 3. Receive cash for services that have been performed. 4. Pay cash fo
> The following information is from the records of Floral Design. Write a brief explanation of the accounting event represented in each of the general journal entries. Date Account Titles Debit Credit Cash Common Stock Jan. 1 18,750 18,750 Feb. 1 Prep
> Required: The preceding 13 different accounting events are presented in general journal format. Use a horizontal statements model to show how each event affects the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. Indicate whether the event
> Many companies must file financial reports with the SEC. Many of these reports are available electronically through the EDGAR database. EDGAR is an acronym for Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis, and Retrieval system, and it is accessible through the Wo
> The following accounting events apply to Little Co. for Year 1: Asset Source Transactions 1. Began operations when the business acquired $40,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Performed services and collected cash of $2,000. 3. Collected $9,000
> The following events apply to Un Enterprises: 1. Acquired $30,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Recognized $28,000 of service revenue on account. 3. Paid cash to rent office space for the next 12 months: $7,800. 514 4. Paid cash of $9,200 for
> Required Indicate whether each of the following accounts normally has a debit or credit balance: a. Retained Earnings b. Prepaid Insurance c. Insurance Expense d. Accounts Receivable e. Salaries Payable f. Cash g. Common Stock h. Rent Expense i. Salaries
> Oaks Company had the following balances in its accounting records as of December 31, Year 1: The following accounting events apply to Oaks’ Year 2 fiscal year: Jan.  1 Acquired an additional $70,000 cash from the iss
> Iowa Service Company was formed on January 1, Year 1. Events Affecting the Year 1 Accounting Period 1. Acquired cash of $60,000 from the issue of common stock. 2. Purchased $1,200 of supplies on account. 3. Purchased land that cost $18,000 cash. 4. Paid
> The following accounts and balances were drawn from the records of Shearer Company at December 31, Year 2: Required: Use the accounts and balances from Shearer Company to construct an income statement, statement of changes in stockholdersâ€&
> Gossett Company had the following beginning balances in its accounting records as of January 1, Year 2: The following accounting events apply to Gossett for Year 2: Jan.  1 Acquired an additional $30,000 cash from the issue of common
> The following events pertain to Weaver Cleaning Company: 1. Acquired $15,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Provided services for $6,000 cash. 3. Provided $18,000 of services on account. 4. Collected $11,000 cash from the account receivable cre
> The following selected accounts and account balances were taken from the records of Wages Company. Except as otherwise indicated, all balances are as of December 31, Year 2, before the closing entries were recorded. Required: a. Prepare the income stat
> Required: Each of the following independent events requires a year-end adjusting entry. Show how each event and its related adjusting entry affect the accounting equation. Assume a December 31 closing date. The first event is recorded as an example. a.
> In the late 1400s, a wealthy land owner named Caster was trying to decide which of his twin sons, Rogan or Argon, to designate as the first heir to the family fortune. He decided to set up each son with a small farm consisting of 300 sheep and 20 acres o
> The following selected financial information is available for Best, Inc. Amounts are in millions of dollars. Required: a. Divide the class into groups of four or five students each. Organize the groups into four sections. Assign Task 1 to the first sec
> Vox Company started the period with cash of $22,000, common stock of $12,000, and retained earnings of $10,000. Vox engaged in the following transactions in Year 2: Transactions during Year 2 1. On January 1, Year 2, purchased a computer for $7,500 cash
> Black Inc. acquired $10,000 cash by issuing a promissory note to the National Bank on November 1, Year 1. The note stipulated a one-year term and a 9 percent annual interest rate. Required: Prepare the general journal entries to record: a. The issue of
> The following information is available for Delaware Company and Florida Company: Required: a. For each company, compute the debt-to-assets ratio and the return-on-equity ratio. b. Determine what percentage of each company’s assets wer
> Anchor Machining experienced the following events during Year 1: 1. Started operations by acquiring $100,000 of cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Paid $12,000 cash in advance for rent during the period from February 1, Year 1, to February 1, Year 2
> The following transactions pertain to Price Corporation for Year 1: Jan. 1 Began operations when the business acquired $25,000 cash from the issue of common stock. Mar. 1 Paid rent for office space for two years: $8,400 cash. Apr. 14 Purchased $400 of
> The following trial balance was prepared from the ledger accounts of Klein Inc.: The accountant for Klein Inc. made the following errors during May, Year 2: 1. The cash purchase of land for $3,000 was recorded as a $5,000 debit to Land and a $3,000 cre
> Each of the following independent events requires a year-end adjusting entry. Record each event and the related adjusting entry in general journal format. The first event is recorded as an example. Assume a December 31 closing date. a. Paid $8,400 cash
> The following business scenarios are independent from one another: 1. Bob Wilder starts a business by transferring $10,000 from his personal checking account into a checking account for his business, Wilder Co. 2. A business that Sam Pace owns earns $4,6
> Required: The preceding 13 different accounting events are presented in general journal format. Use a horizontal statements model to show how each event affects the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. Indicate whether the event
> Toyo Company is holding land that cost $900,000 for future use. However, plans have changed and the company may not need the land in the foreseeable future. The president is concerned about the return on assets. Current net income is $425,000 and total a
> The following events apply to Kate Enterprises: 1. Collected $16,200 cash for services to be performed in the future. 2. Acquired $50,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 3. Paid salaries to employees: $3,500 cash. 4. Paid cash to rent office space f
> Required Indicate whether each of the following accounts normally has a debit or credit balance: a. Interest Receivable b. Interest Revenue c. Prepaid Insurance d. Land e. Salaries Payable f. Salaries Expense g. Supplies Expense h. Consulting Revenue i.
> Porser Company had the following balances in its accounting records as of December 31, Year 1: The following accounting events apply to Porser Company’s Year 2 fiscal year: Jan.  1 Acquired $15,000 cash from the issu
> Pete Chalance is an accountant with a shady past. Suffice it to say that he owes some very unsavory characters a lot of money. Despite his past, Pete works hard at keeping up a strong professional image. He is a manager at Smith and Associates, a fast-gr
> 1. Acquired $20,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Purchased $800 of supplies on account. 3. Purchased land that cost $14,000 cash. 4. Paid $800 cash to settle accounts payable created in Event 2. 5. Recognized revenue on account of $10,500. 6.
> The following information is available for the Maine Company and the Iowa Company: Required: a. For each company, compute the debt-to-assets ratio and the return-on-equity ratio. b. Determine what percentage of each company’s assets w
> Colton Enterprises experienced the following events for Year 1, the first year of operation: 1. Acquired $35,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Paid $12,000 cash in advance for rent. The payment was for the period April 1, Year 1, to March 31, Y
> The following transactions pertain to Smith Training Company for Year 1: Jan. 30 Established the business when it acquired $45,000 cash from the issue of common stock. Feb. 1 Paid rent for office space for two years, $24,000 cash. Apr. 10 Purchased $3,2
> The following events pertain to Super Cleaning Company: 1. Acquired $10,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Provided $15,000 of services on account. 3. Provided services for $5,000 cash. 4. Received $2,800 cash in advance for services to be perfo
> Each of the following independent events requires a year-end adjusting entry. Record each event and the related adjusting entry in general journal format. The first event is recorded as an example. Assume a December 31 closing date. a. Paid $48,000 cas
> The following data were taken from the 2016 annual reports of Biogen Idec, Inc. and Amgen Inc. Both companies are leaders in biotechnology. All dollar amounts are in millions. Required: a. For each company, compute the debt-to-assets ratio, return on-a
> The following information is from the records of attorney Glenn Price. Write a brief explanation of the accounting event represented in each of the general journal entries. Date Account Titles Debit Credit Jan. 1 Cash 40,000 Common Stock 40,000 Feb.
> Bower Consulting Company started the period with cash of $25,000, common stock of $13,000, and retained earnings of $12,000. Bower engaged in the following transactions in Year 2: Transactions during Year 2 1. On January 1, Year 2, purchased office furn
> TARVON Inc. acquired $50,000 cash by issuing a promissory note to the National Bank on May 1, Year 1. TARVON issued a promissory note with a one-year term and a 6 percent annual interest rate. Required: Prepare the general journal entries to record: a.
> Maben Company was started on January 1, Year 1, and experienced the following events during its first year of operation: 1. Acquired $30,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Borrowed $40,000 cash from National Bank. 3. Earned cash revenues of $48,
> Pratt Corp. started the Year 2 accounting period with total assets of $30,000 cash, $12,000 of liabilities, and $5,000 of retained earnings. During the Year 2 accounting period, the Retained Earnings account increased by $7,550. The bookkeeper reported t
> Mark’s Consulting Services experienced the following transactions for Year 1, its first year of operations, and Year 2. Assume that all transactions involve the receipt or payment of cash. Transactions for Year 1 1. Acquired $20,000 by
> The following trial balance was prepared from the ledger accounts of Ricardo Company: When the trial balance failed to balance, the accountant reviewed the records and discovered the following errors: 1. The company received $560 as payment for service
> The following unrelated events are typical of those experienced by business entities: 1. Acquire cash by issuing common stock. 2. Pay other operating supplies expense. 3. Agree to represent a client in an IRS audit and to receive payment when the audit i
> Required: a. Match the terms (identified as a through g) with the definitions and phrases (marked 1 through 7). For example, the term “a. Stockholders’ Equity” matches with definition 2. Common Stock
> Ray Steen recently started a business. During the first few days of operation, Mr. Steen transferred $100,000 from his personal account into a business account for a company he named Steen Enterprises. Steen Enterprises borrowed $60,000 from First Bank.
> The following data were taken from Netflix, Inc.’s 2016 annual report. All dollar amounts are in millions. Required: a. For each year, compute Netflix’s debt-to-assets ratio, return on-assets ratio, and return-on-equ
> Accounting is commonly divided into two sectors. One sector is called public accounting. The other sector is called private accounting. Required: a. Identify three areas of service provided by public accountants. b. Describe the common duties performed
> Resource owners provide three types of resources to conversion agents that transform the resources into products or services that satisfy consumer demands. Required: Identify the three types of resources. Write a brief memo explaining how resource owner
> Ross Company performed services on account for $30,000 in Year 1, its first year of operations. Ross collected $24,000 cash from accounts receivable during Year 1 and the remaining $6,000 in cash during Year 2. Required: a. Record the Year 1 transaction
> Required: Record each of the following Wilson Co. events in T-accounts and then explain how the event affects the accounting equation: a. Received $40,000 cash by issuing common stock. b. Purchased supplies for $1,800 cash. c. Performed services on accou
> Required: For each of the following T accounts, indicate the side of the account that should be used to record an increase or decrease in the financial statement element: Assets Llablitles Stockholders' Equlty Debit Credit Debit Credit Debit Credit
> Identify whether each of the following transactions is an asset source (AS), asset use (AU), asset exchange (AE), or claims exchange (CE). Also explain how each event affects the accounting equation by placing a (+) for increase, (−) fo
> For each of the following independent events, identify the account that would be debited and the account that would be credited. The accounts for the first event are identified as an example. a. Received cash for services to be performed in the future.
> a. In parallel columns, list the accounts that would be debited and credited for each of the following unrelated transactions: (1) Provided services for cash. (2) Recognized accrued salaries at the end of the period. (3) Provided services on account. (4)
> Indicate whether each of the following accounts normally has a debit balance or a credit balance. a. Unearned Revenue b. Service Revenue c. Dividends d. Land e. Accounts Receivable f. Cash g. Common Stock h. Prepaid Rent i. Supplies j. Accounts Payable k
> Using one of the websites referenced in the Focus on International Issues feature earlier in this chapter, define the IASB and describe its function.
> Consider the following brief descriptions of four companies from different industries. Six Flags, Inc. operates regional theme parks. It operates 18 parks in the United States, one in Mexico, and one in Canada. Toll Brothers, Inc. is a home-builder. In i
> The following information was drawn from the balance sheets of two companies: Required: a. Compute the debt-to-assets ratio to measure the level of financial risk of both companies. b. Compare the two ratios computed in Requirement a to identify which
> At the beginning of Year 2, Event Services Co. had the following normal balances in its accounts: The following events apply to Event Services Co. for Year 2: 1. Provided $130,000 of services on account. 2. Incurred $6,200 of operating expenses on acco
> The following financial information was taken from the books of Serenity Spa: Required: a. Prepare the journal entries necessary to close the temporary accounts December 31, Year 2, for Serenity Spa. b. What is the balance in the Retained Earnings acco
> Explain how each of the following posting errors affects a trial balance. State whether the trial balance will be out of balance because of the posting error, and indicate which side of the trial balance will have a higher amount after each independent e
> Jake, Mollie, and Neil, three accounting students, are discussing the rules of debits and credits. Jake says that debits increase account balances and credits decrease account balances. Mollie says that Jake is wrong, that credits increase account balanc
> Required: On December 31, Year 2, Wages Company had the following normal account balances in its general ledger. Use this information to prepare a trial balance. $ 50,000 32,000 3,600 5,000 Common Stock Salaries Expense Office Supplies Advertising E
> The following events apply to Perry Carpet Cleaners in Year 1, its first year of operations: 1. Received $45,000 cash from the issue of common stock. 2. Earned $37,500 of service revenue on account. 3. Incurred $15,000 of operating expenses on account. 4
> The following events apply to Colton Training Co. for Year 1, its first year of operation: 1. Received cash of $60,000 from the issue of common stock. 2. Performed $100,000 worth of services on account. 3. Paid $74,000 cash for salaries expense. 4. Purc
> Virginia Mining began operations by issuing common stock for $150,000. The company paid $135,000 cash in advance for a one-year contract to lease machinery for the business. The lease agreement was signed on March 1, Year 1, and was effective immediately
> On December 31, Year 1, Zeal Company had accrued salaries of $12,000. Required: a. Record in general journal format the adjustment required as of December 31, Year 1. b. Show the above adjustment in a horizontal statements model like the following one:
> The beginning account balances for Miller Company were as follows for Year 2, Year 3, and Year 4: Miller Company experienced the following events for the accounting periods Year 2, Year 3, and Year 4: Year 2 1. Performed services for $36,000 on accoun
> Required: Record each of the following transactions in general journal form and then show the effect of the transaction in the horizontal statements model. The first transaction is shown as an example. a. Performed $50,000 worth of services on account.
> Hun Company began the accounting period with a $36,000 credit balance in its Accounts Payable account. During the accounting period, Hun incurred expenses on account of $108,000. The ending Accounts Payable balance was $48,000. Required: Based on this i
> Barnes Inc. began the accounting period with a $105,000 debit balance in its Accounts Receivable account. During the accounting period, Barnes earned revenue on account of $448,000. The ending Accounts Receivable balance was $86,000. Required: Based on
> James Jones received a $90,000 cash advance on March 1, Year 1, for legal services to be performed in the future. Services were to be provided for a one year term beginning March 1, Year 1. Required: a. Record the March 1 cash receipt in T-accounts. b.
> Laura Moss started and operated a small family consulting firm in Year 1. The firm was affected by two events: (1) Moss provided $36,000 of services on account, and (2) she purchased $10,000 of supplies on account. There were $1,800 of supplies on hand a
> Complete the following table by indicating whether a debit or credit is used to increase or decrease the balance of the following accounts. The appropriate debit/credit terminology has been identified for the first account as an example. Used to Inc

