Question: The two strands of the DNA molecule
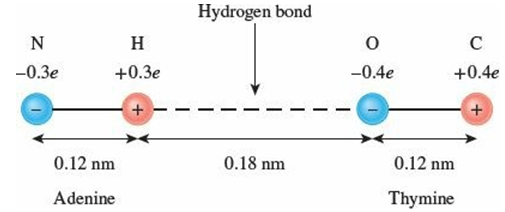
The two strands of the DNA molecule are held together by hydrogen bonds between base pairs (Sec. 16.1). When an enzyme unzips the molecule to separate the two strands, it has to break these hydrogen bonds. A simplified model represents a hydrogen bond as the electrostatic interaction of four point charges arranged along a straight line. The figure shows the arrangement of charges for one of the hydrogen bonds between adenine and thymine. Estimate the energy that must be supplied to break this bond.
> A sine wave is traveling to the right on a cord. The lighter line in the figure represents the shape of the cord at time t = 0; the darker line represents the shape of the cord at time t = 0.10 s. (Note that the horizontal and vertical scales are differe
> Find the electric field at point B, midway between the upper left and right corners.
> Five stretched strings have the following properties. Rank the strings according to their fundamental frequencies (for transverse standing waves), from greatest to least. (a) length L, total mass m, tension F (b) length 2L, total mass m, tension F (c) le
> Rank the waves in order of maximum transverse speed, largest to smallest.
> Rank the waves in order of amplitude, largest to smallest.
> Rank the waves in order of frequency, largest to smallest.
> What is the average binding energy per nucleon for /?
> Five cars are traveling on a highway. Their masses and initial speeds are: (a) 1500 kg, 30 m/s (b) 1500 kg, 20 m/s (c) 1000 kg, 30 m/s (d) 1000 kg, 20 m/s (e) 2000 kg, 40 m/s The cars use the same braking force to slow down and stop. Rank the cars in ord
> Once Rutherford and Geiger determined the charge-to-mass ratio of the alpha particle (see Problem 93), they performed another experiment to determine its charge. An alpha source was placed in an evacuated chamber with a fluorescent screen. Through a glas
> Write the equation for a harmonic wave with amplitude 2.50 cm and angular frequency 2.90 rad/s that is moving in the +x-direction with a wave speed that is 5.00 times as fast as the maximum transverse speed of a point on the string. At t = 0, the point x
> At time t = 0, block A of mass 0.225 kg and block B of mass 0.600 kg rest on a horizontal frictionless surface a distance 3.40 m apart, with block A located to the left of block B. A horizontal force of 2.00 N directed to the right is applied to block A
> A scout troop is practicing its orienteering skills with map and compass. First they walk due east for 1.2 km. Next, they walk 45° west of north for 2.7 km. In what direction must they walk to go directly back to their starting point? How far will they h
> The intensity of the sound wave from a jet airplane as it is taking off is 100 W/m2 at a distance of 5.0 m. What is the intensity of the sound wave that reaches the ears of a person standing at a distance of 120 m from the runway? Assume that the sound w
> In a game of shuffleboard, a disk with an initial speed of 3.2 m/s travels 6.0 m before coming to rest. (a) What was the acceleration of the disk? (b) What was the coefficient of kinetic friction between the floor and the disk?
> (a) Write an equation for a harmonic wave with amplitude 0.750 mm, frequency 36.0 Hz, and wave speed 144 m/s traveling in the +x- direction. At t = 0, the point x = 0 is at its maximum displacement in the +y-direction. (b) What is the maximum accelerati
> Prove that, in an EM wave traveling in vacuum, the electric and magnetic energy densities are equal; that is, prove that at any point and at any instant of time.
> You are swimming in the ocean as water waves with wavelength 9.6 m pass by. What is the closest distance that another swimmer could be so that his motion is exactly opposite yours (he goes up when you go down)?
> What is the mass defect of the 14N nucleus?
> A mass of 1.4 kg of water at 22°C is poured from a height of 2.5 m into a vessel containing 5.0 kg of water at 22°C. (a) How much does the internal energy of the 6.4 kg of water increase? (b) Is it likely that the water temperature increases? Explain.
> Rank the points in order of mechanical energy, from greatest to least, assuming no friction or air resistance.
> Steel railroad tracks of length 18.30 m are laid at 10.0°C. How much space should be left between the track sections if they are to just touch when the temperature is 50.0°C?
> Sketch a graph of y versus x for the function for the times t = 0 and 0.96 s. Make the graphs on the same axes, using a solid line for the first and a dashed line for the second. Use the values k = (Ï€/5.0) rad/cm and ω = (Ï
> The photosensitive cells (rods and cones) in the retina are most densely packed in the fovea—the part of the retina used to see straight ahead. In the fovea, the cells are all cones spaced about 1 µm apart. Would our vision have much better resolution if
> An object of mass m is hung from the base of an ideal spring that is suspended from the ceiling. The spring has a spring constant k. The object is pulled down a distance D from equilibrium and released. Later, the same system is set oscillating by pullin
> Two 35.0 cm metal rods, one made of copper and one made of aluminum, are placed end to end, touching each other. One end is fixed, so that it cannot move. The rods are heated from 0.0°C to 150°C. How far does the other end of the system of rods move?
> A 6.0 pF capacitor is needed to construct a circuit. The only capacitors available are rated as 9.0 pF. How can a combination of three 9.0 pF capacitors be assembled so that the equivalent capacitance of the combination is 6.0 pF?
> Is e the smallest fundamental unit of charge? The smallest observable unit of charge? [Hint: Try to come up with a meson or baryon with a charge that is not an integral multiple of e.] Explain.
> Isolated atoms (or atoms in a dilute gas) radiate photons at discrete energies characteristic of that atom. In dense matter, the spectrum radiated is quasi-continuous. Why doesn’t the same thing happen with nuclear spectra: why do the gamma rays have the
> What is the mass of an 16O atom in units of MeV/c2? (1 MeV/c2 is the mass of a particle with rest energy 1 MeV.)
> A 2.4 m length of copper pipe extends directly from a water heater in a basement to a faucet on the first floor of a house. If the faucet isn't fixed in place, how much will it rise when the pipe is heated from 20.0°C to 90.0°C? Ignore any increase in th
> The size of an atom is about 0.1 nm. Can a light microscope make an image of an atom? Explain.
> You are serving as a consultant for the newest James Bond film. In one scene, Bond must fire a projectile from a cannon and hit the enemy headquarters located on the top of a cliff 75.0 m above and 350 m from the cannon. The cannon will shoot the project
> A radio station wants to ensure good reception of its signal everywhere inside a city. Would it be a good idea to place several broadcasting antennas at roughly equal intervals around the perimeter of the city? Explain.
> Five slabs with temperature coefficients of expansion α have lengths L at Ti = 20°C. Their temperatures then rise to Tf. Rank them in order of how much their lengths increase, greatest to smallest. (a) L = 90 cm, Tf = 40°C, α = 8 × 10−6 K−1 (granite) (b)
> Water entering a house flows with a speed of 0.20 m/s through a pipe of 1.0 cm inside radius. What is the speed of the water at a point where the pipe tapers to a radius of 2.5 mm?
> A 1.5 V flashlight battery can maintain a current of 0.30 A for 4.0 h before it is exhausted. How much chemical energy is converted to electrical energy in this process? (Assume zero internal resistance of the battery.)
> Two antennas driven by the same electrical signal emit coherent radio waves. Is it possible for two antennas driven by independent signals to emit radio waves that are coherent with each other? If so, how? If not, why not?
> Stereo speakers should be wired with the same polarity. If by mistake they are wired with opposite polarities, the bass (low frequencies) sound much weaker than if they are wired correctly. Why? Why is the bass (low frequencies) weakened more than the tr
> Why can you easily hear sound around a corner due to diffraction, although you cannot see around the same corner?
> Estimate the number of nucleons found in the body of a 75 kg person.
> Event A happens at the spacetime coordinates (x, y, z, t) = (2 m, 3 m, 0, 0.1 s) and event B happens at the spacetime coordinates (x, y, z, t) = (0.4 × 108 m, 3 m, 0, 0.2 s). (a) Is it possible that event A caused event B? (b) If event B occurred at (0
> Hannah is standing in the middle of a room with two opposite walls that are separated by 10.0 m and covered by plane mirrors. There is a candle in the room 1.50 m from one mirrored wall. Hannah is facing the opposite mirrored wall and sees many images of
> A 2.0 kg object (the “projectile”) approaches a stationary object (the “target”) at 5.0 m/s. The projectile is deflected through an angle of 60.0° and its speed after the collision is 3.0 m/s. What is the magnitude of the momentum of the target after the
> In the LHC, protons are accelerated to a total energy of 7 TeV. (a) What is the speed of these protons? (b) The LHC tunnel is 27 km in circumference. As measured by an Earth observer, how long does it take the protons to go around the tunnel once? (c)
> What is the average binding energy per nucleon for
> The escape speed from Earth is 11.2 km/s, but that is only the minimum speed needed to escape Earth’s gravitational pull; it does not give the object enough energy to leave the solar system. What is the minimum speed for an object near Earth’s surface so
> The gravitational potential energy of a pendulum is U = mgy. (a) Taking y = 0 at the lowest point, show that y = L(1 − cos θ), where θ is the angle the string makes with the vertical. (b) If θ is s
> Kurt is measuring the speed of light in an evacuated chamber aboard a spaceship traveling with a constant velocity of 0.60c with respect to Earth. The light is moving in the direction of motion of the spaceship. Siu-Ling is on Earth watching the experime
> The Milky Way galaxy rotates about its center with a period of about 200 million yr. The Sun is 2 × 1020 m from the center of the galaxy. How fast is the Sun moving with respect to the center of the galaxy?
> Your car’s wheels are 65 cm in diameter, and the wheels are spinning at an angular velocity of 101 rad/s. How fast is your car moving in kilometers per hour (assume no slippage)?
> About how close to each other are two objects on the Moon that can just barely be resolved by the 5.08 m diameter Mount Palomar reflecting telescope? (Use a wavelength of 520 nm.)
> The forces on a small airplane (mass 1160 kg) in horizontal flight heading eastward are as follows: weight = 11.4 kN downward, lift = 11.4 kN upward, thrust = 1.800 kN eastward, and drag = 1.400 kN westward. At t = 0, the plane's speed is 60.0 m/s. If th
> The Tevatron is a particle accelerator at Fermilab that accelerates protons and antiprotons to high energies in an underground ring. Scientists observe the results of collisions between the particles. The protons are accelerated until they have speeds on
> The mean (average) lifetime of a muon in its rest frame is 2.2 µs. A beam of muons is moving through the lab with speed 0.994c. How far on average does a muon travel through the lab before it decays?
> A satellite travels around Earth in uniform circular motion at an altitude of 35800 km above Earth’s surface. The satellite is in geosynchronous orbit. In the figure with Multiple-Choice Questions 1-4, the satellite moves counterclockwise (ABCDA). State
> An astronaut in a rocket moving at 0.50c toward the Sun finds himself halfway between Earth and the Sun. According to the astronaut, how far is he from Earth? In the frame of the Sun, the distance from Earth to the Sun is 1.50 × 1011 m.
> Why does a helium weather balloon expand as it rises into the air? Assume the temperature remains constant.
> A transverse wave on a string has amplitude 4.0 mm, angular frequency 600 rad/s, and wavenumber 6.0 rad/m. (a) What is the maximum transverse speed of a point on the string? (b) What is the average transverse speed of a point on the string? [Hint: How
> A futuristic train moving in a straight line with a uniform speed of 0.80c passes a series of communications towers. The spacing between the towers, according to an observer on the ground, is 3.0 km. A passenger on the train uses an accurate stopwatch to
> The light-second is a unit of distance; 1 light-second is the distance that light travels in 1 second. (a) Find the conversion between light-seconds and meters: 1 light-second = ? m. (b) What is the speed of light in units of light-seconds per second?
> Fill in the missing algebraic steps in the derivation of the time dilation equation [Eq. (26-4)].
> An engineer in a train moving toward the station with a velocity v = 0.60c lights a signal flare as he reaches a marker 1.0 km from the station (according to a scale laid out on the ground). By how much time, on the station-master's clock, does the arriv
> A 2.00 µF capacitor is charged using a 5.00 V battery, and a 3.00 µF capacitor is charged using a 10.0 V battery. (a) What is the total energy stored in the two capacitors? (b) The batteries are disconnected, and the two capacitors are connected togeth
> A steep cliff west of Lydia's home reflects a 1020 kHz radio signal from a station that is 74 km due east of her home. If there is destructive interference, what is the minimum distance of the cliff from her home? Assume there is a 180° phase shift when
> A sports car traveling along a straight line increases its speed from 20.0 mi/h to 60.0 mi/h. (a) What is the ratio of the final to the initial magnitude of its momentum? (b) What is the ratio of the final to the initial kinetic energy?
> A skier with a mass of 63 kg starts from rest and skis down an icy (frictionless) slope that has a length of 50 m at an angle of 32° with respect to the horizontal. At the bottom of the slope, the path levels out and becomes horizontal, the snow becomes
> An experiment similar to Example 25.1 is performed; the power at the receiver as a function of x is shown in the figure. (a) Approximately what is the wavelength of the microwaves? (b) If the amplitude of the wave entering the detector at the first max
> The current in a 0.080 H solenoid increases from 20.0 mA to 160.0 mA in 7.0 s. Find the average emf in the solenoid during that time interval.
> An unmarked police car starts from rest just as a speeding car passes at a speed of v. If the police car speeds up with a constant acceleration of a, what is the speed of the police car when it catches up to the speeder, who does not realize she is being
> The particle moves along a straight line from b to a.
> The circuit shown has a source voltage of 440 V rms, resistance R = 250 Ω, inductance L = 0.800 H, and capacitance C = 2.22 µF. (a) Find the angular frequency ω0 for resonance in this circuit. (b) Draw a phasor diagr
> A spider’s web can undergo SHM when a fly lands on it and displaces the web. For simplicity, assume that a web is described by Hooke’s law (even though really it deforms permanently when displaced). If the web is initially horizontal and a fly landing on
> When Albert turns on his small desk lamp, the light falling on his book has intensity I0. When this is not quite enough, he turns the small lamp off and turns on a high-intensity lamp so that the light on his book has intensity 4I0. What is the intensity
> Four coherent EM waves have intensities of I0, 0.80I0, 0.60I0, and 0.40I0. The second is 180° out of phase with the first; the third and fourth are in phase with the first. What is the intensity of the superposition of the four?
> Four coherent EM waves are all in phase. Individually, they have intensities of I0, 0.80I0, 0.60I0, and 0.40I0. What is the intensity of the superposition of the four?
> Two coherent EM waves have intensities of I0 and 0.60I0. What is the resulting intensity when they interfere destructively?
> A grating has exactly 8000 slits uniformly spaced over 2.54 cm and is illuminated by light from a mercury vapor discharge lamp. What is the expected angle for the third-order maximum of the green line (λ = 546 nm)?
> A nurse applies a force of 4.40 N to the piston of a syringe. The piston has an area of 5.00 × 10−5 m2. What is the pressure increase in the fluid within the syringe?
> A spaceship resting on Earth has a length of 35.2 m. As it departs on a trip to another planet, it has a length of 30.5 m as measured by the Earthbound observers. The Earthbound observers also notice that one of the astronauts on the spaceship exercises
> You are given a slide with two slits cut into it and asked how far apart the slits are. You shine white light on the slide and notice the first-order color spectrum that is created on a screen 3.40 m away. On the screen, the red light with a wavelength o
> What potential difference must be applied to an x-ray tube to produce x-rays with a minimum wavelength of 45.0 pm?
> Starting from rest, a horse pulls a 250 kg cart for a distance of 1.5 km. It reaches a speed of 0.38 m/s by the time it has walked 50.0 m and then walks at constant speed. The frictional force on the rolling cart is a constant 260 N. Each gram of oats th
> An engine pulls a train of 20 freight cars, each having a mass of 5.0 × 104 kg, with a constant force. The cars move from rest to a speed of 4.0 m/s in 20.0 s on a straight track. Neglecting friction, what is the force with which the tenth car pulls the
> A double slit is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength 600.0 nm. The m = 0 and m = 1 bright fringes are separated by 3.0 mm on a screen 40.0 cm away from the slits. What is the separation between the slits? [Hint: Is the small-angle approxim
> A system consists of three particles with these masses and velocities: mass 3.0 kg, moving north at 3.0 m/s; mass 4.0 kg, moving south at 5.0 m/s; and mass 7.0 kg, moving north at 2.0 m/s. What is the total momentum of the system?
> Light from a helium-neon laser (632.8 nm) is incident on a pair of slits. In the interference pattern on a screen 1.5 m from the slits, the bright fringes are separated by 1.35 cm. What is the slit separation? [Hint: Is the small-angle approximation just
> Light of wavelength 589 nm incident on a pair of slits produces an interference pattern on a distant screen in which the separation between adjacent bright fringes at the center of the pattern is 0.530 cm. A second light source, when incident on the same
> Use a compass to make an accurate drawing of the wavefronts in a double-slit interference experiment similar to Fig. 25.17c. Place the slits 2.0 cm apart and let the wavelength of the incident wave be 1.0 cm. Using a straightedge, draw lines of construct
> The length of the auditory canal in humans averages about 2.5 cm. What are the lowest three standing wave frequencies for a pipe of this length open at one end? What effect might resonance have on the sensitivity of the ear at various frequencies? (Refer
> A Ping-Pong ball that has been dented during hard play can often be restored by placing it in hot water. Explain why this works.
> Block A, with a mass of 220 g, is traveling north on a frictionless surface with a speed of 5.0 m/s. Block B, with a mass of 300 g, travels west on the same surface until it collides with A. After the collision, the blocks move off together with a veloci
> Ramon has a coherent light source with wavelength 547 nm. He wishes to send light through a double slit with slit separation of 1.50 mm to a screen 90.0 cm away. What is the minimum width of the screen if Ramon wants to display five complete bright fring
> Light incident on a pair of slits produces an interference pattern on a screen 2.50 m from the slits. If the slit separation is 0.0150 cm and the distance between adjacent bright fringes in the pattern is 0.760 cm, what is the wavelength of the light? [H
> If the incline is frictionless, find the total work done on the sliding crate. The tension in the rope is 110.5 N.
> Michaela is planning a trip in Ireland from Killarney to Cork to visit Blarney Castle (see Example 3.2). She also wants to visit Mallow, which is located 39 km due east of Killarney and 22 km due north of Cork. Draw the displacement vectors for the trip
> Jim rides his skateboard down a ramp that is in the shape of a quarter circle with a radius of 5.00 m. At the bottom of the ramp, Jim is moving at 9.00 m/s. Jim and his skateboard have a mass of 65.0 kg. How much work is done by friction as the skateboar
> The electric field between plates (A) is zero. As the beam exits the space between plates (B), it has been deflected 2.0 mm downward (Δy = −2.0 mm). What is the electric field between plates (B)?
> While passing a slower car on the highway, you accelerate uniformly from 17.4 m/s to 27.3 m/s in a time of 10.0 s. (a) How far do you travel during this time? (b) What is your acceleration magnitude?
> In a fixed-target experiment, high-energy charged particles from an accelerator are smashed into a stationary target. By contrast, in a colliding beam experiment, two beams of particles are accelerated to high energies; particles moving in opposite direc
> Two coherent EM waves have intensities of I0 and 0.28I0. What is the resulting intensity when they interfere constructively?

