Question: This problem compares the profitability and risk
This problem compares the profitability and risk ratios of three leading discount chains: Cartoo, Taggle, and Wilmet. Cartoo is headquartered in Spain, and Taggle and Wilmet are headquartered in the United States. Exhibits 7.20 and 7.21 present profitability ratios for Cartoo, Taggle, and Wilmet for fiscal years 2011, 2012, and 2013. Exhibit 7.22 presents risk ratios for the three firms. Exhibit 7.23 presents selected other data for these firms. All amounts are expressed in U.S. dollars to permit comparability across the firms. The first item in Exhibit 7.23 shows both the increase in total sales and, in brackets, the increase in sales of stores that have been open for at least two full years (same store sales). The increase in total sales equals the sum of increases in same store sales and increases in sales due to opening new stores and acquiring new stores through corporate acquisitions. Study these financial ratios and respond to the following questions:
a. Wilmet and Taggle follow different strategies. Wilmet consistently has a higher rate of return on assets (ROA) than Taggle. Using information in the exhibits, suggest reasons for these differences in operating profitability.
b. Wilmet and Cartoo follow similar strategies. Wilmet consistently outperforms Cartoo on ROA. Using information in the exhibits, suggest reasons for these differences in operating profitability.
c. Do any of these firms appear unduly risky as of the end of 2013?
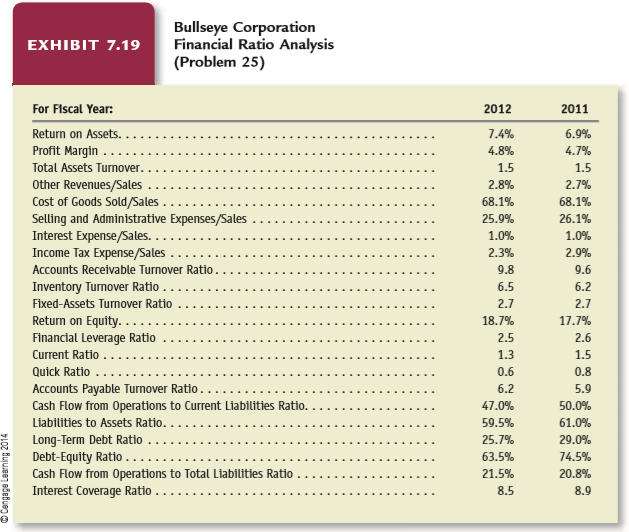
Transcribed Image Text:
Bullseye Corporation Financial Ratio Analysis (Problem 25) EXHIBIT 7.19 For Fiscal Year: 2012 2011 Return on Assets.... Profit Margin ... 7.4% 6.9% 4.8% 4.7% Total Assets Turnover. 1.5 1.5 Other Revenues/Sales Cost of Goods Sold/Sales . Selling and Administrative Expenses/Sales Interest Expense/Sales. ... Income Tax Expense/Sales . 2.8% 2.7% 68.1% 68.1% 25.9% 26.1% 1.0% 1.0% 2.3% 2.9% Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio. 9.8 9.6 Inventory Turnover Ratio . Fixed-Assets Turnover Ratio 6.5 6.2 2.7 2.7 Return on Equity... Financial Leverage-ratio' data-toggle="tooltip" data-placement="top" title="Click to view definition...">Leverage Ratio Current Ratio ... Quick Ratio ... Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio.. 18.7% 17.7% 2.5 2.6 1.3 1.5 0.6 0.8 6.2 5.9 ... Cash Flow from Operations to Current Liabilities Ratio. Liabilities to Assets Ratio. . 47.0% 50.0% 59.5% 61.0% Long-Term Debt Ratio Debt-Equity Ratio ... Cash Flow from Operations to Total Liabilities Ratio . 25.7% 29.0% 63.5% 74.5% 21.5% 20.8% Interest Coverage Ratl . 8.5 8.9 O Cengage Learning 2014
> A firm generated net income for the current year, but cash flow from operations was negative. How can this happen?
> Under what circumstances will the rate of return on equity exceed the rate of return on assets? Under what circumstances will it be less?
> The acquisition of equipment by assuming a mortgage is a transaction that firms cannot report in their statement of cash flows but must report in a supplemental schedule or note. Of what value is information about this type of transaction? What is the re
> Some of the assets of one firm correspond to the liabilities of another firm. For example, an account receivable on the seller’s balance sheet is an account payable on the buyer’s balance sheet. For each of the following items, indicate whether it is an
> Accounting treats cash discounts taken on the purchase of merchandise or equipment as a reduction in the amount recorded for the assets acquired. What justification can you see for this treatment?
> Why is it important to separate the income from discontinued operations from the income from continuing operations on the income statement?
> Both interest expense on borrowing and dividends on common stock reduce net assets and reduce shareholders’ equity. Accountants treat interest as an expense in measuring net income but do not treat dividends on common stock as an expense. Explain the rat
> Distinguish between a cost and an expense.
> “The measurement of assets and liabilities relates closely to the measurement of revenues and expenses.” Explain.
> An entrepreneur claimed that her new company had generated both superior profit margin performance and superior asset turnover performance. Explain whether such an outcome is likely to happen.
> A Japanese car manufacturer (JCM) reported Sales of Products of ¥22,670 billion for the year ended March 31, Year 7. The Cost of Products Sold was ¥18,356 billion. Assume that JCM made all sales on credit. By March 31, Year 7, JCM had collected cash for
> Some have argued that for any given firm at a particular time, there is an optimal inventory turnover ratio. Explain.
> One company president stated, “The operations of our company are such that we must turn our assets over once every four weeks.” A company president in another industry stated, “The operations of our company are such that we can live comfortably with asse
> Explain why the return on equity of a company that has no preferred stock will be smaller than the return on equity of an otherwise similar firm that has preferred stock.
> A firm’s total assets turnover decreased, but its accounts receivable, inventory, and fixed asset turnover increased. Suggest possible explanations.
> In calculating return on assets, the simple ROA formula does not adjust for interest expense. Explain why is it technically more correct to make an adjustment for interest expense in calculating this ratio, and explain the form of the adjustment.
> “Financial ratios are useful metrics for relating two items in the financial statements. Interpreting changes in a particular financial ratio is difficult, however, because the explanation might relate to changes in the numerator, the denominator, or bot
> Given how financial leverage affects ROE, why does a firm not borrow as much as possible? That is, why doesn’t a firm increase borrowing to as close to 100% of financing as it can?
> The statement of cash flows classifies changes in accounts payable as an operating activity but classifies changes in short-term bank borrowing as a financing activity. Explain this apparent paradox.
> Under U.S. GAAP, the statement of cash flows classifies cash expenditures for interest on debt as an operating activity but classifies cash expenditures for dividends to shareholders as a financing activity. Explain this apparent paradox.
> The statement of cash flows classifies cash expenditures for interest expense as an operating activity but classifies cash expenditures to redeem debt as a financing activity. Explain this apparent paradox.
> A South African paper company, SAPC Limited (SAPC), reports noncurrent Interest-Bearing Borrowings of $1,634 million at September 30, Year 6. SAPC applies IFRS and reports its results in millions of U.S. dollars. At September 30, Year 7, this balance had
> A student remarked: “The direct method of computing cash flow from operations is easier to understand than the indirect method. Why do the majority of firms follow the indirect method in preparing their statements of cash flows?” Respond to this student.
> “The statement of cash flows provides information about changes in the structure of a firm’s assets and sources of financing.” Explain.
> “The accrual basis of accounting creates the need for a statement of cash flows.” Explain.
> “One can most easily accomplish the reporting objective of the income statement under the accrual basis of accounting and the reporting objective of the statement of cash flows by issuing a single income statement using the cash basis of accounting.” Eva
> The sale of equipment for an amount of cash greater than the carrying value of the equipment results in a cash receipt equal to the carrying value of the equipment plus the gain on the sale, which appears in income. How might the accountant treat this tr
> A firm operated at a net loss for the current year, but cash flow from operations was positive. How can this happen?
> One writer stated, “Depreciation expense is a firm’s chief source of cash for growth.” A reader criticized this statement by replying, “The fact remains that if companies had elected, in any year, to charge off $10 million more depreciation than they did
> Why might it be difficult to compare two otherwise similar firms in terms of their operating profits?
> Why is it important to separate gains from revenues?
> A customer has paid the firm, in advance, for merchandise the firm will deliver next month. Why is the firm not permitted to recognize revenue when it receives the cash?
> EBB Group (EBB), headquartered in Switzerland, is one of the world’s largest engineering companies. EBB applies U.S. GAAP, and reports its results in millions of U.S. dollars. Based on EBB’s financial reports for Year 7, at January 1, Year 7, EBB reporte
> In an accrual accounting system, firms recognize revenues even if they have not received cash. What criteria must sales transactions meet in order for the seller to recognize revenues before collecting cash?
> A student says, “It is inconceivable to me that a firm could report increasing net income yet run out of cash.” Clarify this seeming contradiction.
> Accounting typically does not recognize either assets or liabilities for mutually unexecuted contracts. What justification can you see for this treatment?
> Identify the underlying accounting principle that guides the items to include in the acquisition cost of inventories, equipment, buildings, and other similar assets. What is the rationale for this accounting principle?
> The word probable appears in the definitions of assets and liabilities and in the recognition criteria for liabilities with uncertain amount and/or timing. a. What is the meaning of probable as used in the definitions of assets and liabilities? b. How do
> What is the amount of the liability that the company recognizes in each of the following independent cases? a. A plaintiff files a lawsuit against the company. The probability is 90% that the company will lose. If it loses, the amount of the loss will mo
> For each of the following items, indicate whether the item meets all of the criteria in the definition of a liability. If so, how does the firm value it? a. Interest accrued but not paid on a note. b. Advances from customers for goods and services to be
> One of the criteria for the recognition of an asset or a liability is that there be an exchange. What justification can you see for this requirement?
> A group of investors owns an office building that it rents unfurnished to tenants. It purchased the building five years previously from a construction company. At that time, it expected the building to have a useful life of 40 years. Indicate the procedu
> Who might the accounting convention of conservatism hurt?
> Bonana Company, a U.S. clothing designer, manufacturer, and retailer, reported a balance in prepaid insurance of $24.0 million, based on its financial reports dated March 31, Year 8, the end of its fiscal year. Assume that all of this balance relates to
> Problem 25 presents financial statements for Bullseye Corporation for its fiscal years ending December 31, 2011, 2012, and 2013, as well as financial statement ratios. a. Prepare a set of pro forma financial statements for Bullseye Corporation for fiscal
> Effective financial statement analysis requires an understanding of a firm’s economic characteristics. The relations among various financial statement items provide evidence of many of these economic characteristics. Exhibit 7.28 pres
> Scantania is a Swedish company that manufactures trucks and other heavy vehicles and provides financing for its customers’ purchases. Exhibit 7.27 presents financial statement ratios for Scantania for 2011, 2012, and 2013. The amount on
> Depkline plc is a pharmaceutical company headquartered in the United Kingdom. Exhibit 7.26 presents financial statement ratios for Depkline for 2011, 2012, and 2013. Respond to each of the following questions. a. What are the likely reasons for the incre
> Gappo Group and Limito Brands maintain leading market positions in the specialty apparel retailing market. The products of Gappo (jeans, blouses, shirts) are more standardized than those of Limito. The products of Limito are more fashion-oriented and gli
> Bullseye Corporation, headquartered in the United States, operates retail stores that offer clothing, household products, electronic products, sports products, toys, and entertainment products at discount prices. Bullseye differentiates itself from compe
> Top financial management wants to increase cash flow from operations. It asks you to implement the following strategies. Which of these, if implemented, will increase cash flow from operations contrasted to the amount if you do not implement the strategy
> Refer to Exhibit 6.35 for Fierce Fighters Corporation, which shows excerpts from its Statements of Cash Flows, with cash flow from operations presented with the indirect method, for three recent years. We use these years to illustrate a period of success
> Exhibit 6.34 presents statements of cash flow for eight companies for the same year: a. American Airlines (airline transportation) b. American Home Products (pharmaceuticals) c. Interpublic Group (advertising and other marketing services) d. Procter &
> On December 31, Year 6, the Merchandise Inventories account of a Japanese electronics firm had a balance of ¥408,710 million, based on the firm’s financial reports for fiscal Year 7. Assume that during Year 7, the firm purchased merchandise inventories o
> Exhibit 6.33 presents statements of cash flows for Spokane Paper Group, a forest products company, for three recent years. During this period, it faced financial difficulty, which you can see by noting the pattern of losses increasing with time. a. Spoka
> Exhibit 6.32 presents a statement of cash flows for Swoosh Shoes, Inc., for three years. a. Why did Swoosh experience increasing net income but decreasing cash flow from operations during this three-year period? b. What is the likely explanation for the
> Quintana Company presents the balance sheet shown in Exhibit 6.30 and the statement of cash flows shown in Exhibit 6.31 for 2013. The firm sold investments, equipment, and land for cash at their net book value. The accumulated depreciation of the equipme
> Refer to information about Carter Corporation in the preceding problem. a. What was the change in accounts receivable during 2012? b. Inventories increased by $624.1 during 2012. What was the change in accounts payable for inventories during 2012? c
> Exhibit 6.28 shows the consolidated income statements for Carter Corporation for three recent years. Carter uses the direct method for presenting its cash flows from operations, which appears in Exhibit 6.29. a. What was the change in accounts receivable
> GTI, Inc., manufactures parts, components, and processing equipment for electronics and semiconductor applications in the communication, computer, automotive, and appliance industries. Its sales tend to vary with changes in the business cycle since the s
> Financial statement data for Dickerson Manufacturing Company for the current year appear in Exhibit 6.25. Additional information includes the following: (1) Net income for the year was $568,000; dividends declared and paid were $60,000. (2) Depreciation
> Condensed financial statement data for Hale Company for the current year appear in Exhibits 6.23 and 6.24. During the current year, the firm sold for $5,000 equipment costing $15,000 with $10,000 of accumulated depreciation. a. Prepare a statement of
> (Based on a problem prepared by Stephen A. Zeff.) You work for the Plains State Bank as an analyst specializing in the financial statements of small businesses seeking loans from the bank. Digit Retail Enterprises Inc. provides you with its balance sheet
> Exhibit 6.20 presents data from the financial statements for Heidi’s Hide-Out, a bar and video-game club, with private party rooms for rent. Heidi’s deals with ■Many employees, to some of whom it has
> The following selected information is based on the Year 7 financial statements adapted from those of Beyond Petroleum (BP). BP applies IFRS and reports its results in millions of U.S. dollars. Compute the missing information in each of the following four
> A multinational computer equipment manufacturer reported the following amounts for two recent years (in millions of U.S. dollars). The firm applies U.S. GAAP. a. Compute the ratio of net income divided by revenues for each year. b. Compute the ratio of
> Dyreng Plc. (Dyreng), a Belgianbased construction firm, reported the following information for Year 11. Dyreng applies IFRS and reports in thousands of euros (€). Further information available to you reveals the following six items, wi
> SeaBreeze Inc., a Taiwan-based semiconductor manufacturer, reported the following information for Year 12. SeaBreeze Inc. applies IFRS and reports in millions of yuan (Â¥). Further information available to you reveals the following five items
> Dragonfly Limited (Dragonfly), a diversified electronics firm headquartered in Singapore, reported the following income statement information for its year ended December 31, Year 7. Dragonfly applies Singapore financial reporting standards and reports it
> Broyo Corporation (Broyo), a large paper company, reported the following income statement for its year ended December 31, Year 13. Broyo applies IFRS and reports its results in millions of euros. Broyo supplied additional information about the followin
> Information from GoodLuck Brands’s income statements for the years ended December 31, Years 6, 7, and 8, is shown next. GoodLuck Brands is a U.S.-based manufacturer and distributor. The company applies U.S. GAAP and reports its results
> Information from Cementex Corporation’s (Cementex) income statements for the years ended December 31, Year 9 and Year 10, is shown in the following display. Cementex is a Mexican construction firm that applies Mexican accounting standar
> Exhibit 4.4 presents the balance sheet of Paul Loren Company for Years 10 and 9. This balance sheet uses the terminology, format, and accounting methods of U.S. GAAP, and Paul Loren reports results in millions of U.S. dollars. (Adapted from the financi
> Exhibit 4.3 presents the balance sheet prepared by Svenson, a Swedish telecommunications firm, for Years 7 and 6. Svenson applies IFRS and reports its results in millions of Swedish kronor (SEK). In addition to the items reported in Svensonâ€&
> Exhibit 4.2 presents the balance sheet prepared by Infotech Limited, an Indian information technology firm, for Years 12 and 11. Infotech applies accounting standards issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India and reports its results in mi
> The following selected information is based on the Year 7 financial statements of the German healthcare firm, adopted from the financial statements Bayer Group. Bayer Group applies IFRS, and reports its results in millions of euros. Compute the missing i
> What is the purpose of temporary accounts?
> What are some of the top issues 3M should consider in developing the Flag Highlighter?
> Most of the ingredients needed for pizza could be acquired from local suppliers located in close proximity to the Domino’s stores in a given city, eliminating the extensive supply chain network that Domino’s utilizes with their hub-and-spoke approach. W
> 1. Review the tactical pricing approaches shown in Exhibit 11.4. Which of these did you see evidence of being part of the SBC pricing strategy? Discuss the evidence you observed. 2. The SBC executive noted that children who start their cycling experienc
> 1. What were the key execution problems noted in the video for the new Wild Ophelia brand (at both WalMart and Walgreen’s? 2. What steps could be taken to ensure that Vosges’ next attempt at distribution for Wild Ophelia is more successful?
> Define GoPro’s product in terms of the essential benefit and core product. How does an understanding of the essential benefit drive product development for a company like GoPro? What kind of enhanced products could GoPro offer to add to the consumer’s
> The marketing manager for McDonald’s has been asked to develop a code of marketing ethics for the company. Develop a marketing code of ethics for McDonald’s, keeping in mind that the company has stores all over the world.
> When going global, one of the most fundamental decisions marketers must make is the standardization/localization decision regarding the different elements of the marketing mix. For the Product component of the mix, Domino’s chose a localization strategy
> The salesperson in this video notes that expanding business with existing customers is one of the best ways to increase total sales. Why is this the case? What are some of the keys (from the video and your own ideas) for increasing the amount of busine
> SBC is effectively using social media to strengthen their brand community, but has made a conscious decision not to offer their bicycles via their websites or other digital channels. Do you agree with this strategy? Why or why not?
> 1. Should Creston Vineyard use a push or pull strategy in its channels? 2. Describe Creston Vineyard's distribution intensity strategy.
> 1. How can Walmart change its image with consumers? 2. Will a change in image allow Walmart to charge a price premium?
> What are the risks BMW faces as it continues to add new cars to its product line?
> By segmenting their product line into 7 segments, has New Balance selected the optimal amount of segments?
> 1. Dole creates partnerships with its vendors, are there any drawbacks with this philosophy? 2. What are some of the criteria that Dole should consider when selecting vendors?
> What are the advantages and disadvantages of Best Buy’s customer centricity strategy?
> What are the long-term consequences for Dole’s decision not to focus primarily on taste?
> You are the market research director for a consumer product company. You have been asked to evaluate China as a potential market for your company’s products and begin a search of secondary data. What types of information would you consider in assessing
> 1. Are people more likely to purchase gas from BP because of its commitment to the environment? 2. In light of the recent crisis in the Gulf of Mexico, how does BP convince the public that they are sincere about caring about the environment?
> 1. What central changes are contributing to the growth of Yum! Brands in global markets? 2. Give some examples of ways that you believe Yum! Brands will have to adapt its offerings to appeal to global customers in different countries.
> 1. Vosge has chosen a premium/luxury positioning strategy. What are the pros and cons of this marketing approach for Vosge? 2. What aspects of Vosge’s marketing strategy supports their experience/storytelling approach? What are the risks to this strate
> Go to the Strategic Business Insights (SBI) website (www.strategicbusinessinsights.com) and click through to the section on VALSTM. Find the VALSTM survey and complete the questionnaire. a. Are the results surprising? Why or why not? Do you see yourse
> The alumni director at your institution wants to know how to serve the alumni better. Design a survey of no more than 10 questions that the alumni director can use to ask alumni about their interest in getting more involved with their school.
> The marketing manager for Disney Cruise Line wants to know what demographic trends will affect the cruise line business over the next five years. What kind of research is needed to address this question? Conduct some secondary research and try to you i

