Question: Velox Inc. began operations last year. For
Velox Inc. began operations last year. For its first two taxable years, Velox’s records show the following.
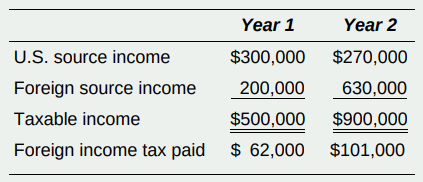
Compute Velox’s U.S. tax for both years, assuming the foreign source income does not qualify as FDII.
Transcribed Image Text:
Year 1 Year 2 U.S. source income $300,000 $270,000 Foreign source income 200,000 630,000 Taxable income $500,000 $900,000 Foreign income tax paid $ 62,000 $101,000
> Mr. and Mrs. Brown report taxable income of $130,000 in 2018. In addition, they report the following. Excess Social Security Withholding Credit ………………$ 2,200 Estimate tax payments 4,000 Withholding ……………….14,200 Compute the amount due or refund claimed
> Firm W, which has a 32 percent marginal tax rate, plans to operate a new business that should generate $40,000 annual cash flow/ordinary income for three years (years 0, 1, and 2). Alternatively, Firm W could form a new taxable entity (Entity N) to opera
> In January, Ms. NW projects that her employer will withhold $25,000 from her 2019 salary. However, she has income from several other sources and must make quarterly estimated tax payments. Compute the quarterly payments that result in a 2019 safe-harbor
> Jaclyn Biggs, who files as a head of household, never paid AMT before 2018. In 2018, her regular tax liability was $102,220 which included 39,900 capital gain taxed at 20 percent, and her AMTI in excess of her exemption amount was $422,500. Compute Jacly
> In each of the following cases, compute AMT (if any). For all cases, assume that taxable income does not include any dividend income or capital gain. a. Mr. and Mrs. Baker’s taxable income on their joint return was $200,000, and their AMTI before exempti
> Mr. and Mrs. Kigali’s AGI (earned income) was $14,610. Their federal income tax withholding was $850. They had no itemized deductions and two dependent children, ages 18 and 19. If Mr. and Mrs. Kigali are entitled to a $4,716 earned income credit, comput
> Mr. and Mrs. Lovejoy are married with no dependent children. Mr. Lovejoy worked for Smart Tech Corporation January through March and for Computer Associates the remainder of the year. Mrs. Lovejoy finished her degree in November and immediately began as
> Mr. and Mrs. Keppner file a joint income tax return. Compute their standard deduction assuming that: a. Mr. Keppner is age 68, and Mrs. Keppner is age 60. b. Mr. Keppner is age 70, and Mrs. Keppner is age 68. c. Mr. Keppner is age 70, and Mrs. Keppner is
> On March 31, Mr. Reinhardt quit his job with MT Inc. and began a new job with PK Company. His salary from MT was $82,600, and his salary from PK was $93,000. Compute his excess Social Security tax withholding credit.
> Mr. and Mrs. Coulter have four dependent children, ages 1, 4, 7, and 11. Mr. Coulter’s salary was $21,400, Mrs. Coulter’s wages totaled $16,200, and the couple had no other income or above-the-line deductions this year. The Coulters paid $3,600 for dayca
> Mr. and Mrs. Alexander have two dependent children. They paid $7,200 wages to a housekeeper to care for the children and $549 employer payroll tax on her wages. Mr. and Mrs. Alexander file a joint return. In each of the following cases, compute their dep
> Mr. and Mrs. Chaulk have three dependent children, ages 3, 6, and 9. Compute their child credit if AGI on their joint return is: a. $88,300. b. $462,700 c. $200,000 and assume that they have one non-child dependent who meets the requirements for the chil
> Corporation R signed a contract to undertake a transaction that will generate $360,000 total cash to the corporation. The cash will represent income in the year received and will be taxed at 21 percent. Corporation R will receive $200,000 in year 0 and $
> Ms. Gleason, an unmarried taxpayer, had the following income items. Salary …………………………………………….$40,000 Net income from a rental house …………..3,200 Ms. Gleason has a four-year-old son who attends a daycare center while she is at work. Ms. Gleason paid $4,3
> Callie is the 11-year-old daughter and dependent of Mr. and Mrs. Santo. This year, Callie filed a Form 1040 on which the only item of gross income was $10,557 interest from an investment bond portfolio that Callie inherited from a great aunt. Compute Cal
> Mrs. Atkinson is an unmarried taxpayer with one dependent child living in her home. Her AGI is $40,000, and she does not itemize deductions. The 18-year-old child earned $12,480 from a part-time job and incurred no deductible expenses. a. Compute Mrs. At
> Mr. Mason’s salary was $397,000, and Mrs. Mason’s salary was $344,000. They had no other income items, no above-the-line or itemized deductions, and no dependents. a. Compute their tax on a joint return. b. Compute their combined tax if they file separat
> Mr. and Mrs. Palio celebrated the birth of their third child on November 18. Compute the effect of this event on their tax liability, assuming that: a. Their AGI was $99,000, and their taxable income before considering the new dependent was $84,200. b. T
> Danny Liu is 20 years old and is considered a dependent of his parents for tax purposes. Compute Danny’s taxable income in each of the following cases. a. Danny’s only income item was $2,712 interest earned on a certificate of deposit. b. Danny had two i
> Mr. Garrett, a single taxpayer, has $15,700 AGI. Compute his taxable income in each of the following cases. a. Mr. Garrett’s AGI consists entirely of interest income. He is 19 years old and is considered a dependent of his parents for tax purposes. b. Mr
> Mr. Rogers, an unmarried individual, had the following income items. Salary ……………………………………………….$512,100 Interest income ……………………………………19,700 Dividend eligible for 20% rate ……………….31,000 Mr. Rogers had $34,000 itemized deductions and four dependent chil
> Mr. and Mrs. Ludwig had the following income items. Dividend eligible for 0% preferential rate ………………….$ 3,400 Capital gain eligible for 0% preferential rate …………………2,900 Mrs. Ludwig’s salary. …………………………………………………24,325 Mr. L is age 66, and Mrs. L is ag
> Mr. Coleman, an unmarried individual, had the following income items. Interest income …………………………………………………$14,200 Ordinary loss from an S corporation ……………………..(8,400) Ordinary income from a partnership …………………….159,000 He had $27,300 itemized deduction
> French Corporation wishes to hire Leslie as a consultant to design a comprehensive staff training program. The project is expected to take one year, and the parties have agreed to a tentative price of $60,000. French Corporation has proposed payment of o
> Mr. Perry is an unmarried individual with no dependent children. He reports the following information. Wages ……………………………………………………………………….$65,000 Schedule C net profit ……………………………………………………..11,650 Interest from savings account ……………………………………………500 Self-e
> Ms. Timmons, an unmarried individual, has the following income items. Schedule C net profit …………………………………..$31,900 NOL carry forward deduction ………………….…….(9,190) Interest income ……………………………………..…………..725 Ms. Timmons’s self-employment tax was $4,507. Sh
> Mr. and Mrs. Simpson have the following income items. Mr. Simpson’s Schedule C net profit ………………………..$91,320 Mrs. Simpson’s Schedule C net loss ………………………….(7,480) Mrs. Simpson’s taxable pension ………………………………….12,300 Mr. Simpson’s self-employment tax was
> Turbo is a U.S. corporation. This year, it earned $5 million before-tax income and paid $175,000 income tax to jurisdictions other than the United States. Compute Turbo’s U.S. federal income tax assuming that: a. The other jurisdictions were Ireland and
> Lido Inc. does business in two states, X and Y. State X uses an equal weighted three-factor apportionment formula and has a 4 percent state tax rate. State Y bases its apportionment only on the sales factor and has a 5 percent state tax rate. Lidoâ
> Cromwell Corporation does business in two states, A and B. State A uses an equal-weighted three-factor apportionment formula and has a 5 percent state tax rate. State B uses an apportionment formula that double-weights the sales factor and has a 6 percen
> Refer to the facts in problem 4. Compute the state income tax savings if Oldham could relocate its personnel so that payroll expense in State M increased to $1,900 (thousand) and payroll expense in State N decreased to $100 (thousand). Data from Problem
> Refer to the facts in the preceding problem. Compute Oldham’s State M and State N tax if State N uses an apportionment formula in which the sales factor is double-weighted. Data from Problem 4: Oldham Inc. conducts business in State M
> Oldham Inc. conducts business in State M and State N, which both use the UDITPA three-factor formula to apportion income. State M’s corporate tax rate is 4.5 percent, and State N’s corporate tax rate is 7 percent. This
> Refer to the facts in the preceding problem. Assume that the tax rate in Country X is 15 percent and Cotton Comfort’s U.S. marginal tax rate is 21 percent. The corporation and its subsidiary have agreed to a transfer price for the cloth of $30 per shirt.
> What is the effect on the NPV of the restructured transaction in the preceding problem if Firm H’s marginal tax rate in year 2 increases to 30 percent?
> Please Cotton Comfort Corporation is a U.S. shirt manufacturer with a foreign subsidiary in Country X. Cloth to make shirts is woven in the United States, at a cost of $14 per shirt and shipped to Country X where it is cut and sewn at a cost of $15 per s
> Alamo, a Texas corporation, manufactures plastic components that it sells to Vegas, a Mexican corporation, for assembly into a variety of finished goods. Alamo owns 60 percent of Vegas’s stock. Alamo’s cost per component is $85, its selling price per com
> Norton Inc. is a domestic corporation with several foreign subsidiaries. This year, Norton has $940 million domestic gross receipts and $800 million of allowable deductions. It made deductible related party payments to its foreign affiliates of $520 mill
> Leming, Inc. is a CFC with total foreign earnings of $90 million, of which $27 million is considered subpart F income. Leming owns tangible business property with an adjusted tax basis of $70 million. Hare Corporation, a U.S. corporation, owns 30 percent
> Fairview, Inc. is a CFC with total foreign earnings of $30 million, of which $8 million is considered subpart F income. Fairview owns tangible business property with an adjusted tax basis of $40 million. Collins Corporation, a U.S. corporation, owns 100
> Grandmere, a calendar year domestic corporation, owns 50 percent of Petit, Inc., a calendar year controlled foreign corporation. At the end of 2017, Petit has accumulated $26 million of undistributed income and has $4.2 million of cash. a. Compute Grandm
> Yasmin Corporation, a calendar year domestic corporation, owns 100 percent of Luna Inc., a calendar year controlled foreign corporation. Luna has never paid a dividend and at the end of 2017 has accumulated $18 million undistributed income (none of which
> Jumper Inc., which has a 21 percent tax rate, owns 40 percent of the stock of a CFC. At the beginning of 2018, Jumper’s basis in its stock was $660,000. The CFC’s 2018 income was $1 million, $800,000 of which was subpart F income. The CFC paid no foreign
> Dixie Inc., a Tennessee corporation, conducts business in South America through two foreign corporations, Dix-Col Inc. and Dix-Per Inc. Dixie formed Dix-Col six years ago and owns 100 percent of its stock. Dix-Per was formed six months ago and Dixie owns
> Omaha Inc. owns 100 percent of the stock in Franco, a foreign corporation. All Franco’s income is foreign source, and its foreign income tax rate is 20 percent. During its fiscal year ended June 30, 2017, Franco distributed a $50,000 dividend to Omaha. a
> Firm H has the opportunity to engage in a transaction that will generate $100,000 cash flow (and taxable income) in year 0. How does the NPV of the transaction change if the firm could restructure the transaction in a way that doesn’t change before-tax c
> This year, Tuna, Inc., a domestic corporation, earned $3 million from sales of goods to unrelated foreign customers. If Tuna has $12 million of depreciable assets, calculate its foreign-derived intangible income.
> Cheeta Corporation earned $5 million this year from both domestic and international operations. Assume $2.2 million of this income qualifies as foreign-derived intangible income (FDII). If Cheeta paid no foreign income tax, calculate its U.S. income tax
> Minden Corporation’s records show the following results for its first three years of operations. In year 4, Minden generated $2 million taxable income ($900,000 of which was foreign source) and paid $370,000 foreign income tax. Assume
> Comet operates solely within the United States. It owns two subsidiaries conducting business in the United States and several foreign countries. Both subsidiaries are U.S. corporations. This year, the three corporations report the following. a. If Come
> The Trio affiliated group consists of Trio, a New Jersey corporation, and its three wholly owned subsidiaries. This year, the four corporations report the following. Net Income (Loss) Trio ………………………………………………$412,000 Subsidiary 1 ………………………………….(180,000)
> For the current year, Harbor Corporation earned before-tax income of $776,000. Harbor operates in a single state with a 10 percent state income tax rate. a. Compute Harbor’s state income tax liability. b. Assuming Harbor deducts state income taxes when a
> Aqua, a South Carolina corporation, is a 20 percent partner in a Swiss partnership. This year, Aqua earned $2 million U.S. source income and $190,000 foreign source income. It paid no foreign income tax. The Swiss partnership earned $1.73 million foreign
> Transcom, an Ohio corporation, earned $700,000 U.S. source income from sales of goods to U.S. customers and $330,000 foreign source income from sales of goods to customers in Canada. Canada’s corporate income tax rate is 15 percent, and the United States
> Axtell Corporation has the following taxable income. U.S. source income ……………………..$1,620,000 Foreign source income: Country A ………………………………………….550,000 Country B ……………………………………….2,000,000 Country C ……………………………………..2,900,000 Taxable income ……………………………
> Firm L has $500,000 to invest and is considering two alternatives. Investment A would pay 6 percent ($30,000 annual before-tax cash flow). Investment B would pay 4.8 percent ($24,000 annual before tax cash flow). The return on Investment A is taxable, wh
> Watch Corporation has U.S. source income for the current year of $2 million, foreign source income from Country X of $3 million, and foreign source income from Country Y of $1 million, for total taxable income of $6 million. Watch paid $900,000 of income
> Elmo Inc. is a U.S. corporation with a branch office in foreign Country Z. During the current year, Elmo had $340,000 of U.S. source income and $60,000 of foreign source income from Z, on which Elmo paid $28,000 of Country Z income tax. a. Calculate Elmo
> Jackson Inc. has the following taxable income. U.S. source income ………………………………$18,800,000 Foreign source income …………………………..2,690,000 Taxable income ……………………………………..$21,490,000 Jackson paid $1,040,000 foreign income tax. Compute its U.S. income tax, a
> Zenon Inc. has the following taxable income. U.S. source income ……………………………$1,900,000 Foreign source income ……………………….240,000 Taxable income ………………………………….$2,140,000 Zenon paid $33,000 foreign income tax. Compute its U.S. income tax, assuming the for
> Akita is a U.S. corporation. This year, it earned $8 million before-tax income and paid $450,000 income tax to jurisdictions other than the United States. Compute Akita’s U.S. income tax assuming that: a. The other jurisdictions were the states of Montan
> This year, Mesa Inc.’s before-tax income was $9,877,000. It paid $419,000 income tax to Minnesota and $385,000 income tax to Illinois. a. Compute Mesa’s federal income tax. b. What is Mesa’s tax rate on its income?
> Angela and Thomas are planning to start a new business. Thomas will invest cash in the business but not be involved in day-to-day operations. Angela plans to work full-time overseeing business operations. The two currently project that the business will
> A number of tax and nontax factors should be considered in choosing the type of pass through entity through which to operate a new business. For each of the following considerations, indicate whether the item favors the partnership form or the S corporat
> WRT, a calendar year S corporation, has 100 shares of outstanding stock. At the beginning of the year, Mr. Wallace owned all 100 shares. On September 30, he gave 25 shares to his brother and 40 shares to his daughter. WRT’s ordinary income for the year w
> Delta Partnership has four equal partners. At the beginning of the year, Drew was one of the Delta partners, but on October 1, he sold his partnership interest to Cody. If Delta’s ordinary income for the year was $476,000, what portion of this income sho
> Jurisdiction X levies a flat 14 percent tax on individual income in excess of $35,000 per year. Individuals who earn $35,000 or less pay no income tax. a. Mr. Hill earned $98,750 income this year. Compute his income tax and determine his average and marg
> Mrs. Franklin, who is in the 37 percent tax bracket, owns a residential apartment building that generates $80,000 annual taxable income. She plans to create a family partnership by giving each of her two children a 20 percent equity interest in the build
> Mr. and Mrs. Lund and their two children (Ben and June) are the four equal partners in LBJ Partnership. This year, LBJ generated $36,000 ordinary income. Compute the tax cost for the business if Mr. and Ms. Lund’s marginal rate is 32 percent, Ben’s margi
> Megan operates a housecleaning business as a sole proprietorship. She oversees a team of 10 cleaning personnel, markets the business, and provides supplies and equipment. The business has been generating net taxable profits of $50,000 per year, before co
> Graham is the sole shareholder of Logan Corporation. For the past five years, Logan has reported little or no taxable income as a result of paying Graham a salary of $500,000 per year. During a recent IRS audit, the revenue agent determined that Graham’s
> During a recent IRS audit, the revenue agent decided that the Parker family used their closely held corporation, Falco, to avoid shareholder tax by accumulating earnings beyond the reasonable needs of the business. Falco’s taxable income was $900,000, it
> In 1994, Mr. and Mrs. Adams formed ADC by transferring $50,000 cash in exchange for 100 shares of common stock and a note from the corporation for $49,000. The note obligated ADC to pay 10 percent annual interest and to repay the $49,000 principal on dem
> Mr. Vernon is the sole shareholder of Teva. He also owns the office building that serves as corporate headquarters. Last year, Teva paid $180,000 annual rent to Mr. Vernon for use of the building. Teva’s marginal tax rate was 21 percent, and Mr. Vernon’s
> Ms. Xie, who is in the 37 percent tax bracket, is the sole shareholder and president of Xenon. The corporation’s financial records show the following. Gross income from sales of goods ……………………….$1,590,000 Operating expenses ………………………………………………(930,000) S
> American Corporation has two equal shareholders, Mr. Freedom and Brave Inc. In addition to their investments in American stock, both shareholders have made substantial loans to American. During the current year, American paid $100,000 interest each to Mr
> Mr. Pauper and Mrs. Queen are the equal shareholders in Corporation PQ. Both shareholders have a 37 percent marginal tax rate. PQ’s financial records show the following. Gross income from sales of goods ……………………………..$980,000 Operating expenses ………………………
> Jurisdiction B levies a flat 7 percent tax on the first $5 million of annual corporate income. a. Jersey Inc. generated $3.9 million income this year. Compute Jersey’s income tax and determine its average and marginal tax rate on total income. b. Leray I
> Mr. Lion, who is in the 37 percent tax bracket, is the sole shareholder of Toto, Inc., which manufactures greeting cards. Toto’s average annual net profit (before deduction of Mr. Lion’s salary) is $200,000. For each of the following cases, compute the i
> Refer to the facts in the preceding problem. a. If the business is operated as a partnership, explain the payroll tax/self-employment tax implications for the entity, Thomas, and Angela. (No calculations are required.) b. If the business is operated as a
> Mr. Tuck and Ms. Under organized a new business as an LLC in which they own equal interests. The new business generated a $4,800 operating loss for the year. a. If Mr. Tuck’s marginal tax rate before consideration of the LLC loss is 35 percent, compute h
> Cranberry Corporation has $3,240,000 of current year taxable income. a. If the current year is a calendar year ending on December 31, 2017, calculate Cranberry’s regular income tax liability. b. If the current year is a calendar year ending on December 3
> This year, Fig Corporation made a $100,000 contribution to charity. In each of the following situations, compute the after-tax cost of this contribution assuming that Fig uses a 6 percent discount rate to compute NPV. a. Fig had $8 million taxable income
> In its first year, Camco Inc. generated a $92,000 net operating loss, and it made a $5,000 cash donation to a local charity. In its second year, Camco generated a $210,600 profit, and it made a $10,000 donation to the same charity. Compute Camco’s taxabl
> This year, GHJ Inc. received the following dividends. Compute GHJ’s dividends-received deduction. BP Inc. (a taxable California corporation in which GHJ holds a 2% stock interest) $17,300 MN Inc. (a taxable Florida corporation in
> This year, Napa Corporation received the following dividends. Napa and Gamma do not file a consolidated tax return. Compute Napa’s dividends-received deduction. KLP Inc. (a taxable Delaware corporation in which Napa holds an 8% st
> Griffin Corporation received $50,000 of dividend income from Eagle, Inc. Griffin owns 5 percent of the outstanding stock of Eagle. Griffin’s marginal tax rate is 21 percent. a. Calculate Griffin’s allowable dividends-received deduction and its after-tax
> Corporation P owns 93 percent of the outstanding stock of Corporation T. This year, the corporation’s records provide the following information. a. Compute each corporation’s taxable income if each files a separate t
> Firm Y has the opportunity to invest in a new venture. The projected cash flows are as follows: Year 0: Initial cash investment in the project of $300,000. Years 1, 2, and 3: Generate cash revenues of $50,000. Years 1, 2, and 3: Incur fully deductible ca
> James, who is in the 35 percent marginal tax bracket, owns 100 percent of the stock of JJ Inc. This year, JJ generates $500,000 taxable income and pays a $100,000 dividend to James. Compute his tax on the dividend under each of the following assumptions:
> In 2017, NB Inc.’s federal taxable income was $242,000. Compute the required installment payments of 2018 tax in each of the following cases: a. NB’s 2018 taxable income is $593,000. b. NB’s 2018 taxable income is $950,000. c. NB’s 2018 taxable income is
> In 2017, Bartley Corporation’s federal income tax due was $147,000. Compute the required installment payments of 2018 tax in each of the following cases: a. Bartley’s 2018 taxable income is $440,000. b. Bartley’s 2018 taxable income is $975,000. c. Bartl
> Callen Inc. has accumulated minimum tax credits of $1.3 million from tax years prior to 2018. The following are Callen’s regular tax before credits for 2018 through 2021. Complete the following table to calculate Callenâ€&#
> Camden Corporation, a calendar year accrual basis corporation, reported $5 million of net income after tax on its current year financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. In addition, the following information is available from Camden’s books
> Grim Corporation has income and expenses for its current fiscal year, recorded under generally accepted accounting principles, as shown in the following schedule. In addition, a review of Grim’s books and records reveals the following i
> EFG, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $479,900 net income after tax on its financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation’s financial records reveal the following information: EFG earned $10,700 on an investmen
> Western Corporation, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $500,000 of net income after tax on its 2018 financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation’s books and records reveal the following information: Western’s
> Cramer Corporation, a calendar year, accrual basis corporation, reported $1 million of net income after tax on its 2018 financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The corporation’s books and records reveal the following information: Cramer’s
> Landover Corporation is looking for a larger office building to house its expanding operations. It is considering two alternatives. The first is a newly constructed building at a cost of $6 million. It would require only minor modifications to meet Lando
> Firm E must choose between two business opportunities. Opportunity 1 will generate an $8,000 deductible loss in year 0, $5,000 taxable income in year 1, and $20,000 taxable income in year 2. Opportunity 2 will generate $6,000 taxable income in year 0 and

