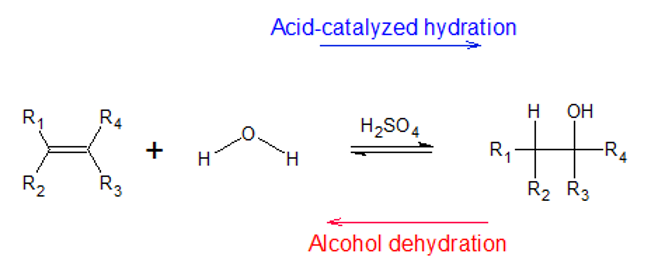
Definition of Acid Catalyzed Hydration
Acid-catalyzed hydration is a chemical reaction in which the hydrogen and the hydroxyl group are added to the two carbons which are sharing a double bond (alkene). This reaction takes place in the presence of a strong acid such as sulphuric acid H2SO4 and is also known as electrophilic hydration. This chemical process is the reverse of the dehydration reaction of alcohol. When the alcohols are dehydrated, they form unsaturated hydrocarbons like alkenes.
The electrophilic hydrogen present in the reaction is used in the breaking of the double bond present in the alkene. Hence, this reaction is employed in the manufacturing of alcohols that are used as fuels and other reagents.
View More Organic Chemistry Definitions
Related Questions of Organic Chemistry
Draw and name four terminal alkynes with the molecular formula C6H10.
Report the result of the following addition to the proper number of
Scorzocreticin (S)-1 was isolated from a plant that is
Write an equation for the proton transfer reaction that occurs when each
87. What is the major product of this reaction?
Propose a stepwise mechanism for the following transformation: /
Identify the sole product of the following reaction: /
Draw the condensation product that is expected when each of the following
Draw a mechanism for each of the following transformations: /
Draw each of the following using condensed formulas and line formulas:
Show All