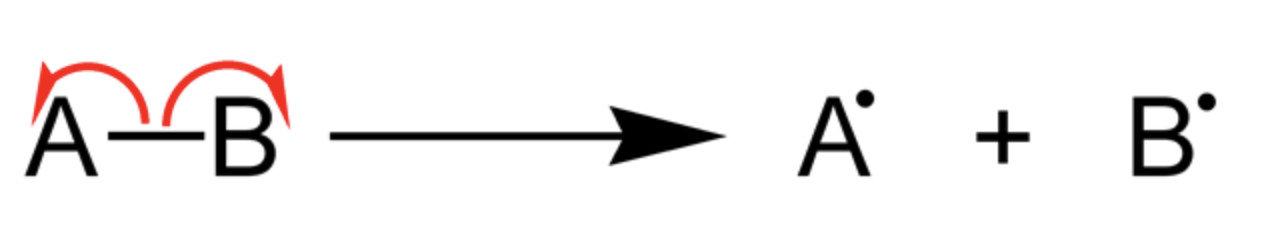
Definition of Homolytic Bond Cleavage
Homolytic bond cleavage is also known as homolytic fission and it is defined as a type of bond breakage that dissociates the molecule in such a way that each of the two fragments retains one electron from the bonding pair. If the targeted molecule is neutral, it dissociates and resultantly forms two free radicals.
Radicals are known to be highly reactive chemical species. It has been noted that a large amount of energy is required to initiate hemolytic fission. It occurs when the molecule is exposed to ultraviolet radiation or is given a large amount of heat that overcomes bond dissociation energy etc.
View More Organic Chemistry Definitions
Related Questions of Organic Chemistry
Draw and name four terminal alkynes with the molecular formula C6H10.
Report the result of the following addition to the proper number of
Scorzocreticin (S)-1 was isolated from a plant that is
Write an equation for the proton transfer reaction that occurs when each
87. What is the major product of this reaction?
Propose a stepwise mechanism for the following transformation: /
Identify the sole product of the following reaction: /
Draw the condensation product that is expected when each of the following
Draw a mechanism for each of the following transformations: /
Draw each of the following using condensed formulas and line formulas:
Show All