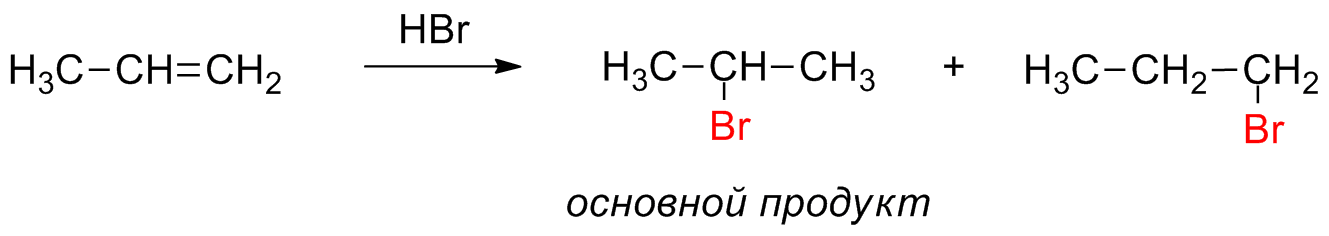
Definition of Markovnikov Addition
Markovnikov addition is the type of addition reaction in which a protic acid reacts and adds into an asymmetric alkene. The hydrogen is acidic and hence gets attached to the carbon which has a greater number of hydrogen substituents. On the other hand, the halide group gets itself attached to the carbon atom which is having more number of alkyl substituents.
In simple words, it can be stated that hydrogen is added into that carbon which has the greatest number of hydrogens, and halide is added into the carbon which has the least number of hydrogens. The hydration of alkenes and the addition of hydrobromic acid (HBr) to propene are examples of Markovnikov addition.
View More Organic Chemistry Definitions
Related Questions of Organic Chemistry
Draw and name four terminal alkynes with the molecular formula C6H10.
Report the result of the following addition to the proper number of
Scorzocreticin (S)-1 was isolated from a plant that is
Write an equation for the proton transfer reaction that occurs when each
87. What is the major product of this reaction?
Propose a stepwise mechanism for the following transformation: /
Identify the sole product of the following reaction: /
Draw the condensation product that is expected when each of the following
Draw a mechanism for each of the following transformations: /
Draw each of the following using condensed formulas and line formulas:
Show All