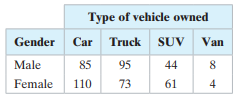
Question: a. find the expected frequency for each
a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table,
b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha,
c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region,
d. find the chi-square test statistic,
e. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and
f. interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
The contingency table shows the results of a random sample of individuals by gender and type of vehicle owned. At α = 0.01, can you conclude that gender is related to the type of vehicle owned?
Transcribed Image Text:
Type of vehicle owned Gender Car Truck SUV Van Male 85 95 44 8 Female 110 73 61 4
> The company in Example 5 claims that the mean conductivity of the river is 1890 milligrams per liter. The conductivity of a water sample is a measure of the total dissolved solids in the sample. You randomly select 39 water samples and measure the conduc
> An industry analyst says that the mean age of a used car sold in the last 12 months is less than 4.1 years. A random sample of 25 used cars sold in the last 12 months has a mean age of 3.7 years and a standard deviation of 1.3 years. Is there enough evid
> Find the critical values -t0 and t0 for a two-tailed test with α = 0.05 and n = 16.
> Find the critical value t0 for a right-tailed test with α = 0.10 and n = 9.
> Find the critical value t0 for a left-tailed test with α = 0.01 and n = 14.
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Right-tailed test, α = 0.08
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Right-tailed test, α = 0.05
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Construct a 99% prediction interval for the average annual sal
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Find the standard error of estimate se and interpret the resul
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Find the coefficient of determination r2 and interpret the res
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Use the regression equation that you found in Exercise 5 to pr
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Find the equation of the regression line for the data. Draw th
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Test the significance of the correlation coefficient r that yo
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Calculate the correlation coefficient r and interpret the resu
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Left-tailed test, α = 0.09
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Construct a scatter plot for the data. Do the data appear to h
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Two-tailed test, z = 2.57, α = 0.10
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Left-tailed test, z = -0.94, α = 0.05
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. p ≥ 0.64
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. σ > 1.9
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ ≠ 150,020
> In hypothesis testing, does using the critical value method or the P-value method affect your conclusion? Explain.
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. P < 0.205
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ = 82
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ ≤ 375
> Find the critical F-value for a right-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.05, d.f.N = 6, d.f.D = 50
> a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table, b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region, d. find the chi-square test statistic,
> a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table, b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region, d. find the chi-square test statistic,
> a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table, b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region, d. find the chi-square test statistic,
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the chi-square test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisi
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the chi-square test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisi
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Left-tailed test, α = 0.03
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the chi-square test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisi
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.01, d.f.N = 11, d.f.D = 13
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.01, d.f.N = 40, d.f.D = 60
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.05, d.f.N = 9, d.f.D = 8
> Use the TI-84 Plus displays to make a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis at the level of significance. α = 0.01 2-Test Inpt:Data Sats HO:742 g:68.1 :763 n:65 2-Test u>742 z=2.486158777 P=.0064565285 R=763 n=65 Calc
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ < 33
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.10, d.f.N = 15, d.f.D = 27
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic x2, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisio
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ ≠ 0.035; α = 0.01. Sample statistics: s = 0.026, n = 16
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ = 1.25; α = 0.05. Sample statistics: s = 1.03, n = 6
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ2 ≤ 60; α = 0.025. Sample statistics: s2 = 72.7, n = 15
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Right-tailed test z = 2.46 α = 0.01
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ2 > 2; α = 0.10. Sample statistics: s2 = 2.95, n = 18
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Left-tailed test, n = 6, α = 0.05
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Two-tailed test, n = 41, α = 0.10
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Two-tailed test, n = 14, α = 0.01
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Right-tailed test, n = 20, α = 0.05
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Left-tailed test z = -1.55 α = 0.05
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. use technology to find the P-value, c. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and d. interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the population is normally
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. use technology to find the P-value, c. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and d. interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the population is normally
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic t, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic t, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ ≠ 3,330,000; α = 0.05. Sample statistics: x = 3,293,995, s = 12,801, n = 35
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ = 195; α = 0.10. Sample statistics: x = 190, s = 36, n = 101
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ < 850; α = 0.025. Sample statistics: x = 875, s = 25, n = 14
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ ≤ 51; α = 0.01. Sample statistics: x = 52, s = 2.5, n = 40
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ ≥ 0; α = 0.10. Sample statistics: x = -0.45, s = 2.38, n = 31
> Explain the difference between the z-test for m using a P-value and the z-test for µ using rejection region(s).
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ > 12,700; α = 0.005. Sample statistics: x = 12,855, s = 248, n = 21
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Two-tailed test, α = 0.02, n = 12
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Left-tailed test, α = 0.005, n = 15
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Left-tailed test, α = 0.05, n = 48
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Right-tailed test, α = 0.02, n = 63
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Right-tailed test, α = 0.01, n = 33
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Two-tailed test, α = 0.05, n = 20
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the standardized test statistic z, c. find the corresponding P-value, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of the original c
> You are given a null hypothesis and three confidence intervals that represent three samplings. Determine whether each confidence interval indicates that you should reject H0. Explain your reasoning. Ho: p20.73 P 0.70 0.71 0.72 a73 0.74 0.75 0.76 (a)

