Question: a. identify the claim and state H0
a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha,
b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region,
c. find the test statistic F,
d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and
e. interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
Assume the samples are random and independent, the populations are normally distributed, and the population variances are equal.
The table shows the annual incomes (in dollars) for a sample of families from four regions of the United States. At α = 0.05, can you conclude that the mean annual income of families is different in at least one of the regions?
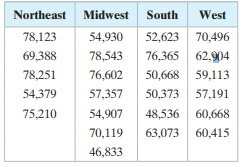
Transcribed Image Text:
Northeast Midwest South West 78,123 54,930 52,623 70,496 69,388 78,543 76,365 62,904 78,251 76,602 50,668 59,113 54,379 57,357 50,373 57,191 75,210 54,907 48,536 60,668 70,119 63,073 60,415 46,833
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test or a t-test. Explain your reasoning. c. Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection r
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Right-tailed test, α = 0.08
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Right-tailed test, α = 0.05
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> In each exercise, a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision i
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Construct a 99% prediction interval for the average annual sal
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Find the standard error of estimate se and interpret the resul
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Find the coefficient of determination r2 and interpret the res
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Use the regression equation that you found in Exercise 5 to pr
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Find the equation of the regression line for the data. Draw th
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Test the significance of the correlation coefficient r that yo
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Calculate the correlation coefficient r and interpret the resu
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Left-tailed test, α = 0.09
> Use the data in the table, which shows the average annual salaries (both in thousands of dollars) for librarians and postsecondary library science teachers in the United States for 12 years. Construct a scatter plot for the data. Do the data appear to h
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Two-tailed test, z = 2.57, α = 0.10
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Left-tailed test, z = -0.94, α = 0.05
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> a. state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim, b. describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim, c. explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, d. expl
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. p ≥ 0.64
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. σ > 1.9
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ ≠ 150,020
> In hypothesis testing, does using the critical value method or the P-value method affect your conclusion? Explain.
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. P < 0.205
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ = 82
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ ≤ 375
> Find the critical F-value for a right-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.05, d.f.N = 6, d.f.D = 50
> a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table, b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region, d. find the chi-square test statistic,
> a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table, b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region, d. find the chi-square test statistic,
> a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table, b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region, d. find the chi-square test statistic,
> a. find the expected frequency for each cell in the contingency table, b. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, c. determine the degrees of freedom, find the critical value, and identify the rejection region, d. find the chi-square test statistic,
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the chi-square test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisi
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the chi-square test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisi
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Left-tailed test, α = 0.03
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the chi-square test statistic, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisi
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value and identify the rejection region, c. find the test statistic F, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of t
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.01, d.f.N = 11, d.f.D = 13
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.01, d.f.N = 40, d.f.D = 60
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.05, d.f.N = 9, d.f.D = 8
> Use the TI-84 Plus displays to make a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis at the level of significance. α = 0.01 2-Test Inpt:Data Sats HO:742 g:68.1 :763 n:65 2-Test u>742 z=2.486158777 P=.0064565285 R=763 n=65 Calc
> The statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha. µ < 33
> Find the critical F-value for a two-tailed test using the level of significance α and degrees of freedom d.f.N and d.f.D. α = 0.10, d.f.N = 15, d.f.D = 27
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic x2, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decisio
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ ≠ 0.035; α = 0.01. Sample statistics: s = 0.026, n = 16
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ = 1.25; α = 0.05. Sample statistics: s = 1.03, n = 6
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ2 ≤ 60; α = 0.025. Sample statistics: s2 = 72.7, n = 15
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Right-tailed test z = 2.46 α = 0.01
> Test the claim about the population variance σ2 or standard deviation s at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: σ2 > 2; α = 0.10. Sample statistics: s2 = 2.95, n = 18
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Left-tailed test, n = 6, α = 0.05
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Two-tailed test, n = 41, α = 0.10
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Two-tailed test, n = 14, α = 0.01
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α. Right-tailed test, n = 20, α = 0.05
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> Find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α. Left-tailed test z = -1.55 α = 0.05
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. use technology to find the P-value, c. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and d. interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the population is normally
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. use technology to find the P-value, c. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and d. interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the population is normally
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic t, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic t, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ ≠ 3,330,000; α = 0.05. Sample statistics: x = 3,293,995, s = 12,801, n = 35
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ = 195; α = 0.10. Sample statistics: x = 190, s = 36, n = 101
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ < 850; α = 0.025. Sample statistics: x = 875, s = 25, n = 14
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ ≤ 51; α = 0.01. Sample statistics: x = 52, s = 2.5, n = 40
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ ≥ 0; α = 0.10. Sample statistics: x = -0.45, s = 2.38, n = 31
> Explain the difference between the z-test for m using a P-value and the z-test for µ using rejection region(s).
> Test the claim about the population mean µ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ > 12,700; α = 0.005. Sample statistics: x = 12,855, s = 248, n = 21
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Two-tailed test, α = 0.02, n = 12
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Left-tailed test, α = 0.005, n = 15
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Left-tailed test, α = 0.05, n = 48
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Right-tailed test, α = 0.02, n = 63
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Right-tailed test, α = 0.01, n = 33
> Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n. Two-tailed test, α = 0.05, n = 20
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), c. find the standardized test statistic z, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the standardized test statistic z, c. find the corresponding P-value, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of the original c
> You are given a null hypothesis and three confidence intervals that represent three samplings. Determine whether each confidence interval indicates that you should reject H0. Explain your reasoning. Ho: p20.73 P 0.70 0.71 0.72 a73 0.74 0.75 0.76 (a)
> a. Identify the claim and state H0 and Ha. b. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed, and whether to use a z-test, a t-test, or a chi-square test. Explain your reasoning. c. Choose one of the options. Option
> a. identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, b. find the standardized test statistic z, c. find the corresponding P-value, d. decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and e. interpret the decision in the context of the original c
> Test the claim about the population mean m at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ = 7450; α = 0.10; σ = 243. Sample statistics: x = 7495, n = 27
> Test the claim about the population mean m at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ < 5.500; α = 0.01; σ = 0.011. Sample statistics: x = 5.497, n = 36
> Test the claim about the population mean m at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed. Claim: µ ≠ 8.45; α = 0.03; σ = 1.75. Sample statistics: x = 7.88, n = 60

