Question: Balance the equation and write the reaction-
Balance the equation and write the reaction-quotient expression, Qc.

For the generic reaction
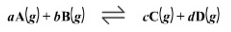
The reaction quotient is
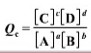
Transcribed Image Text:
uls) + 3F,(s) = UF,(s) - UF (e) aAlg) + bB{g) cClg) + dDlg)
> 4. What are lone pairs in the VSEPR theory? 5. To determine the shape of a molecule using a VSEPR theory chart, what two things do you need to know. 6. Draw the Lewis dot structure (on back) and complete the table for the following compounds. shape
> Fill in the blank spaces in the following chart. Molecule Lewis structure Electron Bond Molecular domain Angles geometry geometry (shape) (VSEPR) XeF2 -Xe, HH BeHz 180° H-BeH F F-As: ASF5 'F F
> Molecule VSEPR shape Bond angle Polar, non-polar, lon Molecule VSEPR shape Bond angle Polar, non-polar, ion SO32 SO3 SO2 CO2 NO: ВеBrz SCl2 BF3 clo H30
> For this discussion, find a covalently bonded molecule that has a particular shape. Post the following information: Name of the molecule Chemical Formula Empirical Formula Embed an image of the structure Shape of the molecule around the central atom,
> 44. This is the strongest type of covalent bond. a. Ionic b. Hydrogen c. Diatomic d. Dispersion e. Polar 45. This type of solution conducts electricity. a. Electrolyte b. Nonelectrolyte c. Saturated d. Unsaturated e. Supersaturated 46. What is
> For the covalent bonded molecule Oxygen please provide the following information: - Chemical Formula - Empirical Formula - Embed an image of the structure -Shape of the molecule around the central atom, or choose an atom to demonstrate the shape -Use the
> Given that, Calculate the value of ΔH°rxn for H,(e) + F,lg) → 2HF(g) AH=- 546.6 kJ • mol rxn 2H,(2) + 0,le) → 2H,0() AH= - 571.6 kJ· mol :- 571.6 kJ · mol 2F,(g) + 2H,0() → 4HF{g)+0,(g)
> How many σ and π bonds are in this molecule?
> What is the bond angle of dsp³ and what is the bond angle of d²sp³?
> Draw the best Lewis Structure for each of the following structures. Determine the electron and molecular geometries for each using the VSEPR chart. 1. CH4 2. H2O 3. NH3 15. O3
> Record the name, formula and pH of each salt solution. If the pH is not neutral, for the ions that undergo hydrolysis, write down the hydrolysis reaction and indicate which species is responsible for the observed pH. pH of sodium chloride 7.07 pH of a
> Fill in the following chart: Molecular Formula Lewis Structure # of Hybrid- Molecular Electronic |Geometry Geometry Molecular Вond Lewis Structure Electron Formula ization Angle(s) Groups CH.CI: OPCI, (violate the octet rule) CH:O NO: PCIS (violate
> Complete the following chart of electronic and molecular structure. # Electron Domains Molecular Geometry Electron Lewis Diagram # Lone Pairs Geometry H:N:H .. H:C:H H H:0:H
> 11. Using the provided chart (under assignments tab) what is the molecular geometry of NF3 a. Bent b. Tetrahedral c. Trigonal pyramidal d. Trigonal planar 12. Using the provided chart what is the molecular geometry of OCS a. Linear b. Tetrahedral
> Determine the Molecule Geometry (refer to the molecular geometry chart given) and Polarity of the following molecules. It is strongly recommended that you also build the molecules using a molecular modeling kit to aid in your determination of the geometr
> Which statement best describes the polarity of SCL4F2? The molecule is always polar. The molecule is always nonpolar. Depending on the arrangement of outer atoms, this molecule could be polar or nonpolar.
> Name the following compounds: a. Spell out the full name of the compound. b. Spell out the full name of the compound. Br OH Br CH3 HO-
> Describe heterocyclic aromatic compounds.
> Which of the following statement concerning aromatic compounds is CORRECT? A. A linear system of conjugated pi electrons is characteristic of aromatic compounds. B. Aromatic compounds contain only carbon atoms in their pi bonding system. C. Hydrogenat
> Which of the following statements is true? 1. Aromatic compounds release more energy on combustion than aliphatic compounds do. 2. Aromatic compounds react faster than aliphatic compounds in radical halogenation. 3. Aromatic compounds release more ene
> Which of the following statements is true? a. Aromatic compounds have longer C-C bonds than CH2-CH2. b. Aromatic compounds release more energy on combustion than aliphatic compounds do. c. Aromatic compounds release more energy per pi bond upon saturat
> Name the following alkenes using the systematic names. H3C CH2 CH CH H3C CH CH2 ČH3 3,4-methylhex-1-ene CH CH CH2 CH CH2 CH2 ČH3 CH CH2 CH2 H3C
> What is the IUPAC name for the following compound? Enter the name of the molecule. CH, CH,CH,CH, сH, —с —сн, —сH—CH, ČH,CH,
> Which statement is true? a. Aromatic compounds release more energy per pi bond upon saturation than simple alkenes b. Aromatic compounds release more energy on combustion than aliphatic compounds do 5 c. Aromatic compounds react faster than aliphatic c
> Define: aromatic ions anti-aromatic nonaromatic benzenoid aromatic compounds non-benzenoid aromatic compounds
> 3. Anti-aromatic compound doesn't follow the one rule with aromatic compound. Write down that rule? 4. What is the Huckle rule for anti-aromatic compound?
> Which of the following statements is true about aromatic compounds? Select the correct answer below: a. Aromatic compounds undergo substitution reactions more readily than addition reactions. b. Aromatic compounds have properties similar to alkenes.
> Circle the aromatic compounds, put a RECTANGLE around ANTI-AROMATIC Compounds, and for the non-aromatic compounds, explain why they are non-aromatic: HO, -NH2 NH2 HN
> Identify true statements concerning aromaticity. Aromatic compounds must contain a ring. Aromatic compounds must have an even number of pi-electron pairs. Aromatic compounds must have have 4n+2 pi-electrons. Aromatic compounds cannot be ionic.
> Identify the following compounds as non-aromatic, aromatic or anti-aromatic. Non-aromatic compounds Aromatic compounds Anti-aromatic compounds D F 0: 0:
> Give the conjugate acid for each compound below. Base Conjugate Acid H2PPO4- ? HPO42- ? NH3 ?
> Which one of the following compounds is antiaromatic? 14 Which one of the following compound ianmatie II IV A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) none of these 15. Which one of the following compounds is antiaromatic? H V II III IV A) I B) II C) II D) IV E) V
> What mass of ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, (Ka = 5.6 x 10^-10) must be added to exactly 500mL of 0.10M NH3 solution to give a solution with a pH of 9.00?
> Draw the Lewis dot structure and draw the hybridized binding structure (just show bonding orbitals) for each of the following molecules. 1. HCN 2. PH3 3. CH3OCH3 4. COCl2 5. NF6- 6. XeF4
> Give the conjugate acid for each compound below. Base Conjugate Acid HS HS НРОН, РО, NH, NHA
> Lewis Dot (include all resonance structures here; *check Name of formal charge to determine preferred structure, if any) Electron Pair Name of Molecular Bond Bond Dipole Lewis Dot (include all resonance structures here: *check Name of Electron Pair N
> For the following molecules give: a) the Lewis dot structure, and b) a drawing of the 3D structure using VSEPR. 1. PCl5 2. BCl3 3. SiF62- 4. XeF4 5. SO3 6. ICl4 -
> Geometrical Structure of Molecules Lewis Structure Electron geometry Molecular Geometry Polar? 1. CH4 2. CH2Cl2 3. CH3OH 4. H2O 5. Н3O+ 6. HF 7. NH3 8. H2O2 9. N2 10. BrI2 11. C2H4 12. C2H4Br2 13. C2H2 14. SO2 15. SO4-2 16. CO2 17. CSN 18. NO3
> Draw the Lewis structure for the following molecule: OPBr3 Which do not obey the octet rule? NO, BF3, ICl2-, OPBr3, XeF4
> What is the best definition of the reaction quotient, Q? A. The reaction quotient is the ratio of the product of the reactant concentrations when a reaction is at equilibrium. B. The reaction quotient is the product of the reactant concentrations to the
> Compare the reaction quotient to Keq. What does it mean when the reaction quotient is greater than Keq, and vice versa?
> a. Write the reaction quotient for A+2B -> 3C. b. Write the reaction quotient for 2A + B -> 2C+ D
> How is the reaction quotient similar from an equilibrium constant for a reaction? Explain. How is the reaction quotient different from an equilibrium constant for a reaction? Explain.
> Post-Lab Experiment 11 XeF4 Lewis Structure VSEPR Structure of electron groups XeF4 Lewis Structure VSEPR Structure of electron groups electron configuration shape orbital hybridization F-Xe-F bond angle
> What will be the reaction quotient expression for the following equilibrium: 2A +B - C+ 2D
> How many groups are in the periodic table? How many periods are in the periodic table?
> Which of the following pairings is incorrect? Au-d area of periodic table Be-s area of periodic table I-s area of periodic table Xe-p area of periodic table
> The molecular geometry of the IF 5 molecule is ____________. trigonal bipyramidal, nonpolar square pyramidal, nonpolar square pyramidal, polar trigonal bipyramidal, polar trigonal planar, polar
> Determine the electron geometry (eg). molecular geometry (mg) and polarity of TeClsF molecule. (Te is in group 6A, Cl and F are in group 7A) a. eg-octahedral, mg-octahedral, nonpolar b. eg-octahedral, mg-octahedral, polar c. eg-trigonal bipyramidal, m
> Choose the best Lewis is structure for SeO42- Determine the electron geometry and polarity of SF6. a. eg = trigonal bipyramidal, mg=trigonal bipyramidal, nonpolar b. eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=see-saw, polar c. eg=octahedral, mg=trigonal bipyramida
> Draw the Lewis structure of PF, and then determine its electron domain and molecular geometries. A. trigonal bipyramidal / trigonal bipyramidal B. square / octahedral C. planar / trigonal bipyramidal D. tetrahedral / square planar E. tetrahedral / s
> For the following complex, [ML5], the possible coordination geometries are. A. Square-pyramidal and Trigonal-bypyramidal B. Square planar and Trigonal-bipyramidal C. Tetrahedral and Trigonal-bipyramidal D. Octahedral and Trigonal-bipyramidal
> Give the electron-domain and molecular geometries for the following molecules and ions. Part A). HCN electron-domain geometry Linear Trigonal planar Tetrahedral Trigonal bipyramidal Octahedral Part B). HCN molecular geometry Linear Bent Trigonal
> Draw a Lewis dot structure for XeF4.
> Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of PI5. eg = trigonal planar, mg = octahedral eg = octahedral, mg = square pyramidal eg = tetrahedral, mg = octahedral eg = trigonal bipyramidal, mg = trigonal bipyramidal eg = trigonal
> For ClF3, the electron-pair geometry is _________ and the molecular geometry is __________ 1. trigonal planar, T shape 2. see saw, trigonal bipyramidal 3. trigonal bipyramidal, Tshape 4. tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal 5. tetrahedral, tetrahedra
> Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of ICl2. A. eg = trigonal bipyramidal, mg = linear B. eg = tetrahedral, mg = trigonal pyramidal C. eg = octahedral, mg = bent D. eg = trigonal bipyramidal, mg = tetrahedral E. eg = tetrah
> Determine the molecular shape of each of the following species. (a) CIF3 (b) NF3 (c) CCI4 bent bent bent linear linear linear see-saw see-saw see-saw square planar square planar square planar tetrahedral tetrahedral tetrahedral trigonal bipyramidal
> Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of PF5. eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=trigonal bipyramidal eg=octahedral, mg-octahedral eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=tetrahedral eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal eg=trigonal planar,
> Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4): linear trigonal planar tetrahedral trigonal bipyramidal octahedral Carbon disulfide (CS2): linear trigonal planar tetrahedral trigonal bipyramidal octahedral Ammonia (NH3): linear trigonal planar tetrahedral t
> Write reaction quotients for the following reactions. Do not include states in the reaction quotient. (a) 2NO(g) + 02(g) N204(8) (b) HCOOH(ag) HC00 (aq) + H"(aq)
> 4. AsFs (As has an expanded octet, greater than 8 electrons) a. Trigonal pyramidal AND trigonal pyramidal b. Trigonal pyramidal AND trigonal bipyramidal c. Trigonal bipyramidal AND trigonal pyramidal d. Trigonal bipyramidal AND trigonal bipyramidal
> 1. Identify the electronic geometry and molecular geometry for bromine pentacloride: trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped trigonal bipyramidal, see saw octahedral, square pyramidal octahedral, octahedral 2. How many
> Determine the electron geometry, molecular geometry and polarity of XeF6. A. eg=octahedral, mg=octahedral, nonpolar B. eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=trigonal bipyramidal, nonpolar C. eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=see-saw, polar D. eg=octahedral, mg=trigo
> Draw the major product of the following reaction. (3 bookmarks) Draw the major product of the following reaction. KOC(CH,), HOC(CH,), Draw the alky lodide starting material that would give the following alkene as the major product of an E2 reaction
> Draw the electron-dot structure for CHClO. Note: Carbon is the central atom and all three atoms (H, Cl, O) are attached to the carbon. Draw the molecule by placing the atoms on the grid and connecting them with bonds. Include all lone pairs of electrons.
> The electron domain and molecular geometry of SF4 are a. trigonal bipyramidal, seesaw b. trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal c. octahedral, square planar d. octahedral, square pyramidal e. trigonal bipyramidal, T-shaped
> Using the VSEPR model, the electron-domain geometry and the molecular geometry of the central atom in SF6 is A. trigonal bipyramidal; T-shaped B. tetrahedral; tetrahedral C. trigonal bipyramidal; trigonal bipyramidal D. trigonal bipyramidal; seesaw (
> The electron domain geometry, molecular geometry, and polarity of IF5 are _____, _____, and _____, respectively. A. Trigonal bipyramidal, Trigonal bipyramidal, and polar B. Octahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and non-polar C. Octahedral, trigonal bipyra
> The electron group geometry of AsCl3 is _______ and its molecular geometry is ________. Select one a. trigonal bipyramidal, trigonal bipyramidal b. tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal c. octahedral; trigonal bipyramidal d. tetrahedral, tetrahedral e tr
> he molecules CH4 and CH3Cl both contains four bonds. Why is CH4 Nonpolar whereas CH3Clis polar?
> The molecular geometry of the CH4 molecule is ________ and the molecule is ________ seesaw, nonpolar linear, polar trigonal pyramidal, polar tetrahedral, polar tetrahedral, nonpolar
> Find the reaction quotient for the reversible reaction below. 2NO(9) + C2(9) = 2NOCI(g)
> What is the molecular geometry of CO2?
> Indicate the electron pair geometry and the molecular geometry for each of the six compounds. Compound Electron palr geometry Molecular geometry CO2 BF3 SO2 SICI4 PF3 OF2
> Indicate the electron pair geometry and the molecular geometry for each of the six compounds. Molecular geometry Compound Electron pair geometry CO, SO, so, CH PF, OF
> Mixture - show any isomers, use multiple bonds if needed, and show any nonzero formal charges. # of val. e's Molecular VSEPR 3-D Structure Formula Lewis Structure Geometry (show polarity) N, co, PBr, scI, CH,0 [(H,C),CO] or CH,COCH,
> Vesper polar Geometry Molecular Lewis Formula Structure Electron Electron Pairs of Geometry Polar Total H of Geometry Lone Molecular Bonds Molecule Total of Geometry Electron Domains Molecule polar Yes Vesper Melecular Formula Lewis Structure Lone Pa
> Indicate the electron pair geometry and the molecular geometry for each of the six compounds. Compound Electron pair geometry Molecular geometry CO, BF, so, CH4 PF3 SCI,
> b. CO2 Electron-Domain Geometry Molecular Geometry: Bond angles: b. CO3 Electron-Domain Geometry: Molecular Geometry: Bond angles:
> Molecules and lons with One Central Atom COâ‚‚ Molecular geometry Ideal bond angles o=c=0 Are polar bonds present? Molecular geometry CO. Ideal bond angles Are polar bonds present? (Indicate on Lewis dot structure.) Is there an overa
> Formula Lewis Dot Structure Drawing Geometry Electron pair geometry Polarity CO2 Molecular geometry CO Electron pair geometry Geometry Electron pair geometry Formula Lewis Dot Structure Drawing Polarity CO2 Molecular geometry Co Electron pair geometr
> Sketch the shape of the following, name the geometry, then draw a dipole arrow if the species is a dipole. AsCls BrFz CBR4 CIO, Molecular Geometry: Molecular Geometry: Molecular Geometry: Molecular Geometry: CO2 CO,- ICL CS2 Molecular Geometry: Molec
> Write an ionic compound from the cation and anion using the correct subscripts and name it. 4. Write an ionic compound from the cation and anion using the correct subscripts and Name it. Cation Formula Name Anion Iron (III) Fe FeCl Iron (III) chlorid
> Arrange each of the following sets of bond in order of increasing polity. Make sure to explain your answers. H-Br, H-F, H-CL, H-I C-H, N-H, F-H, O-H CO, C-C, C-F, C-N spa 8. Complete the below table following the example shown. Counting Electrons & E
> Fill in the blanks. Part A linear Studv View Molecular Lewis Formula Formula Predicted Electron Domain Geometry trigonal planar Bond Angle(s)Model Molecular Shape Name in 3-D linear Study Lewis Formula View Molecular Formula Predicted Bond Angle(s)
> Mixture-show any isomers or resonance structures, use multiple bonds if needed, and show any nonzero formal charges. of Molecular VSEPR 3-D Structure Geometry (show polarity) Formula Lewis Structure val. E's Becl, O, IFs CH.O CIO, PF
> Are the O-N-O bond angles greater in the nitrite ion (NO2-) or the nitrate ion (NO3-)? Please select the answer that best explains your conclusion. a. Nitrite has the greater bond angle because a trigonal planar bond angle is greater than a tetrahedral b
> Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following compounds. Using VSEPR, determine the electron pair geometry, the molecular geometry, and the bond angle (in degrees) for each compound. 7. CIF, Molecular Geometry: Bond Angle(s): Lewis Structure: El
> Lewis Structure Electron geometry 4. H30+ Molecular geometry Valence electrons 5. NH3 Lewis Structure Electron geometry Valence electrons Molecular geometry Electron geometry 4. H3O* Lewis Structure Molecular geometry Valence electrons 5. NH3 Lewis S
> # of Electron Groups IFS Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 10. CS2 Lewis Structure # of Electron Groups Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry Structure: of Electron Groups F5 Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 10. CS: Lewis Structure: of Electron
> 1. Formula SF4 Molecule Geometry: Electron Geometry 2. Formula XeF4 Molecule Geometry Electron Geometry:
> 1. SO Lewis Structure: # of Electron Groups Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 2. SO Lewis Structure: # of Electron Groups Electron Geometry 1. SO, Lewis Structure of Electron Groups Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 2. SO: Lewis Structure: of E
> 5. XeF2 Lewis Structure: # of Electron Groups Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 6. H2S Lewis Structure: # of Electron Groups Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 5. XeF2 Lewis Structure: # of Electron Groups Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 6
> The Atomic radius is one property which is a periodic trend. The atomic radius: A. Deceases continuously as you go left to right across a period on the periodic table B. Increases down a group on the periodic table C. increases continuously as you go lef
> 10. PCI2F3 Lewis Structure* Electron geometry Valence electrons Molecular geometry 11. CIO2 Lewis Structure Electron geometry 10. PCl Fs Lewis Structure Encton gemery Valence olectrons Mclecul gemery Electron geometry 11. CIO2 Lewis Structure Molecul
> 7. AsFs Lewis Structure Electron geometry Valence electrons Molecular geometry Lewis Structure 8. ASF3 Electron geometry 7. AsFs Lewis Structure Ewctron gemetry Valence electrons Mcincuar genmetry Electron geometry B. ASF3 Lewis Structure Molecular g
> Complete the Lewis structures for the following molecules. A complete Lewis structure should show all non-zcro formal charges on atoms. Complete the formal charges on the structures below. CHEM 1430 LEWIS STRUCTURES SPRING 2018 Lewis Structure with
> In the best Lewis structure for XeF2, what are the electron geometry and the molecular shape around the central xenon atom? Electron geometry: Octahedral Molecular shape: Linear Electron geometry: Tetrahedral Molecular shape: Bent O Electron geometry
> Electron geometry 1. CF4 Lewis Structure Molecular geometry Valence electrons Electron geometry Lewis Structure 2. CH2Cl2 Molecular geometry Valence electrons 1. CF4 Lewis Structure Electron geometry Valence electrons Molecular geometry 2. CH2CI2 Ele

