Question: British Beverages bottles two soft drinks under
British Beverages bottles two soft drinks under license to Cadbury Schweppes at its Manchester plant. Bottling at this plant is a highly repetitive, automated process. Empty bottles are removed from their carton, placed on a conveyor, and cleaned, rinsed, dried, filled, capped and heated (to reduce condensation). The only stock held is either direct materials or else finished goods. There is no work in progress. The two soft drinks bottled by British Beverages are lemonade and diet lemonade. The syrup for both soft drinks is purchased from Cadbury Schweppes. Syrup for the regular brand contains a higher sugar content than the syrup for the diet brand. British Beverages uses a lot size of 1000 cases as the unit of analysis in its budgeting. (Each case contains 24 bottles.) Direct materials are expressed in terms of lots, where one lot of direct materials is the input necessary to yield one lot (1000 cases) of beverage. In 2018, the following purchase prices are forecast for direct materials:
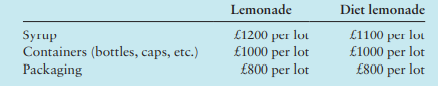
The two soft drinks are bottled using the same equipment. The equipment is cleaned daily, but it is only rinsed when a switch is made during the day between diet lemonade and lemonade. Diet lemonade is always bottled first each day to reduce the risk of sugar contamination. The only difference in the bottling process for the two soft drinks is the syrup. Summary data used in developing budgets for 2018 are as follows:
a: Sales:
◠Lemonade, 1080 lots at £9000 selling price per lot.
◠Diet lemonade, 540 lots at £8500 selling price per lot.
b: Opening (1 January 2018) stock of direct materials:
◠Syrup for lemonade, 80 lots at £1100 purchase price per lot.
◠Syrup for diet lemonade, 70 lots at £1000 purchase price per lot.
◠Containers, 200 lots at £950 purchase price per lot.
◠Packaging, 400 lots at £900 purchase price per lot.
c: Opening (1 January 2018) stock of finished goods:
◠Lemonade, 100 lots at £5300 per lot.
◠Diet lemonade, 50 lots at £5200 per lot.
d: Target closing (31 December 2018) stock of direct materials:
â— Syrup for lemonade, 30 lots.
â— Syrup for diet lemonade, 20 lots.
â— Containers, 100 lots.
â— Packaging, 200 lots.
e: Target closing (31 December 2018) stock of finished goods:
â— Lemonade, 20 lots.
â— Diet lemonade, 10 lots.
f: Each lot requires 20 direct manufacturing labor-hours at the 2018 budgeted rate of £25 per hour. Indirect manufacturing labor costs are included in the manufacturing overhead forecast.
g: Variable manufacturing overhead is forecast to be £600 per hour of bottling time; bottling time is the time the filling equipment is in operation. It takes two hours to bottle one lot of lemonade and two hours to bottle one lot of diet lemonade. Fixed manufacturing overhead is forecast to be £1 200 000 for 2018.
h: Hours of budgeted bottling time is the sole allocation base for all fixed manufacturing overhead.
i: Administration costs are forecast to be 10% of the cost of goods manufactured for 2018. Marketing costs are forecast to be 12% of sales for 2018. Distribution costs are forecast to be
8% of sales for 2018.
Required
Assume British Beverages uses the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method for costing all stock. On the basis of the preceding data, prepare the following budgets for 2018:
1: Revenue budget (in £)
2: Production budget (in units)
3: Direct materials usage budget (in units and £)
4: Direct materials purchases budget (in units and £)
5: Direct manufacturing labor budget
6: Manufacturing overhead costs budget
7: Closing finished goods stock budget
8: Cost of goods sold budget
9: Marketing costs budget
10: Distribution costs budget
11: Administration costs budget
12: Budgeted profit and loss account.
> The ZZ Group has two divisions, X and Y. Each division produces only one type of product: X produces a component, C and Y produces a finished product, FP. Each FP needs one C. It is the current policy of the group for C to be transferred to Division Y at
> ZP Plc operates two subsidiaries, X and Y. X is a component manufacturing subsidiary and Y is an assembly and final product subsidiary. Both subsidiaries produce one type of output only. Subsidiary Y needs one component from Subsidiary X for every unit o
> All personnel, including partners, of public accounting firms must usually turn in biweekly time reports, showing how many hours were devoted to their various duties. These firms have traditionally looked unfavorably on idle or unassigned staff time. The
> Calypso SA manufactures and sells fertilizers. Calypso uses the following standard direct materials costs to produce 1 tons of fertilizer Note that 1.2 tons of input quantities are required to produce 1 ton of fertilizer. No stocks of direct materials ar
> Tropical AB processes tropical fruit into fruit salad mix, which it sells to a food-service company. Tropical has in its budget the following standards for the direct materials inputs to produce 80 kg of tropical fruit salad: Note that 100 kg of input q
> Marko Antero Oy produces perfume. To make this perfume, Marko Antero uses three different types of fluid. Tartars, Erebus and Uranus are used in standard proportions of 4/10, 3/10 and 3/ 10, and their standard costs are €6.00, â
> X Ltd uses an automated manufacturing process to produce an industrial chemical, Product P. X Ltd operates a standard marginal costing system. The standard cost data for Product P is as follows: In order to arrive at the budgeted selling price for Produ
> Deadeye Ltd operates a standard costing system in which all stocks are valued at standard cost. The standard direct material cost of one unit of product MS is £36, made up of 4.8 kg of material Hat £7.50 per kg. Material H is u
> The Antwerp Lions play in the Flemish Football League. The Lions play in the Antwerp Stadium (owned and managed by the City of Antwerp), which has a capacity of 30 000 seats (10 000 lower- tier seats and 20 000 upper-tier seats). The Antwerp Stadium char
> Baden-Möbel GmbH manufactures a variety of prestige boardroom chairs. Its job-costing system was designed using an activity-based approach. There are two direct-cost categories (direct materials and direct manufacturing labour) and three ind
> Les Cliniques du Parc reports the following information for July 2018 regarding its nursing staff consisting of nurses, nursing assistants and orderlies. Required 1. Calculate the total direct nursing labor efficiency variance for July 2018. 2. Calculat
> A company sells three products: D, E and F. The market for the products dictates that the numbers of products sold are always in the ratio of 3D:4E:5F. Budgeted sales volumes and prices, and cost details for the previous period were as follows: The budge
> The Safe Soap Co. makes environmentally-friendly soap using three basic ingredients. The standard cost card for one batch of soap for the month of September was as follows: The budget for production and sales in September was 120 000 batches. Actual prod
> O’Connell & Associates, a firm of architects, has three levels of professional staff: principals (managers), who manage all aspects of the architectural job; senior architects, who are responsible for the main designs; and junior ar
> Mondragon SA assembles its CardioX product at its Toledo plant. Manufacturing overhead (both variable and fixed) is allocated to each CardioX unit using budgeted assembly-time hours. Budgeted assembly time per CardioX product is 2 hours. The budgeted var
> PP Ltd operates a standard absorption costing system. The following information has been extracted from the standard cost card for one of its products: Actual results for the period were as follows: It has subsequently been noted that due to a change in
> Braithwaite Ltd manufactures and sells a single product. The following data have been extracted from the current year’s budget: The company’s production capacity is not being fully utilised in the current year and thre
> Coaldale Ltd manufactures and sells product CC. The company operates a standard marginal costing system. The standard cost card for CC includes the following: The budgeted and actual activity levels for the last quarter were as follows: The actual costs
> Migratory Ltd, which manufactures a single product, uses standard absorption costing. A summary of the standard product cost is as follows: Budgeted and actual production for last month were 10 000 units and 9000 units respectively. The actual costs incu
> Willem Nijmegen manages the warehouse of Stinted NV, a mail-order firm. Nijmegen is concerned about controlling the fixed costs of the 20 workers who collect merchandise in the warehouse and bring it to the area where orders are assembled for shipment. E
> Henriksen AS manufactures and sells packaging machines. It recently used an activity-based approach to refine the job-costing system at its Vejle plant. The resulting job-costing system has one direct-cost category (direct materials) and four indirect ma
> L’Evénement du Demarche budgets to produce 300 000 copies of its monthly newspaper for August 2018. It is budgeted to run 15 000 000 print pages in August with 50 print pages per newspaper. Actual production in August 2018
> Lavertezzo allocates fixed manufacturing overhead to each suit using budgeted direct manufacturing labor-hours per suit. Data pertaining to fixed manufacturing overhead costs for June 2018 are budgeted, SFr 62 400, and actual, SFr 63 916. Required 1. C
> MadetojaOy’s job-costing system has two direct-cost categories: direct materials and direct manufacturing labor. Manufacturing overhead (both variable and fixed) is allocated to products on the basis of standard direct manufacturing lab
> Nolton-Ragnvald AS uses a standard costing system. It allocates manufacturing overhead (both variable and fixed) to products on the basis of standard direct manufacturing labor-hours (DLH). Nolton develops its manufacturing overhead rate from the current
> 1. Prepare a comprehensive set of variances for each of the four categories of cost of L’Evénement du Dimanche. 2. Comment on the results in requirement 1. What extra insights are available with a flexible budget analysis over that of a static-budget ana
> The Olsson-Langkilde Air Force Base has an extensive repair facility for jet engines. It developed standard costing and flexible budgets to account for this activity. Budgeted variable overhead at a level of 8000 standard monthly direct labor-hours was S
> Dansk mat AS operates a home meal delivery service. It has agreements with 20 restaurants to pick up and deliver meals to customers who phone or fax in orders. Dansk mat is currently examining its overhead costs for May 2018. Variable-overhead costs for
> Drogheda Chemical adopts a continuous improvement approach to setting monthly standards’ costs. Assume the direct materials standard quantity input of 10 kg per output unit and the direct manufacturing labor quantity input of 0.5 hours per output unit pe
> Drogheda Chemical Ltd has set-up the following standards per finished output unit for direct materials and direct manufacturing labor: The number of finished output units budgeted for March 2018 was 10 000; 9810 units were actually produced. Actual resu
> Norland-Norge AS produces corporate notebooks. Each notebook is designed for an individual customer. The company’s operating budget for September 2018 included these data: The actual results for September 2018 were: The managing directo
> CJD Ltd manufactures plastic components for the car industry. The following budgeted information is available for three of their key plastic components: The total number of activities for each of the three products for the period is as follows: Overhead
> Ched Ltd manufactures Cheddar cheese pies. For January 2018, it budgeted to purchase and use 15 000 kg of Cheddar cheese at £0.89 per kg; budgeted output was 60 000 pies. Actual purchase and use for January 2018 was 16 000 kg at £0.82 per kg; actual out
> The budgeted prices for direct materials, direct manufacturing labor and direct marketing (distribution) labor per attaché case are €40, €8 and €12, respectively. The chairman is pleased wit
> AKEI is an elite desk manufacturer. At the start of May 2018, the following budgeted unit amounts (based on a standard costing system) related to its manufacture of executive desks (made out of oak): Direct materials: 16 square meters of oak per desk at
> Sharmila Khan is manager of TaxExperts.co.uk, a firm that provides assistance in the preparation of individual tax returns via the internet. Because of the highly seasonal nature of her business, Sharmila employs staff on a monthly basis from two account
> A company manufactures and sells a single product. The company operates a standard marginal costing system that enables the reporting of planning and operational variances. The original standard contribution per unit of the product for October, which was
> Poitou-Chemises SARL manufactures shirts for retail chains. Armand Plessis, the accountant, is becoming increasingly disenchanted with Poitou-Chemises’ six-month-old standard costing system. The budgeted amounts for both its direct mate
> Sam Chase of Flowers.co.ke receives a brochure from the Hackett Group, a consulting firm specializing in benchmarking. He asks the Hackett Group to provide benchmark data from its recent study of the finance function at over 100 retail companies (both tr
> Sam Chase is the Finance Director of Flowers.co.ke, an internet company that enables customers to order home deliveries of flowers by accessing its website. Flowers.co.ke has a network of florists (‘strategic partners’
> AbulafiaSrl manufactures tyres for the Formula 1 motor racing circuit. For August 2018 Abulafia budgeted to manufacture and sell 3000 tyres at a variable cost of €74 per tyre and a total fixed cost of €54 000. The budgeted selling price was €110 per tyre
> ÁgústKarlsson is the purchasing agent for the Akureyri Manufacturing Company. Bjarni Jóhannesson is head of the Production Planning and Control Department. Every six months, Bjarni gives Ágúst a general purchasing programme. Ágúst gets specifications fr
> Wolfgang Iser, the accountant of Starkuchen, wants to further examine the relative profitability of raisin cake and layered carrot cake. He questions the accuracy of the activity-based normal costing numbers. He notes that the 2017 actual manufacturing i
> CasteloBrancoLda is a manufacturer of video-conferencing products. Regular units are manufactured to meet marketing projections, and specialized units are made after an order is received. Maintaining the video-conferencing equipment is an important area
> The Suzuki Company in Japan has a division that manufactures two-wheel motorcycles. Its budgeted sales for Model G in 2016 is 800 000 units. Suzuki’s target closing stock is 100 000 units, and its opening stock is 120 000 units. The company’s budgeted se
> Jack Zielinski, the budget manager at Jelenia-Silesia, a manufacturer of child furniture and carriages, is working on the 2018 annual budget. In discussions with SylwesterCzereszewski, the sales manager, Jack discovers that Sylwester’s sales projections
> TiilikainenOy has prepared a sales budget of 42 000 finished units for a three-month period. The company has a stock of 22 000 units of finished goods on hand at 31 December and has a target finished goods stock of 24 000 units at the end of the succeedi
> Europa-Dyonisos SA produces wine. The company expects to produce 1.5 million two-liter bottles of Chablis in 2018. Europa-Dyonisos purchases empty glass bottles from an outside supplier. Its target closing stock of such bottles is 50 000; its opening sto
> SarandreaSrl had a target closing stock of 70 000 four-liter bottles of burgundy wine. Sarandrea’s opening stock was 60 000 bottles, and its budgeted production was 900 000 bottles. Required Calculate the budgeted sales in number of bottles.
> PB is a car production company. PB uses a system of standard costing to set its budgets. Budgets are set annually by the Finance Department and approved by the Board of Directors of PB. The Finance Department prepares variance reports each month for rev
> ‘The existence of non-output-unit-level costs means that managers should not calculate unit product costs based on total manufacturing costs in all levels of the cost hierarchy.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> Describe four levels of a manufacturing cost hierarchy
> What are the most frequently used allocation bases for manufacturing overhead costs?
> The accountant of a retailer has just had a €50 000 request to implement an activity-based costing system quickly turned down. A senior vice-president, in rejecting the request, noted, ‘Given a choice, I will always prefer a €50 000 investment in improvi
> Define cost smoothing, and explain how managers can determine whether it occurs with their costing system.
> Define contribution margin, gross margin, and contribution margin percentage, variable-cost percentage and margin of safety.
> Distinguish between operating profit and net profit.
> Describe how the special case labeled CVP is different from the general case for predicting total revenues, total costs and operating profit.
> Name one reason why many companies prefer the master-budget utilization-level concept rather than the normal utilization-level concept.
> FG is preparing its cash budgets for January, February and March. Budgeted data are as follows: The selling price per unit is £200. The purchase price per kg of raw material is £25. Each unit of finished product requires 2 kg of
> The term variable costing could be improved by calling it variable manufacturing costing. Do you agree? Why?
> Describe an accounting method that would eliminate some key inconsistencies that often arise in by-product reporting.
> Which joint-cost-allocation method is supported by the cause-and-effect criterion for choosing among allocation methods?
> Define separable costs.
> What does environmental management accounting capture?
> What are the OECD’s corporate governance principles?
> What does the strategic scorecard force board members to do?
> Describe dimensions of the strategic scorecard?
> What is the digitally advanced enterprise control loop?
> What differentiates a digitally advanced firm from a traditional industrial one?
> Nyborg Supermarkets has a kaizen (continuous improvement) approach to budgeting monthly activity area costs for each month of 2018. February’s budgeted cost driver rate is 0.998 times the budgeted January 2018 rate. March’s budgeted cost driver rate is 0
> Starkuchen GmbH has been in the food-processing business for three years. For its first two years (2017 and 2018), its sole product was raisin cake. All cakes were manufactured and packaged in 1 kg units. A normal costing system was used by Starkuchen. T
> What are some key technologies producing data?
> How is data affected by digitization?
> What must management accounting system designers be careful to do?
> What impact is digitization having on firms?
> Describe the three main measures used in the theory of constraints.
> Outline how three di erent versions of back flush costing can di er.
> Companies adopting back flush costing often meet three conditions. Describe these three conditions.
> Describe how JIT systems a ect product costing.
> List five major features of JIT production systems.
> Distinguish a demand-pull from a push-through system.
> M plc designs, manufactures and assembles furniture. The furniture is for home use and therefore varies considerably in size, complexity and value. One of the departments in the company is the Assembly Department. This department is labor intensive; the
> Give examples of non-financial measures of customer satisfaction.
> What is strategic management accounting?
> The manager of a highly automated plant that assembles desktop computers commented, ‘Yield and mix variance information is irrelevant to my cost management decisions.’ Give two possible reasons for the manager’s statement.
> Give an example of an input other than direct materials and direct labor where calculating yield and mix variances might be useful. Explain your reasoning briefly.
> How might managers use information about direct-labour yield and mix variances in improving the performance of a business?
> Changes in the mix of direct materials used from the budgeted mix always hurt yield.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> Name three sources of the standards used in the total direct materials yield and mix variances.
> Direct materials yield and mix variances are particularly useful when materials are substitutable.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> Distinguish between total direct materials yield and mix variances.
> The 4-variance analysis format shows ‘never a variance’ for two areas. Which two areas? Why?
> Embutidos Vallina SA has two direct-cost categories: direct materials and direct manufacturing labor. Its single indirect-cost category (manufacturing overhead) is allocated on the basis of machine-hours. Numbers taken from the monthly budgets for June 2
> Explain how 4-variance analysis differs from 1-, 2- and 3-variance analyses.
> Assume variable manufacturing overhead is allocated using machine-hours. Give three possible reasons for a €25 000favourable variable-overhead efficiency variance.
> Both financial and non-financial measures are used to control variable manufacturing overhead. Give two examples of each type of measure.
> Budgeting for variable manufacturing overhead requires a knowledge of cost drivers. Name three possible cost drivers.
> What are the steps in planning variable-overhead costs?
> How might the continuous improvement theme be incorporated into the process of setting budgeted costs?

