Question: M plc designs, manufactures and assembles
M plc designs, manufactures and assembles furniture. The furniture is for home use and therefore varies considerably in size, complexity and value. One of the departments in the company is the Assembly Department. This department is labor intensive; the workers travel to various locations to assemble and fit the furniture using the packs of finished timbers that have been sent to them.Budgets are set centrally and they are then given to the managers of the various departments who then have the responsibility of achieving their respective targets. Actual costs are compared against the budgets and the managers are then asked to comment on the budgetary control statement. The statement for April for the Assembly Department is shown below
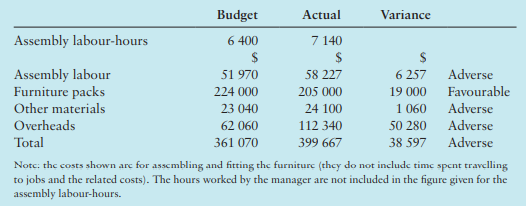
The Manager of the Assembly Department is new to the job and has very little previous experience of working with budgets but he does have many years’ experience as a supervisor in assembly departments. Based on that experience he was sure that the department had performed well. He has asked for your help in replying to a memo he has just received asking him to ‘explain the serious overspending in his department’. He has sent you some additional information about the budget:
1. The budgeted and actual assembly labor costs include the fixed salary of $2050 for the Manager of the Assembly Department. All of the other labor is paid for the hours they work.
2. The cost of furniture packs and other materials is assumed by the central finance office of M plc to vary in proportion to the number of assembly labor-hours worked.
3. The budgeted overhead costs are made up of three elements: a fixed cost of $9000 for services from central headquarters, a stepped fixed cost which changes when the assembly hours exceed 7000 hours, and some variable overheads. The variable overheads are assumed to vary in proportion to the number of assembly labour-hours. Working papers for the budget showed the impact on the overhead costs of differing amounts of assembly labour-hours:

The actual fixed costs for April were as budgeted.
Required
1. Prepare, using the additional information that the Manager of the Assembly Department has given you, a budgetary control statement that would be more helpful to him.
2. a. Discuss the differences between the format of the statement that you have produced and that supplied by M plc;
b. Discuss the assumption made by the central one of M plc that costs vary in proportion to assembly labor-hours.
3. Discuss whether M plc should change to a system of participative budgeting.
> AKEI is an elite desk manufacturer. At the start of May 2018, the following budgeted unit amounts (based on a standard costing system) related to its manufacture of executive desks (made out of oak): Direct materials: 16 square meters of oak per desk at
> Sharmila Khan is manager of TaxExperts.co.uk, a firm that provides assistance in the preparation of individual tax returns via the internet. Because of the highly seasonal nature of her business, Sharmila employs staff on a monthly basis from two account
> A company manufactures and sells a single product. The company operates a standard marginal costing system that enables the reporting of planning and operational variances. The original standard contribution per unit of the product for October, which was
> Poitou-Chemises SARL manufactures shirts for retail chains. Armand Plessis, the accountant, is becoming increasingly disenchanted with Poitou-Chemises’ six-month-old standard costing system. The budgeted amounts for both its direct mate
> Sam Chase of Flowers.co.ke receives a brochure from the Hackett Group, a consulting firm specializing in benchmarking. He asks the Hackett Group to provide benchmark data from its recent study of the finance function at over 100 retail companies (both tr
> Sam Chase is the Finance Director of Flowers.co.ke, an internet company that enables customers to order home deliveries of flowers by accessing its website. Flowers.co.ke has a network of florists (‘strategic partners’
> AbulafiaSrl manufactures tyres for the Formula 1 motor racing circuit. For August 2018 Abulafia budgeted to manufacture and sell 3000 tyres at a variable cost of €74 per tyre and a total fixed cost of €54 000. The budgeted selling price was €110 per tyre
> ÁgústKarlsson is the purchasing agent for the Akureyri Manufacturing Company. Bjarni Jóhannesson is head of the Production Planning and Control Department. Every six months, Bjarni gives Ágúst a general purchasing programme. Ágúst gets specifications fr
> Wolfgang Iser, the accountant of Starkuchen, wants to further examine the relative profitability of raisin cake and layered carrot cake. He questions the accuracy of the activity-based normal costing numbers. He notes that the 2017 actual manufacturing i
> CasteloBrancoLda is a manufacturer of video-conferencing products. Regular units are manufactured to meet marketing projections, and specialized units are made after an order is received. Maintaining the video-conferencing equipment is an important area
> The Suzuki Company in Japan has a division that manufactures two-wheel motorcycles. Its budgeted sales for Model G in 2016 is 800 000 units. Suzuki’s target closing stock is 100 000 units, and its opening stock is 120 000 units. The company’s budgeted se
> Jack Zielinski, the budget manager at Jelenia-Silesia, a manufacturer of child furniture and carriages, is working on the 2018 annual budget. In discussions with SylwesterCzereszewski, the sales manager, Jack discovers that Sylwester’s sales projections
> TiilikainenOy has prepared a sales budget of 42 000 finished units for a three-month period. The company has a stock of 22 000 units of finished goods on hand at 31 December and has a target finished goods stock of 24 000 units at the end of the succeedi
> Europa-Dyonisos SA produces wine. The company expects to produce 1.5 million two-liter bottles of Chablis in 2018. Europa-Dyonisos purchases empty glass bottles from an outside supplier. Its target closing stock of such bottles is 50 000; its opening sto
> SarandreaSrl had a target closing stock of 70 000 four-liter bottles of burgundy wine. Sarandrea’s opening stock was 60 000 bottles, and its budgeted production was 900 000 bottles. Required Calculate the budgeted sales in number of bottles.
> British Beverages bottles two soft drinks under license to Cadbury Schweppes at its Manchester plant. Bottling at this plant is a highly repetitive, automated process. Empty bottles are removed from their carton, placed on a conveyor, and cleaned, rinsed
> PB is a car production company. PB uses a system of standard costing to set its budgets. Budgets are set annually by the Finance Department and approved by the Board of Directors of PB. The Finance Department prepares variance reports each month for rev
> ‘The existence of non-output-unit-level costs means that managers should not calculate unit product costs based on total manufacturing costs in all levels of the cost hierarchy.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> Describe four levels of a manufacturing cost hierarchy
> What are the most frequently used allocation bases for manufacturing overhead costs?
> The accountant of a retailer has just had a €50 000 request to implement an activity-based costing system quickly turned down. A senior vice-president, in rejecting the request, noted, ‘Given a choice, I will always prefer a €50 000 investment in improvi
> Define cost smoothing, and explain how managers can determine whether it occurs with their costing system.
> Define contribution margin, gross margin, and contribution margin percentage, variable-cost percentage and margin of safety.
> Distinguish between operating profit and net profit.
> Describe how the special case labeled CVP is different from the general case for predicting total revenues, total costs and operating profit.
> Name one reason why many companies prefer the master-budget utilization-level concept rather than the normal utilization-level concept.
> FG is preparing its cash budgets for January, February and March. Budgeted data are as follows: The selling price per unit is £200. The purchase price per kg of raw material is £25. Each unit of finished product requires 2 kg of
> The term variable costing could be improved by calling it variable manufacturing costing. Do you agree? Why?
> Describe an accounting method that would eliminate some key inconsistencies that often arise in by-product reporting.
> Which joint-cost-allocation method is supported by the cause-and-effect criterion for choosing among allocation methods?
> Define separable costs.
> What does environmental management accounting capture?
> What are the OECD’s corporate governance principles?
> What does the strategic scorecard force board members to do?
> Describe dimensions of the strategic scorecard?
> What is the digitally advanced enterprise control loop?
> What differentiates a digitally advanced firm from a traditional industrial one?
> Nyborg Supermarkets has a kaizen (continuous improvement) approach to budgeting monthly activity area costs for each month of 2018. February’s budgeted cost driver rate is 0.998 times the budgeted January 2018 rate. March’s budgeted cost driver rate is 0
> Starkuchen GmbH has been in the food-processing business for three years. For its first two years (2017 and 2018), its sole product was raisin cake. All cakes were manufactured and packaged in 1 kg units. A normal costing system was used by Starkuchen. T
> What are some key technologies producing data?
> How is data affected by digitization?
> What must management accounting system designers be careful to do?
> What impact is digitization having on firms?
> Describe the three main measures used in the theory of constraints.
> Outline how three di erent versions of back flush costing can di er.
> Companies adopting back flush costing often meet three conditions. Describe these three conditions.
> Describe how JIT systems a ect product costing.
> List five major features of JIT production systems.
> Distinguish a demand-pull from a push-through system.
> Give examples of non-financial measures of customer satisfaction.
> What is strategic management accounting?
> The manager of a highly automated plant that assembles desktop computers commented, ‘Yield and mix variance information is irrelevant to my cost management decisions.’ Give two possible reasons for the manager’s statement.
> Give an example of an input other than direct materials and direct labor where calculating yield and mix variances might be useful. Explain your reasoning briefly.
> How might managers use information about direct-labour yield and mix variances in improving the performance of a business?
> Changes in the mix of direct materials used from the budgeted mix always hurt yield.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> Name three sources of the standards used in the total direct materials yield and mix variances.
> Direct materials yield and mix variances are particularly useful when materials are substitutable.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> Distinguish between total direct materials yield and mix variances.
> The 4-variance analysis format shows ‘never a variance’ for two areas. Which two areas? Why?
> Embutidos Vallina SA has two direct-cost categories: direct materials and direct manufacturing labor. Its single indirect-cost category (manufacturing overhead) is allocated on the basis of machine-hours. Numbers taken from the monthly budgets for June 2
> Explain how 4-variance analysis differs from 1-, 2- and 3-variance analyses.
> Assume variable manufacturing overhead is allocated using machine-hours. Give three possible reasons for a €25 000favourable variable-overhead efficiency variance.
> Both financial and non-financial measures are used to control variable manufacturing overhead. Give two examples of each type of measure.
> Budgeting for variable manufacturing overhead requires a knowledge of cost drivers. Name three possible cost drivers.
> What are the steps in planning variable-overhead costs?
> How might the continuous improvement theme be incorporated into the process of setting budgeted costs?
> ‘There are many costs associated with acquiring and using materials over and above materials purchase costs.’ Give three examples.
> ‘Performance may be both effective and efficient, but either condition can occur without the other.’ Do you agree? Give an example of effectiveness. Give an example of efficiency
> What is the key question in deciding which variances should be calculated and analyzed?
> What is a benchmark? Give an example of three types of benchmark of interest to managers.
> A toy manufacturer that specializes in making fad items has just developed a £50 000 molding machine for producing a special toy. The machine has been used to produce only one unit so far. The company will depreciate the £50 000 initial machine investmen
> Outline three criticisms of traditional budgeting and a related proposal for change.
> Define responsibility accounting.
> Cite three benefits companies report from using an activity-based budgeting approach.
> ‘Budgets are wonderful vehicles for communication.’ Comment.
> ‘Discounted cash flow techniques are relevant only to for-profit organizations.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> What approaches might be used to recognize risk in capital budgeting?
> Corporation tax only plays a role in capital budgeting because of capital allowances.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> How is the accounting rate of return method different from the payback method?
> How is an activity-based approach different from a traditional approach to designing a job-costing system?
> When explaining a motor vehicle market-share turnaround, a car manufacturer stated: ‘We listened to what our customers wanted and acted on what they said. Good things happen when you pay attention to the boss.’ How might management accountants apply the
> Assume that six projects, A–F in the table that follows, have been submitted for inclusion in the coming year’s budget for capital expenditures: Required 1. Calculate the internal rates of return (to the nearest half
> Peter Drucker, a noted business observer, made the following comment in an address to management accountants: ‘I am not saying that you do not need a “cop on the beat”, you do . . . But your great challenge is to get across to your associates your abilit
> Explain the meaning of cost management.
> The accounting system should provide information for five broad purposes. Describe them.
> Describe two consequences of using direct manufacturing labour-hours as an allocation base in a machine-paced work environment.
> Why is the distinction between labour-paced and machine-paced operations important when selecting indirect-cost allocation bases?
> Different costs for different purposes means that a cost allocated for one purpose is not allocated for another purpose. Do you agree?
> How do cost–benefit considerations affect choices by a company about the allocation of indirect costs to products, services or customers?
> How can an individual cost item, such as the salary of a plant security guard, be both a direct cost and an indirect cost at the same time?
> Why might the classification of a cost as a direct cost or an indirect cost of a cost object change over time?
> Previous department costs are those incurred in the preceding accounting period.’ Do you agree? Explain.
> The manager of the Robin Hood Company is considering two investment projects that are mutually exclusive. The after-tax required rate of return of this company is 10%, and the anticipated cash flows are as follows: Required 1. Calculate the internal ra
> Why should the accountant distinguish between transferred-in costs and additional direct material costs for a particular department?
> What problems might arise in estimating the degree of completion of an aircraft blade in a machining shop?
> Changes in the way managers operate require rethinking the design and operation of management accounting systems. Describe five themes that are affecting both the way managers operate and developments in management accounting.
> A leading management observer stated that the most successful companies are those which have an obsession for their customers. Is this statement pertinent to management accountants? Explain.
> Which costs are considered direct? Indirect? Give an example of each.
> What are the three major categories of the inventorial costs of a manufactured product?
> What is a cost driver? Give one example for each area in the value chain.

