Question: CHM 221-M50 Lab 02 Resonance Structures &
CHM 221-M50 Lab 02 Resonance Structures & N =
CHM 221-M50 Lab 02 Resonance Structures NH2 LNH м Ñно N CHO

Transcribed Image Text:
Resonance Structum NEN N: H. O: :NH2 H LE Resonance Structure K :NH2 E L : NH2 M CHO -E CHO
> Write a Lewis structure for each of the following negative ions, and assign the formal negative charge to the correct atom: (a) H3CO- (b) NH2 (c) CN (d) HCO2 (e) HCO3 (f) HC2 CTICE PROBLEM 1.11 Assign the proper formal charge to the colored atom in
> Determine the overall charge on each complex. hexacyanoferrate(II)
> Write the Lewis dot structure for HC2-
> Identify the conjugate base for each acid. Conjugate base of H3PO4 Conjugate base of HS- Conjugate base of NH4+
> Which of the following is a correct statement? Flammable gasses burn in the presence of oxygen. Inert gases and noble gases are explosive. Flammable gases are not explosive in the correct proportions. Nitrogen and helium are flammable gasses.
> Which of the following is a correct statement of Henry's Law (for real solutions)? PA = P°A "XA PA = POA "aA PA = KA "XA PA = KA "aA
> Do the following for the compound C2H5NO: 1. Complete the two resonance structures below. Add all necessary bonds and lone pairs 2. For both structures (A and B) assign the formal charges for atoms 1-3. 3. Based on the formal charges which is the best Le
> Part B AlH3 Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule. Include all lone pairs of electrons. If resonance structures are needed to describe the Lewis structure, draw all possible resonance structures. Part C N3− Draw the molecule by placing atoms on
> a. Draw the Lewis structure of BF3 and dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3). b. Determine the hybridization of the boron in BF3 and the oxygen in dimethyl ether. c. Sketch the 3D structure of the Lewis acid-base adduct that forms in the reaction between BF3 and di
> For the half-reaction below, which of the following is a correct statement? X* +e > X(s) E° = -2.174 V a) X* is readily reduced b) X* is a good oxidizing agent c) X is a poor reducing agent d) X is a good oxidizing agent e) X is readily oxidized
> Which of the following is a correct statement of Charles Law.
> Which is the most likely first step in the mechanism for this reaction? H20 H3O* + H,O + H2O + H20 + H20
> Which mechanism is most likely in this reaction? SN1 SN2 E1 E2 What is the major product of this reaction sequence? A B C What product is not formed of the reaction shown? A B C HBr Br HO. но. 1. TSCI, pyridine Meo 2. NaOMe C ОН H2SO4 A) B) C)
> The(The order o differential rate law for the balanced chemical reaction: f- kinetics in A aA(aq)+bB(aq)+ cC(a)products is given by The order of kinetics in B The order of) kinetics in C What are the order in each chemical, as well as the overall order o
> 1. Where do water and hydrochloric acid lie on the pH scale in relation to each other? 2. Give an example of a buffer and describe what it is used for. 3. Explain why conjugate pairs must be composed of weak acids and bases. 4. Is water a good buffering
> 1. What is chemical kinetics? 2. What do you understand by the rate of reaction? 3. What are the units of rate of reaction? 4. why certain reactions are very fast? 5. how does catalyst affect rate of reaction?
> Identify the conjugate base for each acid. Conjugate base of H2CO3 Conjugate base of HS- Conjugate base of NH4+
> Identify the conjugate base for each acid. Conjugate base of H2S Conjugate base of HCO3- Conjugate base of NH4+
> Identify the conjugate base for each acid. Conjugate base of H3PO4 Conjugate base of HPO42- Conjugate base of NH4+
> Identify the conjugate base for each acid. conjugate base of H2S: conjugate base of HCO3: conjugate base of NH4+:
> What is the lewis structure of NOF?
> which of these species have resonance or isomers? CH4, CH2Cl2, CH4O, H2O, H3O+, HF, NH3, H2O2, N2, P4
> Molecular Species Lewis structure Molecular geometry around central atom(s) (from the number of electron groups predict the shape) Polar or nonpolar? Structural isomers? CH4 CH2Cl2 CH4O H2O C2H2Br2
> Name the following alkenes using systematic names. 1. 2. 3. H3C, CH2 CH CH H3C CH CH2 by CH CH2 CH H2C CH CH2 CH2 CH CH2 CH2 H3C
> Which of the following statements is ALWAYS true about deposition? None of the other answers are correct AH <0 AG<0 As>0
> Explain why conjugate pairs must be composed of weak acids and bases.
> Do the lewis structure for ethanol and dimethyl ether.
> Consider the following statements and determine which are true and which are false. KrF4 has a tetrahedral structure. Bond angles for IF6+ are 60°. KrF4 is a non-polar molecule. SeF4 is a polar molecule. Silane (SiH4) is a non-polar molecule. NO3- h
> What is the pH of a 1.0 L of a 0.45 M solution of propionic (a.k.a. propanoic) acid? (pKa of propanoic acid is 4.88).
> Mass of flask and foil (g) = 63.4842 Mass of flask, foil, and condensed vapor (g) = 63.6995 Temperature of boiling water bath (C) = 95 degrees C Volume of flask (mL) = 134 Barometric pressure (mmHg) = 763.8 Room temperature (C) = 21.0 degrees C Vap
> Mass of flask and foil(g) - 64.5297g Mass of flask, foil and condensed vapor - 64.9787g Temperature of boiling water bath - 101.2 C Volume of flask (mL) - 153.0 Barometric pressure - 762.4 mmHg Room temp - 23 C Vapor pressure at room temperature - 100 mm
> Given: Mass of flask and foil (g) = 60.1560 Mass of flask, foil, and condensed vapor (g) = 60.4312 Temperature of boiling water bath (C) = 98.7 Volume of flask (mL) = 165 Barometric pressure (mmHg) = 752 Room Temperature (C) = 21.8 Vapor pressure at room
> Given: 1. Uncorrected mass of condensed vapor(g)= 0.2752 2. Corrected density of air(g/L)= 1.668 3. Average volume of flask (L)= 0.165 4. Initial mass of air in flask (g)= 0.2752 5. Final partial pressure of air in flask (mmHg)= 318 6. Final mass of air
> Two reactions between a Grignard reagent and a carbonyl compound are given below. Draw the main organic product for each reaction and indicate if H+ or H- is needed to complete each reaction. Two reactions between a Grignard reagent and a carbonyl co
> a. Draw both chair-flip conformations for trans-1-ethyl-4-isopropylcyclohexane b. Draw both chair-flip conformations for trans-1-ethyl-2-isopropylcyclohexane c. Using the axial energy values listed (the A-Values), calculate the relative energy differen
> Draw a stereoisomer of trans-1-ethyl-4-isopropylcyclohexane. *Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists.
> What happened when the cola and borax solution was each added to the water? Is water a good buffering system? Why or why not, chemically speaking?
> Draw and use chair conformations for conformational analysis. Draw both chair conformations for trans-1-ethyl-4-isopropylcyclohexane and circle the more stable conformer.
> Which of the following processes are exothermic, and which are endothermic? a. sweat evaporates from your skin endothermic exothermic b. clothes dry on a clothesline endothermic exothermic c. gasoline burns in your car endothermic exothermic
> 1. Give the common name for the following compound: Ph−C≡C−Ph 2. Give the common name for the following compound: 2,2-dimethyloct-3-yne 3. Give the common name for the following compound: hexa-1,5-dien-3-yne
> Give the common name for the following compound. N.
> Give the common names for the following compounds: NH2 он click to edit
> Which of the following processes are exothermic? Which of the following processes are exothermic? NaF(s) ? Na*(g) + F'(g) Li(s) ? Li(g) CI2(g) ? 2CI(g) Br(g) + e ? Br (g) None of the above are exothermic.
> Fenofibrate, a benzophenone derivative, has been used until recently to lower triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, thus increasing high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). Starting from benzene and any other necessary reagents, complete
> Draw two additional resonance structures for the diene given below to illustrate that the formyl group (-CHO) is an electron withdrawing group by resonance. :
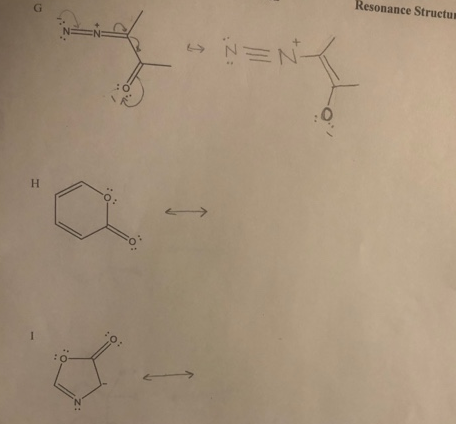
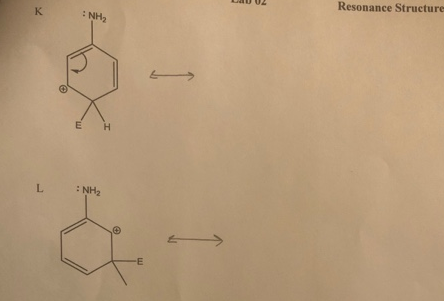
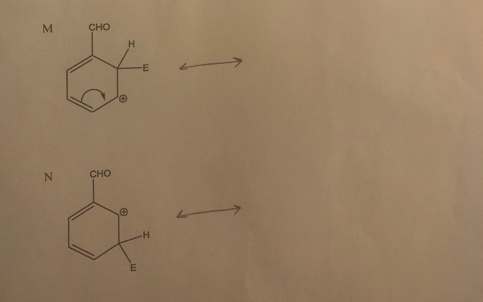
> Draw resonance structures for the following structures, and include the electron movement. СHM 221-M50 Lab 02 Resonance Structures K : NH2 E L : NH2 -E m. M CHO H. -E N сно --
> Provide five additional resonance structures (excluding the original structure) for the molecule shown below. CH30- -CEN
> Is water a good buffer? Confirm your answer by referring to your experimental results in Table 4.1.
> Identify the product of the Diels-Alder reaction below, taking effects of the substituents into account (draw resonance structures!!) CHO CHO CHO CHO CHO CHO CHO
> Rank the indicated bonds in order of increasing bond polarity. H3C. H3C H. C=S C=0 H3C. NH HạC. CH2 C=CH C=N
> Determine the overall charge on each complex. a. hexafluoroaluminate(lll) b. triamminetriiodocobalt(lll) c. diaquadichloroethylenediaminecobalt(lll)
> Metanoia requires 0.045 M of KF solution during lab; however, her instructor warns about the danger of placing a solution of less than 4 pH in a bucket susceptible to breakdown. To mitigate this risk, she wishes to calculate the pH to guarantee that her
> What is the best acid-base description of the image? A. diprotic acid B. A binary acid C. An amphiprotic molecule D. A Bronsted-Lowry base H.
> Calculate the pH of a 0.045 M KF solution Hint: Evaluate if the cation or the anion disturbs water's equilibrium. If the cation disturbs water equilibrium, find Ka and solve as an acid. If the anion disturbs water's equilibrium, then find Kb and solve as
> A 10.8 g sample of methylammonium chloride, CHNHCl, is dissolved in enough water to make 250. mL of solution. Calculate the pH. Use Table 15.4 for relevant K values. Calculate the pH of a 0.045 M KF solution.
> a. What are the requirements for hydrogen bond formation? b. Alcohols are organic molecules defined by the hydroxyl (OH) functional group. The simplest alcohol is methanol, CH3OH. Draw Lewis structures showing two methanol molecules interacting with each
> Provide the IUPAC name for this compound.
> Is water a good buffering system? Explain your scientific reasoning.
> For each of the following: Determine the total valence count Draw a valid Lewis structure Determine whether the molecule is polar or nonpolar CH2Br2 SeS2 KrF4
> Draw the Lewis structure for KrF4 and answer the following question. What is the hybridization on the central atom? dsp3 sp sp2 sp3 d-sp
> Label the functional groups in the molecule. alkaxy group -> halo group hydroxy group alkoxy group Br halo group amino group halo group → Hơ NH - amino group halo group amino group → HƏN
> CIO2 KrF4 Lewis structure Total # of valence electrons electron groups (domains) on central atom resonance structures (Yes or No) Molecular geometry Angles around central atom Formal charge on central atom Polar CIO2 KRF4 Lewis structure Total # of v
> Draw the Lewis structure for the trisulfur (S3) rule molecule. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule.
> Select the statements below that are TRUE. A. Benzene and its derivatives tend to undergo electrophilic aromatic addition reactions. B. Benzene and its derivatives tend to undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. C. Substitution reactions h
> A. For each formula, write the name for each compound (Don't forget Roman Numerals, if necessary.), and circle if the compound is Ionic or Molecular. Circle Compound Name Ionic or Molecular Fe(NOz)2 Ionic or Molecular 2 KCr;O, Ionic or Molecular (NH)
> For the molecule TeF6 give the following: Lewis Structure (include normal, wedge, and dotted lines when necessary), Number of valence electrons, Number of bonded atoms on central atom, Number of lone pairs on central atom, Central atom steric number, Bon
> Show how to carry out the following transformation. Br
> Show how to carry out the following transformation in the highest yield possible. Select the appropriate reagents and draw the correct organic product at each step. Overall reaction (not graded) Br Select answer Select answer
> Using Lewis structures, show the interaction between two molecules of C2H5NH2 and name the type(s) of interactions involved.
> Show how to carry out the following transformation in the highest yield possible. Select the appropriate reagents and draw the correct organic product at each step. Overall reaction (not graded) Select answer Select answer
> Show how to carry out the following transformations: CH3 CH3 HN CH3 CH3 HN OH a. b. HN CH3 CH3 HN CH3 CH3
> Show how to carry out the following transformations. Include all reagents, all intermediates and relevant. a. Ph ? b. C. ?
> Show how to carry out the following transformations: а. Но NH HN CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3
> Synthesis problems: show how to carry out the following transformations. CI N. H HO, H. NHCH3 OCH3
> For a particular isomer of C8H18, the following reaction produces 5093.7 kJ of heat per mole of C8H18(g) consumed, under standard conditions. For a particular isomer of CeHsg, the following reaction produces 5093.7 kJ of heat per mole of CeHelg) cons
> Draw the mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol to yield 2-methyl-1-butene.
> Provide detailed mechanisms for the dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol. OH H2SO4, H2O THF, heat
> What is the mechanism for the complete dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol?
> Which product(s) would be produced by acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol? and and
> Structural formula Condensed Structural Formula Lewis Structure CH3OCH2CH3 Condensed Structural Formula Lewis Structure CH;OCH;CH; CH,CO,CCH, C;H;NH2 C,H,CO;CH3 CH.CONHCH, CH;COCH, CH,COH CH,OH CH;CH;CO,H
> The names of some compounds and values of Lattice energy are given B below. (Not in any order) Compounds: MgBr2, AlBr3, CaBr2, LiBr Lattice energy KJ/mol: 2176, 5361, 807, 2440 The Lattice energy of CaBr2 is A. 2440 KJ/mol B. 2176 KJ/mol C. 5361 KJ
> The lattice energy of CaBr2 can be calculated using the BornHaber Cycle. Explain in words why you would expect aluminum chloride to have higher magnitude lattice energy.
> Draw the following line structure. a. 6-neopentylnonadecane b. 1-cyclopropylpentane c. Trans-1-ethyl-4-isopropylcyclohexane
> For trans-1-ethyl-4-isopropylcyclohexane, which two chair conformations are in equilibrium? A A D
> 4. Consider the two possible Lewis structures of NOF: / a. Are the two Lewis structures resonance structures? Answer: Yes or No b. Identify the most likely structure of NOF. Answer: Structure (I) or Structure (II) 5. Draw all the resonance structures
> Give the IUPAC name for each compound. 10.72 Give the IUPAC name for each compound. H CH3 CH,CH2CH2CH3 (a. GH,-c-CHCH, ČH,CH3 c.) CH,CH,CHCH,CH,CH,CH3 CH3 b. gH,CH2 CH2-C-CH,CH2CH d. (CH,CH),CHCH(CH,CH3)2
> for a particular reaction, delta H= -144.6 kJ and delta S = -301.2 J/K Calculate the delta G for this reaction at 298k 1. delta G in KJ? 2. what can be said about the spontaneity of the reaction at 298k? a. spontaneous in the reverse direction b. spontan
> Draw the main Lewis structure of NOF.
> Write the common names for these amines. In each reaction box. place the best reagent and conditions from the list below. a) HạC-N--CH2-CH3 H b) propanamine NH2 1) 2) 3) 4) NO2 5) 6) HNO2, H2SO4 CH3COOH H2. Pd NaNO3 HNO3, H2SO4 acetyl chloride, pyri
> Draw the electron-dot structure for CHClO. Can someone explain to me why Oxygen bonds to carbon and not to chlorine. As well as why carbon takes electrons from Oxygen and not Chlorine?
> The following reactions convert 5-bromo-S-methyl-hexanol I (C7H15BrO) into a structure with molecular formula C7H14O. Reactions A and B provide the same product while reaction C provides more than one product / (two)What organic product do reactions A
> 1. Draw the Lewis structure for O? 2. Draw the Lewis structure for Ca2+ 3. Draw the Lewis structure for S2- 4. Draw the Lewis structure for CH2Cl2. 5. Draw the Lewis structure for Bel2. 6. Draw the Lewis structure for OF2.
> 21. Draw the Lewis electron structure for the sulfide ion 22. Draw the Lewis electron structure for the chlorine atom. 23. Draw the Lewis electron structure for the Cl; molecule. 24. Draw the Lewis electron structure for the HI molecule. 25. Draw th
> Draw the electron-dot structure for CHClO.
> Rank these compounds by boiling point. Pentane, neopentane, and hexane.
> In each reaction box, place the reagent and conditions from the list below. 1) E-H 2) CH2 3) 4) 5) 6) но H2О2, NaOH, H20 CH3B H2, Pt NANH2 На, Lindlar's catalyst CrO3, H2SO4, H2O CH3CH;Br NaBH4 N2OH CH3CH2CH2B BH3/THF
> In each reaction box, place the best reagent from the list below. Draw the intermediate compound. -OH PCC Reagent A ethyl acetate NABH4 Mg in Etz0 PBr3 NaH ethylene oxide acetone 1) Reagent B 2) CO2 3) H30* -соон CH2CN 1) H. 2) 3) CH;NH2 Mg, Etz0
> Give the products in the following acid-base reactions. Identify the conjugate acid-base pairs. ) NH,* + CH,COO- Conjugate acid-base pairs: NH, NH,. CH3CO0", 6 s* + H2SO, Conjugate acid-base pairs: H2SO,, HCIO, + N¿H4 - Conjugate acid-base pairs: H
> What is a correct conjugate acid-base pair in the following reaction? NH3 + NgH5 = NH4* + N2H4 A NH3, N2H4 NH3, NH4+ NH4+, N2H5 NH4, N2H4
> 1. Which acid is the strongest? a. boric acid b. phosphoric acid c. sulfurous acid d. chloric acid 2. The position of equilibrium lies to the right in each of these reactions: N2H5+ + NH3 → NH4+ + N2H4 NH3 + HBr → NH4

