Question: Consider PepsiCo’s quarterly net revenue as
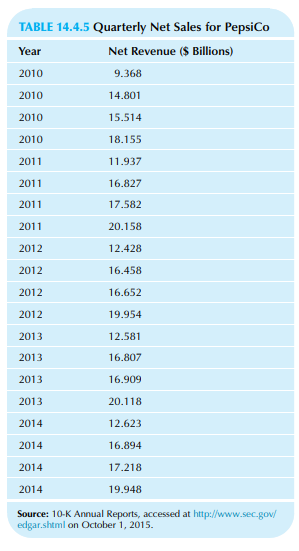
Consider PepsiCo’s quarterly net revenue as shown in Table 14.4.5.
a. Draw a time-series plot for this data set. Describe any trend and seasonal behavior that you see.
b. Plot the moving average values on the same graph as the original data. Comment on what you see. c. Find the seasonal index for each quarter. Which is generally the best quarter for PepsiCo? About how much larger are net sales in this quarter, as compared to a typical quarter?
d. Plot the seasonally adjusted series with the original data.
e. Find the regression equation to predict the long-term trend in seasonally adjusted sales for each time period, using 1, 2,… for the X variable.
f. Does PepsiCo show a significant trend (either up or down) over this time period as indicated by the regression analysis in the previous part of this problem?
g. If we omit the first year (the four observations in 2010) but still use the other seasonally adjusted values as we did in the previous regression, does PepsiCo show a significant trend (either up or down) over this time period?
Table 14.4.5:
Transcribed Image Text:
TABLE 14.4.5 Quarterly Net Sales for PepsiCo Year Net Revenue ($ Billions) 2010 9.368 2010 14.801 2010 15.514 2010 18.155 2011 11.937 2011 16.827 2011 17.582 2011 20.158 2012 12.428 2012 16.458 2012 16.652 2012 19.954 2013 12.581 2013 16.807 2013 16.909 2013 20.118 2014 12.623 2014 16.894 2014 17.218 2014 19.948 Source: 10-K Annual Reports, accessed at http://www.sec.gov/ edgar.shtml on October 1, 2015.
> Draw a histogram of the average hospital charge in ($ thousands) for treating a patient who had the diagnosis group “Inguinal & femoral hernia procedures w MCC” for a group of hospitals in Washington State (data accessed at http://wwwdoh.wa.gov/EHSPHL/h
> Consider the percent change in revenues for food-related companies in the Fortune 500, in Table 3.8.5. a. Construct a histogram for this data set. b. Describe the distribution shape. c. Land O’Lakes had the largest decrease, falling by
> Table 2.6.1 shows some items from a human resources database, representing the status of five people on May 3, 2015. a. What is an elementary unit for this data set? b. What kind of data set is this: Univariate, bivariate, or multivariate? c. Which of th
> Look through the data. Do you find anything that calls into question the regression results? Perform further analysis as needed.
> Consider the 20,000 median household income values in the donations database (available at the companion site). These represent the median household income for the neighborhood of each potential donor in the database. a. Construct a histogram. b. Describ
> Consider CREF, the College Retirement Equities Fund, which manages retirement accounts for employees of nonprofit educational and research organizations. CREF manages a large and diversified portfolio in its growth stock account, somewhere around $22.5 b
> Consider the percentage change in stock price of the most active issues traded on the NASDAQ stock exchange, as shown in Table 3.8.3. a. Construct a histogram of this data set. b. Describe the distribution shape. c. Identify the outlier. d. Interpret the
> Business firms occasionally buy back their own stock for various reasons, sometimes when they view the market price as a bargain compared to their view of its true worth. It has been observed that the market price of stock often increases around the time
> Consider the yields (as an interest rate, in percent per year) of municipal bonds, as shown in Table 3.8.1. a. Construct a histogram of this data set. b. Based on the histogram, what values appear to be typical for this group of tax-exempt bonds? c. Desc
> Many countries (but not the United States) have a “value added tax” that is paid by businesses based on how much value they add to a product (e.g. the difference between sales revenues and the cost of materials). This
> Mutual funds that specialize in the stock of natural resources companies showed considerable variation in their performance during the 12-month period ending July 2010. Consider the Rate of Return column in Table 5.5.3. a. Find the average rate of return
> Consider the Internet advertising budgets from problem 1, but expressed in European euros instead of U.S. dollars. Use the exchange rate listed in a recent issue of The Wall Street Journal or another source. Based on your answers to problem 1 (ie, withou
> Table 4.3.1 provides a list of the amounts that your regular customers spent on your products last month: a. Find the average sales per regular customer. b. Find the median and quartiles. c. Draw the box plot. d. Find the outliers, if any. e. Draw the de
> Refer to the data for problem 6. a. Find the critical value from the F table at the 10% level and report the result of the F test at this level. b. Summarize what this F test has told you about the comparative abilities of these additives to reduce waste
> What are the “obvious conclusions” from the hypothesis tests in the regression output?
> Refer to the data for problem 6. Would it be appropriate to use the least-significant-difference test to find out whether Cleen Up has significantly lower waste than Sludge Away (at the 5% level)? Why or why not? Data from problem 6: Three companies ar
> Refer to the data for problem 6. a. Find the F statistic and its numbers of degrees of freedom. b. Interpret the F statistic in terms of how many times more volatile one source of variability is than another. c. Find the critical value from the F table a
> Three companies are trying to sell you their additives to reduce waste in a chemical manufacturing process. You are not sure their products are appropriate because your process is different from the industry standard (it is a proprietary trade secret). Y
> Refer to the data for problem 1. a. Find the average difference and its standard error for every pair of advertisements (computed as ad 2minus ad 1, ad 1minus ad3, and ad 2minusad 3). b. Test every pair of advertisements atthe1%level and report the resul
> Refer to the data for problem 1. a. Find the average difference between the effectiveness of ad 1 and that of ad 2 (computed as ad 2 minus ad 1). b.* Find the standard error for this average difference. c. How many degrees of freedom does this standard e
> Refer to the data for problem 1. a. Find the critical value from the F table at the 0.1% level and report the result of the F test at this level. b. Summarize what this test has told you about any differences among these ads for consumers in general in t
> Another experiment in the report by Meyers-Levy and Peracchio involved the evaluation of bicycle pictures taken with various camera angles, as evaluated by two groups of individuals with different levels of motivation. (The high-motivation group believed
> Camera angle can make a difference in advertising; it can even affect the viewer’s evaluation of a product. A research article reported a main effect for camera angle (F2,29 = 14.48, p
> Are prices really higher in department stores as compared to off-price stores? Kirby and Dardis examined prices of 20 items (shirts, pants, etc.) for 13 weeks and found that prices are indeed 40% higher in department stores.12 The ANOVA table, adapted fr
> Refer to the data for problem 1. a. Find the F statistic and its numbers of degrees of freedom. b. Interpret the F statistic in terms of how many times more volatile one source of variability is than another. c. Find the critical value from the F table a
> What would you recommend? Are there any other considerations that might change your mind?
> Which is better: competition or cooperation? And does the answer depend on whether the participants share the same values? A study by Cosier and Dalton sheds light on these issues.11 One of their ANOVA tables provides the basis for Table 15.5.5. a.* The
> Is there a significant interaction between supplier and shift in Table 15.5.4? Justify and interpret your answer. Table 15.5.4: TABLE 15.5.4 Average Quality Scores and ANOVA Table Day Shift Night Shift Swing Shift Average Supplier A 77.06 93.12 77.
> Compare the overall average for the day shift to that for the night and swing shifts (refer to Table 15.5.4). Does it appear that there are large differences (more than two or three quality points) among shifts? Are these differences significant? How do
> Use multiple regression with indicator variables, instead of one-way ANOVA, to test whether the quality data in show significant differences from one supplier to another. (You may wish to review the material on indicator variables from Chapter 12.) a. Cr
> Refer to the data for problem 11. Continue using the logarithms of the lengths of calls. a. Find the average difference and its standard error for every pair of types of calls (subtracting smaller from larger in each case). b. Which pairs of types of cal
> Refer to the data for problem 11. Continue using the logarithms of the lengths of calls. a. Find the F statistic and its numbers of degrees of freedom. b. Find the critical value from the F table at the 5% level. c. Report the result of the F test at the
> In an attempt to regain control of your time, you have been recording the time required, in minutes, to respond to each telephone call for the day. Before you make changes (such as referring certain types of calls to subordinates), you would like to have
> Refer to the data for problem 6. Select the two additives with the largest average difference in waste and answer the following. (Use the least-significant difference test method for this problem, subtracting smaller from larger even if you feel that it
> Three advertisements have been tested, each one using a different random sample of consumers from the same city. Scores indicating the effectiveness of the advertisement were analyzed; the results are shown in Table 15.5.1. a. Which advertisement appears
> Table 14.4.3 shows the quarterly net sales of Mattel, a major designer, manufacturer, and marketer of toys. Because of seasonal gift giving, you might expect fourth-quarter sales to be much higher, generally, than those of the other three quarters of the
> Does the amount of purifier have a significant effect on yield, according to this regression analysis? Based on this alone, would you be likely to recommend including a purifying step in the production process?
> Consider Intel’s Net Revenue in Table 14.4.2. a. Construct a time-series plot for this data set. Describe the seasonal and cyclic behavior that you see, as well as any evidence of irregular behavior. b. Which quarter(1,2,3, or4) appears
> Consider the Walt Disney Company’s quarterly revenues as shown in Table 14.4.1. a. Draw a time-series plot for this data set. Describe any trend and seasonal behavior that you see. b. Find the moving average values and plot them on the
> At a meeting, everyone seems to be pleased by the fact that sales increased from $21,791,000 to $22,675,000 from the third to the fourth quarter. Given that the seasonal indices are 1.061 for quarter 3 and 1.180 for quarter 4, write a paragraph analyzing
> The number of job openings fluctuates through time, providing useful information about the current state of the economy and possibilities for the future. Table 14.4.11 shows the computer results of a Box Jenkins analysis of job openings in thousands, ann
> Tables 14.4.9 and 14.4.10 show basic computer results from a Box-Jenkins analysis of yields on 3-month U.S. Treasury bills each year from 1970 through 2009. a. What kind of process has been fitted? b. Write the model in a way that shows how the next obse
> Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is an important measure of total production and is used by business to help guide their planning for the future. Table 14.4.8 shows a Box Jenkins analysis of the percentage change in GDP (from the same quarter of the previous
> Table 14.4.7 shows basic computer results from a Box Jenkins analysis of the daily percentage changes in the Dow Jones Industrial stock market index from Jul. 31 to Oct. 9, 1987, prior to the crash of 1987. a. What kind of process has been estimated? b.
> For each of the following, tell whether it is likely to be stationary or non stationary and why. a. The price per share of Google stock, recorded daily. b. The prime rate, recorded weekly. This is the interest rate that banks charge their best customers
> Consider the time series of quarterly sales in thousands shown in Table 14.4.6. The seasonal indices are 0.89 for quarter 1, 0.88 for 2, 1.27 for 3, and 0.93 for 4. a. Find the seasonally adjusted sales corresponding to each sales value. b. In which quar
> The number of diners per quarter eating at your apre `s-ski restaurant has been examined using trend-seasonal analysis. The quarterly seasonal indexes are 1.45, 0.55, 0.72, and 1.26 for quarters 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. A linear trend has been estim
> What is your interpretation of the effectiveness of the ads in this study? What would you recommend in this situation?
> Based on past data, your firm’s sales show a seasonal pattern. The seasonal index for November is 1.08, for December it is 1.38, and for January it is 0.84. Sales for November were $285,167. a. Would you ordinarily expect an increase in sales from Novemb
> Amazon.com is an e-commerce firm that has shown considerable growth since its founding in 1995, and its quarterly net sales are shown in Table 14.4.4. Their 2014 annual report includes a section titled “Seasonality” th
> What important information is missing from each of the following references? a.* Personal communication, 2016. b. Business Week, p. 80. c. Basic Business Communication (Burr Ridge, Ill.: Richard D. Irwin). d. James A. White, “Will the Real S&P 500 Please
> Arrange selected information to form a proper reference for each of the following cases. a.* The title of the article from the Wall Street Journal is “Tallying Up Viewers: Industry Group to Study How a Mobile Nation Uses Media.” It appeared on July 26, 2
> Your boss has just asked you to write a report. Identify the purpose and audience in each of the following situations: a.* The firm is considering expansion of the shipping area. Background material is needed on the size of facilities at other firms. b.
> The unemployment rate can vary from one state to another, and in 2008 the standard deviation was 1.2% for the percent unemployed, which averaged 5.3% at the time. Table 12.5.5 shows these unemployment rates together with two possible explanatory variable
> Networked computers tend to slow down when they are overloaded. The response time is how long it takes from when you press the Enter key until the computer comes back with your answer. Naturally, when the computer is busier (either with users or with oth
> One might expect the price of a tent to reflect various characteristics; for example, we might expect larger tents to cost more, all else equal (because they will hold more people) and heavier tents to cost less, all else equal (because they are harder t
> How are prices set for computer processor chips? At one time, the frequency was a good indicator of the processing speed; however, more recently manufacturers have developed alternative ways to deliver computing power because a high frequency tends to le
> If the type I error is supposed to be controlled at 5%, how is it that in the computer simulation model, type I errors occurred 70% of the time?
> Table 12.5.1 shows data on Picasso paintings giving the price, area of canvas, and year for each one. a. Find the regression equation to predict price from area and year. b. Interpret the regression coefficient for area. c. Interpret the regression coeff
> sider the interest rates on securities with various terms to maturity, shown in Table 12.5.18. a. Find the regression equation to predict the long-term interest rate (Treasury bonds) from the two shorter term rates. b. Create a new variable, â€
> Consider the magazine advertising page-cost data. a. Which X variable is the least helpful in explaining page costs? How do you know? b. Rerun the regression analysis omitting this X variable. c. Compare the following results without the X variable to th
> Table 12.5.17 shows the results of a multiple regression analysis designed to explain the salaries of chief executive officers based on the sales of their firm and the industry group.36The Y variable represents CEO salary (in thousands of dollars). The X
> Setting prices is rarely an easy task. A low price usually results in higher sales, but there will be less profit per sale. A higher price produces higher profit per sale, but sales will be lower overall. Usually, a firm wants to choose the price that wi
> Consider Table 12.5.15, showing the partial results from a multiple regression analysis (with significant F test) that explains the annual sales of 25 grocery stores by some of theircharacteristics.Thevariable“mall”is1
> How do individual companies respond to economic forces throughout the globe? One way to explore this is to see how well rates of return for stock of individual companies can be explained by stock market indexes that reflect particular parts of the world.
> By switching suppliers, you believe that the standard deviation of the key input component can be reduced from 0.62 to 0.38, on average. Based on the multiple regression output from the preceding problem, what size reduction in defect rate should you exp
> A coworker of yours is very pleased, having just found an R2 value of 100% , indicating that the regression equation has explained all of the variability in Y (“profits”) based on the X variables “revenues” and “costs.” You then amaze this person by corr
> Consider the computer output in Table 12.5.12, part of an analysis to explain the final cost of a project based on management’s best guess of labor and materials costs at the time the bid was placed, computed from 25 recent contracts. All variables are m
> Choose two ads, one that is significant and one that is not. Verify significance based on the average, standard error, and n, to make sure that they are correct. Is it appropriate to use one-sided tests here?
> In many ways, nonprofit corporations are run much like other businesses. Charity organizations with larger operations would be expected to have a larger staff, although some have more overhead than others. Table 12.5.11 shows the number of paid staff mem
> Consider the multiple regression results shown in Table 12.5.10, which attempt to explain compensation of the top executives of 9 selected major motion picture corporations based on the revenues and the return on equity of the firms.35 For example, the d
> Table 12.5.9 shows some of the results of a multiple regression analysis to explain money spent on home food-processing equipment (Y) based on income (X1), education (X2), and money spent on sporting equipment(X3). All money variables represent total dol
> What explains the financial performance of brokerage houses? Table 12.5.8 shows the 1-year performance of asset-allocation blends of selected brokerage houses, together with the percentages recommended in stocks and bonds at the end of the period. a. Wha
> There is considerable variation in the amount CEOs of different companies are paid, and some of it might be explained by differences in company characteristics. Consider the information in Table 12.5.7 on CEO salaries, sales, and return on equity (ROE) f
> Using the donations database on the companion site, and using only people who made a donation in response to the current mailing, consider predicting the amount of a donation (named “Donation_D1” in the worksheet) from the indicator variable that tells i
> Using the donations database on the companion site, and using only people who made a donation in response to the current mailing, consider predicting the amount of a donation (named “Donation_D1” in the worksheet) from the median years of school complete
> In the territory versus sales example (based on the data from Table 11.2.3), the least-squares line to predict sales based on the population of the territory was found to be Expected sales = $1,371,744+$0:23675045 Population ð Þ
> This problem continues the analysis of McDonald’s and Dow Jones stock market data. a. Find the 95% confidence interval for the percent change in McDonald’s stock on a day in which the Dow Jones Index is unchanged. b. Find the 95% confidence interval for
> Consider the daily percent changes of McDonald’s stock price and those of the Dow Jones Industrial Average for trading days in the months of Jan. and Feb. 2010, as shown in Table 11.3.5. a. Draw a scatterplot of McDonaldâ€
> What is your best estimate, with confidence limits, for potential catalog sales?
> Consider the slightly scary topic of business bankruptcies. Table 11.3.4 shows data for each state on the number of failed businesses and the population in millions. a. Construct a scatterplot of business bankruptcies (Y) against population (X). Describe
> Consider the number of transactions and the total dollar value of merger and acquisition deals in the oil and gas industry, from Table 11.1.6. a. Find the regression equation for predicting the dollar value from the number of transactions. b. What is the
> Closed-end funds sell shares in a fixed basket (portfolio) of securities (as distinguished from ordinary mutual funds, which continuously buy and sell shares of securities). Consider the net asset value and the market price for Sector Equity Funds, as sh
> Your firm is having a quality problem with the production of plastic automotive parts: There are too many defectives. One of your engineers thinks the reason is that the temperature of the process is not controlled carefully enough. Another engineer is s
> Microsoft is a company that sells its products in many countries all over the world. Use the data from Table 11.3.18 to explore how its market price movements relate to more general movements in the global economy. a. Is Microsoft significantly related t
> Many companies do not restrict themselves to operating inside any particular country, instead choosing to participate in the global economy, and stock market movements should reflect this reality. Consider data on the monthly percentage changes in stock
> Now consider also the daily percentage changes in the price of a dollar in Japanese yen from Table 11.3.17, along with the euro. a. Create a scatterplot of the euro’s against the yen’s percentage changes. b. Given that
> Consider the international currency markets and, in particular, whether geographical proximity implies association with respect to market movements. Because the United Kingdom kept the pound and did not convert to the euro, we can examine changes of thes
> Table 11.3.2 shows the on-time performance of nine airlines, both for 1 month (May 2010) and for the preceding 4 months (Jan. to Apr. 2010). These numbers represent percentages off lights that arrived on time. We will investigate the consistency of perfo
> From Table 11.3.16, consider the daily production and the number of workers assigned for each of a series of days. a. Find the regression equation for predicting production from the number of workers. b. What is the estimated production amount attributab
> Should anything else trouble you about this situation?
> Table11.3.15 compares short-term bond funds, showing the average maturity (in years until the fund’s bonds mature) and the rate of return as a percentage. a. Find the correlation between maturity and return and interpret it. b. Find the
> Table 11.3.14 gives mailing-list size (thousands of names) and sales (thousands of dollars) for a group of catalogs. a. How strong is the association between these two variables? Find the appropriate summary measure and interpret it. b. Find the equation
> High salaries for presidents and high executives of charitable organizations have been in the news from time to time. Consider the information in Table 11.3.13 for the United Way in 10 major cities. a. What percent of the variation in presidentsâ&#
> Consider the retail price of regular gasoline at selected locations and times shown in Table 11.3.12. a. How strong is the association between prices in 2010 and prices a year earlier? Please give both a number and its interpretation in words. b. Find th
> A linear regression analysis has produced the following equation relating profits to hours of managerial time spent developing the past year’s projects at a firm: Profits= -$957+$85 × Number of hours a. According to this estimated relationship, how large
> Are top executives of larger companies paid significantly more than those of smaller companies? Consider data on CEO pay (dollars) and market capitalization (the total market value of stock, in $millions) for a sample of companies, as shown in Table 11.3
> Consider the weight and price of gold coins from Table 11.3.10. a. How strong is the association between weight and price for these coins? Please give both a number and its interpretation in words. b. Find the regression equation to predict price from we
> Gaining visibility for your products can be expensive, and television advertising during the Super Bowl is a good example, with a cost of nearly $2 million for a 30-s message. This high cost is due, in part, to the large number of Super Bowl viewers. Tab
> How predictable are advertising budgets from year to year? Consider the 2008 and 2009 advertising spending of selected firms as reported in Table 11.3.8. a. Summarize the strength of the year-to-year relationship in advertising budget by computing and in

