Question: Draw the enantiomer of each of the
Draw the enantiomer of each of the following compounds:
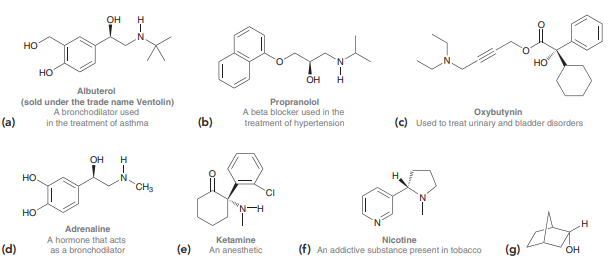
Transcribed Image Text:
он но 'N HO HO OH Albuterol (sold under the trade name Ventolin) Propranolol A beta blocker used in the treatment of hypertension Oxybutynin (c) Used to treat urinary and bladder disorders A bronchodilator used (a) in the treatment of asthma (b) OH H но CH3 CI но Adrenaline A hormone that acts as a bronchodlator Ketamine Nicotine (d) (e) An anesthetic (f) An addictive substance present in tobacco OH
> Each of the following compounds possesses a plane of symmetry. Find the plane of symmetry in each compound. In some cases, you will need to rotate a single bond to place the molecule into a conformation where you can more readily see the plane of symmetr
> (R)-Limonene is found in many citrus fruits, including oranges and lemons: For each of the following compounds identify whether it is (R)-limonene or its enantiomer, (S)-limonene: (a) (b) (c) (d)
> When 0.075 g of penicillamine is dissolved in 10.0 mL of pyridine and placed in a sample cell 10.0 cm in length, the observed rotation at 20°C (using the D line of sodium) is −0.47°. Calculate the specific rotation of penicillamine.
> Draw the enantiomer of each compound in the previous problem.
> Determine the configuration for every chiral center in each of the following compounds: OH он он он но- -H но -H HO H но—н H- OH H- -OH HO H HO H ČH,OH CH,OH CH,OH (a) (b) (c)
> Draw a plausible mechanism for each of the following transformations он Br conc. H2SO4 HBr heat (b) OH Он conc. HSO4 HBr HO. Br (d) heat
> Determine whether each statement is true or false: a. A racemic mixture of enantiomers is optically inactive. b. A meso compound will have exactly one nonsuperimposable mirror image. c. Rotating the Fischer projection of a molecule with a single chira
> For each of the following pairs of compounds, determine the relationship between the two compounds: CI (a) (b) он OH (c) CI (d)
> For each of the following pairs of compounds, determine the relationship between the two compounds: но—н но—н CI H OH но- (a) CH,OH CH,OH (b) 'ci 'CI (c) (d)
> The specific rotation of l-alanine in water (at 25°C) is +2.8. A chemist prepared a mixture of l-alanine and its enantiomer, and 3.50 g of the mixture was dissolved in 10.0 mL of water. This solution was then placed in a sample cell with a pathlength of
> The specific rotation of (S)-2-butanol is +13.5. If 1.00 g of its enantiomer is dissolved in 10.0 mL of ethanol and placed in a sample cell with a length of 1.00 dm, what observed rotation do you expect?
> Predict the value for the specific rotation of the following compound. Explain your answer. он HO.
> You are given a solution containing a pair of enantiomers (A and B). Careful measurements show that the solution contains 98% A and 2% B. What is the ee of this solution?
> Identify the configuration of each chiral center in the following compounds: CI Et OH NH, Me (b) (c) HO H F Et (d) CI (e) Me H- OH Cl HO H (f) Me (g)
> Draw the enantiomer for each of the following compounds: OH (а) (b) (с) H- -OH он он ÇI OH H -OH но (d) ČH, (е) Me Me
> Identify the number of stereoisomers expected for each of the following: Me он CI он Me (а) OH (b) Он (с) (d) (е) Но OH (f)
> Predict the major product for each of the following reactions. OH он ? ? HBr conc. H2SO4 heat (a) (b)
> For each of the following pairs of compounds, determine the relationship between the two compounds: Br (a) (b) Br (c) (d) он он (e) (f) (g) он он (h)
> Carbon is not the only element that can function as a chiral center. In Problem 5.6 we saw an example in which a phosphorus atom is a chiral center. In such a case, the lone pair is always assigned the fourth priority. Using this information, assign the
> Assign the configuration of the chiral center in the following compound:
> Paclitaxel (marketed under the trade name Taxol) is found in the bark of the Pacific yew tree, Taxus brevifolia, and is used in the treatment of cancer: a. Draw the enantiomer of paclitaxel. b. How many chiral centers does this compound possess? он
> Atropine, extracted from the plant Atropa belladonna, has been used in the treatment of bradycardia (low heart rate) and cardiac arrest. Draw the enantiomer of atropine: CH -OH
> Atorvastatin is sold under the trade name Lipitor and is used for lowering cholesterol. Annual global sales of this compound exceed $13 billion. Assign a configuration to each chiral center in atorvastatin: он он но. F
> Bogorol A is a natural product with the potential to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Shown below is an intermediate that was used in a synthesis of bogorol A. Assign the configuration of the alkene unit as either E or Z. R. N. OMe Intermediate i
> For each of the following alkenes, assign the configuration of the double bond as either E or Z: (a) (b) CI (c) (d)
> Determine whether each of the following allenes is chiral or achiral: H3C H3C CC=C CH, *CH3 C=C=c "CH,CH3 C=C=C CH3 (a) H (b) (c) (d) CH3
> Protease inhibitors are a class of anti-viral drugs that have had success in treating HIV/AIDS. The following molecules were synthesized as potential HIV protease inhibitors. Compound 1 was found to be an effective protease inhibitor, while compound 2 wa
> Predict the major and minor products for each of the following reactions. OTs NaOE OTs ? ? NaOH (a) (b) LOTS OTs ? NaH ? NASH (c) (d) CH3 1) TSCI, py 2 BUOK ? 1) TsCI, py 2) NaOE! ? HO, (e) (f)
> Identify the configuration of the chiral center in each of the following compounds: OH CH,OH CH;OH H- (а) -NH2 но но -H Br- CH,OH (b) CH3 (с) ČH,CH, (d) CH3
> A racemic mixture with the constitution shown below was isolated from the Maytenus apurimacensis plant that is used in South American folk medicine. In an effort to find another source of these compounds, all of the stereoisomers with this constitution h
> Draw all possible stereoisomers for each of the following compounds. Each possible stereoisomer should be drawn only once: он OH но OH (a) (b) (c) (d) (е)
> Each of the following molecules has one plane of symmetry. Find the plane of symmetry in each case: (Hint: A plane of symmetry can slice atoms in half.) Me (a) Mе Br (b) HO он Me (с) Me (d) (е) (f) CI
> In the previous problem, one object has three planes of symmetry. Identify that object.
> For each of the following objects determine whether or not it possesses a plane of symmetry: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)
> In the field of chemical research, one area of interest is the study of how variations in structure, including stereochemical variations, affect the biological activity of natural products. (−)-Lariciresinol, shown on the right, is a na
> Identify whether each of the following pairs of compounds are enantiomers or diastereomers: (a) (Ь) он он он он (c) CI (d) (е)
> Synthetic chemists often employ enzymes to conduct asymmetric syntheses that favor the production of one enantiomer over another. Baker’s yeast was used to convert the diketone shown into alcohol 1, with an ee of 84%. The specific rotat
> The specific rotation of vitamin B7 in water (at 22°C) is +92. A chemist prepared a mixture of vitamin B7 and its enantiomer, and this mixture had a specific rotation of +85. Calculate the % ee of this mixture.
> An unknown compound with the molecular formula C6H13Cl is treated with sodium ethoxide to produce 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene as the major product. Identify the structure of the unknown compound.
> A common method for confirming the proposed structure and stereochemistry of a natural product is to synthesize the proposed structure and then compare its properties with those of the natural product. This technique was used to verify the structure of c
> The specific rotation of ephedrine in ethanol (at 20°C) is −6.3. A chemist prepared a mixture of ephedrine and its enantiomer, and this mixture had a specific rotation of −6.0. Calculate the % ee of this mixture.
> The specific rotation of l-dopa in water (at 15°C) is −39.5. A chemist prepared a mixture of l-dopa and its enantiomer, and this mixture had a specific rotation of −37. Calculate the % ee of this mixture.
> Levetiracetam is used for the treatment of seizures in patients with epilepsy. For patients who have a hard time swallowing the needed pills twice daily, relief is in sight now that the FDA has granted approval for the use of rapidly dissolving, porous t
> When 1.30 g of menthol is dissolved in 5.00 mL of ether and placed in a sample cell 10.0 cm in length, the observed rotation at 20°C (using the D line of sodium) is +0.57°. Calculate the specific rotation of menthol.
> When 0.095 g of cholesterol is dissolved in 1.00 mL of ether and placed in a sample cell 10.0 cm in length, the observed rotation at 20°C (using the D line of sodium) is −2.99°. Calculate the specific rotation of cholesterol.
> When 0.575 g of monosodium glutamate (MSG) is dissolved in 10.0 mL of water and placed in a sample cell 10.0 cm in length, the observed rotation at 20°C (using the D line of sodium) is +1.47°. Calculate the specific rotation of MSG.
> In Chapter 24, we will see that amino acids (like the ones shown below) can be linked together to give short chains, called peptides, or longer chains (≈50–2000 amino acids linked together) called proteins. High-protei
> Each of the following compounds possesses carbon atoms that are chiral centers. Locate each of these chiral centers and identify the configuration of each one: он H Br .H он (a) (b) CI Br Ephedrine A bronchodilator and decongestant obtained from the
> Ixabepilone is a cytotoxic compound approved by the FDA in 2007 for the treatment of advanced breast cancer. Bristol-Myers Squibb is marketing this drug under the trade name Ixempra. Draw the enantiomer of this compound: OH .N. H OH Ixabepilone
> Compound A and compound B are constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C4H9Cl. Treatment of compound A with sodium methoxide gives trans-2-butene as the major product, while treatment of compound B with sodium methoxide gives a different disubst
> Do you expect the following compound to be chiral? Explain your answer (consider whether this compound is superimposable on its mirror image).
> Draw all constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C4H9Br and identify the isomer(s) that possess chiral centers.
> Identify all chiral centers in each of the following compounds: OH Но но. но OH Ascorbic acid (a) (vitamin C) (b) Vitamin Da OH но OH Mestranol Fexofenadine OH (c) An oral contraceptive (d) A nonsedating antihistamine
> Compound X and compound Y are constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C5H10. Compound X possesses a carbon-carbon double bond in the trans configuration, while compound Y possesses a carbon-carbon double bond that is not stereoisomeric: a. Ide
> Identify the number of stereoisomers that are possible for a compound with the following constitution: H2C=CHCH2CH2CH2CH=CH2.
> In the following compound, identify each C=C unit as cis, trans, or not stereoisomeric.
> The pKa of the most acidic CH2 group in each of the following compounds was measured in DMSO as solvent. Given the data above, determine which of the following two compounds (5 or 6) is more acidic by comparing the stability of the corresponding conjuga
> Crude extracts from the ginkgo tree, Ginkgo biloba, have been used for centuries to alleviate symptoms associated with asthma. There are four principal components of Ginkgo extracts, called ginkgolide A B, D, and M. During E. J. Corey’s
> Phakellin (3), a natural product isolated from marine organisms, has been studied for its potential use as an antibiotic agent. During studies aimed at developing a strategy for the synthesis of phakellin and its derivatives, compound 1 was investigated
> Aspernomine, a natural product isolated from the fungus Aspergillus nomius, was found to be an antiinsectan (it protects against predation by insects). a. Two of the six-membered rings are represented in chair conformations. Is the connection between th
> Compound A and compound B are constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C3H7Cl. When compound A is treated with sodium methoxide, a substitution reaction predominates. When compound B is treated with sodium methoxide, an elimination reaction pred
> The structural unit below has been incorporated into a synthetic polymer designed to mimic the skeletal muscle protein titin. In its most stable conformation (shown), it forms one intramolecular hydrogen bond and four intermolecular hydrogen bonds to an
> Consider the structures of cis-decalin and trans-decalin: a. Which of these compounds would you expect to be more stable? b. One of these two compounds is incapable of ring flipping. Identify it and explain your choice. H H. H cis-Decalin trans-Dec
> Consider the following tetra-substituted cyclohexane: a. Draw both chair conformations of this compound. b. Determine which conformation is more stable. c. At equilibrium, would you expect the compound to spend more than 95% of its time in the more st
> Determine whether the following compounds are constitutional isomers: H H. H3C CH CH H3C CH3 H
> Compare the three staggered conformations of ethylene glycol. The anti conformation of ethylene glycol is not the lowest energy conformation. The other two staggered conformations are actually lower in energy than the anti conformation. Suggest an explan
> Consider the structures of cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane and trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane: a. Which compound would you expect to be more stable? Explain your choice. b. Predict the difference in energy between these two compounds. A A
> For each pair of compounds below, determine whether they are identical compounds, constitutional isomers, or stereoisomers: CH,CH, CH CH, H. H,C- CH,CH, H CH,CH, (b) H (a) (c) (d) CH, CH, H H CH, CH, H CH, CH, (F) H CH, H CH, H (e) H CH, H. H H (g)
> trans-1,3-Dichlorocyclobutane has a measurable dipole moment. Explain why the individual dipole moments of the C−Cl bonds do not cancel each other to produce a zero net dipole moment. CI- trans-1,3-Dichlorocyclobutane
> Derivatives of griselimycin, a natural product isolated in the 1960s, are being investigated for the treatment of tuberculosis. For each of the highlighted substituents in the griselimycin derivative shown below, indicate the systematic name as well as t
> There are 18 constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C8H18. Without drawing all 18 isomers, determine how many of the isomers will have a parent name of heptane.
> Identify the major and minor product(s) that are expected for each of the following reactions. Br Br ? ? Naci NaOH DMSO (a) (b) Br ? I-BUOK DBN (c) (d) ? ? 1-BUOK NASH (e) (f) Br ? Br ? NaOH NaOE (g) (h) Br ? ? EIOH NaOH Heat (i) Br Br ? NaOMe NaOMe
> Below is the numbered skeleton of trans-decalin: Identify whether each of the following substituents would be in an equatorial position or an axial position: a. A group at the C-2 position, pointing UP b. A group at the C-3 position, pointing DOWN c.
> myo-Inositol is a polyol (a compound containing many OH groups) that serves as the structural basis for a number of secondary messengers in eukaryotic cells. Draw the more stable chair conformation of myo-inositol. OH но HO он HO,
> Consider the following two conformations of 2,3-dimethylbutane. For each of these conformations, use Table 4.6 to determine the total energy cost associated with all torsional strain and steric strain. CH, H- CH, H,C H CH3 CH H CH3 (a) (b) HCH, I I
> Rank the following conformations in order of increasing energy: Br Br Br Br Br H H Br H- H. Br H- H H. H YH HH Br
> Sketch an energy diagram showing a conformational analysis of 2,2,3,3-tetramethylbutane. Use Table 4.6 to determine the energy difference between staggered and eclipsed conformations of this compound.
> Glucose (a sugar) is produced by photosynthesis and is used by cells to store energy. Draw the most stable conformation of glucose: OH но, O. HO OH OH Glucose
> Draw a Newman projection of the following compound as viewed from the angle indicated: CI Br CI Br
> For each of the following pairs of compounds, determine which compound is more stable (you may find it helpful to draw out the chair conformations): (b) (c) (d)
> Draw both chair conformations for each of the following compounds. In each case, identify the more stable chair conformation: a. Methylcyclohexane b. trans-1,2-Diisopropylcyclohexane c. cis-1,3-Diisopropylcyclohexane d. trans-1,4-Diisopropylcyclohexa
> Menthol, isolated from various mint oils, is used in the treatment of minor throat irritation. Draw both chair conformations of menthol and indicate which conformation is lower in energy. он Menthol
> Identify whether each of the following reactions is expected to exhibit a primary isotope effect if (CD3)3CBr is used instead of (CH3)3CBr. Explain your reasoning in each case. Br Br, NaCEt EIOH (a) (b)
> The barrier to rotation of bromoethane is 15 kJ/mol. Based on this information, determine the energy cost associated with the eclipsing interaction between a bromine atom and a hydrogen atom.
> Assign IUPAC names for each of the following compounds: H H H- H. H ČH, H. H. (a) (b) H H CH3 CH, H- H- H- H- (c) (d) CH3
> Draw a bond-line structure for each of the following compounds: CH, H H CH, CH,CH3 CH - H. CH CH,CH3 H H- (a) (b) CH3 (c) H H
> In the following compound, identify the number of hydrogen atoms that occupy axial positions as well as the number of hydrogen atoms that occupy equatorial positions:
> Draw a relative energy diagram showing a conformational analysis of 1,2-dichloroethane. Clearly label all staggered conformations and all eclipsed conformations with the corresponding Newman projections.
> For each of the following pairs of compounds, identify the compound that would have the higher heat of combustion: (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Draw the ring flip for each of the following compounds: CI он -OH (a) CI (b) OH (c) CI
> What are the relative energy levels of the three staggered conformations of 2,3-dimethylbutane when looking down the C2−C3 bond?
> Sketch an energy diagram that shows a conformational analysis of 2,2-dimethylpropane. Does the shape of this energy diagram more closely resemble the shape of the energy diagram for ethane or for butane?
> Draw each of the following compounds: a. 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane b. 1,2,3,4-Tetramethylcycloheptane c. 2,2,4,4-Tetraethylbicyclo[1.1.0]butane
> For each pair of compounds below, identify which one is expected to undergo elimination more rapidly when treated with a strong base. Br CD Br Br. H Br D D D (a) D.C (b) D;C CD3 (c) D
> Identify which of the following compounds is expected to have the larger heat of combustion:
> Use a Newman projection to draw the most stable conformation of 3-methylpentane, looking down the C2−C3 bond.
> For each of the following pairs of compounds, identify whether the compounds are constitutional isomers or different representations of the same compound: (a) (b) (c)
> Provide a systematic name for each of the following compounds: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (g) (h) (1)
> Draw Haworth projections for cis-1,3-di-tert-butylcyclohexane and trans-1,3-di-tert-butylcyclohexane. One of these compounds exists in a chair conformation, while the other exists primarily in a twist boat conformation. Offer an explanation.
> Draw Haworth projections for cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane and trans-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane. Then for each compound, draw the two chair conformations. Use these conformations to determine whether the cis isomer or the trans isomer is more stable.

