Question: For the hydraulic lift shown in Fig.
For the hydraulic lift shown in Fig. 12.7, what must be the ratio of the diameter of the vessel at the car to the diameter of the vessel where the force F1 is applied so that a 1520-kg car can be lifted with a force F1 of just 125 N?
Fig. 12.7:
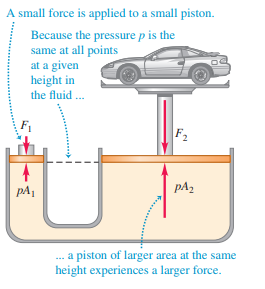
Transcribed Image Text:
A small force is applied to a small piston. Because the pressure p is the same at all points at a given height in the fluid .. F1 F2 pA1 pA2 a piston of larger area at the same height experiences a larger force.
> A cord is wrapped around the rim of a solid uniform wheel 0.250 m in radius and of mass 9.20 kg. A steady horizontal pull of 40.0 N to the right is exerted on the cord, pulling it off tangentially from the wheel. The wheel is mounted on frictionless bear
> The flywheel of an engine has moment of inertia 1.60 kg.m2 about its rotation axis. What constant torque is required to bring it up to an angular speed of 400 rev/min in 8.00 s, starting from rest?
> A uniform disk with mass 40.0 kg and radius 0.200 m is pivoted at its center about a horizontal, frictionless axle that is stationary. The disk is initially at rest, and then a constant force F = 30.0 N is applied tangent to the rim of the disk. (a) What
> A machinist is using a wrench to loosen a nut. The wrench is 25.0 cm long, and he exerts a 17.0-N force at the end of the handle at 37° with the handle (Fig. E10.7). (a) What torque does the machinist exert about the center of the nut? (b) Wha
> A ball is rolling along at speed v without slipping on a horizontal surface when it comes to a hill that rises at a constant angle above the horizontal. In which case will it go higher up the hill: if the hill has enough friction to prevent slipping or i
> A metal bar is in the x y-plane with one end of the bar at the origin. A force
> One force acting on a machine part is F =(-5.00 N)
> Three forces are applied to a wheel of radius 0.350 m, as shown in Fig. E10.4. One force is perpendicular to the rim, one is tangent to it, and the other one makes a 40.0° angle with the radius. What is the net torque on the wheel due to these
> A square metal plate 0.180 m on each side is pivoted about an axis through point O at its center and perpendicular to the plate (Fig. E10.3). Calculate the net torque about this axis due to the three forces shown in the figure if the magnitudes of the fo
> Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in Fig. E10.2. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page. Fig. E10.2: Figure E10.2 F2 = 12.0 N F, = 8.00 N 30.0° K-2.00 mK 3.00 m
> Calculate the torque (magnitude and direction) about point O due to the force
> Scientists have found evidence that Mars may once have had an ocean 0.500 km deep. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 3.71 m/s2. (a) What would be the gauge pressure at the bottom of such an ocean, assuming it was freshwater? (b) To what depth wo
> Black smokers are hot volcanic vents that emit smoke deep in the ocean floor. Many of them teem with exotic creatures, and some biologists think that life on earth may have begun around such vents. The vents range in depth from about 1500 m to 3200 m bel
> A hollow cylindrical copper pipe is 1.50 m long and has an outside diameter of 3.50 cm and an inside diameter of 2.50 cm. How much does it weigh?
> (a) What is the average density of the sun? (b) What is the average density of a neutron star that has the same mass as the sun but a radius of only 20.0 km?
> A hoop, a uniform solid cylinder, a spherical shell, and a uniform solid sphere are released from rest at the top of an incline. What is the order in which they arrive at the bottom of the incline? Does it matter whether or not the masses and radii of th
> A pressure difference of 6.00 × 104 Pa is required to maintain a volume flow rate of 0.800 m3/s for a viscous fluid flowing through a section of cylindrical pipe that has radius 0.210 m. What pressure difference is required to maintain the same volume fl
> A uniform lead sphere and a uniform aluminum sphere have the same mass. What is the ratio of the radius of the aluminum sphere to the radius of the lead sphere?
> Viscous blood is flowing through an artery partially clogged by cholesterol. A surgeon wants to remove enough of the cholesterol to double the flow rate of blood through this artery. If the original diameter of the artery is D, what should be the new dia
> A soft drink (mostly water) flows in a pipe at a beverage plant with a mass flow rate that would fill 220 0.355-L cans per minute. At point 2 in the pipe, the gauge pressure is 152 kPa and the cross-sectional area is 8.00 cm2. At point 1, 1.35 m above po
> A golf course sprinkler system discharges water from a horizontal pipe at the rate of 7200 cm3/s. At one point in the pipe, where the radius is 4.00 cm, the water’s absolute pressure is 2.40 × 105 Pa. At a second point in the pipe, the water passes throu
> At one point in a pipeline the water’s speed is 3.00 m/s and the gauge pressure is 5.00 × 104 Pa. Find the gauge pressure at a second point in the line, 11.0 m lower than the first, if the pipe diameter at the second point is twice that at the first.
> At a certain point in a horizontal pipeline, the water’s speed is 2.50 m/s and the gauge pressure is 1.80 × 104 Pa. Find the gauge pressure at a second point in the line if the cross-sectional area at the second point is twice that at the first.
> A small circular hole 6.00 mm in diameter is cut in the side of a large water tank, 14.0 m below the water level in the tank. The top of the tank is open to the air. Find (a) the speed of efflux of the water and (b) the volume discharged per second.
> What gauge pressure is required in the city water mains for a stream from a fire hose connected to the mains to reach a vertical height of 15.0 m? (Assume that the mains have a much larger diameter than the fire hose.)
> A medical technician is trying to determine what percentage of a patient’s artery is blocked by plaque. To do this, she measures the blood pressure just before the region of blockage and finds that it is 1.20 × 104 Pa, while in the region of blockage it
> A wheel is rolling without slipping on a horizontal surface. In an inertial frame of reference in which the surface is at rest, is there any point on the wheel that has a velocity that is purely vertical? Is there any point that has a horizontal velocity
> A sealed tank containing seawater to a height of 11.0 m also contains air above the water at a gauge pressure of 3.00 atm. Water flows out from the bottom through a small hole. How fast is this water moving?
> You need to extend a 2.50-inch-diameter pipe, but you have only a 1.00-inch-diameter pipe on hand. You make a fitting to connect these pipes end to end. If the water is flowing at 6.00 cm/s in the wide pipe, how fast will it be flowing through the narrow
> You win the lottery and decide to impress your friends by exhibiting a million-dollar cube of gold. At the time, gold is selling for $1282 per troy ounce, and 1.0000 troy ounce equals 31.1035 g. How tall would your million-dollar cube be?
> Water is flowing in a pipe with a circular cross section but with varying cross-sectional area, and at all points the water completely fills the pipe. (a) At one point in the pipe the radius is 0.150 m. What is the speed of the water at this point if wat
> Water is flowing in a pipe with a varying cross-sectional area, and at all points the water completely fills the pipe. At point 1 the cross-sectional area of the pipe is 0.070 m2, and the magnitude of the fluid velocity is 3.50 m/s. (a) What is the fluid
> A shower head has 20 circular openings, each with radius 1.0 mm. The shower head is connected to a pipe with radius 0.80 cm. If the speed of water in the pipe is 3.0 m/s, what is its speed as it exits the shower-head openings?
> Water runs into a fountain, filling all the pipes, at a steady rate of 0.750 m3/s. (a) How fast will it shoot out of a hole 4.50 cm in diameter? (b) At what speed will it shoot out if the diameter of the hole is three times as large?
> A rock is suspended by a light string. When the rock is in air, the tension in the string is 39.2 N. When the rock is totally immersed in water, the tension is 28.4 N. When the rock is totally immersed in an unknown liquid, the tension is 21.5 N. What is
> A solid aluminum ingot weighs 89 N in air. (a) What is its volume? (b) The ingot is suspended from a rope and totally immersed in water. What is the tension in the rope (the apparent weight of the ingot in water)?
> A cubical block of wood, 10.0 cm on a side, floats at the interface between oil and water with its lower surface 1.50 cm below the interface (Fig. E12.33). The density of the oil is 790 kg/m3. (a) What is the gauge pressure at the upper face of the block
> A certain solid uniform ball reaches a maximum height h0 when it rolls up a hill without slipping. What maximum height (in terms of h0) will it reach if you (a) double its diameter, (b) double its mass, (c) double both its diameter and mass, (d) double i
> A hollow plastic sphere is held below the surface of a freshwater lake by a cord anchored to the bottom of the lake. The sphere has a volume of 0.650 m3 and the tension in the cord is 1120 N. (a) Calculate the buoyant force exerted by the water on the sp
> A rock with density 1200 kg/m3 is suspended from the lower end of a light string. When the rock is in air, the tension in the string is 28.0 N. What is the tension in the string when the rock is totally immersed in a liquid with density 750 kg/m3?
> You are preparing some apparatus for a visit to a newly discovered planet Caasi having oceans of glycerine and a surface acceleration due to gravity of 5.40 m/s2. If your apparatus floats in the oceans on earth with 25.0% of its volume submerged, what pe
> You purchase a rectangular piece of metal that has dimensions 5.0 × 15.0 × 30.0 mm and mass 0.0158 kg. The seller tells you that the metal is gold. To check this, you compute the average density of the piece. What value do you get? Were you cheated?
> An ore sample weighs 17.50 N in air. When the sample is suspended by a light cord and totally immersed in water, the tension in the cord is 11.20 N. Find the total volume and the density of the sample.
> A slab of ice floats on a freshwater lake. What minimum volume must the slab have for a 65.0-kg woman to be able to stand on it without getting her feet wet?
> A 950-kg cylindrical can buoy floats vertically in seawater. The diameter of the buoy is 0.900 m. Calculate the additional distance the buoy will sink when an 80.0-kg man stands on top of it.
> A rock has mass 1.80 kg. When the rock is suspended from the lower end of a string and totally immersed in water, the tension in the string is 12.8 N. What is the smallest density of a liquid in which the rock will float?
> The surface pressure on Venus is 92 atm, and the acceleration due to gravity there is 0.894g. In a future exploratory mission, an upright cylindrical tank of benzene is sealed at the top but still pressurized at 92 atm just above the benzene. The tank ha
> The piston of a hydraulic automobile lift is 0.30 m in diameter. What gauge pressure, in pascals, is required to lift a car with a mass of 1200 kg? Also express this pressure in atmospheres.
> Why must a water skier moving with constant velocity lean backward? What determines how far back she must lean? Draw a free-body diagram for the water skier to justify your answers.
> A closed container is partially filled with water. Initially, the air above the water is at atmospheric pressure (1.01 × 105 Pa) and the gauge pressure at the bottom of the water is 2500 Pa. Then additional air is pumped in, increasing the pressure of th
> A cylindrical disk of wood weighing 45.0 N and having a diameter of 30.0 cm floats on a cylinder of oil of density 0.850 g /cm3 (Fig. E12.21). The cylinder of oil is 75.0 cm deep and has a diameter the same as that of the wood. (a) What is the gauge pres
> A tall cylinder with a cross-sectional area 12.0 cm2 is partially filled with mercury; the surface of the mercury is 8.00 cm above the bottom of the cylinder. Water is slowly poured in on top of the mercury, and the two fluids don’t mix. What volume of w
> A cube 5.0 cm on each side is made of a metal alloy. After you drill a cylindrical hole 2.0 cm in diameter all the way through and perpendicular to one face, you find that the cube weighs 6.30 N. (a) What is the density of this metal? (b) What did the cu
> An electrical short cuts off all power to a submersible diving vehicle when it is 30 m below the surface of the ocean. The crew must push out a hatch of area 0.75 m2 and weight 300 N on the bottom to escape. If the pressure inside is 1.0 atm, what downwa
> The lower end of a long plastic straw is immersed below the surface of the water in a plastic cup. An average person sucking on the upper end of the straw can pull water into the straw to a vertical height of 1.1 m above the surface of the water in the c
> The liquid in the open-tube manometer in Fig. 12.8a is mercury, y1 = 3.00 cm, and y2 = 7.00 cm. Atmospheric pressure is 980 millibars. What is (a) the absolute pressure at the bottom of the U-shaped tube; (b) the absolute pressure in the open tube at a d
> If the force on the tympanic membrane (eardrum) increases by about 1.5 N above the force from atmospheric pressure, the membrane can be damaged. When you go scuba diving in the ocean, below what depth could damage to your eardrum start to occur? The eard
> You are designing a diving bell to withstand the pressure of seawater at a depth of 250 m. (a) What is the gauge pressure at this depth? (You can ignore changes in the density of the water with depth.) (b) At this depth, what is the net force due to the
> Two identical masses are attached to frictionless pulleys by very light strings wrapped around the rim of the pulley and are released from rest. Both pulleys have the same mass and same diameter, but one is solid and the other is a hoop. As the masses fa
> Does a rigid object in uniform rotation about a fixed axis satisfy the first and second conditions for equilibrium? Why? Does it then follow that every particle in this object is in equilibrium? Explain.
> What is the momentum of one drop of water immediately after it leaves the fish’s mouth? (a) 7.5 × 10-4 kg . m/s; (b) 1.5 × 10-4 kg.m/s; (c) 7.5 × 10-3 kg.m/s; (d) 1.5 × 10-3 kg.m/s.
> A thin, light wire is wrapped around the rim of a wheel as shown in Fig. E9.45. The wheel rotates about a stationary horizontal axle that passes through the center of the wheel. The wheel has radius 0.180 m and moment of inertia for rotation about the a
> The pulley in Fig. P9.76 has radius 0.160 m and moment of inertia 0.380 kg . m2. The rope does not slip on the pulley rim. Use energy methods to calculate the speed of the 4.00-kg block just before it strikes the floor. Fig. P9.76: Figure P9.76 4.0
> A physics student of mass 43.0 kg is standing at the edge of the flat roof of a building, 12.0 m above the sidewalk. An unfriendly dog is running across the roof toward her. Next to her is a large wheel mounted on a horizontal axle at its center. The whe
> Starting at t = 0, a horizontal net force
> A radio-controlled model airplane has a momentum given by [(-0.75 kg. m/s3)t2 +(3.0 kg. m/s)]
> (a) Derive Eq. (9.12) by combining Eqs. (9.7) and (9.11) to eliminate t. (b) The angular velocity of an airplane propeller increases from 12.0 rad/s to 16.0 rad/s while turning through 7.00 rad. What is the angular acceleration in rad/s2?
> The rotating blade of a blender turns with constant angular acceleration 1.50 rad/s2. (a) How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 36.0 rad/s, starting from rest? (b) Through how many revolutions does the blade turn in this time interva
> An electric fan is turned off, and its angular velocity decreases uniformly from 500 rev/min to 200 rev/min in 4.00 s. (a) Find the angular acceleration in rev/s2 and the number of revolutions made by the motor in the 4.00-s interval. (b) How many more s
> (a) What angle in radians is subtended by an arc 1.50 m long on the circumference of a circle of radius 2.50 m? What is this angle in degrees? (b) An arc 14.0 cm long on the circumference of a circle subtends an angle of 128°. What is the radius of the c
> A 0.160-kg hockey puck is moving on an icy, frictionless, horizontal surface. At t = 0, the puck is moving to the right at 3.00 m/s. (a) Calculate the velocity of the puck (magnitude and direction) after a force of 25.0 N directed to the right has been a
> A baseball has mass 0.145 kg. (a) If the velocity of a pitched ball has a magnitude of 45.0 m/s and the batted ball’s velocity is 55.0 m>s in the opposite direction, find the magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball and of the impulse applied to i
> A 0.0450-kg golf ball initially at rest is given a speed of 25.0 m/s when a club strikes it. If the club and ball are in contact for 2.00 ms, what average force acts on the ball? Is the effect of the ball’s weight during the time of contact significant?
> The mass of a regulation tennis ball is 57 g (although it can vary slightly), and tests have shown that the ball is in contact with the tennis racket for 30 ms. (This number can also vary, depending on the racket and swing.) We shall assume a 30.0-ms con
> One 110-kg football lineman is running to the right at 2.75 m/s while another 125-kg lineman is running directly toward him at 2.60 m/s. What are (a) the magnitude and direction of the net momentum of these two athletes, and (b) their total kinetic energ
> Two vehicles are approaching an intersection. One is a 2500-kg pickup traveling at 14.0 m/s from east to west (the -x-direction), and the other is a 1500-kg sedan going from south to north (the +y-direction) at 23.0 m/s. (a) Find the x- and y-components
> You are testing a new amusement park roller coaster with an empty car of mass 120 kg. One part of the track is a vertical loop with radius 12.0 m. At the bottom of the loop (point A) the car has speed 25.0 m/s, and at the top of the loop (point B) it has
> A 1050-kg sports car is moving westbound at 15.0 m/s on a level road when it collides with a 6320-kg truck driving east on the same road at 10.0 m/s. The two vehicles remain locked together after the collision. (a) What is the velocity (magnitude and dir
> In July 2005, NASA’s “Deep Impact” mission crashed a 372-kg probe directly onto the surface of the comet Tempel 1, hitting the surface at 37,000 km>h. The original speed of the comet at that time was about 40,000 km>h, and its mass was estimated to be
> Two fun-loving otters are sliding toward each other on a muddy (and hence frictionless) horizontal surface. One of them, of mass 7.50 kg, is sliding to the left at 5.00 m/s, while the other, of mass 5.75 kg, is slipping to the right at 6.00 m/s. They hol
> A 15.0-kg fish swimming at 1.10 m/s suddenly gobbles up a 4.50-kg fish that is initially stationary. Ignore any drag effects of the water. (a) Find the speed of the large fish just after it eats the small one. (b) How much mechanical energy was dissipate
> Two skaters collide and grab on to each other on frictionless ice. One of them, of mass 70.0 kg, is moving to the right at 4.00 m/s, while the other, of mass 65.0 kg, is moving to the left at 2.50 m/s. What are the magnitude and direction of the velocity
> Two asteroids of equal mass in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter collide with a glancing blow. Asteroid A, which was initially traveling at 40.0 m/s, is deflected 30.0° from its original direction, while asteroid B, which was initiall
> An astronaut in space cannot use a conventional means, such as a scale or balance, to determine the mass of an object. But she does have devices to measure distance and time accurately. She knows her own mass is 78.4 kg, but she is unsure of the mass of
> Objects A, B, and C are moving as shown in Fig. E8.3. Find the x- and y-components of the net momentum of the particles if we define the system to consist of (a) A and C, (b) B and C, (c) all three objects. Fig. E8.3: Figure E8.3 10.0 m/s A 5.0 kg
> You (mass 55 kg) are riding a frictionless skateboard (mass 5.0 kg) in a straight line at a speed of 4.5 m/s. A friend standing on a balcony above you drops a 2.5-kg sack of flour straight down into your arms. (a) What is your new speed while you hold th
> You are standing on a large sheet of frictionless ice and holding a large rock. In order to get off the ice, you throw the rock so it has velocity 12.0 m/s relative to the earth at an angle of 35.0° above the horizontal. If your mass is 70.0 kg and the r
> A 25.0-kg child plays on a swing having support ropes that are 2.20 m long. Her brother pulls her back until the ropes are 42.0° from the vertical and releases her from rest. (a) What is her potential energy just as she is released, compared with the pot
> Two ice skaters, Daniel (mass 65.0 kg) and Rebecca (mass 45.0 kg), are practicing. Daniel stops to tie his shoelace and, while at rest, is struck by Rebecca, who is moving at 13.0 m/s before she collides with him. After the collision, Rebecca has a veloc
> An atomic nucleus suddenly bursts apart (fissions) into two pieces. Piece A, of mass mA, travels off to the left with speed vA. Piece B, of mass mB, travels off to the right with speed vB. (a) Use conservation of momentum to solve for vB in terms of mA,
> A hunter on a frozen, essentially frictionless pond uses a rifle that shoots 4.20-g bullets at 965 m/s. The mass of the hunter (including his gun) is 72.5 kg, and the hunter holds tight to the gun after firing it. Find the recoil velocity of the hunter i
> Block A in Fig. E8.24 has mass 1.00 kg, and block B has mass 3.00 kg. The blocks are forced together, compressing a spring S between them; then the system is released from rest on a level, frictionless surface. The spring, which has negligible mass, is n
> Two identical 0.900-kg masses are pressed against opposite ends of a light spring of force constant 1.75 N/cm, compressing the spring by 20.0 cm from its normal length. Find the speed of each mass when it has moved free of the spring on a frictionless, h
> When cars are equipped with flexible bumpers, they will bounce off each other during low-speed collisions, thus causing less damage. In one such accident, a 1750-kg car traveling to the right at 1.50 m/s collides with a 1450-kg car going to the left at 1
> On a frictionless, horizontal air table, puck A (with mass 0.250 kg) is moving toward puck B (with mass 0.350 kg), which is initially at rest. After the collision, puck A has a velocity of 0.120 m/s to the left, and puck B has a velocity of 0.650 m/s to
> You are standing on a sheet of ice that covers the football stadium parking lot in Buffalo; there is negligible friction between your feet and the ice. A friend throws you a 0.600-kg ball that is traveling horizontally at 10.0 m/s. Your mass is 70.0 kg.
> In a certain track and field event, the shotput has a mass of 7.30 kg and is released with a speed of 15.0 m/s at 40.0° above the horizontal over a competitor’s straight left leg. What are the initial horizontal and vertical components of the momentum of
> Squids and octopuses propel themselves by expelling water. They do this by keeping water in a cavity and then suddenly contracting the cavity to force out the water through an opening. A 6.50-kg squid (including the water in the cavity) at rest suddenly
> A small rock with mass 0.20 kg is released from rest at point A, which is at the top edge of a large, hemispherical bowl with radius R = 0.50 m (Fig. E7.9). Assume that the size of the rock is small compared to R, so that the rock can be treated as a par
> Two figure skaters, one weighing 625 N and the other 725 N, push off against each other on frictionless ice. (a) If the heavier skater travels at 1.50 m/s, how fast will the lighter one travel? (b) How much kinetic energy is “created” during the skaters’

