Question: From the information in Exercises 4-4A
From the information in Exercises 4-4A and 4-5A,
Exercises 4-4A and 4-5A:
Diane Bernick has opened Bernick’s Consulting. Journalize the following transactions that occurred during January of the current year. Use the following journal pages: January 1–10, page 1, and January 11–29, page 2. Use the following chart of accounts:
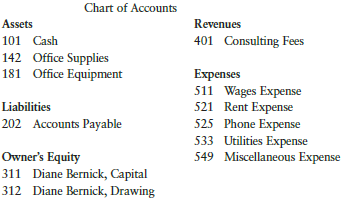
Jan. 1 Bernick invested cash in the business, $12,000.
2 Paid office rent, $750.
3 Purchased office equipment on account, $1,300.
5 Received cash for services rendered, $950.
8 Paid phone bill, $85.
10 Paid for a magazine subscription (miscellaneous expense), $20.
11 Purchased office supplies on account, $250.
15 Made a payment on account (see Jan. 3 transaction), $200.
18 Paid part-time employee, $600.
21 Received cash for services rendered, $800.
25 Paid utilities bill, $105.
27 Bernick withdrew cash for personal use, $400.
29 Paid part-time employee, $600.
Set up general ledger accounts using the chart of accounts provided in Exercise 4-4A.
Exercise 4-4A:
Diane Bernick has opened Bernick’s Consulting. Journalize the following transactions that occurred during January of the current year. Use the following journal pages: January 1–10, page 1, and January 11–29, page 2. Use the following chart of accounts:
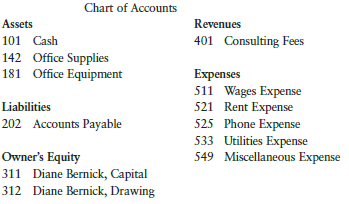
Jan. 1 Bernick invested cash in the business, $12,000.
2 Paid office rent, $750.
3 Purchased office equipment on account, $1,300.
5 Received cash for services rendered, $950.
8 Paid phone bill, $85.
10 Paid for a magazine subscription (miscellaneous expense), $20.
11 Purchased office supplies on account, $250.
15 Made a payment on account (see Jan. 3 transaction), $200.
18 Paid part-time employee, $600.
21 Received cash for services rendered, $800.
25 Paid utilities bill, $105.
27 Bernick withdrew cash for personal use, $400.
29 Paid part-time employee, $600.
Post the transactions from Exercise 4-4A to the general ledger accounts and prepare a trial balance.
Prepare an income statement, a statement of owner’s equity, and a balance sheet.
Transcribed Image Text:
Chart of Accounts Assets Revenues 101 Cash 401 Consulting Fees 142 Office Supplies 181 Office Equipment Еxpenses 511 Wages Expense 521 Rent Expense 525 Phone Expense 533 Utilities Expense 549 Miscellaneous Expense Liabilities 202 Accounts Payable Owner's Equity 311 Diane Bernick, Capital 312 Diane Bernick, Drawing
> Listed below are the weekly cash register tape amounts for service fees and the related cash counts during the month of July. A change fund of $100 is maintained. REQUIRED 1. Prepare the journal entries to record the cash service fees and cash short and
> Mary’s Luxury Travel in Problem 8-9A keeps employee earnings records. Problem 8-9A: Mary Losch operates a travel agency called Mary’s Luxury Travel. She has five employees, all of whom are paid on a weekly basis. The
> Portions of the payroll register for Barney’s Bagels for the week ended July 15 are shown below. The SUTA tax rate is 5.4%, and the FUTA tax rate is 0.6%, both of which are levied on the first $7,000 of earnings. The Social Security tax
> Mary Losch operates a travel agency called Mary’s Luxury Travel. She has five employees, all of whom are paid on a weekly basis. The travel agency uses a payroll register, individual employee earnings records, and a general journal. Mar
> Donald Chin works for Northwest Supplies. His rate of pay is $8.50 per hour, and he is paid 1½ times the regular rate for all hours worked in excess of 40 per week. During the last week of January of the current year, he worked 48 hours. Chin is married
> Journalize the following data taken from the payroll register of Copy Masters as of April 15, 20: Regular earnings ………………………………………. $5,715.00 Overtime earnings ………………………………………... 790.00 Deductions: Federal income tax ………………………………………. 625.00 Social Sec
> On December 31, the payroll register of Hamstreet Associates indicated the following information: Determine the amount of Social Security and Medicare taxes to be withheld and record the journal entry for the payroll, crediting Cash for the net pay.
> What steps are followed in posting sales from the general journal to the accounts receivable ledger?
> Mary Sue Guild works for a company that pays its employees 1½ times the regular rate for all hours worked in excess of 40 per week. Guild’s pay rate is $10 per hour. Her wages are subject to deductions for federal income t
> Assume a Social Security tax rate of 6.2% is applied to maximum earnings of $118,500 and a Medicare tax rate of 1.45% is applied to all earnings. Calculate the Social Security and Medicare taxes for the following situations: Cumul. Pay Before Curren
> Using the table in Figure 8-4 on pages 288 and 289, Figure 8-4: Determine the amount of federal income tax an employer should withhold weekly for employees with the following marital status, earnings, and withholding allowances: SINGLE Persons-W
> Rebecca Huang receives a regular salary of $2,600 a month and is paid 1½ times the regular hourly rate for hours worked in excess of 40 per week. (a) Calculate Huang’s overtime rate of pay. (b) Calculate Huang’s total gross weekly pay if she works 45 hou
> Ryan Lawrence’s regular hourly rate is $15. He receives 1½ times the regular rate for any hours worked over 40 a week and double the rate for work on Sunday. During the past week, Lawrence worked 8 hours each day Monday through Thursday, 10 hours on Frid
> The book balance in the checking account of Lyle’s Salon as of November 30 is $3,282.95. The bank statement shows an ending balance of $2,127. By examining last month’s bank reconciliation, comparing the deposits and checks written per books and per bank
> The book balance in the checking account of Johnson Enterprises as of October 31 is $5,718. The bank statement shows an ending balance of $5,217. The following information is discovered by (1) comparing last month’s deposits in transit
> Based on the following information, prepare the weekly entries for cash receipts from service fees and cash short and over. A change fund of $100 is maintained. Cash Register Receipt Amount $268.50 237.75 Actual Cash Change Fund $100 Date Counted Apr
> Based on the following petty cash information, prepare (a) the journal entry to establish a petty cash fund, and (b) the journal entry to replenish the petty cash fund. On January 1, 20--, a check was written in the amount of $300 to establish a petty
> Based on the following bank reconciliation, prepare the journal entries: Carmen Lui Associates Bank Reconciliation July 31, 20-- Bank statement balance, luly 31 Add deposits in transit $3 3 16 80 $300 00 118 00 4 18 00 $3 73 4 80 Deduct outstanding
> What steps are followed in posting sales from the general journal to the general ledger?
> In a format similar to the following, indicate whether the action at the left will result in an addition to (+) or subtraction from (–) the ending bank balance or the ending checkbook balance. Ending Ending Bank Checkbook Balance B
> Based on the following information, prepare a check and stub: January 15, 20- $2,841.50 Date: Balance brought forward: Deposit: Check to: (from Exercise 7-2A) J. M. Suppliers $150.00 Office Supplies Sign your name Amount: For: Signature:
> Based on the following information, prepare a deposit ticket: Date: January 15, 20- $396.00 Currency: Coin: 23.20 Checks: No. 4-12 372.00 No. 80-318 127.00 No. 3-8 44.00
> A petty cash fund was established for $150. The following vouchers were issued during May: REQUIRED 1. Prepare the journal entry to establish the petty cash fund. 2. Record the vouchers in the petty cash record. Total and rule the petty cash record. 3.
> Match the following words with their definitions: 1. An endorsement where the payce simply signs on the back of the check a. signature card b. canceled check c. blank endorsement d. drawer c. restrictive endorscment f. drawce g. payce 2. An endorsem
> The capital account for Autumn Chou, including an additional investment, and a partial work sheet are shown below and on page 208. REQUIRED Prepare a statement of owner’s equity. GENERAL LEDGER AONE Autumn Chou, Capital MCONT 311 P
> Refer to the work sheet in Problem 6-7A for Megaffin’s Repairs. The trial balance amounts (before adjustments) have been entered in the ledger accounts provided in the working papers. If you are not using the working papers that accompa
> Page 206 shows a work sheet for Megaffin’s Repairs. No additional investments were made by the owner during the month. REQUIRED 1. Prepare an income statement. 2. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity. 3. Prepare a balance sheet.
> Using the following partial listing of T accounts, prepare closing entries in general journal form dated January 31, 20--. Then post the closing entries to the T accounts. Accum. Depr.- Del. Equip Wages Еxpense Bal. 1,800 Electricity Еxpense 185.1 5
> Using the following partial listing of T accounts, prepare closing entries in general journal form dated April 30, 20--. Then post the closing entries to the T accounts. Income Supplies Еxpense Bal. 500 Cash 101 Summary 313 524 Bal. 500 Accounts Gol
> Describe how each of the following accounts is used: (1) Sales, (2) Sales Tax Payable, (3) Sales Returns and Allowances, and (4) Sales Discounts.
> Set up T accounts for Major Advising based on the work sheet in Exercise 6-1A and the chart of accounts provided below. Enter the existing balance for each account. Prepare closing entries in general journal form. Then post the closing entries to the T a
> From the partial work sheet below, prepare a balance sheet. Major Advising Work Sheet (Partlal) For Month Ended January 31, 20 -- IIE MALANIS 1339 00 935 00 3 46 00 800 00 3500 00 1 Can 2 Acounts Recehable 3 Supplies 4 Prepald Insurance 5 omce Equip
> From the partial work sheet below, prepare a statement of owner’s equity, assuming no additional investment was made by the owner.
> Indicate with an “X” whether each account total should be extended to the Income Statement Debit or Credit or to the Balance Sheet Debit or Credit columns on the work sheet. Income Statement Balance Sheet Debit Cr
> From the adjustments columns in Exercise 5-9A, Exercise 5-9A: A partial work sheet for Jim Jacobs’ Furniture Repair is shown as follows. Indicate by letters (a) through (d) the four adjustments in the Adjustments columns of the work
> From the partial work sheet for Major Advising below, prepare an income statement.
> A partial work sheet for Jim Jacobs’ Furniture Repair is shown as follows. Indicate by letters (a) through (d) the four adjustments in the Adjustments columns of the work sheet, properly matching each debit and credit. Complete the Adju
> Two adjusting entries are in the following general journal. Post these adjusting entries to the four general ledger accounts. The following account numbers were taken from the chart of accounts: 141, Supplies; 219, Wages Payable; 511, Wages Expense; and
> Analyze each situation and indicate the correct dollar amount for the adjusting entry. 1. Amount of insurance expired is $970. (Balance Sheet) Prepaid Insurance (Income Statement) Insurance Expense TB 1,450 Bal. 2. Amount of unexpired insurance is
> Analyze each situation and indicate the correct dollar amount for the adjusting entry. 1. Ending inventory of supplies is $260. (Balance Sheet) Supplies (Income Statement) Supplies Expense TB 580 Bal. 2. Amount of supplies used is $230. (Balance She
> Describe the net effect of the four closing entries on the balance of the owner’s capital account. Where else is this same amount calculated?
> A depreciable asset was acquired for $6,840. The asset has an estimated useful life of six years (72 months) and no salvage value. Using the straight-line depreciation method, calculate the book value as of December 31, 20--.
> Delivery equipment was purchased for $7,200. The delivery equipment has an estimated useful life of four years (48 months) and no salvage value. Using the straight-line depreciation method, analyze the necessary adjusting entry as of December 31 (one mon
> The trial balance shows wages expense of $600. An additional $200 of wages was earned by the employees, but has not yet been paid. Analyze this adjustment for wages using T accounts, and then formally enter this adjustment in the general journal.
> A six-month liability insurance policy was purchased for $900. Analyze the required adjustment as of December 31 using T accounts, and then formally enter this adjustment in the general journal.
> The trial balance indicates that the supplies account has a balance, prior to the adjusting entry, of $320. A physical count of the supplies inventory shows that $90 of supplies remain. Analyze this adjustment for supplies using T accounts, and then form
> Annette Creighton opened Creighton Consulting. She rented a small office and paid a part-time worker to answer the phone and make deliveries. Her chart of accounts is as follows: Creighton’s transactions for the first month of business
> Joe Adams bought $500 worth of office supplies on account. The following entry was recorded on May 17. Find the error(s) and correct it (them) using the ruling method. On May 25, after the transactions had been posted, Adams discovered that the followin
> From the following trial balance taken after one month of operation, prepare an income statement, a statement of owner’s equity, and a balance sheet. TJ's Paint Service Trial Balance July 31, 20-- ACOUNT ACCDUNT DET BALANE CREDIT BA
> Set up general ledger accounts using the chart of accounts provided in Exercise 4-4A. Exercise 4-4A: Diane Bernick has opened Bernick’s Consulting. Journalize the following transactions that occurred during January of the current year
> List the four steps for closing the temporary accounts.
> Diane Bernick has opened Bernick’s Consulting. Journalize the following transactions that occurred during January of the current year. Use the following journal pages: January 1–10, page 1, and January 11â€&
> Set up T accounts for each of the general ledger accounts needed for Exercise 4-2A and post debits and credits to the accounts. Exercise 4-2A: For each of the following transactions, list the account to be debited and the account to be credited in the
> For each of the following transactions, list the account to be debited and the account to be credited in the general journal. 1. Invested cash in the business, $5,000. 2. Paid office rent, $500. 3. Purchased office supplies on account, $300. 4. Received
> Prepare an income statement for Jay Pembroke for the month of April 20--.
> Label each of the following accounts as an asset (A), a liability (L), or owner’s equity (OE), using the following format: Item Account Classification Money in bank Office supplies Money owed Office chairs Net worth of owner Cash Su
> Refer to the trial balance in Problem 3-13A and to the analysis of the change in owner’s equity in Problem 3-14A. REQUIRED 1. Prepare an income statement for Kohl’s Home Repair for the month ended May 31, 20--. 2. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity f
> To determine the following information. Use the format provided below. 1. a. Total revenue for the month b. Total expenses for the month c. Net income for the month 2. a. Wilhclm Kohl's original investment in the business + Net income for the month
> Wilhelm Kohl started a business in May 20-- called Kohl’s Home Repair. Kohl hired a part-time college student as an assistant. Kohl has decided to use the following accounts for recording transactions: The following transactions occurre
> From the information in the trial balance presented for Juanita’s Delivery Service on page 76, prepare a balance sheet for Juanita’s Delivery Service as of September 30, 20--.
> Assuming that all entries have been posted, prepare correcting entries for each of the following errors. 1. The following entry was made to record the purchase of $700 in supplies on account: Supplies 142 700 Cash 101 700 2. The following entry was m
> Why is it important to total and verify the totals of the payroll register after the data for each employee have been entered?
> Jim Andrews opened a delivery business in March. He rented a small office and has a part-time assistant. His trial balance shows accounts for the first three months of business. Andrews’ transactions for the month of June are as follow
> Source documents trigger the analysis of events requiring an accounting entry. Match the following source documents with the type of information they provide. 1. Check stubs or check register 2. Purchase invoice from suppliers (vendors) a. A good or
> The following accounts have normal balances. Prepare a trial balance for Kenny’s Lawn Service as of September 30, 20--. Cash …………………………………………………………... $10,000 Accounts Receivable ……………………………………… 6,000 Supplies ………………………………………………………... 1,600 Prepaid Insu
> Prepare a trial balance for Charlie’s Detective Service as of January 31, 20--.
> Charles Chadwick opened a business called Charlie’s Detective Service in January 20--. Set up T accounts for the following accounts: Cash; Accounts Receivable; Office Supplies; Computer Equipment; Office Furniture; Accounts Payable; Charles Chadwick, Cap
> Foot and balance the T accounts prepared in Exercise 3-5A if necessary. Exercise 3-5A: Analyze the following transactions for the first month of business using T accounts. Label each T account with the title of the account affected and then place the t
> Analyze the following transactions for the first month of business using T accounts. Label each T account with the title of the account affected and then place the transaction letter and the dollar amount on the debit or credit side. (a) Invested cash in
> Indicate the normal balance (debit or credit) for each of the following accounts: 1. Cash 2. Wages Expense 3. Accounts Payable 4. Owner's Drawing 5. Supplies 6. Owner's Capital 7. Equipment
> Richard Gibbs began a business called Richard’s Shoe Repair. 1. Create T accounts for Cash; Supplies; Richard Gibbs, Capital; and Utilities Expense. Identify the following transactions by letter and place them on the proper side of the T accounts: (a) In
> Complete the following statements using either “debit” or “credit”: (a) The cash account is increased with a _________. (b) The owner’s capital account is increased with a _________. (c) The delivery equipment account is increased with a _________. (d) T
> Identify all items that are debited or credited to Social Security Tax Payable and to Medicare Tax Payable.
> From the information in the trial balance presented above, prepare a statement of owner’s equity for Juanita’s Delivery Service for the month ended September 30, 20--.
> From the information in the trial balance presented above, prepare an income statement for Juanita’s Delivery Service for the month ended September 30, 20--.
> Foot and balance the cash T account shown below. Cash 500 100 400 200 600
> Jay Pembroke started a business. During the first month (April 20--), the following transactions occurred. (a) Invested cash in business, $18,000. (b) Bought office supplies for $4,600: $2,000 in cash and $2,600 on account. (c) Paid one-year insurance pr
> Dr. John Salvaggi is a chiropractor. As of December 31, he owned the following property that related to his professional practice. Cash……………â€
> Prepare a statement of owner’s equity assuming Ray had a net loss of $3,000.
> Ray started an accounting service on June 1, 20--, by investing $20,000. Her net income for the month was $10,000, and she withdrew $8,000. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity for the month of June.
> Label each of the following accounts as an asset (A), liability (L), owner’s equity (OE), revenue (R), or expense (E). Indicate the financial statement on which the account belongs—income statement (IS), statement of o
> Assume John Sullivan completed the following additional transactions during February. Show the effect of each transaction on the basic elements of the expanded accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity (Capital – Drawing + Revenues – Exp
> John Sullivan started a business. During the first month (February 20--), the following transactions occurred. Show the effect of each transaction on the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity. After each transaction, show the new tot
> Identify the sources of the information needed to prepare the balance sheet.
> Using the accounting equation, compute the missing elements. Owner's Equity $17,000 Assets Liabilities + $27,000 $18,000 $32,000 $27,000 $20,000 IL || || |
> List the six major steps of the accounting process in order (1–6) and define each. Recording Summarizing Reporting Analyzing Interpreting Classifying
> Match the following users with the information needed. 1. Owners 2. Managers 3. Creditors 4. Government agencies a. Whether the firm can pay its bills on time b. Detailed, up-to-date information to measure business performance (and plan for future op
> Prepare a balance sheet for Jay Pembroke as of April 30, 20--.
> Prepare a statement of owner’s equity for Jay Pembroke for the month of April 20--.
> A beginning accounting student tried to complete a work sheet for Joyce Lee’s Tax Service. The following adjusting entries were to have been analyzed and entered onto the work sheet. The work sheet is shown on page 167. (a) Ending inventory of supplies a
> Refer to Problem 5-15A and the following additional information: REQUIRED 1. Journalize the adjusting entries on page 5 of the general journal. 2. Post the adjusting entries to the general ledger. (If you are not using the working papers that accompany t
> Jason Armstrong started a business called Campus Delivery Service. After the first month of operations, the trial balance as of November 30, 20--, is as shown on the next page. REQUIRED 1. Analyze the following adjustments and enter them on the work she
> The following is a list of outstanding notes payable as of December 31, 20--: REQUIRED 1. Compute the accrued interest at the end of the year. 2. Prepare the adjusting entry in the general journal. Maker Date of Note No. of Days Principal $1,000 Inte
> Martin Manufacturing issued the following bonds: Date of issue and sale: …………………………………………………………………… April 1, 20-1 Principal amount: ………………………………………………………………………………. $500,000 Sale price of bonds: ……………………………………………………………………………………. 100 Denomination of bonds
> What is the relationship between the revenue and expense accounts and the owner’s equity account?
> In what two ways can the information necessary to compute departmental gross profit be accumulated?
> Financial statements for McDowell Company as well as additional information relevant to cash flows during the period are given on pages 926–927. Additional information: 1. Store equipment was sold in 20-2 for $25,000. Additional infor
> Horn Company’s condensed income statement for the year ended December 31, 20-2, was as follows: Net sales ………………&ac
> M. Evans & Sons manufactures parts for radios. For each job order, it maintains ledger sheets on which it records direct labor, direct materials, and factory overhead applied. The factory overhead control account contains postings of actual overhead cost
> Stone street Enterprises makes garage doors. During the month of February, the company had four job orders: 205, 206, 207, and 208. Overhead was applied at predetermined rates, while actual factory overhead was recorded as incurred. All four jobs were co

