Question: Greenwood Company manufactures two products—14,000
Greenwood Company manufactures two products—14,000 units of Product Y and 6,000 units of Product Z. The company uses a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. It is considering implementing an activity-based costing (ABC) system that allocates all of its manufacturing overhead to four cost pools. The following additional information is available for the company as a whole and for Products Y and Z:

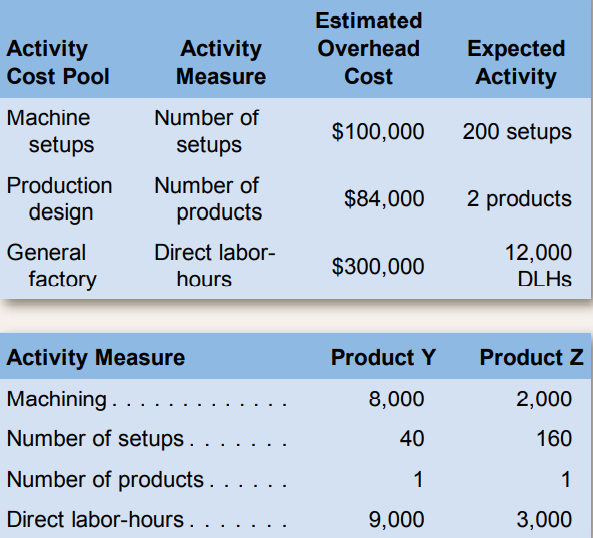
1. What is the company’s plantwide overhead rate?
2. Using the plantwide overhead rate, how much manufacturing overhead cost is allocated to Product Y? How much is allocated to Product Z?
3. What is the activity rate for the Machining activity cost pool?
4. What is the activity rate for the Machine Setups activity cost pool?
5. What is the activity rate for the Product Design activity cost pool?
6. What is the activity rate for the General Factory activity cost pool?
7. Which of the four activities is a batch-level activity? Why?
8. Which of the four activities is a product-level activity? Why?
9. Using the ABC system, how much total manufacturing overhead cost would be assigned to Product Y?
10. Using the ABC system, how much total manufacturing overhead cost would be assigned to Product Z?
11. Using the plantwide overhead rate, what percentage of the total overhead cost is allocated to Product Y? What percentage is allocated to Product Z?
12. Using the ABC system, what percentage of the Machining costs is assigned to Product Y? What percentage is assigned to Product Z? Are these percentages similar to those obtained in question 11? Why?
13. Using the ABC system, what percentage of Machine Setups cost is assigned to Product Y? What percentage is assigned to Product Z? Are these percentages similar to those obtained in question 11? Why?
14. Using the ABC system, what percentage of the Product Design cost is assigned to Product Y? What percentage is assigned to Product Z? Are these percentages similar to those obtained in question 11? Why?
15. Using the ABC system, what percentage of the General Factory cost is assigned to Product Y? What percentage is assigned to Product Z? Are these percentages similar to those obtained in question 11? Why?
> Vail Resorts, Inc. (MTN), announced a $415 million expansion of lodging properties, ski lifts, and terrain in Park City, Utah. Assume that this investment is estimated to produce $99 million in equal annual cash flows for each of the first 10 years of th
> Diamond & Turf Inc. is considering an investment in one of two machines. The sewing machine will increase productivity from sewing 150 baseballs per hour to sewing 290 per hour. The contribution margin per unit is $0.32 per baseball. Assume that any
> Tasty Doughnuts has computed the net present value for capital expenditure at two locations. Relevant data related to the computation are as follows: a. Determine the present value index for each proposal. b. Which location does your analysis support? E
> Carnival (CCL) has recently placed into service some of the largest cruise ships in the world. One of these ships, the Carnival Breeze, can hold up to 3,600 passengers, which can cost $750 million to build. Assume the following additional information: &a
> Jones Excavation Company is planning an investment of $125,000 for a bulldozer. The bulldozer is expected to operate for 1,000 hours per year for five years. Customers will be charged $90 per hour for bulldozer work. The bulldozer operator costs $30 per
> A company is considering replacing an old piece of machinery, which cost $400,000 and has $175,000 of accumulated depreciation to date, with a new machine that has a purchase price of $550,000. The old machine could be sold for $250,000. The annual varia
> Somerset Computer Company has been purchasing carrying cases for its portable computers at a purchase price of $24 per unit. The company, which is currently operating below full capacity, charges factory overhead to production at the rate of 40% of direc
> On the basis of the following data, the general manager of Hawkeye Shoes Inc. decided to discontinue Children’s Shoes because it reduced operating income by $30,000. What is the flaw in this decision, if it is assumed fixed costs would
> Charles Schwab Corporation (SCHW) is one of the more innovative brokerage and financial service companies in the United States. The company recently provided information about its major business segments as follows (in millions): a. How does a brokerage
> The condensed product-line income statement for Rhinebeck Company for the month of October is as follows: Fixed costs are 20% of the cost of goods sold and 30% of the selling and administrative expenses. Rhinebeck Company assumes that fixed costs would
> When might activity-based costing be preferred overusing a relative amount of product sales in allocating selling and administrative expenses to products?
> A condensed income statement by product line for Warrick Beverage Inc. indicated the following for Mango Cola for the past year: It is estimated that 30% of the cost of goods sold represents fixed factory overhead costs and that 25% of the operating exp
> Laredo Corporation is considering new equipment. The equipment can be purchased from an overseas supplier for $120,000. The freight and installation costs for the equipment are $1,500. If purchased, annual repairs and maintenance are estimated to be $2,2
> Box Elder Power Company expects to operate at 85% of productive capacity during May. The total manufacturing costs for May for the production of 40,000 batteries are budgeted as follows: The company has an opportunity to submit a bid for 5,000 batteries
> Dakota Coffee Company produces Columbian coffee in batches of 7,500 pounds. The standard quantity of materials required in the process is 7,500 pounds, which cost $6.00 per pound. Columbian coffee can be sold without further processing for $9.80 per poun
> Boyer Digital Components Company assembles circuit boards by using a manually operated machine to insert electronic components. The original cost of the machine is $60,000, the accumulated depreciation is $24,000, its remaining useful life is five years,
> Burlington Construction Company is considering selling excess machinery with a book value of $115,000 (original cost of $275,000 less accumulated depreciation of $160,000) for $90,000, less a 6% brokerage commission. Alternatively, the machinery can be l
> Championship Sports Inc. operates two divisions—the Winter Sports Division and the Summer Sports Division. The following income and expense accounts were provided from the trial balance as of December 31, 20Y9, the end of the fiscal yea
> Rocky Mountain Airlines Inc. has two divisions organized as profit centers, the Passenger Division and the Cargo Division. The following divisional income statements were prepared: The support department allocation rates for the support department costs
> Horton Technology has two divisions, Consumer and Commercial, and two corporate support departments, Tech Services and Purchasing. The corporate expenses for the year ended December 31, 20Y7, are as follows: Tech Services Department …
> Varney Corporation, a manufacturer of electronics and communications systems, allocates Computing and Communications Services Department (CCS) costs to profit centers. The following table lists the types of services and cost drivers for each service. The
> Why would a manufacturing company with multiple production departments still prefer to use a single plantwide overhead rate?
> For each of the following support departments, select the cost driver listed that is most appropriate for allocating support department costs to responsible units:
> For each of the following support departments, identify a cost driver that could be used for allocating the support department costs to the profit center: a. Legal b. Duplication services c. Electronic data processing d. Central purchasing e. Telecommuni
> The following data were summarized from the accounting records for Ruiz Industries Inc. for the year ended November 30, 20Y8: Prepare divisional income statements for Ruiz Industries Inc.
> Based on Ziegler Inc.’s data in Exercise 17, assume that a transfer price of $1,200 has been established and that 75,000 units of materials are transferred, with no reduction in the Components Division’s current sales. a. How much would Ziegler Inc.’s to
> Materials used by the Instrument Division of Ziegler Inc. are currently purchased from outside suppliers at a cost of $1,350 per unit. However, the same materials are available from the Components Division. The Components Division has unused capacity and
> Data are presented in the following table of returns on investment and residual incomes: Determine the missing items, identifying each item by the appropriate letter.
> The Walt Disney Company (DIS) has four business segments, described as follows: • Media Networks: Television and radio • Parks and Resorts: Resorts, including Disneyland • Studio Entertainment: Motion
> The condensed income statement for the Consumer Products Division of Tri-State Industries Inc. is as follows (assuming no support department allocations): The manager of the Consumer Products Division is considering ways to increase the return on invest
> Based on the data in Exercise 10 assume that management has established a 15% minimum acceptable return for invested assets. a. Determine the residual income for each division. b. Which division has the most residual income? Data from Exercise 10:
> The operating income and the amount of invested assets in each division of Conley Industries are as follows: a. Compute the return on investment for each division. b. Which division is the most profitable per dollar invested?
> How can activity-based costing be used in service companies?
> Partially completed budget performance reports for Delmar Company, a manufacturer of light duty motors, follow: a. Complete the budget performance reports by determining the correct amounts for the lettered spaces. b. Compose a memo to Randi Wilkes, vic
> Glacier Bicycle Company manufactures commuter bicycles from recycled materials. The following data for October are available: Quantity of direct labor used …………………….. 5,000 hrs. Actual rate for direct labor ………………….. $22.75 per hr. Bicycles completed in
> H.J. Heinz Company uses standards to control its materials costs. Assume that a batch of ketchup (7,650 pounds) has the following standards: The actual materials in a batch may vary from the standard due to tomato characteristics. Assume that the actual
> De Soto Inc. produces tablet computers. The company uses Thin Film Crystal (TFC) LCD displays for its products. Each tablet uses one display. The company produced 770 tablets during July. However, due to LCD defects, the company actually used 800 LCD dis
> The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 50,000 automobile tires: Actual: …………………… 725,000 lbs. at $3.00 per lb. Standard: ……………….. 730,000 lbs. at $2.95 per lb. a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct
> Salisbury Bottle Company manufactures plastic two-liter bottles for the beverage industry. The cost standards per 100 two-liter bottles are as follows: At the beginning of March, Salisbury’s management planned to produce 500,000 bottle
> Lowell Manufacturing Inc. has a normal selling price of $20 per unit and has been selling 125,000 units per month. In November, Lowell Manufacturing decided to lower its price to $19 per unit expecting it can increase the units sold by 16%. a. Compute th
> Rosenberry Company computed the following revenue variances for January: Revenue price variance ……………. $(350,000) Favorable Revenue volume variance …………… 50,000 Unfavorable Assuming that the planned selling price per unit was $10 and that actual sales we
> Dickinsen Company gathered the following data for December: a. Compute the revenue price variance. b. Compute the revenue volume variance. c. Compute the total revenue variance.
> Rockport Industries Inc. gathered the following data for March: a. Compute the revenue price variance. b. Compute the revenue volume variance. c. Compute the total revenue variance.
> How does the “Cost of goods sold” section of the income statement differ between retail and manufacturing companies?
> Why would management be concerned about the accuracy of product costs?
> “Two dollars of gross margin per briefcase? That’s ridiculous!” roared Roy Thurmond, president of First-Line Cases, Inc. “Why do we go on producing those standard briefcases when we&
> Granger Stokes, managing partner of the venture capital firm of Halston and Stokes, was dissatisfied with the top management of PrimeDrive, a manufacturer of computer disk drives. Halston and Stokes had invested $20 million in PrimeDrive, and the return
> In recent years, public universities have experienced major budget cuts due to reduced funding from their state governments. These budget cuts usually occur at the most inopportune time—during the school year when contractual commitments with faculty and
> A form for using Excel to recreate the Review Problem related to Aerodec, Inc., is shown below. For simplicity, the form excludes the Parts Administration and Material Receipts activities that were included in the Review Problem. Download the workbook co
> Comparative financial statements for Weaver Company follow. During this year, Weaver sold some equipment for $20 that had cost $40 and on which there was accumulated depreciation of $16. In addition, the company sold long-term investments for $10 that ha
> Refer to the financial statement data for Joyner Company in Problem 13–10. Sam Conway, president of the company, considers $15,000 to be the minimum cash balance for operating purposes. As can be seen from the balance sheet data, only $4,000 in cash was
> Refer to the financial statement data for Weaver Company in Problem 13–7. Required: 1. Using the direct method, adjust the company’s income statement for this year to a cash basis. 2. Using the information obtained in
> Refer to the financial statements for Rusco Company in Problem 13–13. Because the Cash account decreased so dramatically during this year, the company’s executive committee is anxious to see how the income statement would appear on a cash basis. Required
> Adria Company recently implemented an activity-based costing system. At the beginning of the year, management made the following estimates of cost and activity in the company’s five activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activity
> Puget World, Inc., manufactures two models of television sets, the N 800 XL model and the N 500 model. Data regarding the two products follow: Additional information about the company follows: a. Model N 800 XL requires $75 in direct materials per unit,
> For many years, Thomson Company manufactured a single product called LEC 40. Then three years ago, the company automated a portion of its plant and at the same time introduced a second product called LEC 90 that has become increasingly popular. The LEC 9
> Marine, Inc., manufactures a product that is available in both a flexible and a rigid model. The company has made the rigid model for years; the flexible model was introduced several years ago to tap a new segment of the market. Since introduction of the
> Why do departmental overhead rates sometimes result in inaccurate product costs?
> Gino’s Restaurant is a popular restaurant in Boston, Massachusetts. The owner of the restaurant has been trying to better understand costs at the restaurant and has hired a student intern to conduct an activity-based costing study. The
> Mitchell Corporation manufactures a variety of products in a single facility. Consultants hired by the company to do an activity-based costing analysis have identified the following activities carried out in the company on a routine basis: a. Milling mac
> Precision Manufacturing Inc. (PMI) makes two types of industrial component parts—the EX300 and the TX500. It annually produces 60,000 units of EX300 and 12,500 units of TX500. The company’s conventional cost system all
> Refer to the information pertaining to Endless Mountain Company that is provided in Integration Exercise 11. In addition to the budget schedules that you prepared in Integration Exercise 11, insert a new tab in your Microsoft Excel worksheet titled &acir
> Refer to the information pertaining to Endless Mountain Company that is provided in Integration Exercise 11. Required: 1. Assume that the company expects to collect all of its credit sales in the quarter of sale rather than the original assumption that i
> Refer to the information pertaining to Endless Mountain Company that is provided in Integration Exercise 11. In addition to the budget schedules that you prepared in Integration Exercise 11, insert two new tabs in your Microsoft Excel worksheet titled &a
> Pacifica Industrial Products Corporation makes two products, Product H and Product L. Product H is expected to sell 40,000 units next year and Product L is expected to sell 8,000 units. A unit of either product requires 0.4 direct labor-hours. The compan
> Refer to the data for Carmono Company in Exercise 13–6. Required: Using the direct method, convert the company’s income statement to a cash basis.
> Northwest Hospital is a full-service hospital that provides everything from major surgery and emergency room care to outpatient clinics. Required: For each cost incurred at Northwest Hospital, indicate whether it would most likely be a direct cost or an
> Refer to the data for Pavolik Company in Exercise 13–4. Required: Use the direct method to convert the company’s income statement to a cash basis. Data from Exercise 13-4:
> Discuss some of the major reasons why companies prepare budgets.
> Sultan Company uses an activity-based costing system. At the beginning of the year, the company made the following estimates of cost and activity for its five activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial data for this year: 1. Earnings per share. 2. Price-earnings ratio. 3. Dividend payout ratio. 4. Dividend yield ratio. 5. Book value pe
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial data for this year: 1. Gross margin percentage. 2. Net profit margin percentage. 3. Return on total assets. 4. Return on equity. Data
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial ratios for this year: 1. Times interest earned ratio. 2. Debt-to-equity ratio. 3. Equity multiplier. Data from Exercise 14-2: Comparat
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial data for this year: 1. Accounts receivable turnover. (Assume that all sales are on account.) 2. Average collection period. 3. Inventory
> The company actually washed 8,800 cars in August. Required: Using Exhibit 9–5 as your guide, prepare the company’s flexible budget for August. Data from Exhibit 9-5:
> Refer to the data in Exercise 9–13. Assume that instead of producing 4,000 units during the month, the company produced only 3,000 units, using 14,750 pounds of material. (The rest of the material purchased remained in raw materials inv
> The auto repair shop of Quality Motor Company uses standards to control the labor time and labor cost in the shop. The standard labor cost for a motor tune-up is given below: The record showing the time spent in the shop last week on motor tune-ups has b
> Refer to the data in Exercise 7–14 for Chuck Wagon Grills. Assume in this exercise that the company uses absorption costing. Required: 1. Compute the unit product cost for one barbecue grill. 2. Prepare an income statement for last year
> Kunkel Company makes two products and uses a conventional costing system in which a single plantwide predetermined overhead rate is computed based on direct labor-hours. Data for the two products for the upcoming year follow: These products are customize
> What is a perpetual budget?
> Various activities at Companhia de Textils, S.A., a manufacturing company located in Brazil, are listed below. The company makes a variety of products in its plant outside São Paulo. a. Preventive maintenance is performed on general-purpose production eq
> Larner Corporation is a diversified manufacturer of industrial goods. The company’s activity-based costing system contains the following six activity cost pools and activity rates: Cost and activity data have been supplied for the follo
> Rustafson Corporation is a diversified manufacturer of consumer goods. The company’s activity-based costing system has the following seven activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool. 2. Compu
> The following activities occur at Greenwich Corporation, a company that manufactures a variety of products: a. Various individuals manage the parts inventories. b. A clerk in the factory issues purchase orders for a job. c. The personnel department train
> Rusties Company recently implemented an activity-based costing system. At the beginning of the year, management made the following estimates of cost and activity in the company’s five activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activi
> Rocky Mountain Corporation makes two types of hiking boots—Xactive and Pathbreaker. Data concerning these two product lines appear below: The company has a conventional costing system in which manufacturing overhead is applied to units
> Med Max buys surgical supplies from a variety of manufacturers and then resells and delivers these supplies to dozens of hospitals. In the face of declining profits, Med Max decided to implement an activity-based costing system to improve its understandi
> Performance Products Corporation makes two products, titanium Rims and Posts. Data regarding the two products follow: Additional information about the company follows: a. Rims require $17 in direct materials per unit, and Posts require $10. b. The direct
> Kubin Company’s relevant range of production is 18,000 to 22,000 units. When it produces and sells 20,000 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Required: 1. Assume the cost object is units of production: a. What is the total
> Cherokee Inc. is a merchandiser that provided the following information: Required: 1. Prepare a traditional income statement. 2. Prepare a contribution format income statement.
> What are the four hierarchical levels of activity discussed in the chapter?
> You are auditing a manufacturing company and have drafted a management letter that contains reference to matters to increase the efficiency of company systems and the general profitability of the company. Your audit assistant has asked you if this is app
> You are auditing a company engaged in the development and sale of games software over the internet. You are satisfied that the software is of high quality and are now directing your attention to the controls over the sale of their products. You have conf
> Give some examples of qualitative characteristics an auditor might take into account when deciding if a particular item in the financial statements is materially misstated.
> In this chapter we noted that Roberts and Dwyer (1998) appear to suggest that auditors should disclose the level of materiality they have used when conducting the audit. Given that this is now a requirement for companies that are required to follow the U
> In Appendix 11.2 on the Cengage companion website we suggest steps that could be included in the audit programme for accommodation income of The County Hotel Ltd received in cash. Reread this appendix and now suggest steps that should be included in the
> Two questions are placed within the text (10.5) Case study 10.3 Troston plc; (10.6) Case study 10.4 Burbage Limited: General and application controls in a sales system.
> This question is taken from a past paper of the Final Admitting Examination of CAI. Only the dates have been changed. You are undertaking the fieldwork for the audit of the financial statements of CAREFREE Limited for the year ended 31 December 2020. CA
> Munro Limited is a small company with two divisions. One division trades in specialized equipment for walkers and mountaineers, and the other sells artists’ materials. The company has acquired rights of access to a rocky area near a major city, where it
> In this chapter we referred to the term non-sampling risk. Outline what you believe the term means and give some examples of what you consider to be a non-sampling risk.

