Question: The company actually washed 8,800 cars
The company actually washed 8,800 cars in August.
Required:
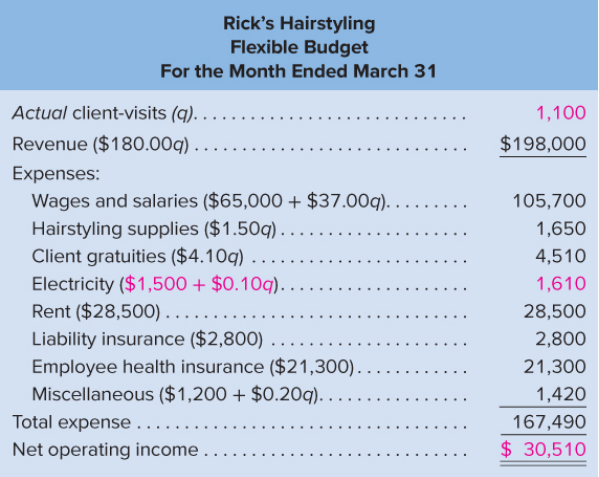
Using Exhibit 9–5 as your guide, prepare the company’s flexible budget for August.
Data from Exhibit 9-5:
> Materials used by the Instrument Division of Ziegler Inc. are currently purchased from outside suppliers at a cost of $1,350 per unit. However, the same materials are available from the Components Division. The Components Division has unused capacity and
> Data are presented in the following table of returns on investment and residual incomes: Determine the missing items, identifying each item by the appropriate letter.
> The Walt Disney Company (DIS) has four business segments, described as follows: • Media Networks: Television and radio • Parks and Resorts: Resorts, including Disneyland • Studio Entertainment: Motion
> The condensed income statement for the Consumer Products Division of Tri-State Industries Inc. is as follows (assuming no support department allocations): The manager of the Consumer Products Division is considering ways to increase the return on invest
> Based on the data in Exercise 10 assume that management has established a 15% minimum acceptable return for invested assets. a. Determine the residual income for each division. b. Which division has the most residual income? Data from Exercise 10:
> The operating income and the amount of invested assets in each division of Conley Industries are as follows: a. Compute the return on investment for each division. b. Which division is the most profitable per dollar invested?
> How can activity-based costing be used in service companies?
> Partially completed budget performance reports for Delmar Company, a manufacturer of light duty motors, follow: a. Complete the budget performance reports by determining the correct amounts for the lettered spaces. b. Compose a memo to Randi Wilkes, vic
> Glacier Bicycle Company manufactures commuter bicycles from recycled materials. The following data for October are available: Quantity of direct labor used …………………….. 5,000 hrs. Actual rate for direct labor ………………….. $22.75 per hr. Bicycles completed in
> H.J. Heinz Company uses standards to control its materials costs. Assume that a batch of ketchup (7,650 pounds) has the following standards: The actual materials in a batch may vary from the standard due to tomato characteristics. Assume that the actual
> De Soto Inc. produces tablet computers. The company uses Thin Film Crystal (TFC) LCD displays for its products. Each tablet uses one display. The company produced 770 tablets during July. However, due to LCD defects, the company actually used 800 LCD dis
> The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 50,000 automobile tires: Actual: …………………… 725,000 lbs. at $3.00 per lb. Standard: ……………….. 730,000 lbs. at $2.95 per lb. a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct
> Salisbury Bottle Company manufactures plastic two-liter bottles for the beverage industry. The cost standards per 100 two-liter bottles are as follows: At the beginning of March, Salisbury’s management planned to produce 500,000 bottle
> Lowell Manufacturing Inc. has a normal selling price of $20 per unit and has been selling 125,000 units per month. In November, Lowell Manufacturing decided to lower its price to $19 per unit expecting it can increase the units sold by 16%. a. Compute th
> Rosenberry Company computed the following revenue variances for January: Revenue price variance ……………. $(350,000) Favorable Revenue volume variance …………… 50,000 Unfavorable Assuming that the planned selling price per unit was $10 and that actual sales we
> Dickinsen Company gathered the following data for December: a. Compute the revenue price variance. b. Compute the revenue volume variance. c. Compute the total revenue variance.
> Rockport Industries Inc. gathered the following data for March: a. Compute the revenue price variance. b. Compute the revenue volume variance. c. Compute the total revenue variance.
> How does the “Cost of goods sold” section of the income statement differ between retail and manufacturing companies?
> Why would management be concerned about the accuracy of product costs?
> “Two dollars of gross margin per briefcase? That’s ridiculous!” roared Roy Thurmond, president of First-Line Cases, Inc. “Why do we go on producing those standard briefcases when we&
> Granger Stokes, managing partner of the venture capital firm of Halston and Stokes, was dissatisfied with the top management of PrimeDrive, a manufacturer of computer disk drives. Halston and Stokes had invested $20 million in PrimeDrive, and the return
> In recent years, public universities have experienced major budget cuts due to reduced funding from their state governments. These budget cuts usually occur at the most inopportune time—during the school year when contractual commitments with faculty and
> A form for using Excel to recreate the Review Problem related to Aerodec, Inc., is shown below. For simplicity, the form excludes the Parts Administration and Material Receipts activities that were included in the Review Problem. Download the workbook co
> Greenwood Company manufactures two products—14,000 units of Product Y and 6,000 units of Product Z. The company uses a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. It is considering implementing an activity-based costing (ABC) s
> Comparative financial statements for Weaver Company follow. During this year, Weaver sold some equipment for $20 that had cost $40 and on which there was accumulated depreciation of $16. In addition, the company sold long-term investments for $10 that ha
> Refer to the financial statement data for Joyner Company in Problem 13–10. Sam Conway, president of the company, considers $15,000 to be the minimum cash balance for operating purposes. As can be seen from the balance sheet data, only $4,000 in cash was
> Refer to the financial statement data for Weaver Company in Problem 13–7. Required: 1. Using the direct method, adjust the company’s income statement for this year to a cash basis. 2. Using the information obtained in
> Refer to the financial statements for Rusco Company in Problem 13–13. Because the Cash account decreased so dramatically during this year, the company’s executive committee is anxious to see how the income statement would appear on a cash basis. Required
> Adria Company recently implemented an activity-based costing system. At the beginning of the year, management made the following estimates of cost and activity in the company’s five activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activity
> Puget World, Inc., manufactures two models of television sets, the N 800 XL model and the N 500 model. Data regarding the two products follow: Additional information about the company follows: a. Model N 800 XL requires $75 in direct materials per unit,
> For many years, Thomson Company manufactured a single product called LEC 40. Then three years ago, the company automated a portion of its plant and at the same time introduced a second product called LEC 90 that has become increasingly popular. The LEC 9
> Marine, Inc., manufactures a product that is available in both a flexible and a rigid model. The company has made the rigid model for years; the flexible model was introduced several years ago to tap a new segment of the market. Since introduction of the
> Why do departmental overhead rates sometimes result in inaccurate product costs?
> Gino’s Restaurant is a popular restaurant in Boston, Massachusetts. The owner of the restaurant has been trying to better understand costs at the restaurant and has hired a student intern to conduct an activity-based costing study. The
> Mitchell Corporation manufactures a variety of products in a single facility. Consultants hired by the company to do an activity-based costing analysis have identified the following activities carried out in the company on a routine basis: a. Milling mac
> Precision Manufacturing Inc. (PMI) makes two types of industrial component parts—the EX300 and the TX500. It annually produces 60,000 units of EX300 and 12,500 units of TX500. The company’s conventional cost system all
> Refer to the information pertaining to Endless Mountain Company that is provided in Integration Exercise 11. In addition to the budget schedules that you prepared in Integration Exercise 11, insert a new tab in your Microsoft Excel worksheet titled &acir
> Refer to the information pertaining to Endless Mountain Company that is provided in Integration Exercise 11. Required: 1. Assume that the company expects to collect all of its credit sales in the quarter of sale rather than the original assumption that i
> Refer to the information pertaining to Endless Mountain Company that is provided in Integration Exercise 11. In addition to the budget schedules that you prepared in Integration Exercise 11, insert two new tabs in your Microsoft Excel worksheet titled &a
> Pacifica Industrial Products Corporation makes two products, Product H and Product L. Product H is expected to sell 40,000 units next year and Product L is expected to sell 8,000 units. A unit of either product requires 0.4 direct labor-hours. The compan
> Refer to the data for Carmono Company in Exercise 13–6. Required: Using the direct method, convert the company’s income statement to a cash basis.
> Northwest Hospital is a full-service hospital that provides everything from major surgery and emergency room care to outpatient clinics. Required: For each cost incurred at Northwest Hospital, indicate whether it would most likely be a direct cost or an
> Refer to the data for Pavolik Company in Exercise 13–4. Required: Use the direct method to convert the company’s income statement to a cash basis. Data from Exercise 13-4:
> Discuss some of the major reasons why companies prepare budgets.
> Sultan Company uses an activity-based costing system. At the beginning of the year, the company made the following estimates of cost and activity for its five activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial data for this year: 1. Earnings per share. 2. Price-earnings ratio. 3. Dividend payout ratio. 4. Dividend yield ratio. 5. Book value pe
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial data for this year: 1. Gross margin percentage. 2. Net profit margin percentage. 3. Return on total assets. 4. Return on equity. Data
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial ratios for this year: 1. Times interest earned ratio. 2. Debt-to-equity ratio. 3. Equity multiplier. Data from Exercise 14-2: Comparat
> Refer to the data in Exercise 14–2 for Weller Corporation. Required: Compute the following financial data for this year: 1. Accounts receivable turnover. (Assume that all sales are on account.) 2. Average collection period. 3. Inventory
> Refer to the data in Exercise 9–13. Assume that instead of producing 4,000 units during the month, the company produced only 3,000 units, using 14,750 pounds of material. (The rest of the material purchased remained in raw materials inv
> The auto repair shop of Quality Motor Company uses standards to control the labor time and labor cost in the shop. The standard labor cost for a motor tune-up is given below: The record showing the time spent in the shop last week on motor tune-ups has b
> Refer to the data in Exercise 7–14 for Chuck Wagon Grills. Assume in this exercise that the company uses absorption costing. Required: 1. Compute the unit product cost for one barbecue grill. 2. Prepare an income statement for last year
> Kunkel Company makes two products and uses a conventional costing system in which a single plantwide predetermined overhead rate is computed based on direct labor-hours. Data for the two products for the upcoming year follow: These products are customize
> What is a perpetual budget?
> Various activities at Companhia de Textils, S.A., a manufacturing company located in Brazil, are listed below. The company makes a variety of products in its plant outside São Paulo. a. Preventive maintenance is performed on general-purpose production eq
> Larner Corporation is a diversified manufacturer of industrial goods. The company’s activity-based costing system contains the following six activity cost pools and activity rates: Cost and activity data have been supplied for the follo
> Rustafson Corporation is a diversified manufacturer of consumer goods. The company’s activity-based costing system has the following seven activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool. 2. Compu
> The following activities occur at Greenwich Corporation, a company that manufactures a variety of products: a. Various individuals manage the parts inventories. b. A clerk in the factory issues purchase orders for a job. c. The personnel department train
> Rusties Company recently implemented an activity-based costing system. At the beginning of the year, management made the following estimates of cost and activity in the company’s five activity cost pools: Required: 1. Compute the activi
> Rocky Mountain Corporation makes two types of hiking boots—Xactive and Pathbreaker. Data concerning these two product lines appear below: The company has a conventional costing system in which manufacturing overhead is applied to units
> Med Max buys surgical supplies from a variety of manufacturers and then resells and delivers these supplies to dozens of hospitals. In the face of declining profits, Med Max decided to implement an activity-based costing system to improve its understandi
> Performance Products Corporation makes two products, titanium Rims and Posts. Data regarding the two products follow: Additional information about the company follows: a. Rims require $17 in direct materials per unit, and Posts require $10. b. The direct
> Kubin Company’s relevant range of production is 18,000 to 22,000 units. When it produces and sells 20,000 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Required: 1. Assume the cost object is units of production: a. What is the total
> Cherokee Inc. is a merchandiser that provided the following information: Required: 1. Prepare a traditional income statement. 2. Prepare a contribution format income statement.
> What are the four hierarchical levels of activity discussed in the chapter?
> You are auditing a manufacturing company and have drafted a management letter that contains reference to matters to increase the efficiency of company systems and the general profitability of the company. Your audit assistant has asked you if this is app
> You are auditing a company engaged in the development and sale of games software over the internet. You are satisfied that the software is of high quality and are now directing your attention to the controls over the sale of their products. You have conf
> Give some examples of qualitative characteristics an auditor might take into account when deciding if a particular item in the financial statements is materially misstated.
> In this chapter we noted that Roberts and Dwyer (1998) appear to suggest that auditors should disclose the level of materiality they have used when conducting the audit. Given that this is now a requirement for companies that are required to follow the U
> In Appendix 11.2 on the Cengage companion website we suggest steps that could be included in the audit programme for accommodation income of The County Hotel Ltd received in cash. Reread this appendix and now suggest steps that should be included in the
> Two questions are placed within the text (10.5) Case study 10.3 Troston plc; (10.6) Case study 10.4 Burbage Limited: General and application controls in a sales system.
> This question is taken from a past paper of the Final Admitting Examination of CAI. Only the dates have been changed. You are undertaking the fieldwork for the audit of the financial statements of CAREFREE Limited for the year ended 31 December 2020. CA
> Munro Limited is a small company with two divisions. One division trades in specialized equipment for walkers and mountaineers, and the other sells artists’ materials. The company has acquired rights of access to a rocky area near a major city, where it
> In this chapter we referred to the term non-sampling risk. Outline what you believe the term means and give some examples of what you consider to be a non-sampling risk.
> It is early December 2020, and you approach the Chief Financial Officer of Pitscottie Limited, a trading company, to ask him to send the 31 December year-end inventory count instructions for review. He informs you that the directors wish to rely on inven
> You ask your audit assistant to carry out a review of after-date receipts from credit customers. Explain to them the reason for such a review and show how it should be performed. What kind of conclusion might they be able to form after carrying out such
> To what extent are the determinants and characteristics of audit quality similar to those of the audit expectations gap?
> You have completed the audit of Magnolia Ltd for the year ended 31 December 2018. The financial statements show turnover of £10 000 000 – down 10 per cent on the prior year – and losses of £75 000. The company has net assets of £1 000 000 (2017: £1 100 0
> The characteristics of suitable criteria are: relevance, completeness, reliability, neutrality and understandability. Explain what these characteristics mean, illustrating your answer by reference to KPIs in an hotel. You may refer to Case Study 6.4 (Cou
> Your audit assistant on the Greenburn Ltd assignment has asked you where the following working schedules should be filed: a. Summary of the details of a construction contract for the supply of goods to a customer. b. Letter to the company from the compa
> Explain why it is so important for auditors to identify the points at which management is making judgemental decisions about accounting matters. Give examples.
> ‘If management review useful lives annually, impairment reviews will rarely be necessary.’ Give your views on this statement. What audit procedures should you carry out to see if an impairment review is necessary?
> In previous chapters we discussed the significance of risk facing auditors in the process of forming audit conclusions. Explain how auditors address risk at the prefinal stage of the audit process.
> The division of management assertions into genuine, accurate and complete is a useful aid to auditors. Discuss.
> Set out in Figure 9.6 is a systems flowchart for a production payroll system. Explain what is happening in the two routines ‘transaction file update’ and ‘salary run’. In addition, e
> As organizations have become more dependent on the reliability of information systems, they have become more aware of the need to maintain quality of systems and the data/information derived from them. If you were asked to set up a quality standards grou
> An important objective of the business risk approach is to make the audit more profitable by cutting down on the amount of evidence obtained by substantive tests of detail. Discuss.
> Insufficient attention is being paid to the needs, nature and size of the multinational companies the Big Four presently audit when there is discussion of the ways in which competition for such audits can be enhanced. Discuss.
> The audit expectations gap will never be closed. Discuss.
> The willingness of large audit firms to provide forensic audit services indicates that they have the ability and techniques available to detect fraud. It would seem a short step to suggest that auditors should have a greater responsibility for fraud dete
> This question is based on an ACCA question in their Advanced Audit and Assurance Paper P7, June 2012. Snipe Ltd has in place a defined benefit pension plan for its employees. An actuarial valuation on 31 January 2018 indicated that the plan is in deficit
> Consider whether the following statements are true or false: a. The same standards of independence need not be applied in assurance engagements as in the statutory audit of financial statements. b. A review engagement results in a conclusion in the assur
> Lundin plc operates a number of divisions, but the board of directors has been considering closing those that no longer fit into the future plans of the company. On 30 November 2020 (year-end is 31 December 2020), the board decided to close two of the di
> Blackford Ltd is a company engaged in two diverse activities, the manufacture of lawnmowers and trading in the hardware sector, selling its lawnmowers through its own hardware outlets. The company decided to discontinue its loss-making lawnmower operatio
> Consider the following items of income and expense and state: whether they bear a relationship to each other or not; if they are related in any way, in what way they should move in relation to each other; the reasons for your answer in each case. a. New
> Crail Limited analytical review. The profit and loss account for the year ended 31 December 2020 and balance sheet at 31 December 2020 of Crail Limited, a trading company, are set out below. Required: Perform an analytical review of these figures and s
> Refer to questions 9.2 and 9.3 and explain how a data flow diagram would help the auditor to understand how the entity’s order entry system is operating. Why would a data flow diagram be better than a document flowchart for this purpose?
> Figure 8.1 showed that there are two broad levels of regulation and control relating to both external and internal environment. You are the auditor of an entity providing advice to clients on financial matters. You are aware that there have been serious
> Discuss what you understand by the following terms: a. foreseeability b. proximity c. assumption of responsibility
> New rules have been introduced by the European Parliament, and it is anticipated that these new rules will lead to considerable improvements in audit quality. Evaluate the extent to which new legislation can contribute towards improving audit quality.

