Question: Identify the alkene that would yield the
Identify the alkene that would yield the following products via ozonolysis:
Transcribed Image Text:
TH. + (a) H (b) H. H. (c) (d)
> (−)-Lepadiformine A, isolated from the marine organism Clavelina lepadiformis, is observed to be toxic to several tumor cell lines. During a recent synthesis of (−)-lepadiformine A, compound 3 was made from compounds 1
> Starting with acetylene, show reagents that you would use to prepare each of the following compounds: a. 1-Butyne b. 2-Butyne c. 3-Hexyne d. 2-Hexyne e. 1-Hexyne f. 2-Heptyne g. 3-Heptyne h. 2-Octyne i. 2-Pentyne - (k) (i)
> An alkyne with the molecular formula C4H6 was treated with ozone followed by water to produce a carboxylic acid and carbon dioxide. Draw the expected product when the alkyne is treated with aqueous acid in the presence of mercuric sulfate.
> An alkyne with the molecular formula C6H10 was treated with ozone followed by water to produce only one type of carboxylic acid. Draw the structure of the starting alkyne and the product of ozonolysis.
> Draw the major products that are expected when each of the following alkynes is treated with O3 followed by H2O: (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Proteases are enzymes that can break covalent bonds in proteins. Proteases play major roles in the regulation of biological processes, so compounds that inhibit their function, called protease inhibitors, have potential as therapeutic agents. While prepa
> Identify reagents that you could use to achieve each of the following transformations: (а) (b)
> Identify the alkyne you would use to prepare each of the following compounds via hydroboration-oxidation: (a) H. (b) (c)
> Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) is used in the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness (narcolepsy), but when mixed with alcohol, it can cause loss of consciousness, which explains why it is sometimes referred to as a “date rape drug.
> Butane (C4H10) exhibits only two different kinds of protons, shown here in red and blue. a. Explain why all four protons shown in red are chemically equivalent. b. Explain why all six protons shown in blue are chemically equivalent. c. How many differ
> Draw the major product for each of the following reactions: ? 1) 9-BBN 2) H,O,, NaOH (a) 1) Disiamylborane 2) H,O, NaOH (b) 1) R,BH 2) Н,О. NaOH (c)
> Identify the alkyne you would use to prepare each of the following ketones via acid-catalyzed hydration: (a) (b) (с)
> Draw the major product(s) expected when each of the following alkynes is treated with aqueous acid in the presence of mercuric sulfate (HgSO4): (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Warfarin is a blood-thinning drug (anticoagulant) that is used to prevent heart attacks and strokes. Including stereoisomers, there are at least 40 distinct tautomer forms of warfarin. Shown below are two enol forms of warfarin. Draw a tautomer form of w
> The following enols cannot be isolated. They rapidly tautomerize to produce ketones. In each case, draw the expected ketone and show a mechanism for its formation under acid-catalyzed conditions (H3O+). он он но OH (а) (Ь) (с) (d)
> An alkyne with the molecular formula C5H8 is treated with excess HBr, and two different products are obtained, each of which has the molecular formula C5H10Br2. a. Identify the starting alkyne. b. Identify the two products.
> Suggest reagents that would achieve the following transformation: .CI CI
> Predict the major product(s) expected for each of the following reactions: 1) xs NANH,NH, ? 2) H,0 CI , ? HC HBr (a) (b) (c) Br Br CI 1) xs NANH, NH, ? 1) xs NANH, NH, ? ? 1) xs NaNH NH, 2) H,0 3) HBr, ROOR O'HE 3) xs HBr 2) H,0 (e)
> An alkyne with the molecular formula C5H8 was treated with sodium in liquid ammonia to give a disubstituted alkene. Draw the structure of the alkene.
> Identify reagents that you could use to achieve each of the following transformations: (a) (b)
> Draw the expected 1H NMR spectrum for each of the following compounds: (а) H (b) H.
> Draw the major product expected when each of the following alkynes is treated with sodium in liquid ammonia: (al (b) (c) (d)
> Draw the major product expected from each of the following reactions: H2 Lindlar's catalyst ? H2 Pt (a) ? H2 NigB ? H2 (b) Ni
> When 3,3-dichloropentane is treated with excess sodium amide in liquid ammonia, the initial product is 2-pentyne: H H CI H H I ! ! !! н-с-с-с—с-с-н нн H xs NaNH, H-Ç-Ç-CEC-Ç-H H H ČI H H H 2-Pentyne
> For each of the following transformations, predict the major product and draw a mechanism for its formation: CI ? 1) xs NaNH, NH, 2) H,0 ? 1) xs NANHNH, -Br 2) HO (a) Br (b)
> Treatment of acetylene with a suitable base affords lithium acetylide, which was used as a reagent in a partial synthesis of the antitumor natural product (+)-acutiphycin. a. Draw the structure of lithium acetylide, and show a mechanism for its formatio
> In each of the following cases, determine if the base is sufficiently strong to deprotonate the terminal alkyne: + NaNH2 (a) H (Ь) NaH t-BUOK (c) H
> (+)-Citronellal is the main compound responsible for the lemon scent of citronella oil. In addition to its well-known insect repellant properties, it also has some antifungal properties. (+)-Citronellal also has been used as a starting material to make c
> When naming cycloalkynes that lack any other functional groups, the triple bond does not require a locant, because it is assumed to be between C1 and C2. Draw the structure of (R)-3-methylcyclononyne.
> Draw a bond-line structure for each of the following compounds: a. 4,4-Dimethyl-2-pentyne b. 5-Ethyl-2,5-dimethyl-3-heptyne
> Provide a systematic name for each of the following compounds: (a) (b) (0) (f) (g) CCla
> Each of the three vinylic protons of styrene is split by the other two, and the J values are found to be Jab=11 Hz, Jac=17 Hz, and Jbc=1 Hz. Using this information, draw the expected splitting pattern for each of the three signals (Ha, Hb, and Hc). H
> Propose a plausible mechanism for each of the following reactions: [H,SO (a) но Conc. H,S04 HO (b) о
> Muscalure is the sex pheromone of the common housefly and has the molecular formula C23H46. When treated with O3 followed by DMS, the following two compounds are produced. Draw two possible structures for muscalure. H. H.
> Compound Y has the molecular formula C7H12. Hydrogenation of compound Y produces methylcyclohexane. Treatment of compound Y with HBr in the presence of peroxides produces the following compound: Predict the products when compound Y undergoes ozonolysis
> When (R)-2-chloro-3-methylbutane is treated with potassium tert-butoxide, a monosubstituted alkene is obtained. When this alkene is treated with HBr, a mixture of products is obtained. Draw all of the expected products.
> The accepted mechanism for the following transformation involves a carbocation rearrangement. Rather than occurring via a methyl shift or a hydride shift, a carbon atom of the ring migrates, thereby converting a secondary carbocation into a more stable,
> When 1-methoxy-2-methylpropene is treated with HCl, the major product is 1-chloro-1-methoxy-2-methylpropane. Although this reaction proceeds via an ionic mechanism, the Cl is ultimately positioned at the less substituted carbon. Draw a mechanism that is
> Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish each of the following transformations: a. Convert 2-methyl-2-butene into a monosubstituted alkene b. Convert 2,3-dimethyl-1-hexene into a tetrasubstituted alkene
> Identify the reagents you would use to achieve each of the following transformations: a. Convert tert-butyl bromide into a primary alkyl halide b. Convert 2-bromopropane into 1-bromopropane
> Identify what reagents you would use to achieve each transformation: a. Conversion of 2-methyl-2-butene into a secondary alkyl halide b. Conversion of 2-methyl-2-butene into a tertiary alkyl halide c. Conversion of cis-2-butene into a meso diol d. Co
> In much the same way that they react with H2, alkenes also react with D2 (deuterium is an isotope of hydrogen). Use this information to predict the product(s) of the following reaction: Pt
> Below are NMR spectra of several compounds. Identify whether these compounds are likely to contain ethyl, isopropyl, and/or tert-butyl groups: Proton NMR CgH12 6 2 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 Chemical Shift (ppm) Chemical Shift (ppm) Prot
> Compound A has the molecular formula C5H10. Hydroborationoxidation of compound A produces an alcohol with no chiral centers. Draw two possible structures for compound A.
> Predict the major product(s) of the following reaction: Br2 H2S ?
> Identify which of the following two reactions you would expect to occur more rapidly: 1. addition of HBr to 2-methyl-2-pentene or 2. addition of HBr to 4-methyl-1-pentene. Explain your choice.
> Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish each of the following transformations: Br но. но OH Br OH Br OH OH En OH OH + En
> Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish each of the following transformations: OH + En Br + En HO,
> The following reaction is observed to be regioselective. Draw a mechanism for the reaction and explain the source of regioselectivity in this case: Br HBr
> Compound X is treated with Br2 to yield meso-2,3-dibromobutane. What is the structure of compound X?
> Explain why each of the following alcohols cannot be prepared via hydroboration-oxidation: он OH OH (a) (b) (c)
> Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: ? H2 (PPhg)gRhCI ? (a) (b) 1) BH, - THF 2) H,O, NaOH ? (c) ? 1) RCO3H 2) H,0* (d)
> The volatile organic compounds (VOCs) produced by decomposing tissue and organs were studied in an effort to identify possible human-specific markers. Of 452 VOCs isolated, six were found to be unique to humans, so this may prove to be a useful tool for
> Propose a mechanism for the following transformation: OH H30
> Propose a mechanism for the following transformation: OH MEOH Меб
> Suggest suitable reagents to perform the following transformation: OH Racemic
> (R)-Limonene is found in many citrus fruits, including oranges and lemons: Draw the structures and identify the relationship of the two products obtained when (R)-limonene is treated with excess hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst.
> Suggest suitable reagents to perform each of the following transformations: Br- + En Br OH HỒ. + En
> Compound A has the molecular formula C7H15Br. Treatment of compound A with sodium ethoxide yields only one elimination product (compound B) and no substitution products. When compound B is treated with dilute sulfuric acid, compound C is obtained, which
> Suggest an efficient synthesis for each of the following transformations: OH OH (a) Br (b) Br OH OH OH (c) (d)
> Compound A is an alkene that was treated with ozone (followed by DMS) to yield only (CH3CH2CH2)2C=O. Identify the major product that is expected when compound A is treated with a peroxy acid (RCO3H) followed by aqueous acid (H3O+).
> How many different alkenes will produce 2,4-dimethylpentane upon hydrogenation? Draw them.
> Suggest an efficient synthesis for the following transformation: он
> For each of the following compounds, determine the multiplicity of each signal in the expected 1H NMR spectrum: (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Suggest an efficient synthesis for each of the following transformations: (a) (b)
> Compound A reacts with one equivalent of H2 in the presence of a catalyst to give methylcyclohexane. Compound A can be formed upon treatment of 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane with sodium methoxide. What is the structure of compound A?
> Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions: OH H,0* (a) OH (b) Br (c) Br HBr (d)
> Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: ? 1) вн, - THF 2) H,02, NaOH ? 1) RCO,H 2) H,0 HBr Bl2 ? ? H2. Pt
> Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: ? 1) Hg(OAc), H,0 2) NABH, -? NaOH, cold HCI Brz, H0 ? H2, Pt ?
> At high temperatures, alkanes can undergo dehydrogenation to produce alkenes. For example: This reaction is used industrially to prepare ethylene while simultaneously serving as a source of hydrogen gas. Explain why dehydrogenation only works at high te
> Compound 3 below, called mycoepoxydiene, has been isolated from a marine fungus and has been shown to possess anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. It contains an unusual oxygen-bridged cyclooctadiene skeleton. Both enantiomers of this compound w
> Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish each of the following transformations: (a) (b) レー人 (c) (d)
> Bioethanol, ethanol produced by fermentation of sugars, is a desirable starting material for chemical synthesis since it comes from renewable resources. Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish the following industrial transformation that conver
> Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish each of the following transformations: он но (a) (b) он Br но En (c) (d) "OH
> In the human body, the amino acid phenylalanine is normally processed by an enzyme that converts it to cinnamic acid. Infants with phenylketonuria (PKU) have a defective enzyme, resulting in a buildup of phenylalanine that can damage a developing brain.
> AZT was the first HIV treatment to be approved by the Food and Drug Administration. HIV may become AZT-resistant over time, so new drugs are always being sought. As part of this effort, compound 2 was made from compound 1 and was shown to have modest act
> Identify the reagents that you would use to accomplish each of the following transformations: Br En (a) (b) Br (c) OH En (e) (f) Br Br | (g) (h)
> Compound A has the molecular formula C5H10. Hydroboration-oxidation of compound A produces a pair of enantiomers, compounds B and C. When treated with HBr, compound A is converted into compound D, which is a tertiary alkyl bromide. When treated with O3 f
> Determine whether syn dihydroxylation of trans-2-butene will yield the same products as anti dihydroxylation of cis-2-butene. Draw the products in each case and compare them.
> Syn dihydroxylation of the compound below yields two products. Draw both products and describe their stereoisomeric relationship (i.e., are they enantiomers or diastereomers?): KMNO4, NaOH ? Cold
> Predict the products of each of the following reactions: 1) вн, - THF 2) H,0, NaOH ? ? PI (a) (Ь) ? :? 1) CH,CO,H 1) OsO, 2) H,0 2) NaHSO,H,O (c) (d) ? HBr ? (е) (f) 1) RCO,H 2) H,0 ? 1) вн, - THF 2) H,O, NaOH ? (g) (h) Оs0, (catalytic) NMO (i)
> Synthetic chemists utilize a large variety of strategies for the synthesis of natural products. Indeed, new strategies are constantly being developed, many of which are inspired by (and mimic) the synthetic pathways employed by nature. As part of the dev
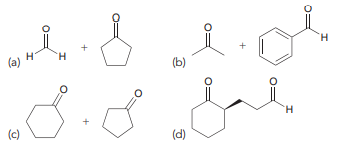
> Identify the structure of the starting alkene in each of the following cases: C3H14 1) Og C10H16 1) O, (a) 2) DMS 2) DMS (b) (c) 1) O 2) DMS
> Predict the products that are expected when each of the following alkenes is treated with ozone followed by DMS: (а) (Ь) (с) (d) (е) (f)
> Predict the product(s) for each of the following reactions. In each case, make sure to consider the number of chiral centers being formed. ? KMno NaOH Oso, (catalytic) NMO 1) Oso, 2) NaHSO, / H,0 ? Cold (al (b) (c) ? Os0, (catalytic) ? ? KMNO,, NaOH
> A compound with the molecular formula C4H6O2 has the following 1H NMR spectrum. Determine the number of protons giving rise to each signal. Proton NMR 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2,5 2.0 1.5 ppm 18.92 Integration Values 19.77 19.46
> Compound A and compound B both have the molecular formula C6H12. Both compounds produce epoxides when treated with a peroxy acid (RCO3H). a. The epoxide resulting from compound A was treated with aqueous acid (H3O+) and the resulting diol had no chiral
> Under acid-catalyzed conditions, epoxides can be opened by a variety of nucleophiles other than water, such as alcohols. In such a case, the nucleophile will generally attack at the more substituted position. Using this information, predict the products
> Predict the products that are expected when each of the following alkenes is treated with a peroxy acid (RCO3H) followed by aqueous acid: (f)
> When trans-1-phenylpropene is treated with bromine, some syn addition is observed. Explain why the presence of a phenyl group causes a loss of stereospecificity. Br Br + En + En Br Br trans-1-Phenylpropene anti addition products (83%) syn addition pr
> Bromonium ions can be captured by nucleophiles other than water. Predict the products of each of the following reactions: ? Bra EINH, ? HO. (a) (b)
> Predict the major product(s) that are expected when each of the following alkenes is treated with Br2/H2O: (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: „I - ? , - ? ? ? Br (b) (c)
> Compound 1 has been shown to be a useful precursor in the synthesis of natural products. In principle, four stereoisomers are possible when this compound is subjected to catalytic hydrogenation. Draw these stereoisomers and describe their relationships:
> Predict the product(s) for each of the following reactions: ? ? Ni Ni (a) (Ь) (c) ? H2 Pt Pd (d) (e)
> α-Pinene can be isolated from pine resin and is a primary constituent of turpentine (paint thinner). Both enantiomers of α-pinene are naturally occurring. To determine the enantiomeric excess (% ee) of α-pinene i
> A compound with the molecular formula C10H10O has the following 1 H NMR spectrum. Determine the number of protons giving rise to each signal. Proton NMR 10 6 5 1 ppm 17.1 87.1 18.7 Integration Values 51.1
> Predict the product(s) for each of the following transformations:
> Compound A has the molecular formula C5H10. Hydroborationoxidation of compound A produces 2-methylbutan-1-ol. Draw the structure of compound A:
> Below are several examples of hydroboration-oxidation. In each case, consider the expected regioselectivity and then draw the product:

